Operating principle and product types
After igniting the mercury, ultraviolet begins to interact with the phosphor applied to the walls, which causes it to emit a visible spectrum of light. Thus, the phosphor performs the function of a transformer, or converter, and allows us to sense the light that is easily perceived by the human eye and is capable of illuminating the environment.
Thanks to the unique property of glass not to transmit ultraviolet rays, it protects us and completely blocks their release into the environment and protects our eyes from its direct effects, which are harmful.
But there are lamps that do not interfere with such radiation. They are made from uviol and quartz glass; these types of materials are capable of transmitting ultraviolet rays. As a rule, such lamps are used to clean and disinfect various devices. In the store you can find them as bactericidal; they are specially designated where this is indicated.
To increase the thermal output of light, low-pressure lamps with the addition of indium and cadmium amalgam or other similar elements are used. Thus, the temperature range can expand to sixty degrees, compared to the standard filling of the lamp, when the temperature is no more than twenty-five degrees.
A significant decrease in performance is noticed when the ambient temperature is low, below the minimum acceptable level. Under such conditions, the warm-up and ignition time of the lamp increases significantly, the intensity and quality of the glow decreases several times.
For such conditions it is necessary to use special insulation and heaters. In this regard, lamps that do not contain mercury vapor, which operate exclusively on low pressure of an inert gas inside the bulb, are gaining relevance.
Mercury Vapor Lamps
UV radiation is dangerous for the eyes (very, very dangerous - it causes retinal damage and cataracts) and skin, so you should never use a lamp without an external bulb. Not to mention the fact that its efficiency will be lower due to the incorrect temperature conditions of the internal flask. Many modern lamps have a fuse that turns off the lamp if the outer bulb is broken (safety lifeguard mercury lamps). It is best to have additional protection against UV radiation - protective glass, etc.
The base of these lamps is usually screwed in (mogul base), but it is made in such a way that it does not screw into a regular light bulb socket (or it is screwed in, but does not reach the central contact)
| to the top of the page back to the table of contents |
Tips for choosing
When choosing fluorescent lighting sources, the following recommendations must be taken into account:
- The most profitable , from an economic point of view, are class A lighting fixtures, which have an efficiency ratio of 1:6 with incandescent lamps and are characterized by savings of up to 80% of electricity.
- To illuminate streets, bridges and other objects , it is possible to use 2-in-1 lamps that have 2 modes: normal operation and a mode with an energy consumption of less than 1 W, using sensors to switch to another mode under changing external conditions.
- the buyer needs to evaluate energy savings, power consumption and its service life.
- It is necessary to focus on the base of the lighting source and its dimensions and their compliance with the operating conditions of the buyer.
- When choosing a lamp, you need to pay attention to its color rendition and the temperature it reaches, since insufficient lighting in the room may result in a blue tint of the spectrum, which is unpleasant for family members.
- Do not buy lighting sources of this design for conditions with frequent switching on and off of the lighting device.
Classification and marking of lamps
The marking is applied to the flask itself and metal parts. The ability to decipher the symbols greatly facilitates the selection of the desired light source.
Letter designations correspond to the following indicators:
- L means fluorescent lamp,
- B white light,
- D daylight,
- It's a universal option.
For example, LB corresponds to a white light fluorescent lamp.
Marking the diameter and shape of the flask
The diameter of a glass bulb is designated in inch units in accordance with international standards. The unit of measurement is considered to be 1/8 of it. The size itself is designated by the letter T, and in full it looks like T8, which corresponds to 26 mm, since 8/8 of an inch is one or one whole inch (25.4 mm), which will be almost equal to 26 mm.
Some manufacturers use conventional indicators in marking, for example, 26/604 means the diameter of the flask and its length in mm.
The designation of the shape of the bulb of fluorescent lamps is also present, despite the fact that it can be seen visually. The linear configuration is not displayed in any way, and the others are marked as follows:
- U arc shape,
- S in the form of a spiral,
- C in the form of a candle,
- G in the shape of a ball,
- R reflector,
- T in tablet form.
Exactly the same designations are applied to energy-saving lamps. The arrangement of symbols may differ for different manufacturers, but all the main parameters will be present in the marking of each lamp.
