What is a ground wire
The main purpose of such a cable is to protect against indirect contact with live parts of an electrical installation. Indirect contact is indirect human contact with parts of equipment that are not normally energized, such as motor housings, transformers, or the handle of a hair dryer.
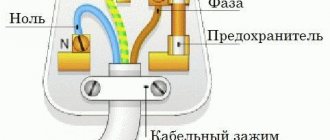
Ground wire
But due to a violation of the insulation of live parts (wires), they may become energized. It is to protect against such accidents that emergency grounding is intended.
The grounding switch must reduce the potential on the protected device to zero. As a rule, with the help of this element in electrical systems, a current is passed equal to the short circuit current. This element must be able to pass current.
At first glance, we can say that the cross-section of such a cable should be no less than that of the main working conductor, but this opinion is erroneous. Each phase cable, unlike the ground electrode, must provide long-term passage of high-rated currents. The selection of cross-section is carried out according to an elementary principle - power cables with conductor dimensions from 16 to 35 mm2 must have a protective grounding conductor thickness of 16 mm2.
Designation of conductors in electrical installations up to 1000 V
In accordance with generally accepted rules at the state level, the marking of the cross-section of conductors is determined in accordance with the standards laid down in the current GOST.
In practice, such options are considered when, to achieve optimal accuracy, a separate calculation of the cable cross-section is carried out. To determine the numerical value of the area, it is necessary to use a special formula that will take into account the short circuit current indicator, the remaining time when the protection is triggered, the type of insulation and the type of conductor laying. However, in practice this formula is not always applied.
When carrying out electrical installation work, you should pay attention to the cable designation. In addition to the letter abbreviation, there is also a color designation. The neutral wire is indicated by the letter N, in blue. Combined neutral protective and neutral working conductors must have the letter designation PEN and a color designation: blue along the entire length and yellow-green stripes at the ends.
The quality of grounding plays an equally important role. To determine this characteristic, you need to measure its resistance. As a rule, the voltage in a three-phase network with a linear connection is 380V.
You may be interested in Checking the cable cross-section
Protective conductors - their color coding
When carrying out installation work, the question of color identification of power cable cores often arises. When it is required to install a PVZ for a PE conductor in the grounding circuit, the color scheme of the insulation itself should be yellow-green. Options are being considered when the PVZ is installed as a neutral conductor, and blue insulation is selected.
What size wire should I lay for grounding?
The main feature of choosing a grounding wire is its cross-section. According to PUE-7, the cross-section of the grounding cable must be no less than the cross-section of the phase conductor. Otherwise, the grounding will be considered poor quality and even dangerous.
If the diameter of the phase wire cannot be determined, then you should refer to the input cable. Most often this is SIP-16, which means that the cross-section of the grounding wire must also be at least 16 square meters. In any case, it is better not to use a wire less than 10 mm² for grounding installation.
For example, when connecting an electric stove with a 4 mm² copper cable, the grounding wire must be of the same cross-section. In the case of a water cable of 50 mm² or more, the cross-section of the grounding wire should be at least half, that is, no less than 25 mm².
Wire Specifications
The main indicators of PVZ can be classified into mechanical, thermal and electrical. Using the presented characteristics, you can easily determine the operability of the conductor, in particular:
- The main indicator is the flexibility of the product. The permissible radius (size) of a cable determines the amount at which a given conductor can be bent without risk of damage. The specified parameter is checked immediately after the product is manufactured.
- Temperature has a strong influence on the performance of the conductor, so when laying the product you need to pay attention to this characteristic. For example, the question often arises at what temperature a conductor of the PVZ type cannot be laid. Electrical installation work can be carried out at temperatures from -50 to +50 degrees.
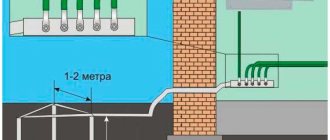
The smallest dimensions of grounding conductors laid in the ground
- An emergency situation may cause short-term overheating. If problems occur, this indicator can reach +150 degrees. In addition, good insulation helps maintain dielectric and mechanical parameters.
- How many single impacts can the insulating layer withstand? This indicator is important for communication lines, as well as when working with specific equipment.
- The main property of a conductor is its insulation resistance. This parameter depends on the cross-section and temperature conditions. To check the indicator, the wire is immersed in water for 2-3 minutes. Subsequent voltage supply is 2.5 kV.
Purpose and structure of the ground wire
The premises of residential, public and industrial buildings must be equipped with a protective grounding system. Before drawing up a report on the condition of the electrical wiring, the inspecting person is obliged to check the operability and safety of operation of each device.
Element structure
The grounding switch is designed to fully protect a person from electric shock. For example, if electrical contact occurs between live parts and the body of the device, there is a possibility of serious injury. Sometimes the slightest touch to such a device can lead to death or serious health consequences.
Note! To eliminate the danger described above, it is recommended that each electrical appliance be equipped with a grounding device.
