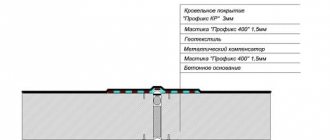
Classification of foundations
It is customary for civil engineers to classify foundations into 2 types:
- According to the type of material used.
- According to manufacturing technology.
Why do you need a foundation?
The foundation of a house is a foundation that is laid underground (in some cases under water) and takes on all the static and dynamic loads that are created by the structures above and external factors. Its function is not only to withstand significant loads, but also to distribute them evenly over the area.
A properly laid foundation of a building is distinguished by strength, durability, efficiency, and individuality. A foundation that meets these requirements does not allow the building to settle and prevents the walls from collapsing. Any foundation requires an individual approach. It consists not only in choosing the appropriate type of structure, but also the material.
Based on the material, steel rubble, rubble concrete, concrete and reinforced concrete foundations are distinguished. The first three types are rigid, the fourth is flexible. The main classification is based on construction technology and includes six types of foundations:
- Tape
- Pile
- Slab
- Columnar
- Floating
Classification of foundations by type (technology) of device
- tape (monolithic and prefabricated);
- columnar;
- slab.
Strip foundation
This type of foundation is suitable for all load-bearing walls of the building, and can be made in a prefabricated structure or monolithic. For a prefabricated foundation structure, builders use reinforced concrete or concrete blocks that form underground concrete “walls.”
To make a monolithic foundation, it is necessary to install formwork, into which the concrete mixture is then poured.
Disadvantages of this type include massiveness and high labor-intensive costs. But all this is more than compensated by the high reliability of such a foundation and the range of its applications.
Types of foundations
1. The service life of the structure may not comply with the requirements of GOST 27751-2014 “Interstate standard. Reliability of building structures and foundations. Basic provisions".
This will inevitably happen if, when developing a project, the degree of corrosive aggressiveness of soils at the construction site is not taken into account (for more details, “Geotechnical and geological-lithological studies and measurements of corrosive aggressiveness of soils”), as well as the presence of stray currents.
Only by selecting the thickness of the barrel wall and blade (more details: “Calculating the thickness of the barrel wall”), the grade of steel (more details: “What does the grade of steel affect?”) in accordance with the specified data, determining the procedure for reducing corrosion (water drainage, use of zinc anodes - more details) “Corrosion: causes, methods of protection”), it is possible to ensure the standard service life of the foundation structure and the entire structure.
2. It is possible for single-blade disaxial screw piles to “fail” at normalized settlements if their shaft diameter is less than 159 mm.
When calculating pile-screw foundations, the formulas laid down in SP 24.13330.2011 “Pile foundations” are used. These formulas were developed back in the 60s of the 20th century and are based on simplified interaction models (for example, the Mariupolsky model for anchors), and therefore do not take into account many features of the joint work of piles and soils.
Therefore, when calculating the bearing capacity of a screw foundation, it is necessary to take into account the results of field tests of soils performed in accordance with GOST 5686-2012.
3. It may be necessary to concrete the base of the column or carry out work to create a rigid interface for single-blade piles of small diameters (57-76 mm).
Due to the insufficient trunk diameter, these varieties do not provide adequate resistance to horizontal loads without additional measures.
To avoid concreting the base of a column or creating a rigid interface, it is enough to use a lateral load resistance element (LESRL).
4. It is possible that the soil structure may be disrupted when driving screw piles and a subsequent reduction in its load-bearing capacity.
Such situations arise when the calculations take into account only the diameter of the blade, but not its configuration.
The configuration of the screw pile blade, selected for specific soil conditions, allows minimizing disturbances to the soil structure during immersion, which ensures proper perception of design loads (for more details, “Principles for selecting blade parameters”).
5. Piles with two or more blades may be inferior in the perception, for example, of horizontal loads even to single-blade disaxial structures.
The reason for this phenomenon is the incorrect (often simply thoughtless) location of the second and subsequent blades on the trunk.
In order for multi-blade piles to properly carry the design loads, the distance between the blades, pitch, and inclination angle must be calculated taking into account data on the soil conditions of the construction site and data on the loads from the structure (more details: “Features of calculating multi-blade screw piles”).
6. Uneven distribution of safety margins across the foundations of individual housing construction projects, which reduces their level of reliability and shortens their service life.
The reason is the failure to take into account the various magnitudes of loads acting on the foundations of even simple structures (under critical load-bearing units and structures of the structure, under load-bearing and self-supporting walls, under non-load-bearing partitions and floor joists).
To avoid this, for each type of load you need to use a certain modification of piles (more details: “Calculation of a pile foundation”).
Thus, all the disadvantages of a pile-screw foundation are largely associated with ignoring its features and strengths.
Slab foundation
This type is the most rigid structure, since when laying such a foundation, a slab is used over the entire area. This slab can be solid or composed of cross-joined and well-fixed reinforced concrete beams.
Such a construction will be justified when the house is being built on very unstable soil, where subsidence may occur. When using this type, there is a large consumption of reinforcement and concrete and therefore it will be an expensive option.
Pile foundation
Pile foundations are installed on soils with insufficient bearing capacity. The design of the bottom foundation is based on individual piles or groups of piles. They are pillars with pointed lower ends. The piles are driven into the ground and connected on top with a special reinforced concrete beam or slab called a grillage.
