Fluorescent lamps: description and device
Fluorescent lamps, in appearance, are a glass bulb of various shapes, white in color with connection contacts protruding from the edges.
Reference: The first fluorescent lamps were created in Russia in 1936-40 by a group led by S.I. Vavilov.
The shape of fluorescent lamps can be in the form of a rod (tube), torus, or spirals. During production, air is pumped out of the lamp bulb and inert gas is pumped in. It is the behavior of the inert gas under the influence of electricity that causes the lamp to glow, creating streams of cold or warm light, which is commonly called “daylight”. Hence the second name for these lamps, fluorescent lamps.
It is worth noting that the lamp could not shine if a phosphor was not applied to the inside of the bulb, and if there was no mercury in the lamp itself.
It is mercury that has become the factor that pushes this type of lamp out of the market. The danger of mercury pollution from broken lamps raises many questions among environmentalists around the world.
Characteristics of special-purpose fluorescent lamps
Special-purpose lamps are installed in public places in order to further highlight certain features of the interior, accent lighting in a certain spectrum for a more accurate reproduction of the colors and shades of objects. Areas in which they are used:
- in the entertainment club industry.
- in medical institutions as ultraviolet bactericidal lamps.
- for illuminating shop windows, exhibits at exhibitions, etc.
The following parameters of fluorescent lamps with specific purposes of use are distinguished:
- Power: 18-58V
- Luminous flux: 550-3700 lm
- Variability:
- with colored phosphor;
- blue reflex;
- ultraviolet.
- Color temperature: 3000-7000 K.
- Base: G13.
- Length: 600-1500 mm.
Thus, fluorescent lamps emit a powerful luminous flux, provide adequate color reproduction of illuminated objects, allow you to choose the most suitable light in terms of color temperature, have an adequate cost and a long service life.
For all their attractiveness, fluorescent lamps have a big disadvantage: mercury vapor inside the lamp tube. This creates a danger if it is damaged, and also requires special disposal measures, which makes its use not entirely convenient.
Despite the massive distribution of fluorescent lamps, it should be recognized that they are rather a thing of the past and, like incandescent lamps, will give way to more advanced technology. Which is absolutely safe, does not require special disposal measures, has a long life cycle and, in addition, is more energy efficient. The name of this technology is diode lamps for the home.
How does a fluorescent lamp work?
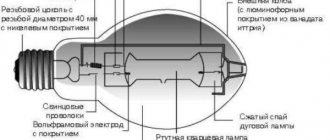
The inert gas in the lamp is needed to create a glow discharge (a flow of ionized particles of inert gas). Mercury is needed to enhance this discharge. A phosphor is needed to convert ultraviolet light into visible light. Electrodes are needed to connect the lamp to an electrical circuit and create a discharge of electrons.
After applying voltage to the lamp contacts, the electrodes inside the bulb begin to emit electrons, which, moving around the bulb, try to create a discharge. However, in normal circuit settings, the current is not sufficient to create a discharge. Therefore, the connection diagram for a fluorescent lamp must include a device that creates a one-time electrical discharge to start the glow.
Related articles: Dimmer connection diagrams in an apartment
This device is called a photo starter. Its task is to briefly increase the current strength by 3-4 times when electricity is supplied.
To ensure the start and operation (glow) of a fluorescent lamp (group of lamps), you need another device, simply called a choke. This name is actually outdated, but is actively used.
The correct name for the throttle is ballast (ballast). Today, the name choke (ballast) has been transformed into Emballast and electronic ballast.
- Electromagnetic control gear: electromagnetic start-control device;
- Electronic ballasts: electronic start-control device (electronic ballast).
The electronic ballast lights the lamp more quickly, does not hum during operation and regulates starting at low voltages. If the old choke was, in fact, a heavy electromagnetic coil, then modern electronic ballasts are compact, even elegant devices.
Fluorescent lamps (aka fluorescent lamps)
A fluorescent lamp is a gas-discharge device where the light source is a discharge between the anode and the cathode. This discharge, passing through mercury vapor, produces ultraviolet light, which, under the influence of a phosphor, is converted into a visible glow. Fluorescent lamps have replaced the inefficient incandescent lamp: while consuming less electricity, they create the same amount of light and last up to 70 times longer.
Within the group, fluorescent lamps are divided into subtypes - general and special purpose. The former are used in indoor and outdoor lighting systems, the latter in bactericidal installations for disinfecting water, air and surfaces. Lamps are produced with a power from 5 to 80 W in flasks of various formats: twisted, linear, ring and others. The efficiency is twice that of incandescent lamps, since the devices spend 70% of the energy received to produce light.
Due to the low heating of the bulb, the fluorescent lamp is fire safe, and the light bulbs themselves can be installed even in luminaires with limited operating temperatures. A 20-watt fluorescent lamp replaces a 100-watt incandescent lamp, producing an equal amount of light with improved color. Depending on the model, the lamps operate from a 220 V household network or are connected via ballasts to stabilize the voltage to the specified parameters. They last from 5 to 70 thousand hours.