How does a ground wire work?
Many people often wonder how a ground wire works. For example, if the slightest malfunction occurs during the operation of household appliances, this may be due to damage to the phase cable or the occurrence of an electric current leak. As for residents of the private sector, these areas are mainly electrified by installing overhead power lines. As a rule, these are two-wire lines that consist of phase and neutral wires.
You may be interested in this Features of the frls cable
Checking the functionality of the ground loop
Important! Gusts of wind, falling branches and precipitation can break the power cable at any time, and if the building does not have a protection system in the form of grounding and an RCD device, then not only the owner of the house, but also his household appliances may suffer.
Marking
You need to know what color the ground wire is.
Typically, the ground wire, in the form of a separate conductor, is part of the stranded wire that powers an electrical appliance or outlet.
Thus, in a 1-phase network it will be the 3rd conductor, and in a 3-phase network it will be the 5th.
In this case, a special marking is provided for the grounding wire, which makes it possible to distinguish it from the phase or neutral conductors and thus prevents confusion when connecting:
- Letter. PUEs require that the letters “PE” be applied to the insulation of the grounding wire. The same designation is provided for in international standards. Indication of the cross-sectional area, grade and material is optional.
- Colored. Domestic and foreign standards specify a combination of yellow and green colors for the ground wire. Some foreign manufacturers of cable products designate such a core only in yellow or only in green.
In addition to grounding conductors, combined conductors are used, which simultaneously perform the functions of zero working and zero protective. They are designated by the letters “PEN” and a combination of blue with yellow or green. One color of the ground wire is the main one, the second is applied in the form of stripes at the ends.
Thus, it is quite simple to distinguish the ground wire from the neutral wire, which is marked with a blue color and the letter “N,” and from the phase wire (it has brown, black or white insulation, designated by the letter “L”). Color coding has simplified not only the installation of electrical systems, but also such tasks as finding and replacing burnt, broken or overloaded wires.
Some manufacturers paint the phase conductor in other colors: gray, purple, red, turquoise, pink, orange.
Please note that color coding cannot determine whether the network is 1-phase or 3-phase, or whether it is supplied with alternating or direct current. Thus, the cores and buses of DC networks (used in construction, electric transport, substations, etc.) are also painted in red (“+”), blue (“-”) and blue (zero bus) colors. In 3-phase networks, phases A, B and C are usually designated yellow, green and red, respectively.
The designation of cores in different colors is not used in all wires. So, in a 3-core cable of the PPV brand, which seems attractive due to its relatively low cost, you will not find yellow-green insulation, so it is very easy to confuse the cores when connecting.
If the marking is not visible or missing, you can determine the grounding conductor in a wire connected to the network using a voltmeter: the voltage is measured between the phase conductor (it is determined by the phase indicator) and each of the two remaining ones. When the probe contacts the “ground”, the value on the device display will be higher than when it contacts “zero”.
You can also measure the voltage between the conductors being tested and any grounded device, for example, an electrical panel housing or a heating battery. If the core is zero, the device will show some small value; if it is “ground”, the display will display zero.
The phase indicator, which is used to determine the wire connected to the phase, is similar to a screwdriver, only on the handle there is a diode light bulb and a special contact (usually in the form of a ring under the light bulb). To determine the phase, you need to place your finger on this contact and at the same time the tip of a screwdriver on the conductor being tested. If it is energized, the light will light up.
Marking of ground wires
Any electrical connection diagram contains generally accepted symbols, each of which must be deciphered for easy reading:
- A - conductor core made of aluminum. If there is no letter A on the marking, then copper was used to make the core.
- AA - designation of a stranded conductor. The core is made of aluminum material. Typically, additional aluminum braiding is used to ensure reliability.
- AC - the cable is equipped with an additional lead braid.
- B - the conductor has an increased degree of moisture resistance. Two-component steel is used to make the braid.
- BN - a distinctive feature of the braid is its resistance to fire and extreme temperatures.
- B - the outer part is made of polyvinyl chloride.
- G - conductor without sheath.
- r - the conductor cable has a moisture-proof effect.
- K - control cord, which has a wire winding.
- R - rubber is used to make the shell.
- NP - insulation includes a non-flammable polymer shell.
Protective grounding system
NYM cable
NYM category cord is in great demand among consumers. It can be used to efficiently transport electricity under standard conditions. The purpose of the cable is to transmit alternating voltage with a frequency of up to 50 Hz. Any electrical equipment can be connected to this type of cable. The cable must have the first security class. Features of NYM brand cable:
- The presence of a copper core;
- Intermediate shell;
- Color compliance with PUE standards;
- Easy to use.
NYM conductor
VVG cable
This type of VVG cable has copper conductors, categories 1 and 2 twist classes. Today you can find stranded or polyvinyl chloride conductor models. For example, a three-wire, 4 or 5 cord has a neutral and a ground. Many people often wonder what color ground wire is used in a three-wire wire? Green-yellow polyvinyl chloride plastic is always used to insulate the core.
