What costs does a traditional lighting system require?
A traditional household lighting system includes 220V wiring, switches, lighting fixtures, and lamps. If the power of all lighting devices exceeds 3.5 kW, the system is divided into subsystems that are connected to a separate residual current device (relevant for large country houses).
When using incandescent lamps, the consumer can choose lighting fixtures at his own discretion. The final cost of the system depends on their price. Lamps are sold at different prices, depending on the design and manufacturer. The price of incandescent lamps also varies. For products from Russian manufacturers, the average value is 15 rubles.
Other manufacturers have different prices:
- Philips 60W – 30 rub., 40W – 35 rub., color 10W – 38;
- “candle” Foton 25W – 29 rubles;
- “pear” Osram 75W – 31 rubles, 40W – 32.
The final cost will depend not only on the area of the home and the power of the lighting fixtures, but also on the preferences and financial capabilities of the family. When purchasing expensive lamps and switches, dimmers, and imported light bulbs, the initial costs will increase not only during purchase, but also during the installation process. To include dimmers in the circuit, you will have to invite a specialist who knows exactly how to do this work.
Attention! Energy consumption can be affected by illuminated switches and dimmers. The former consume a small amount of watts, the latter allow, if necessary, to reduce the intensity of the glow while simultaneously reducing the power.
Total: what to buy?
Obviously, foreign brands OSRAM and Philips hold the mark. But the domestic ERGOLUX and Navigator were almost as good as them in our test, and they cost significantly less. Of course, the issue of resource remains open, but even if these lamps last less, the savings will still be noticeable.
This is interesting:
- How to fix an LED light bulb yourself: step-by-step instructions
Consumption calculations
To calculate how much electricity any light source consumes, several steps are required:
- look at the power indicated as W on the product or packaging;
- divide the number by 1000 (to get the value in kilowatts);
- determine how many hours a day the family uses the lamp;
- multiply the number by 30.
Next, the power (item 2) is multiplied by hours (item 4).
To find out how much one lamp consumes in rubles, the final calculation result is multiplied by the tariff.
LED light bulbs
For example, you can take a two-room apartment, in which there are 3 lamps of 100 W each (in living quarters and in the kitchen) and 3 lamps of 60 W each (in the bathroom, toilet and hallway).
If they are on:
- in the living room 4 hours in the evening and 1 in the morning;
- in the bedroom 2 hours in the evening and 2 in the morning;
- in the kitchen 3 hours in the evening and 1 in the morning;
- in the hallway and toilet for an hour a day;
- in the bathroom 2 hours in the evening and 1 in the morning.
When replacing with LED sources, 3 products of 14 W and 3 of 10 W are used.
Per day, such a system consumes:
12*14+4*10=208 W=0.208 kW
With an average tariff of 4 rubles. for 1 kW per month we will pay 24.96 rubles.
Energy saving light bulbs
If filament sources are replaced with energy-saving ones, then you need to buy 3 products for 20 W and 3 for 12 W.
All appliances consume per day:
12*26+4*15=372W=0.372 kW
You need to pay 44.64 rubles per month.
Incandescent light bulbs
An incandescent lamp converts only 10-20% of electricity into light, the rest is spent on heat.
For the same apartment, when using sources with incandescent filament, they consume per day:
12*100+4*60=640 W=0.64 kW
You need to pay 76.80 rubles per month.
How we took measurements
As a tester, we used the universal Power Meter, which allows us to almost instantly obtain data on the energy consumption of any household appliance. In addition to power consumption, we also simultaneously measured the heating temperature of the light bulb body using an XL830L multimeter, because overheating is one of the most common reasons for lamp failure.
1 of 4
To eliminate the possibility of defects or accidents, we took three copies of each lamp model (8 brands in total). Each was previously operated for 500 hours. You can see the measurement results in our table.
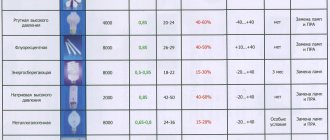
| Model name | Light type | Analog of incandescent lamp power, W | Declared power, W | Measured power, W | Measured case temperature, °C |
| Philips | cold white | 80 | 9 | 10.4 | 65 |
| OSRAM | warm white | 75 | 9 | 9.3 | 82 |
| ERGOLUX | cold white | 80 | 10 | 10.4 | 85 |
| Navigator | cold white | 75 | 10 | 10.3 | 75 |
| Camelion | cold white | 65 | 9 | 8.3 | 72 |
| REV | warm (2700K) | 75 | 10 | 9.2 | 75 |
| ONLITE | cold white | 75 | 10 | 8.4 | 75 |
| Smartbuy | warm | 100 | 13 | 11.0 | 87 |
Main conclusions
The newest LEDs have become a worthy replacement for filament sources. When purchasing quality products, there is no difference in lighting. If you think about the long term, using a traditional lighting system is not practical. Incandescent light bulbs create significant waste due to low efficiency and the need for frequent replacement.
Another important factor is the reluctance of ordinary consumers to do something new. Those who dared to upgrade their lighting system appreciated the convenience of LED products. The amounts on bills have become smaller, and there is no longer a need to turn the lights on and off several times during the evening or morning in order to save money. There is an opportunity to do what is convenient.
How many watts are in an LED light bulb?
One way to reduce energy consumption is to replace outdated lighting fixtures in your home or apartment. Today everyone should think about how many watts a light bulb with an incandescent filament consumes and how much it costs to pay bills for “light” in an apartment with several rooms. If you do some small calculations, the result will be impressive.
