Xenon device
Halogen, xenon or LED, which is better - before answering, you need to determine the characteristics of each type of headlight. Let's start with xenon, because most drivers have heard this word at least once in their lives. The operating principle of these headlights is based on the ignition of an electric arc in a special gas. As the name suggests, sealed designs use xenon. A voltage of 25 thousand volts is applied to the contacts inside the gas flask. The electric arc in xenon emits powerful light, which is concentrated using special lenses, directing the light onto the road surface.
Depending on the lamp model, color temperature varies from 3 to 12 thousand kelvins. 10-12 thousand headlights visually emit a bluish light, however, most cars use products with operating temperatures from 4.5 to 6 thousand kelvins. In this case, the glow will be whiter compared to high-temperature xenon. Please note that there is a misconception among drivers that the higher the operating temperature of xenon, the brighter it shines. Only the spectrum, that is, the color of the radiation, depends on this parameter.
In cloudless weather, it is optimal to use 6 thousand Kelvin models. In this case, of course, the level of road illumination will be the best. Moreover, in fog or rain, such lamps will complicate driving, since drivers will see only a bluish curtain in front of them. Xenon at 4300 has a yellowish tint; therefore, it is practically not reflected in water drops and fog, so it is ideal for trips in rain or snowfall. Additionally, yellow light is better reflected from road markings. In this regard, many drivers strive to install xenon at 5 thousand Kelvin (it can be used comfortably in any weather).
The light power from xenon is 3-5 thousand lumens. In comparison, halogen bulbs produce up to 2 thousand, so in this regard xenon is more preferable. Xenon energy consumption is only 40-45 watts.
LED and halogen lamps comparison
Buying lighting fixtures is a fairly serious decision. Light today is one of the benefits we take for granted, and its poor quality can greatly affect not only the entire interior of the house, but also the health of a person’s eyes. Even an ideal product can have drawbacks, so it’s worth starting from real facts about light bulbs when choosing them.
LED lamps advantages:
- Long-term operation. Having bought one lamp, you can never buy a second one again; the use of LEDs reaches 100,000 hours - approximately 25 years. Therefore, the light bulb is purchased “for life.” The models are made on the basis of crystals; they cannot burn out or break. In this case, the high price of the product will pay off within a few months;
- Economical. Lamps require 20 times less electricity, although they emit light much better than ordinary lamps;
- Ultraviolet. This device does not have such a function, which means that the beam will not heat the objects at which it is directed. Thus, the top ball of furniture and other interior components will not deteriorate;
- The lamps contain no toxic components. Even though the flask cannot break from an impact, there are conditions under which it can be damaged. In this case, the human body is not susceptible to the effects of negative chemical elements.
LED lamps disadvantages
- More than once we have mentioned the high price of the product, but this drawback can be accepted, since the lamp’s performance will be at a high level;
- Lamps do not tolerate too high air temperatures. Innovative models have a cooling radiator, but they are still not recommended for use in closed lighting fixtures;
- Focus. LEDs only emit light in a direction, so it will be difficult to illuminate a large space with one device. It is better to use lamps with many bulbs or distribute lighting evenly throughout the room;
- Weight. Oddly enough, LED lamps have a lot of mass. The fact is that each of them is equipped with a radiator. Therefore, screwing it into a light and fragile lamp would be a mistake.
Halogen lamps advantages
- Economical. This type is a great saver for the family budget; even buying the light bulb itself will cost less than, for example, an LED one. The lamp consumes low power. This is reflected in its performance. The device will produce up to 15 lumens;
- Compared to LED lighting, they are used very little, but in the case of other options, they are superior. The average lamp operation is designed for 3.5 thousand hours;
- Compactness. Halogen light sources are almost always miniature models, so they can be used for any lighting fixture.
Halogen lamps disadvantages
- The following products are used: quartz, volatile halogens, buffer gases - all these materials are expensive, but still cheaper than LED;
- This type needs to be maintained. Once every six months you need to wipe its legs from dirt and the flask from dust. Accumulated dirt can lead to a rapid end of service life;
- Unfortunately, the lamp can cause a fire, so you should take safety precautions during installation in advance;
- The lamp may break. The problem is not that it can no longer be used, but that the gases in it can cause headaches for several days.
Halogen and LED lamps differ not only in design, but also in thermal power, shelf life and durability.