Search for fluorescent lamps:
Lamp specifications
Fluorescent lamps are tubular linear lamps, familiar to everyone in office lighting, that provide even daylight. Technically, they are low-pressure gas-discharge mercury lamps, which imposes some peculiarities on operating conditions. Thus, they do not like to work in cold environments, they require additional equipment for startup and operation (electronic ballasts), and they contain mercury, and therefore require special disposal.
However, the advantages of such lamps outweigh all their disadvantages - they are light, cheap, have an energy efficiency 10 times greater than incandescent lamps and the same as that of LEDs, and for lighting large warm spaces (offices and shops) they are the most advantageous light source.
There are two types - linear and compact fluorescent lamps, which are distinguished by the type of design, base and have different applications. Linear types of light bulbs are produced in three formats: ring-shaped, U-shaped, and in the form of a straight tube.
Types of fluorescent lamps:
All types of linear lamps are equipped with a “G” type pin base located on both sides or on one side of the device. To connect to the power supply, lamps need ballasts, which are responsible for stable starting and, by adjusting voltage parameters, extend their effective service life. Compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs) have more varieties, and in everyday life they have a more common name - energy saving:
• twisted; • pear-shaped; • spherical; • in the shape of a lotus; • tablet lamps; • candle and candle in the wind.
CFLs are equipped with two types of bases - screw (E14, E27), pin (G23, GX53 and others). The housing of compact sources is equipped with a built-in choke, so they can be connected directly to the voltage network. That is, they were originally designed as a direct replacement for an incandescent lamp - so that energy-saving lamps could be installed in the same place and simply turned on. Despite the fact that energy-saving lamps are still the most profitable source of light for the home, they are considered morally obsolete, and under pressure from LED manufacturers, fewer and fewer of them are being produced.
Application options:
Within each type, light bulbs are divided into categories - general and special purpose, depending on the luminescence spectrum. Devices for general lighting systems are produced with a power from 20 to 80 W with a wide choice of color temperatures: warm (from 2,700 K), daylight (from 3,500 K), cold light (from 4,500 K) and very cold (from 5,000 K ). Both linear and compact lamps have high color rendering, so surrounding colors are perceived in natural shades without visual distortion. In special-purpose fluorescent lamps, ultraviolet and blue light spectrum predominate. They are divided into several types:
1. Lamps for lighting underwater plants in aquariums
. They produce a red-blue glow, which promotes proper development (prevents the stretching of algae) and stimulates the active growth of aquarium flora. The devices are produced in linear form of varying power.
2. Special lamps for turtles, fish and other aquarium animals
with a predominance of blue color in the spectrum. Such lighting provides the necessary amount of light and also helps create natural (close to sea) living conditions. Decorative lamp models are used to illuminate corals and fish for a rich color effect. To obtain comfortable illumination of the water column, lamps with a high light temperature (also considered special) are used - from 8000K to 20000K.
3. Colored fluorescent lamps
. The flask of such devices is coated with varnish of various colors: red, green, blue and others. Used in decorative lighting and organizing holiday illuminations. At the same time, lamps with a colored glow do not produce ultraviolet radiation, which allows them to be used in general lighting, as well as mounted at production facilities under sterile conditions (manufacturing printed circuit boards or microcircuits in which individual elements react negatively to UV - these are lamps with the Chipcontrol index).
4. Lamps for organizing light in poultry houses
. They produce near-ultraviolet light “A”, which helps birds see clearly. The fact is that birds have four-component vision and ordinary daylight is uncomfortable for them. The spectrum of the lamp, on the contrary, creates light that is natural for their perception.
5. Product lighting
fluorescent lamps with a predominance of the red spectrum. With the help of such devices, meat or fish acquire an appetizing color that attracts the attention of buyers. Some models with a yellow spectrum are used in baking lighting. Lamps with an excess of blue are used to illuminate dairy products. Such lamps enrich shades without distorting the natural color of products, and the products themselves sell better with such light.
6. Lamps for solariums
. They are produced in different power options and in a combination of two spectra - near and mid ultraviolet. The latter is formed in a minimal amount or in equal quantities with the first, protecting the skin from thermal burns. There are lamps for obtaining and maintaining an artificial tan. The main thing is that lamps in tanning salons must be changed periodically, because after the end of their service life they begin to produce harsher ultraviolet radiation, which can lead to pigmentation or skin cancer!
7. Lamps in a black glass bulb
with a special layer of phosphor that produces long-wave UV without transmitting visible light (above the maximum 400 nm for ultraviolet of this group). Black fluorescent lamps are used when working with objects that create a fluorescent effect: upon contact with ultraviolet light, substances invisible in daylight become clearly visible. They are used in forensic science, in food and textile production, for checking banknotes and for other purposes where a certain luminescence spectrum is required to detect defects.
8. Lamps for drying paint and varnishes, polymerization of plastics
. The blue tint predominates in the glow spectrum. Similar devices are used in dentistry and other fields where materials with a high sensitivity to blue color are processed. Lamps are also mounted into insect traps: by flocking to a specific light and flying up to the grille of the lamp, which is energized, the pests die.