Power
The power indicator is of great importance. It is the power that is used in calculating the lighting of a particular room, when the required number of lamps is determined. In the marking, this parameter is indicated by the letter W and at this stage it will look entirely: LB T8 W8.
Another parameter is the mains voltage, which is indicated as 127 V or 220 V.
Other markings
The number of socles and their characteristics are also noted. There are designations for this: FS 1, FD 2 base, and FB is a compact lamp with electronic ballasts built into the base.
When choosing a lamp, you need to know whether it requires a starter, or whether it is connected to a ballast without special starting devices. In the first case, the RS marking is used, and in the second, PHs. Lamps with universal start are designated US.
On some products you can find spectrum and luminosity values indicated by numbers. The higher these indicators, the higher the luminosity parameters and the brightness of the lamp itself. The color of the glow is determined by the outer color of the glass bulb. Color temperature is displayed in Kelvin, that is, 2700 K will be marked as 27.
When purchasing fluorescent lamps, it is recommended that in addition to the markings, you study the passport data. Most likely, there will be parameters that are not noted in the printed characteristics. One of these indicators is the permissible limit of voltage drops, exceeding which will damage the lamp. There may also be temperature ranges that have a strong effect on sensitive fluorescent lamps.
Marking
The designation system for fluorescent light bulbs determines their main parameters. However, depending on the country of origin, the designation standards will also differ. For comparison, let’s consider both labeling options using the example of domestic and foreign manufacturers.
Domestic
Domestic marking includes an alphanumeric designation, which includes four positions for letters and one for numbers. For example: LBTSK-60 .
The first letter in the marking L means lamp. The second position is more complex, it can be expressed as one or a pair of letter combinations, it denotes color rendering indices, the following options are possible in it:
- D – daytime spectrum;
- ХБ – cold white glow;
- B – white;
- TB – white warm shades;
- EB – natural spectrum white;
- UV – ultraviolet spectrum;
- G – blue;
- C – blue tint;
- K – red radiation spectrum;
- F - yellow tint
- Z – green.
The third position determines the quality of color rendering, but there are only two options for C - improved quality or CC - especially high quality, which is often used in decorative lighting.
The fourth position indicates the design of the lamp. There are five main positions:
- A – amalgam type;
- B – with quick start;
- K – ring type;
- R – reflector lamps
- U - U shaped.
Foreign
Foreign-made fluorescent lamps have identical marking principles. At the beginning, the power of the product is indicated in watts; it is easily recognized by the Latin letter W.
The type of glow is determined by a digital code with a letter explanation in English:
- 530 is a warm tone of fluorescent lamps, but relatively poor color rendering;
- 640/740 – not quite cold, but close to it with a mediocre level of color rendering;
- 765 – blue tint with a mediocre level of color reproduction;
- 827 – close to an incandescent lamp, but with good color rendition;
- 830 – close to a halogen bulb, with a good level of color rendering;
- 840 – white shade with a good level of color reproduction;
- 865 – daylight spectrum with good color rendering;
- 880 – daylight spectrum with an excellent degree of light transmission;
- 930 – warm tone with excellent color parameters and low light output;
- 940 – cool tone with excellent color rendering and average light output.
- 954/965 – luminescent devices with a continuous spectrum.
Fluorescent lamps. Types and work. Application and labeling
Fluorescent lamps begin their history with gas-discharge devices invented in the 19th century. In terms of light output and efficiency, they are significantly superior to incandescent lamps. They are used for lighting residential premises, institutions, hospitals, sports facilities, and workshops of manufacturing enterprises.
Operating principle and main properties
For a discharge to occur, electrodes are connected to the flask on opposite sides.
Gas-discharge lamps cannot be connected directly to the network. Starting control devices - ballasts - must be used. If the number of starts does not exceed 5 times a day, then the luminescent source is guaranteed to last 5 years. This is almost 20 times more than for incandescent lamps.
Among the disadvantages of fluorescent lamps are:
- Unstable operation at low temperatures.
- Need for proper disposal due to mercury vapor.
- The presence of flicker, to combat which it is necessary to complicate the circuit.
- Relatively large sizes.
However, fluorescent lamps are extremely economical because they consume little energy, produce more light and last longer. Not surprisingly, they have replaced conventional light bulbs in almost all institutions and businesses.