A halogen light bulb creates excess heat, so when used for a long time (2-3 hours), a person will be able to feel it if he is close to the lamp. Because of this feature, such lamps cannot be used in places where objects are too sensitive, such as art galleries. The energy of the device is largely directed not at bright radiation and illumination of the room, but at generating heat. An LED lamp, on the other hand, works purely for brightness. If the first lamp heats up to 250 degrees Celsius, then the maximum temperature of the LED does not exceed the threshold of 70 degrees.
In addition to performance characteristics, it is also important how the lamp will fit into the interior of the room. If it is used in a closed room, then ordinary white light is enough, which a halogen lamp can easily provide. But this species does not have variety in its color scheme. At this time, the LED can be of different colors, while having a warm or cold tint. It can be used not only for direct lighting, but also for decorative purposes. Thus, LED lights of different colors decorate swimming pools, gardens, and paths. They can also be easily used in residential areas.
Advantages and disadvantages
Let's determine the main advantages of xenon lighting:
- High level of luminosity (up to 5 thousand lumens). This is enough to efficiently illuminate the road at a distance of up to 60 meters.
- Durability. Xenon lamps can operate up to 3 thousand hours, although in practice this figure may be less.
- In xenon lamps, only 5-10% of the energy is converted into heat, which means there is less chance of critical overheating in hot weather.
- It is possible to install the headlights yourself, but it is better to adjust them using specialized stands.
Xenon has several disadvantages. Firstly, it fades over time, so if one bulb changes color, you will have to change all the headlights. It is almost impossible to match a new xenon to your old headlight. Secondly, homemade xenon models strongly dazzle other drivers, so if you have them installed, be prepared for unpleasant conversations with traffic police officers.
LED device
These are one of the most modern lighting devices, so you can often come across the question on the Internet: what to use: xenon or LEDs? To answer this question, it is necessary to consider the design and characteristics of LED lamps. They are semiconductor elements that emit light when exposed to electric current.
Modern LED lamps have a built-in driver that allows you to increase luminosity several times. In this regard, the indicators reach an impressive 4 thousand lumens. Thanks to this, LEDs compete quite successfully with xenon headlights. The design assumes the presence of “plus” and “minus” connectors, so polarity must be observed when connecting.
The technology is rapidly growing in popularity and becoming universally available. If previously LEDs were installed only on expensive foreign cars, now every driver can install such headlights.
Comparison of parameters
The main characteristics by which the comparison is made:
- LED energy consumption is several times lower than that of halogen lamps;
- service life - for halogen lamps about 2.5 thousand hours, for LED lamps from 50 thousand and above;
- power – 100 W incandescent lamp corresponds to 60 W halogen and 12 W LED bulbs;
- color temperature – halogen is close to sunlight, LED has a wide range (from 2000 K to 6500 K);
- Maximum power for both sources is achieved in 3 seconds;
- price - halogen lamps cost about 5 times less than LED lamps;
- Halogen lamps cannot be placed in closed lamps and other devices with difficult heat dissipation.
Advantages and disadvantages
LED lighting has many advantages, including:
- Sufficiently high luminosity with a pleasant shade of color to the eye.
- Low consumption (only 20-30 watts).
- Absolutely legal. You can install LED light bulbs without fear of being fined.
- High mean time between failures (up to 30 thousand hours). This is the highest figure among the compared headlights.
- The presence of low and high scattering light, which does not blind other road users.
Along with these advantages, it is worth noting a number of important disadvantages. LEDs get very hot, so special coolers are installed to cool them. In this regard, the design turns out to be quite massive, and if the cooling system fails, the LED may burn out. LEDs are extremely susceptible to power surges, which can significantly shorten their lifespan. In practice, the resource is limited to 8-12 months of work.
We looked at xenon and LEDs, and the difference is now not difficult to determine. These two technologies now dominate the market, which is why many foreign cars have xenon or LEDs .
Light bulb design
To more accurately understand LED and halogen lamps, you should study their design, which is what we will do now. Let's look at their structure separately, starting with an LED light bulb.
It consists of the following elements:
- Base made of glass or plastic. It is worth noting that plastic bases are of higher quality, as they are more impact-resistant and durable. It has a standard shape and can be installed in any lighting device. Compatible with all cartridges.
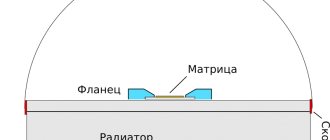
- Actually the LED itself. It is the main component of this device. In turn, it consists of a cathode, anode and a semiconductor, on the quality of which most of the characteristics of the device depend.