9. Quartz and bactericidal lamps
. They are designed to disinfect water, rooms, surfaces and air. They produce hard ultraviolet radiation (short-wave “C”), which effectively destroys groups of microbes, viruses and various fungi. Depending on their purpose, lamps are used in closed or open irradiators, carrying out processing in apartments, kindergartens and schools, in hospitals and in enterprises of various profiles. All types of fluorescent lamps are highly efficient, since they spend 70% of electricity to produce light, creating a minimal thermal effect. All fluorescent lamps have a long lifespan - from 5 to 80 thousand hours, depending on the type of device and the quality of the starting and control equipment.
Source: expert-po-lampam.ru
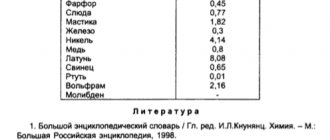
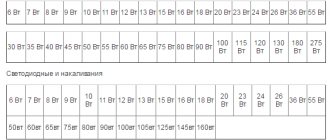
| Luminous flux, Lm | |||
| 20 W | 5-7 W | 2-3 W | About 250 lm |
| 40 W | 10-13 W | 4-5 W | About 400 lm |
| 60 W | 15-16 W | 8-10 W | About 700 lm |
| 75 W | 18-20 W | 10-12 W | About 900 lm |
| 100 W | 25-30 W | 12-15 W | About 1200 lm |
| 150 W | 40-50 W | 18-20 W | About 1800 lm |
| 200 W | 60-80 W | 25-30 W | About 2500 lm |
Types of fluorescent lamps
Modern fluorescent lamps differ in:
- Standard (one layer phosphor);
- With improved light transmission (phosphor in three or five layers);
- Special (luminescent powder with special additives: bactericidal, UV tanning, show business).
According to the lighting spectrum, LLs are divided into:
- Soft light lamps: t=2.7×1000 g;
- Daylight: (2.7 – 4.2)×1000 gr.;
- Cold light: (4.2 – 6.4)×100 gr.
Hence the notation:
- D - daytime;
- ХБ - cool white;
- B - white;
- TB - warm white;
- E - natural white;
- K, F, 3, G, S - colors;
- UV - ultraviolet;
- C-improved light transmission;
- CC - ultra-improved light transmission.
The last letters in the lamp markings indicate the design feature:
- R - reflector,
- U - in the shape of the letter U,
- K - ring,
- A – amalgama (mercury alloy),
- B – quick start.
- TL – glow discharge.
Varieties
Depending on the type of light output, lamps are divided into seven types:
- luminescent (L);
- daylight (D);
- white light (B);
- warm white light (TB);
- cool white light (CB);
- amalgam (A);
- improved color rendering (C).
You might be interested in this: Features of the HPS lamp
Blue energy-saving light bulb
Depending on the use case, the lamps are divided into two types:
- Linear.
- Compact.
Each of these types has its own characteristics.
Linear
Linear fluorescent lamps are used as a local lighting option:
- at workplaces;
- on store shelves;
- furniture lighting;
- wardrobe.
Connected lamp
Linear type equipment can be used as lighting for administrative, public premises and commercial areas.
The advantages of using such lamps are as follows:
- Improved color rendering.
- The equipment has a long service life - a maximum of ten to thirteen thousand hours.
- High light intensity - from 55 lm/W.
Note! Linear light sources are available in the form of long, wide or thin devices, depending on the location.
Compact
The technical characteristics of compact fluorescent lamps allow the use of this light source with significant savings thanks to energy-saving technologies. They reduce energy costs by up to 80% compared to simple incandescent light bulbs of similar brightness.
Multi-colored lamp
Compact fluorescent lamps can become a complete replacement for standard incandescent lamps. Their scope of application is quite wide:
- indoor lighting (offices; cabinets; warehouse, industrial type halls; residential premises; retail premises, areas);
- lighting outside premises (pedestrian areas, shopping areas).
The use of compact energy-saving lamps can reduce energy consumption by 80%.
Connecting fluorescent lamps
To finish, I will show three diagrams for simple connection of fluorescent lamps in a fluorescent lamp for one and two lamps.
Related articles: How to make a switch from a switch to control lighting from two places
Designation:
- SF- starter;
- LL - throttle;
- EL lamp;
- C is a capacitor.
Characteristics
Evaluation of the effectiveness of this type of lighting element is based on the compliance of its parameters with the planned operating conditions. Fluorescent lamps have the following characteristics that you should pay attention to when purchasing:
- Product designation. Daylight is defined by the letter D.
- Diameter of the flask. This parameter affects the working time: the higher the value, the longer the useful life of the product.
- The power value by which you can determine the ability of the lamp to illuminate the desired area. Compared to incandescent lamps, the product in question can save up to 80% energy due to the low power level for the same amount of light emitted.
- Type of base. In linear variations, the G13 type is usually used.
- Supply voltage. Differentiated fluorescent lamps are designed for 220 or 127 V.
- Flask shape.
- Colorful temperature. Depending on the model, the temperature of the lighting components can exceed 5000 K.
- Color rendering index - shows the quality of lighting.
- Tube diameter.
- Luminous flux of the product.