Types of fluorescent lamps
Lamps come in low and high pressure. Low pressure pipes are installed in rooms, high pressure pipes are installed on streets and in powerful lighting fixtures.
The range of fluorescent lighting devices is quite wide. They differ in the size and shape of the tube, type of base, power, color temperature, light output and other characteristics.
Depending on the shape of the tube, fluorescent lamps are:
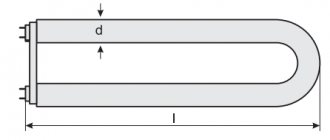
- Tubular (straight), designated by the letter T or t, have a straight shape.
- U-shaped.
- Ring.
- Compact, used for lamps.
Straight, U-shaped and ring types will be combined into one type of linear lamps. The most common lighting fixtures are in the form of tubes. After the letter T or t there is a number. It indicates the diameter of the tube, expressed in eighths of an inch. T8 means the diameter is 1 inch or 25.4 mm, T4 means 0.5 inch or 12.7 mm, T12 means 1.5 inch or 38.1 mm.
To make the lamp more compact, its bulb is bent. To start such lamps, a built-in electronic choke is used. The base is made either for standard lamps or for special lamps.
The fluorescent lamp base can be type G (pin with two contacts) or type E (screw). The latter type is used in compact models. The numbers after the letter G indicate the distance between the contacts, and after the letter E the diameter in millimeters.
Marking
Domestic and international labeling is different. Russian originates from the times of the Soviet Union and uses Cyrillic letters. The meanings of the letters are as follows:
- L lamp;
- D daylight;
- B white;
- T warm;
- E natural;
- X is cold.
Power and spectrum
In order for the lighting source to work normally, it must be connected to a 220 V network with a frequency of 50 Hz. Deviation may negatively affect the stability of lighting, significantly shortening the service life.
Voltage fluctuations can change the power of an electrical appliance, reducing its efficiency. Even the most powerful lamp will glow dimly if there is insufficient voltage.
Must watch: a ban on fluorescent lamps will come into force in 2021.
Modern LLs have almost any shade. The color temperature spectrum varies from classic warm to daylight. Each lamp is marked accordingly by shade.
Separately, it is worth considering lighting devices with ultraviolet glow. They are marked LUF, while reflective blue devices are marked LSR. UV lamps are used for bactericidal treatment of premises.
Most fluorescent lamps produce a flux similar in length to ordinary sunlight. You can see the similarities between the spectra in the picture below.
The spectrum of sunlight is shown on the left; the spectrum of a high-quality fluorescent lamp is shown on the right. The light from the sun has a more even characteristic, but the similarities are definitely there. LL has a pronounced peak in the green region, while in the red region there is a decrease.
It has been scientifically proven that the closer the light from an artificial source is to natural light, the better it is for health. For this reason, fluorescent lamps are preferable to LED fixtures.
Sodium lamps (Sodium Lamps, HPS, LPS)
In these lamps, the discharge occurs in sodium and mercury vapor. These lamps come in high (HPS lamps, High-Pressure Sodium - HPS) and low (Low-Pressure Sodium - LPS) pressures. LPS produce an almost monochromatic yellow color (albeit with very high efficiency up to 180-200 Lm/W), so they are used only for special lighting. for example, car parks.
As you can see, there are practically no blue components in the spectrum, so the radiation of such a lamp is yellow and the color temperature is low - 2100-2200K, color rendering index (CRI) is about 20. The service life of these lamps reaches 20-24 thousand hours. Their luminous efficiency reaches 80-100 Lm/W
New HPS lamps have a higher color temperature - 2700K (Philips - White SOH HPS Lamps) and CRI=85. These lamps are used as a replacement for incandescent lamps and can be used in combination with fluorescent lamps. These lamps have a service life of about 10,000 hours, luminous efficiency is about 50 Lm/W.
Sodium lamps are widely used in growing plants and agricultural technology because they provide a lot of light in the red region of the spectrum. Plants typically have several light-sensitive pigments located in the blue and red regions of the spectrum. For example, pigments whose peak sensitivity in the red region of the spectrum are responsible for the growth of the root system, ripening of fruits, and flowering of plants. Therefore, in greenhouses, where the ultimate goal is to get tulips by March 8 and no earlier and no later, sodium lamps are used.
