Advantages and disadvantages
Mercury gas-discharge lamps are an electric light source, one of the types of gas-discharge models. Their work is based on the passage of an electrical discharge through a gaseous medium.
DRL and DRV lamps are gas discharge lamps
Important! To designate light sources of this type, the term “discharge lamp” or RL is used.
Mercury lamps are divided into:
- DRV (interpretation - arc mercury-tungsten);
- DRL (or arc mercury phosphor).
The advantages of direct switching lamps DRV include:
- Ease of connection, use and replacement: they can operate on 220 V AC power and do not require ballasts;
- When warmed up, the resistance increases and stabilizes the network voltage - even at low voltage the light will be stable;
- They can operate from different power sources;
Lamps provide high-quality light
- The light sources are both tungsten filament and fluorescent radiation, that is, cold and warm white colors are mixed. This allows you to get more even light;
- Low price.
The disadvantages are:
- Low luminous efficiency. For example, the efficiency of Philips lamps does not exceed 30 lm/W, although other types of light bulbs from the same company have an output of up to 50 lm/W;
- A small selection of models: in stores there are only 5 models of different power;
- Short service life - no more than 3-4000 hours, and more often less. Replacement is quite expensive, this increases the final cost of the lamps.
Explanation of markings
In the name of the DRV lamp, the decoding of the symbols is as follows: “arc mercury-tungsten.” According to the principle of operation, it is similar to sodium and mercury light sources, but unlike them, it has a tungsten spiral, which allows you to turn on the device without an external ballast that regulates the starting voltage.
All fluorescent type spotlights operate on alternating current from a 220 V network. Chokeless devices with an e40 base have increased luminous efficiency compared to conventional incandescent lamps and have a long service life. When they fail, they require special conditions for disposal.
Decoding the alphabetic and digital markings allows you to select a device with optimal power in accordance with the user’s requirements. The lamps are recommended for use in lighting systems for public areas. Depending on the characteristics of the device, a direct stream of light will help illuminate a parking lot, park area, greenhouse, street, construction site, room for animals and poultry, and utility yard.
Technical characteristics of DRV and DRL lamps
There are models of various powers on the market: 160 W, 250, 500, and occasionally you can find 700 and 1000 W.
Light bulbs available in different wattages
Below is a technical description for DRV 250 lamps (they are used for artificial lighting in greenhouses):
- Lamp length is 22.5 cm, diameter - 9.1 cm;
- Service life - 3000 hours (on average);
- Luminous flux - 4700 lm;
- Light output level - 18.8 lm/W;
- The voltage is 220 W;
- Nominal power level - 250 W;
- An E40 type base is inserted.
You may be interested in Features of light bulb sockets
Other models will have different characteristics.
Features of the DRV 250 lamp
The mercury-type energy-saving lamp is produced by the largest world-famous companies specializing in the supply of lighting fixtures and equipment components. Products are manufactured from modern materials using innovative technologies.
The DRV 250 light bulb consists of a flask with a high-pressure argon medium, a tungsten spiral and a mercury discharge torch. It does not require a starting control device . The product can be installed in ordinary sockets, just like the usual incandescent light bulbs.
There is an opinion that in everyday life and at work it is better to use a hybrid light source with increased emission potential. In practice, it turns out that the performance characteristics of e40 are 50% lower compared to inductive choke DRL devices. The reduction in pulse efficiency occurs due to the limitation of the voltage flowing through the burner head. Its power and resistance are controlled by a starting device.
When the light bulb is activated, a cathode drop in the operating mode to 20 V occurs in the choke light source. After the main element of the e40 gas-discharge lamp lights up, its voltage rises, and the voltage readings on the tungsten coil decrease exponentially. The technical characteristics and design of the working elements, compared to an incandescent lamp, which can be distinguished by the design of the working elements and appearance, provide a brighter glow. The spiral has 30% less electrical energy.
Principle of operation
The operating principle of gas-discharge lamps is a little more complicated than that of incandescent light bulbs.