Wire brand VVG
Cable PV-3
As a rule, a PV-3 cable consists of one core with a twisted copper wire inside. To highlight the outer shell with color, you can use different colors.
Cable brand PV-3
Cable PV-6
The PV-6 brand cord contains a conductive copper core. To create the insulating layer, high quality polyvinyl chloride transparent plastic is used. A distinctive feature of this material is its increased resistance to mechanical stress. If necessary, you can monitor accidental damage to a transparent product. In this case, it is not necessary to adhere to certain standards for the color of the external surface.
You might be interested in Homemade heating cable
Description of conductor of category PV-6
Note! In order to carry out electrical installation work in compliance with all norms and regulations, the conductor is marked with the appropriate color according to international standards.
ESUY cable
A cord of this category can be used to protect the network from short circuits. Power systems with significant currents often resort to using cables of this brand. The main feature of power cable products is resistance to temperature influences. This low-mass conductor is easy to use for electrical work. The voltage rating for ESUY is not specified. This indicator must be set to transport current through the wires. When laying the cable yourself, it is imperative to apply color markings.
Ground wire color coding
According to the latest rules, wiring in a house or apartment must be grounded. In recent years, all household and construction equipment have been produced with a grounding wire. Moreover, the factory warranty is maintained only if the power supply is supplied with a working grounding.
To avoid confusion, it is customary to use a yellow-green color for the ground wire. The hard solid wire has a green base color with a yellow stripe, while the soft stranded wire has a yellow base color with a green longitudinal stripe. Occasionally there may be specimens with horizontal stripes or just green, but this is not standard.
Sometimes the cable only has a bright green or yellow wire. In this case, they are used as “earthen”. On diagrams, “ground” is usually drawn in green. On the equipment, the corresponding contacts are signed in Latin letters PE or in the Russian version they write “earth”. A graphic image is often added to the inscriptions (in the figure below).
Ground wire size
To determine the efficiency, as well as the response speed of the RCD, the most important indicator is calculated - the active resistance of the grounding conductor. By obtaining the correct results, maximum safety from electric shock can be ensured.
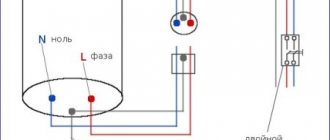
Designation of the ground loop on the diagram
Important! The grounding conductor is not subjected to the full load that the phase and neutral conductors must produce. Based on this, the cross-section of the grounding conductor is adopted with reduced parameters.
How to choose the right wire
Before choosing a grounding wire, you need to familiarize yourself with the basic technical and operational characteristics.
Those owners who live in private houses or in old apartments have to ground household equipment with their own hands. It is important to note that most modern apartment buildings have a ready-made grounding system. Before making the right choice, the owner of a residential premises must clarify which system is installed on a particular site. Considering this indicator, it is necessary to select a conductor of the appropriate type.
Grounding diagram
When determining the type of installed system, you should take into account the basic rules of electrical devices:
- TN-S - the device can be grounded using a separate wire in the AC system;
- TN-C - “zero” and “ground” cables, they are included in a continuous electrical circuit;
- TT - serves for direct protective grounding, which is installed on electrical equipment;
- IT - is responsible for the operation of the device through increased resistance.
You can also determine the correct conductor cross-section by the type of grounding. Among them, stationary or portable ones stand out. For ordinary household grounding, you can use a stationary option, which allows the use of both stranded and single-wire cables.
In conclusion, it should be noted that grounding the neutral wire plays a very important role not only in creating safe operating conditions for devices, but also for the performance of the entire electrical system. Therefore, such measures for the safe use of electrical installations should not be neglected.
We select a cable for grounding.
Before selecting a ground wire, there are several other fundamental issues to consider.
Owners of private houses or country cottages, as well as old apartments built before 1998, have to carry out grounding themselves. Modern houses already have a ready-made grounding system, unlike all old ones. To select the correct section, you need to find out what system exists in the house.
There are only four main ones, according to the Electrical Installation Rules (hereinafter PUE):
- TN-S - grounding is carried out using a separate wire and neutral in an alternating current system;
- TN-C - the “zero” and “ground” cables are combined into one wire, the neutral is separate, most common in houses of the last century;
- TT - direct protective grounding installed on electrical equipment;
- IT - working with the device body through resistance or complete insulation of all current-carrying cables.
Directly on the grounding diagram you should find one of the markings:
- PE - “grounding”,
- PEN - “zero” and “ground” in one cable.
The next important selection factor that will help determine the correct cross-section of the conductor is the type of grounding. Stationary or portable - depending on the purpose. For ordinary household grounding, a sufficient and stationary type, which in turn allows both multi-wire and single-wire multi-core cables.
When we have decided on the type, material of the cable and the type of system, we move on to the main step - selecting the cable cross-section.