Pigments that peak in the blue region are responsible for leaf development, plant growth, etc. Therefore, plants grown with insufficient blue light are taller - they stretch upward, trying to get more of this blue light (if you are growing roses in a greenhouse for sale, then you need plants with long stems). The pigment that is responsible for turning the plant toward light is also sensitive to blue rays.
For an aquarium, their value is questionable, although they can probably be used in combination with lamps that produce light in the blue region of the spectrum.
Unlike metal halide lamps, the orientation of a sodium lamp does not affect its performance.
| to the top of the page back to the table of contents |
Some information to make your choice easier
Naturally, the power of the lamp determines its durability, as well as the strength of the luminous flux, including after some time of operation. Knowing these parameters of fluorescent lamps, you can choose the optimal lighting device that will not spoil the mood during installation.
For example, with a power consumption of such a lighting device of 30 watts, the average service life will be 15,000 hours. The average luminous flux after 100 hours of burning for white (LB) will be equal to 140 lm, warm and cold white - 100 lm. For daytime it is 180 lm, and for daytime color this figure will be 80 lm. But the parameters of the LDC will be different.
Unusual fluorescent lamp
Do not forget that starterless lamps, although they consume no less electricity than lamps with a starter, still have a slightly longer lifespan. Therefore, the best option would be to purchase just such fluorescent lamps and then exclude starters from their circuit. This is not difficult to do, and such work will not take much time.
Application area
Fluorescent lamps are used in all spheres of human activity. Availability on the market and cost-effectiveness of operation make CFLs the number one choice for public organizations and administrative centers.
They can often be found in educational institutions, shopping centers, gyms and medical or banking institutions. Fluorescent lamps with a threaded base are used even in everyday life.
Important! To increase the durability of a luminescent product, it is necessary to guarantee a stable voltage without fluctuations, and also to minimize the number of switching on and off.
For domestic use, it is recommended to buy lamps with electronic ballast, which eliminates flickering. Due to the low mercury content in the flask, devices should be disposed of separately from other waste.
Nuances of choosing fluorescent lamps
If you are looking for a replacement lamp, then first of all you need to determine the models that are compatible with your existing lamp. To do this, look at the instructions for the lighting device, where the type and parameters of suitable light sources are usually indicated. If this is not possible, unscrew the old light bulb and use the markings on it to select a new one with similar parameters. If there are no markings, use the illustrations in this article to visually identify the type of lamp.
For the compatibility of the lamp and luminaire, the type of base and dimensions of the bulb are important. You can make sure that the standard size of the base fully corresponds by taking simple measurements - the numbers in its designation are equal to the distance in millimeters between the contact pins or the diameter of the screw part.
To get the maximum effect when using lighting devices, when choosing lamps for them, you must take into account all the basic parameters:
- luminous flux - measured in lumens. The higher this indicator, the larger the area the lamp can illuminate;
- power - characterizes, first of all, electricity consumption and indirectly the intensity of the glow, which largely depends on the production technology used;
- color temperature is an important parameter that affects the comfort of a long stay in a room with artificial lighting, performance, fatigue and emotional background;
- color rendering - by choosing a lamp with good color rendering, you can visually change your usual surroundings, making the colors brighter and more saturated.
In the Maxidom online store you can select suitable fluorescent lamps and other lighting products and purchase goods at a favorable price with delivery.
Main types, types and modifications
Compared to other light sources, fluorescent lamps are represented by a wide range of models, with various shapes, sizes, individual parameters and technical characteristics.
First of all, fluorescent lamps are classified according to high and low pressure. The first option is used for lighting industrial facilities and public places where high quality color rendering is not required. The second type of lamps, low pressure, is used mainly in everyday life. Such products are also known as energy-saving.
The form of fluorescent lamps is divided into two main types:
- Linear. Most of them are made in the form of straight tubes of various lengths and diameters. The most exotic products resemble the letter U or are made in the shape of a ring.
- Compact. They are distinguished by curved flasks, the shape of which significantly expands the scope of use. The sockets can be pin or threaded for standard sockets.
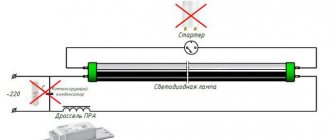
The current parameters in the network are not fully suitable for light bulbs for their normal functioning. Therefore, ballast is added to the structure. Modern fluorescent lamps use two types of such devices.