- When current is applied, voltage is transmitted to the current-carrying parts of the base;
- Then the energy passes through the circuit to the electrodes located in the burner, and a glow discharge appears between them. Ions and free electrons begin to accumulate on the surface;
- As ions and electrons accumulate, the internal space of the burner begins to heat up, and the mercury evaporates. The discharge occurs from a glowing state to an arc state, which creates blue or violet radiation;
- This glow causes the phosphor to glow, which creates a reddish light. When all colors are mixed, the result is white.
You can examine the lamp inside only by breaking the glass flask.
The more mercury vapor evaporates, the more the brightness of the discharge increases. On average, it takes 4-5 minutes for the DRL to light up, while the DRL lights up almost immediately.
Important! The higher the air temperature, the less time it will take.
DRL and DRV lamps. Device and operation. Application and features
DRL and DVR lamps are a common type of gas-discharge mercury lamps. They are used for street and indoor lighting. Both types are almost identical in appearance, especially when turned off. These are very efficient light sources in terms of energy saving, with a luminescence rate of 30 lm/W. This is quite a lot, but more modern varieties of light bulbs can have an output of 50 lm/W. Such lighting equipment is produced by many world-famous brands. It should be noted that due to the mercury content in lamps, they are prohibited in many countries, so the number of DRLs and DVRs is gradually decreasing.
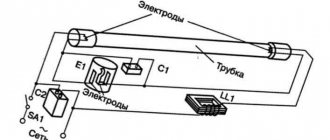
How do DRL and DRV lamps work?
A quick glance at these lighting devices reveals some similarities with ordinary incandescent lamps with an E27 base. However, HID lamps have white tinted glass, with a transparent area just in front of the base. It is precisely because of the opacity that it is impossible to see that such devices have a specific structure inside.
Design and principle of combustion of DRL lamps
DRL (Arc Mercury Phosphor) lamp. Its design provides:
1 - Threaded base 2 - Resistor 3 - Molybdenum foil 4 - Ignitor (auxiliary) 5 - Supporting frame 6 - Outer bulb 7 - Compressed junction 8 - Mercury quartz arc discharge lamp 9 - Nitrogen filler 10 - Tungsten electrode (main) 11 - Lead wire
The base has a standard design, like the vast majority of household light bulbs used in chandeliers and lanterns. It receives electricity transmitted to its surface. It has two reception points. One electrode is located in the center, and the side of the base serves as the second electrode. The base is threaded into the lamp socket.
The main working element of the lamp is a quartz burner. On its sides there is a pair of electrodes. One is main and the other is auxiliary. They are located in an internal quartz flask filled with argon and mercury vapor.
The glass flask is placed on top of the quartz flask. To fill the space, nitrogen gas is pumped into it. The inside of the flask is painted with a white phosphor, so it is not transparent.
The operating principle of such lamps is more complex than that of incandescent lamps. When electricity is supplied to nearby electrodes, a glow discharge is created. This causes a breakdown of energy between them. As a result, the glow discharge develops into an arc discharge. It creates blue or violet radiation in the lamp. It provokes a bright glow of the phosphor, which colors the inside of the glass bulb. The phosphor itself produces a reddish light. As a result of mixing shades of red, blue, violet, a bright, almost white color is created.
Initially, the lamp produces a small amount of light, and gradually increases its efficiency. After 10-15 minutes from the moment of switching on, maximum brightness is reached, the speed depends on the external temperature.
Current fluctuations greatly affect the efficiency of the DRL glow. Even with electrical voltage surges of up to 15%, brightness drops can be as much as 30%. If the voltage drops to 80%, the lamp will go out.
The big disadvantage of such light bulbs is their strong heating. As a result, the insulation on the wire may burn out. Therefore, when connecting, you need to use only specialized heat-resistant cartridges and cable. In the light bulb itself, the pressure increases greatly during operation. In this regard, after turning it off, you need to wait until the flask has completely cooled down. If you turn on a hot light bulb again, it simply won’t light up.