Pile foundations are installed on unstable soils, as well as in places where it is necessary to make a passage through soft soil in order to support the foundation structure on stronger layers. It is advisable to construct pile foundations on sandy, water-saturated soils, which, when exposed to external loads, can cause significant shrinkage. In most cases, piles are used when arranging foundations for powerful construction projects with a load on the base of the foundation of 15-25t/sq.m.
In private construction, pile foundations are rarely used. Short wooden or reinforced concrete piles are used only in cases where it is not possible to equip other types of foundations.
Pile foundations differ in the material of manufacture:
- Reinforced concrete. In their production, reinforced concrete of class B10-B20 is used. Their scope of application is the construction of heavy buildings with reinforced concrete structures.
- Wooden. Made from specially treated pine. They are used in frequent construction in the construction of small and light wooden buildings that have no more than 2 floors.
- Metal. Made from metal pipes. Heavy buildings can be erected on such foundations in cases where it is impossible to use reinforced concrete piles.
- Combined. Such piles are made of concrete and metal. They are used in difficult engineering and geological conditions during the construction of heavy high-rise buildings. In this way, construction of objects is carried out, for example, on loose or marshy soils.
Piles are classified according to the type of foundation made into:
- Hammers. To immerse them in the ground, special machines are used - pile drivers. They are used only when carrying out construction work in undeveloped territories. There should be no operating buildings nearby, since high impact loads transmitted through the ground can lead to structural failure of nearby buildings.
- Printed.
They are made by drilling holes and subsequently filling them with concrete. - Pressable.
This type of piles is pressed into the ground using powerful hydraulic pumps under high pressure. Pressed and driven piles are intended for constructing foundations in cramped conditions. They can be used in the construction of heavy reinforced concrete or high-rise brick buildings in close proximity to old buildings.Screw.
These piles are equipped with a thread in the form of a blade, the diameter of which ranges from 3-3.5 of the diameter of the pile. They are screwed into the ground with a special machine, like a screw. Screw piles are widely used in the construction of bridge supports and power lines, as well as in the construction of foundations for masts or towers for various purposes. The main advantage of screw piles is the possibility of their use on any soil.
Foundations based on screw piles are expensive. They require the use of specialized equipment to transport and install the pile. A positive aspect when arranging this type of foundation is the reduction in the amount of excavation work and the reduction in material consumption.
Installation of foundations for old houses
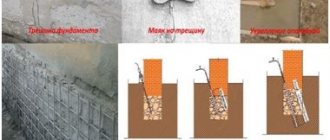
Sooner or later, a moment may come when a crack appears on the base of the building, or the supporting structure becomes distorted.
This is a consequence of the fact that the foundation has weakened under the influence of constant stress and the environment. In this case, it is urgent to repair the foundation and replace its damaged parts.
If only some part of the foundation is destroyed, then it is necessary to build up the sides with masonry of the required width, which will provide a connection between the old and new masonry.
If weakening of the foundation is found in some places, then a “cage” should be made for the reinforced concrete, which is firmly attached to the existing masonry using through anchors.
Fastenings are carried out in such a way that the new sections work together with the old part of the foundation.
Replacing rotten crowns of a wooden house
Many wooden houses that have been standing for many decades require replacement of the lower crowns. Corrosion of crowns occurs due to poor or completely absent waterproofing between the base of the foundation of a wooden house and the lower logs.
First you need to dismantle the foundation under the lowest log to a height where the log can be easily pulled out. We prepare in advance a new log of the same size as the old one.
The bottom of the log should be prepared evenly so that it fits snugly against the foundation lining. 3-4 layers of roofing felt should be placed on the lining.
A special material is placed on the top of the log and the log is placed in its original place. Similar actions are carried out around the entire perimeter of the house.
Columnar foundation
A columnar foundation is a system of pillars connected by a grillage or reinforced concrete beams. Depending on the immersion method, the pillars are either hanging or supporting. The first ones are shorter and stay in the ground due to friction. In order for them to fully fulfill their function, their number must be significant. Retaining pillars are longer, their lower end rests on solid rock.
Based on the nature of the installation of the grillage, the columnar foundation is divided into three types: shallow, shallow, and recessed. In the first option, the grillage lies on columns above the surface of the ground (at a height of up to 50 cm). With a shallow foundation, the grillage goes underground by 40-60 cm. In the third case, the reinforced concrete connection is below the soil freezing line.
The columnar type of foundation is ideal for light buildings (frame houses, sheds, bathhouses, greenhouses, garages). Its construction does not require the use of special equipment and is relatively cheap. This foundation allows you to build houses on slopes and heaving soils. But when choosing, it is worth considering that this foundation is sensitive to lateral loads, is not suitable for construction on swampy soils and does not make it possible to make a basement.
Glass type foundation
This is a type of columnar foundation, characterized by greater stability. This support property is ensured by a special structure. The lowest part is a concrete base on which the kneecap (shoe) rises. The third structural element is the supporting column, which is installed in the cavity of the shoe.
The blocks are manufactured by the factory, the task of the builders is to install them, so all work goes quickly. Spot construction not only speeds up the work, but also extends the shelf life of the glass foundation. Thanks to the monolithic slab, the supports standing on it are protected from ground moisture. The structures themselves can be dismantled and moved to another point. This type of foundation is used in industrial construction and in the construction of bridges.
Photos of foundations
Did you like the article?
0