Electromagnetic ballast
Until recently, electromagnetic ballast circuitry was widely used in products. The basic principle of operation is based on the inductive reactance of a choke connected in series to the light source. Due to this, the normal operating voltage necessary for the normal glow of the lamp is maintained. However, despite the low cost and simplicity of design, electromagnetic ballast is used less and less due to its significant disadvantages:
- Long ignition time, which even in the initial period of operation is 1-3 seconds.
- Higher power consumption compared to electronic circuits.
- The operation of the ballast is accompanied by light flickering, which negatively affects vision, as well as a characteristic unpleasant hum.
Electronic ballast
Constantly developing innovative technologies have made it possible to replace electromagnetic circuits with more efficient electronic devices. When using these circuits, the lamp is powered with simultaneous voltage conversion. At the start, instant or soft start can be used.
Electronic ballast allows you to save 20-25% of electricity; there is no flickering or humming during its operation. Production and disposal require significantly fewer resources and material costs.
Types of mercury lamps and the specifics of their operation
Lamps of this type are produced with a power from 8 to 1000 W and are divided into 2 groups:
- general purpose;
- highly specialized applications.
By internal filling pressure:
Especially hot, the tungsten wire parts, reduced in diameter by evaporation, thicken again, so that the lamp can operate at higher temperatures with better light output. Drawing of lamps in halogen lamps is minimal; the lamps have a constant luminous flux until the end of their technical service life. To reduce the brightness of clear glass lamps, incandescent lamps are made of frosted or cloudy material. Dark lamps have colored glass bulbs.
Incandescent lamps can be used almost everywhere for lighting or displaying information, despite their relatively low light output. Many technical special forms are tested, such as miniature lamps, projection lamps, automobile lamps, photographic lamps, flood incandescent lamps, decorative lamps, reflector lamps, signal lamps with particularly high performance lamps and tungsten incandescent lamps as radiance standards. A special type of incandescent lamp is an infrared emitter.
- low pressure lamps (mercury vapor pressure > 100 Pa)
- high pressure lamps (partial pressure value = 100 kPa);
- ultra-high pressure lamps (value = 1 MPa and
High pressure mercury instruments
A mercury gas discharge lamp (MDL) operates on the principle of optical radiation generated from mercury vapor by a gas discharge.
Incandescent lamps are not very effective in ultraviolet light. The second main group, in addition to incandescent lamps, are gas-discharge lamps. These lamps are characterized by the highest luminous flux outputs. However, the spectral power distribution is very different for these lamps. Often they are combined radiators. The release is achieved by the fact that due to the electrical voltage between the two electrodes, a current passes through the gas or metal vapor. This current should be understood as the transfer of charged particles, which is constantly maintained by the supply of electrical energy.
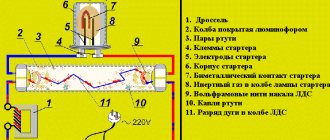
Until 1970, lamps had only 2 electrodes. This made lighting the light bulbs difficult and the devices themselves unreliable. Then another pair of electrodes was added, located next to the main ones and connected to the opposite ones through resistors - current limiters.
When switched on, small discharges heat the gas and transfer to the main arc. Such a connection system also depends on the temperature of the surrounding space, so it is impossible to determine with accuracy how long the light passes from glowing to arcing. Probably 1.5 to 8 minutes.
The variety of possibilities for generating light using gas discharge lamps requires a subgroup. Combinations of incandescent lamps and discharge lamps are called compound lamps. Discharge lamps can also be divided into low pressure, high pressure and high pressure lamps. Low-pressure lamps are gas-discharge lamps with elongated outlet vessels that are filled with noble gases or mixtures of noble gases with metal vapor, which is in equilibrium with its solid phase.
These lamps primarily use a positive column of gas discharge to generate light and require built-in electrodes and a current limiting device to maintain operation. Typical low pressure lamps are fluorescent lamps. An incandescent lamp and a short-range glow discharge tube with a bimetallic electrode are connected in parallel with the lamp. Their job is to preheat the filament electrodes for a short time when the lamp is started to create thermal radiation conditions.