The use of a DRL lamp implies the mandatory use of ballasts. A throttle is usually used as it. It limits the current that is supplied to power the lamp. The throttle matches the light fixture's power and directs the optimal amount of energy to it to minimize overheating and prevent uncomfortable lighting. If you do not use a ballast when turning on the lamp, the lamp will fail almost instantly.
The ballast can be built into the lamp or connected externally. The first option is more convenient because it does not require upgrading the electrical wiring.
DRV device
MRV (Mercury-Tungsten Arc) Lamp:
It is a hybrid between incandescent lamps and DRL. It contains a tungsten helix. It is located together with the burner in a quartz flask with an argon environment. Moreover, if a DRL lamp requires an induction ballast, then DRL devices do not need it. Its functions are taken over by a tungsten filament.
Tungsten filaments act as limiters, which are capable of passing only a certain amount of current. Their potential is calculated according to the characteristics of the lamp. The tungsten filament has high resistance, so it burns energy, which reduces the efficiency of such light bulbs. This element is the weak link, which is why the glow period of the DRV rarely exceeds 1200 hours.
The filament is in argon, an inert gas, which causes rapid wear of the filament. For example, in incandescent light bulbs, a vacuum is maintained in the bulbs, so even thinner tungsten filaments last much longer.
Application area
DRL and DVR lamps can be found quite often.
What is usually illuminated with DRL lamps:
- Roads and streets.
- Squares, parks.
- Car parks and gas stations.
- Warehouses and industrial workshops.
What is illuminated most often with DRV lamps:
- City blocks.
- Boulevards, parks and squares.
- Warehouses and industrial workshops.
- Car parks and garages.
- Construction sites.
- Plants in greenhouses (DRV 250 only).
Such lamps are produced with power from 150 to 1000 W. It is very rare to find 80 and 125 W DRL bulbs. The most powerful lamp can create a glow of 50 thousand lumens. At the same time, the color temperature reaches 4000 Kelvin. Low-power light bulbs are produced with E27 sockets. Thanks to this, they can be screwed into standard chandeliers in city apartments and lampshades in hallways. Larger DRLs and DVRs are made with an E40 base. Today they can be found on lamp posts.
Lamp marking
DRL and DRV have a digital addition after the letter abbreviation. The size of the numbers represents the number of watts. For example, DRL-400 means that it is a mercury arc phosphor lamp with a power of 400 W. DRV 250 is a mercury-tungsten arc lamp with a power of 250 W.
Advantages and disadvantages
DRL and DVR differ from each other in design, which naturally affects the efficiency of their work. In particular, DRLs have a glow of the inner bulb that is 30% less than DRLs.
The positive aspects of choosing to use DRL lamps are:
- One of the best light output indicators in its price class.
- Compact dimensions for demonstrated efficiency.
- Long service life without voltage surges.
As for the disadvantages, they are:
- Visible pulsation of light flux.
- Probability of breakdown due to strong power surges.
- Impossibility of quickly restarting until the flask has completely cooled.
When describing DRV lamps, we can name several positive points:
- No need to connect a throttle.
- Pleasant spectrum of light for the human eye.
Such designs are not without their drawbacks. First of all, such lighting devices have a very modest service life. In addition, they have a much lower efficiency than standard mercury lamps.
DRL and DVR are a pretty good light source for equipment in this price segment. By choosing such equipment, you can improve the performance of old lamps while reducing energy consumption. A huge disadvantage of such light bulbs is their internal content, which is dangerous for humans. In this regard, it is better not to use such equipment in buildings, especially in apartments and houses. Although the light bulb uses very little mercury, if the bulb is broken, the evaporation will spread throughout the room
Government policies in many countries are aimed at reducing the use of mercury-containing equipment. For this reason, in many places such light sources are prohibited. In Russia, utilities almost no longer use DRL and DVR lamps when servicing lighting systems, which was a consequence of the corresponding government order. Soon the production and sale of such light bulbs will be completely stopped. In fact, only medical devices containing mercury will remain, for which there is no safer analogue.