- Matrix or driver. Responsible for the operation and controls the operation of the device. It contains a capacitor and a diode bridge, and some additional elements to stabilize operation. But there are varieties that require an additional connection to the power supply to operate from a 220 volt network.
Halogen lamp design
As you can see, there is nothing exorbitant or complicated in the design of an LED lamp. Let's now look at what halogen lamps consist of:
- This light bulb has the shape of a regular incandescent lamp. That is, the standard E27 base.
- Inside there is a tungsten filament, surrounded by an additional glass body of a specific cylindrical shape.
- The internal space of the additional flask is filled with special buffer gases, halogens. This gas consists of iodine or bromine vapor. Thanks to this environment, the light bulb emits an intense glow and is able to illuminate the room well.
LED lamp device
Due to the presence of harmful substances, namely halogen vapors, such light bulbs should not be thrown away, disassembled or broken. They must be disposed of at special collection points, but for this you will need to pay a certain amount of money.
The device of halogen lamps
Structurally, these models resemble classic incandescent lamps. There is a base, inside of which there is an incandescent filament. The latter, under the influence of voltage, heats up and emits light. Classic light bulbs use tungsten filament. To prevent its oxidation, air is removed from the base. The main problem with such lamps is the peeling of tungsten atoms, which then settle on cooled surfaces, such as the walls of the bulb. As a result, the level of illumination decreases, and the thread gradually becomes thinner until it breaks completely.
Halogen models use iodine or bromine halogens instead of vacuum. In practice, this prevents the filament atoms from settling on the walls of the flask. Additionally, the service life and temperature of the filament increased, which led to better light emission.
The industry creates halogen headlights with different glow temperatures. This makes it easy to choose headlights to suit your taste, as well as buy so-called universal models that provide excellent visibility not only at night, but also in fog or rain. Comparing the latter with other types of headlights, halogen has a luminous flux of only 1-2 thousand lumens. In this case, energy consumption is 55-60 watts.
Such lamps are a relatively old technology, but many motorists still install such headlights. This is largely due to the fact that there is no option to install LEDs or xenon, but halogen is better than standard headlights.
Lamp arrangement
A halogen lamp may look different, even like a regular incandescent lamp, but the principle of its operation is practically unchanged. There is a gas inside, and it contains small additions of halogens, these may be different components in different types. Usually this role is played by:
- Chlorine;
- Bromine;
- Iodine;
- Fluorine;
- Mixtures of them.
It is these additives that distinguish a halogen lamp from an incandescent lamp; if in that case the glass bulb darkened due to tungsten fumes, here it remains clean and transparent until the end of use. Although the filament itself still consists of tungsten.
The filament process occurs as follows: an electric current heats a tungsten filament to a high temperature. When heated, the filament produces light.
When exposed to temperature, tungsten atoms begin to evaporate, and then try to settle on the less hot walls of the flask as condensate. The difference between a halogen lamp and others is in its chemical composition. Here the tungsten filament is surrounded by volatile impurities of iodine or other chemicals. Due to the increased temperature, impurities come into contact with the tungsten particles and prevent them from settling. This process is reversible, it occurs constantly when the light is on. Tungsten atoms cannot leave the filament and settle directly on it, then evaporate again.
In order to slow down the evaporation process, small flasks are used, they have higher pressure. Thus, more expensive gases such as xenon or krypton can be used in flasks. Because of this design, the lamps are characterized by bright white light, compactness and improved light output.
LED samples are somewhat different in appearance from conventional or even halogen ones. But the differences don't end there. These devices use diodes as a light source. The principle of LEDs makes the lamp safe for human health, which means it can be used in almost any room.
The LED itself is an electronic device that creates optical radiation when connected to the network. What distinguishes diodes from tungsten and halogens is their light emission spectrum. If a halogen lamp has a wide spectrum, but color filters need to be used for them, then here the device itself emits the necessary light.
The operating principle of such devices is based on electroluminescence, while the operating range of an LED lamp will still depend on the chemical composition of the LEDs in it.
In recent years, electricity has become increasingly more expensive, which means that it is necessary to enter into austerity mode, or do things a little differently. Due to their compositions, and most importantly, sizes, LED and halogen lamps have different prices. This fact may influence the purchase, but it is also worth considering that the use of lighting will be constantly paid for by you, and here you already need to think about which lamp will be cheaper to operate.