To ensure normal “entry” into the light mode, a regulating device is needed - a throttle. It partially absorbs the voltage from the network and creates an even background necessary for the lamps to work. Recently, lighting devices for DRL lamps have replaced the choke in their configuration with ballasts - a new generation ballast electronic ballast. The introduction of ballasts helped reduce the noise of lamps and improve the quality of light. Ignition time has been reduced to a minimum.
It automatically turns off when the discharge begins, creating a voltage pulse that fully ignites the lamp. Compact fluorescent lamps now operate by igniting a transistor. Using suitable phosphors, the color tone of the lamp can be adjusted within wide limits. You can get a light-like appearance or an incandescent-like light. For special radiation purposes, phosphors can be selected so that the plant promotes plant growth. Fluorescent lamps have their maximum luminous output at approximately room temperature.
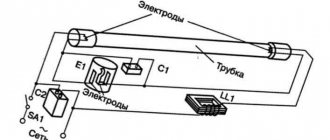
The lamp contains:
- glass flask;
- base;
- a glass quartz tube containing argon gas and mercury vapor under pressure. The inside of the bulb is coated with phosphor to improve the quality of the light flux;
- limiting resistor;
- main electrode;
- additional electrode.
Arc metal halide (MAH)
a lamp with emissive additives that increase the efficiency of light transmission. In DRIs, not quartz, but ceramic burners are often installed, and a choke is included in the circuit. Power varies from 125 to 1000 W. Thanks to the added elements - metal halides, the lamp can emit different colors.
At very low temperatures their luminous efficiency decreases. Modern compact fluorescent lamps, especially in the screw design, will further reduce the use of incandescent lamps for general indoor lighting in the future. A special low-pressure mercury vapor lamp with a quartz vessel without phosphor coating is the ultraviolet standard. Higher light output than mercury fluorescent lamps include low-pressure and high-pressure sodium lamps. Low pressure sodium lamps are sensitive to low ambient temperatures, by the way.
Metal halide lamp (DRIZ)
with a mirror layer. These mercury devices have a special base and one side is coated with a mirror layer, which makes it possible to obtain a directed light flux.
Mercury-tungsten arc lamp (MAT)
does not require ballasts due to the presence of a tungsten spiral. This high-pressure mercury lamp is also distinguished by the fact that its bulb, in addition to mercury vapor, is filled with a mixture of nitrogen and argon. Tungsten lamps produce bright, pleasant light and are the most durable.
Following the development of sodium-resistant and heat-resistant exhaust vessels made from sintered corundum, high-pressure sodium lamps became especially popular for outdoor lighting. Besides sodium, they also contain mercury, argon and the like. to ignite the lamp and to adjust the operating voltage to the supply voltage of the lighting network. Steam vapor pressure is more than 10 4 Pa. Higher color temperatures can be achieved using high pressure mercury lamps, metal halide lamps and xenon lamps.
High-pressure continuous xenon lamps produce, although not the highest luminous flux, light similar to daylight, so they are used in particular for color testing. If the working pressure of a xenon lamp with a special geometric shape of the lamp vessel has increased to more than 10 6 Pa, it is called a high pressure lamp.
Mercury-quartz (straight) bulb (PRK)
or
a high-pressure tubular mercury arc lamp (HART)
. They have cylindrical flasks with electrodes located at the ends.
Mercury-quartz ball lamp (DSH).
Distinctive features: spherical bulb and high level of lighting brightness along with ultraviolet radiation. The lamp operates under very high pressure with a cooling system.
Electrode frequencies are often low in high-pressure lamps, so the lamps have high brightness. Xenon lamps and other noble gas lamps can also be pulsed. Depending on the filling gas pressure, the distance between the electrodes, the diameter of the discharge container and external parameters such as voltage and capacitance, the spectral distribution of power is very different. Xenon flash lamps are used as incandescent electron lamps for short exposures in photography and as pump light sources for optically excited lasers or, intermittently fired, as stroboscopic lamps.
High pressure mercury ultraviolet lamp (DRUF, DRUFZ)
Made from uviol black glass. Another option for creating such bulbs is to use europium-doped strontium borate to coat the inside of the bulb. They practically do not produce visible light.