What costs does a traditional lighting system require?
Let's do the calculations for an apartment with 2 rooms. Let's imagine that they have chandeliers with 3 sockets installed. Knowing how many watts are in a light bulb (let's say 60 W) and what is the total number of lighting fixtures in the house (taking into account the kitchen, bathroom and hallway, 12 pieces), you can calculate the amount of electricity consumed: 60x12 = 720 (Wh).
Let's convert this value into kilowatt-hours: 720:1000=0.72 (kWh). If all lamps work for an average of 5 hours a day, then the total electrical energy consumption will be: 0.72x5=3.6 (kWh). Let's calculate the monthly consumption: 3.6x30=108 (kWh).
Tariffs are constantly rising, so paying for electricity usually takes up a significant part of the family budget. It is not surprising that many are looking for an opportunity to reduce costs on this item. But it is better to do this not by reducing the operating time of chandeliers and floor lamps, but in another way, more profitable. We are talking about the most promising technology for producing artificial light - LED.
How many watts does an LED light bulb consume?
The working elements of the new lamps are light-emitting diodes (LED). These are semiconductor crystals that produce light not by heating, but by a completely different method. Once connected to the network, LEDs convert electrical current into light, and only a small part of the energy is transformed into heat.
The luminous efficiency of modern LEDs is 100 lm/W or more. While this same parameter for other lighting devices is much lower. For incandescent lamps it is only 12-13 lm/W. It is easy to find out the light output of a device. Divide the luminous flux by the power. The first parameter is measured in lumens (lm). The second is in watts (W). Both characteristics are indicated on the lamp packaging.
So, how many watts are in an LED light bulb that is as bright as the incandescent bulb that came before it? Since the difference in the efficiency of these illuminators is 8-9 times, the power varies to the same extent.
The 60-watt “Ilyich lamp” can be replaced with a seven-watt LED.
How many times will energy consumption decrease when replacing old lighting fixtures with new ones?
What savings can be achieved
If in the above-mentioned apartment you replace 12 lamps with LED analogues, you will be able to significantly reduce energy consumption. Let's calculate how much. Let's multiply the power of the new lamps by the number of devices: 7x12=84 (W). This is 0.084 kWh. In 5 hours of operation, 0.42 kWh will be accumulated, in 30 days – 12.6 kWh. Let us remember that when operating incandescent lamps, the electricity consumption was 108 kWh, that is, 8.6 times more.
At the same time, LED lighting is just as bright, but in some respects it is better. For example, such an important parameter as the light pulsation coefficient, on which a person’s well-being and performance depends, is 1.5-5% for LED lamps. For other lighting devices it is several times higher, and for some it significantly exceeds the values permissible by sanitary standards (5-20%). Therefore, replacing the lighting system makes sense not only for the purpose of saving money.
How to calculate the required power of a diode lamp
If you decide to install LEDs instead of incandescent lamps, the power of the latter should be approximately 8 times lower. But provided that the luminous efficiency of the device is 100 lm/W or higher. For a lower value (80-90 lm/W), buy LED lamps with a 6-7-fold difference in power. Savings in energy consumption in this case will also be significant.
Video on the topic
How to choose an LED lamp:
How does an LED lamp work?
The operating principle of LED lamps is not much different from incandescent lamps. In an LED lamp, many small LEDs and a yellow luminescent layer create the effect of incandescent filaments with almost omnidirectional radiation. Due to their low power consumption, there may be a misconception that LED lamps do not emit heat. In fact, LEDs convert more than 70% of their power consumption into heat, which is significantly less than incandescent bulbs.
Because LEDs use less power, you can touch the dome of most light bulbs when they are on, but the base temperature can reach 85°. After all, most of the heat generated by electronic components is dissipated through the heatsink and housing into the environment.
Essential LED Terms
| Radiation angle (degrees) | The area in which the lamp reaches at least 50% luminous intensity (in candelas). |
| Efficiency (lumens per watt) | Modern high-quality LED lamps reach values above 75 lm/W |
| Color temperature (in Kelvin) | LEDs up to 3300K glow with warm white light (similar to incandescent lamps), up to 5000K - neutral white, starting from 5000K - cool white light. |
| Color rendering index (CRI) | Shows how closely the body color in the light emitted by the lamp corresponds to natural light. Incandescent lamps reach an index value of almost 100 units, modern LED lamps often reach values from 80 to 95. |
| Power consumption (in Watts) | Unlike incandescent lamps, the power of LED lamps does not measure brightness, but only energy consumption. |
| Luminous intensity (in candelas) | The brightness of a light source in a certain direction (spatial angle). |
| Luminous flux (lumens) | Overall lamp brightness. Daylight brightness, depending on conditions, ranges from 250 lm (approx. 25 W) to 1100 lm (approx. 75 W). |
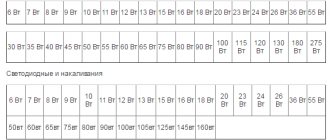
Comparison of lighting lamps
| Light. flow, lm | Incandescent, W | Luminescent, W | LED, W |
| 250 | 20 | 5-7 | 2-3 |
| 400 | 40 | 10-13 | 4-5 |
| 700 | 60 | 15-16 | 6-10 |
| 900 | 75 | 18-20 | 10-12 |
| 1200 | 100 | 25-30 | 12-15 |
| 1800 | 150 | 40-50 | 18-20 |
| 2500 | 200 | 60-80 | 25-30 |
You can find the most important terms in the glossary below. Manufacturers are required to indicate these values on the packaging.