Halogen lamps are cheap, but more expensive than incandescent and energy-saving lamps. Therefore, they are bought a lot, especially often they are used in large lamps, which are designed for 6 or more copies. They give off light perfectly, so the room becomes instantly illuminated.
LED models are very expensive - this is their significant drawback, and it is this fact that often scares buyers away from these products. But you need to understand that LEDs are bright electrical devices, their lighting is enough for entire landscape parks, they illuminate gardens, roads and ordinary streets.
The secret is that the lamp consumes little power to be efficient and saves a lot on your budget. And also from an economic point of view, the purchase of such types for one large room is limited to just a few copies, if not one, so this also helps to save money.
Advantages and disadvantages
Halogen lamps have one significant advantage, thanks to which they remain on the market. This is an affordable price. For drivers of classics and other old cars, such headlights become a real salvation. Additionally, you can easily select the required level of glow.
In all other respects, halogen is inferior to the two options described above:
- These are incandescent lamps, albeit improved ones, and therefore have high energy consumption, which means additional fuel consumption.
- Difficulty of installation work. When installing, do not touch them with your hands, as there is a chance of darkening the base.
- Relatively low resource. Manufacturers claim a service life of up to 1000 hours, but in practice the average is 500 hours.
This is key information regarding halogen headlights.
Drawing conclusions
Let's try to answer the main question: halogen xenon or LEDs - what to choose? To make it easier to decide, here is a comparative table of all three technologies according to the main parameters:
| Parameter | Halogen | Xenon | Light-emitting diode |
| Power, Watt | 55-60 | 35-45 | 20-40 |
| Brightness, Lumen | 1200-1500 | 3000-5000 | 2000-4000 |
| Color temperature, Kelvin | 2800 | 4300-5000 | 5000-6000 |
| Work resource, hour | 500 | 3 000 | 10 000 |
| Cost of the set, USD | 15-20 | 40-50 | 40-80 |
Thus, the cheapest lamps have the worst performance. Halogen consumes the most energy, has a minimal operating life and relatively low brightness. These headlights are suitable for those who have a limited budget or simply do not want to install expensive models on their old car.
Xenon and LEDs can conditionally be called competing technologies. If you need better road illumination, then choose xenon. It offers the highest lumen output available. Additionally, such a kit costs less than LED.
LED lamps are inferior in brightness to xenon, but their main advantage is low energy consumption and long service life. Thanks to this, buying LED headlights is a profitable investment. Due to low consumption, you can save 100-200 milliliters of fuel per hundred kilometers, which is a very pleasant fact. These are just the most expensive bulbs. Of course, everything may change in the near future. The technology is improving, which means that production costs will be reduced, and the brightness may well reach the levels of xenon.
Headlights of the future
Following LEDs, a new technology has already been created, which is gradually being introduced into the automotive industry - laser headlights. If we consider the design of such headlights, we can highlight the frame on which 3 lasers are mounted. Additionally, mirror reflectors and a “phosphorus” lens are mounted. Laser beams are directed through a reflector onto the lens, and yellow phosphorus emits light when exposed. Similar technology has already been tested on the latest BMW i8.
It is still difficult to give exact operational parameters, since laser headlights are being improved and finalized for the mass consumer. According to various statements from the developers, they will have a brightness higher than LEDs with lower power consumption, as well as a temperature of 5500 Kelvin. The service life is about 10 thousand hours. Laser models are completely safe, since the light flow is generated by yellow phosphorus.
The technology is being developed by several brands, including Osram, Philips, Valeo, Bosch and Hella. They plan to make the headlights intelligent. They will have an infrared sensor built into them that will be able to detect pedestrians and other obstacles. Such objects will be illuminated by laser headlights more intensely, attracting the driver’s attention.
Mass production of laser models will begin after 2021, but the technology is already being used by the Audi R18 E-tron Quattro, Audi Quattro Sport Laserlight, Audi R8 LMX, and BMW M4. It is likely that this list will expand significantly; accordingly, laser headlights will become a direct competitor to LEDs.
Now you know all the advantages and disadvantages of the main types of headlights. When purchasing, consider the cost of the kit in your region, the brightness level and compatibility with your car model. When using xenon, be sure to order special lenses so that the light does not blind oncoming drivers.