High-pressure mercury lamps with quartz discharge vessels surrounded by fluorescent-coated glass vessels can be used for outdoor lighting and, among other things, for lighting workshops, railway stations and for special photochemical processes. Their luminous efficiency is lower than that of high-pressure sodium lamps, but at a significantly higher color temperature. For lighting applications with higher color rendering requirements, such as color television or color film recording in studios, metal halide lamps are used.
Low pressure mercury instruments
A fluorescent mercury lamp is a gas-discharge lamp and is designed on the same principle as high-pressure lamps.
Compact fluorescent lamp (CFL)
appeared on the territory of our country in 1984. Such devices were initially equipped with standard types of bases with electric ballasts mounted inside.
These lamps are usually high pressure mercury lamps with fluorescent additives in the form of metal halides such as indium iodide, thallium iodide, tin chloride and the like. Thus, the light from these lamps can be mixed with both halogen incandescent lamps and daylight. A special class of gas discharge lamps are spectral lamps, usually medium pressure discharge lamps. Depending on their filling, they show the spectra of alkali metals, noble gases and the metals mercury, zinc, thallium and cadmium.
Therefore, in view of the energy-saving characteristics declared by the manufacturer, KKL models quickly appeared in many apartments. Unlike other types of mercury fluorescent lamps, compact devices light up immediately and operate silently. The flickering frequency of such light bulbs is perceptible to the human eye, but not as clearly as in the case of other gas-discharge lamps.
They are primarily used for wavelength calibration of spectrophotometers or, with filters, as monochromatic light sources. The lines of commonly used mercury spectral lamps are listed in the table. Hollow cathode lamps are special spectral lamps for atomic absorption spectrometry. Capillary lamps filled with hydrogen or deuterium gas, called short hydrogen or deuterium lamps, are glow discharge lamps that are in addition to linear spectra.
Examples include the light-emitting capacitor, which relies on excitation of a phosphor in an alternating electric field, and optical displays, which use light-emitting diodes or take advantage of electroluminescence.
Light source 2: spectral power distribution of tungsten strip 100 mm 2. The parameter is the temperature of the tungsten strip.
Linear mercury-containing lamp
presented in the form of a long flask with two electrodes at the ends, filled with gas and mercury vapor. The flask itself is coated inside with a phosphor. When the lamp is turned on, an electric arc discharge occurs, the filling of the lamp heats up to the required level, and the device flares up at full power.
Light source 3: spectral intensity distribution of a metal halide lamp. Beck, Jena Joachim Bergner, Jena Eberhard Dietsch, Jena Kurt Enz, Berlin Prof. Joachim Epperlein, Wilkau-Hasslau Prof. Erwin Hoffmann, Berlin Christian Hofmann, Jena Wolfgang Högner, Tautenburg Dipl. -Eng. Hans-Jürgen Jüpner, Berlin Prof. Christoph Ludwig, Germsdorf Rolf Martin, Jena Ulrich Max, Rostock Olaf Minet, Berlin Gerhard Müller, Berlin Günter Osten, Jena Prof. Wolfgang Radloff, Berlin Prof. Karl Regensburger, Dresden Werner Reichel, Jena Rolf Rieker, Berlin Rolf Röseler, Berlin Günter Schmuhl, Rathenow Johannes Schweider, Erlangen Rainer Spolaczyk, Hamburg Professor Johannes Tilch, Berlin Joachim Träger, Berlin Bernd Weidner, Berlin Ernst Werner, Jena Professor Ludwig Wenzorek, Berlin Wolfgang Wilhelmy, Berlin Olaf Ziemann, Berlin.
In this case, the phosphor absorbs ultraviolet radiation emitted during operation. If you supplement the chemical composition of the phosphor with various additives, you can thus change the color of the light flux. Linear lamps differ in the types of base and diameter of the devices.
Low Pressure Quartz Mercury Arc Fluorescent Lamp
produces powerful ultraviolet radiation. Used for disinfection of drinking water and air. Produces ozone in increased concentration. Requires further ventilation of the room.
Germicidal lamp
Made from uviol glass. There is another technology when the inner surface of the flask is treated with a special chemical composition (see DRUF). Producing powerful ultraviolet radiation, the lamp does not emit too much ozone. Therefore, there may be people in the room where the device is used.