Disposal problems
Lamps of this class contain mercury, so they belong to the first hazard class. In this regard, their disposal must be carried out using special equipment. They should not be disposed of in general waste bins. Many stores that sell lighting equipment have special bins into which you can throw away burnt-out DRL and DRL lamps for free. They are subsequently sent for processing. Burnt-out light sources can be treated in various ways. This may be high heating with firing or the use of chemical reagents. The end products of processing are mercuric chloride and sorbent.
DRV and DLR lamp - which is better to choose
DLR stands for "Arc Mercury Fluorescent Lamp". The active luminous element in it is an electric arc that occurs between 2 electrodes and operates in mercury vapor.
The DRV lamp is a mercury tungsten lamp that operates without a choke. It looks like a combination of a DRL burner and a tungsten filament, the latter performing the function of an induction ballast.
On the right is a DRL lamp, on the left is a DRL lamp, the power of both is the same
Despite the similarity of DRL and DVR, there is still a difference between them:
- To ignite a DRL, a ballast is required; for a DRL it is not needed (this is a chokeless bulb);
- The luminous flux of the DRL is 40-50% lower than that of the DRL, but it turns on immediately and does not warm up for several minutes;
- The service life of DRL is longer than that of DVR, since the tungsten filament breaks down quite quickly;
- Many users also note that DRV light bulbs are more energy-consuming.
Alternative lighting sources
An energy-saving LED lamp is an excellent analogue to other lighting sources, including DRL; if you buy it, you can significantly save on electricity. Replacing street lighting will pay for itself after three years of operation, even taking into account the refurbishment work.
Many well-known foreign and Russian companies (for example, Lisma) are engaged in the production of these lighting devices. Currently, the price of these devices is slightly higher than the cost of a DRL lamp, but in the near future this problem will be eliminated, which will make LED lighting sources more accessible in Moscow, St. Petersburg, as well as in cities such as Saransk or Yekaterinburg.
The article talks about popular hybrid mercury-tungsten lamps.
Sometimes lighting technology brings surprises: an unsuccessful light source becomes so popular that leading lighting companies produce it on a mass scale.
We are talking about mercury-tungsten arc lamps (MAT) .
Structurally, a mercury-tungsten lamp is a discharge mercury torch, similar to DRL lamps. But in addition, a tungsten spiral is mounted in the flask in series with the burner. It is placed in an external flask, in an argon environment, and serves as a current-limiting element for the burner. Such a lamp does not require external ballasts and can be directly installed in the lamp instead of incandescent lamps.
It was this opportunity that determined the commercial success of DRV lamps. The point here is not only the poverty of enterprises in the CIS countries - the demand for this type of lamps is very high in countries with developed economies. The reason is that a huge fleet of umbrella-type lamps was inherited from powerful incandescent lamps. Replacing such lamps, especially in industrial premises, is associated with costs not only for the lighting fixtures themselves, but also for the mounting systems and wiring of lighting lines.
Therefore, the possibility of directly replacing traditional lamps with more efficient hybrid sources has ensured a very high demand for DRV lamps. In Ukraine, more than 60% of purchases of high-pressure mercury lamps are for mercury-tungsten light sources .
But you need to be aware that the light parameters of such sources are much worse than even not very efficient DRL lamps. The reasons and features of the operation of DRV lamps will be discussed below.
At first glance, the efficiency of the hybrid source should be higher than that of each individual source: the mercury burner excites the phosphor, and the tungsten filament additionally makes a small but contribution to the total luminous flux. In practice, the opposite picture turns out: the efficiency of DRL lamps is 30-50% lower than that of DRL lamps with an inductive choke.
Let's try to understand the reasons for this phenomenon. First of all, about the efficiency of the glow of the tungsten filament, which plays the role of a current limiter through the torch. Its resistance and power are calculated from the starting conditions of the mercury burner. During initial ignition, the voltage on the burner is equal to two cathode potential drops, i.e. about 20V.
As the burner heats up, the voltage on it increases to 60-70V, and on the coil it correspondingly decreases. Therefore, in operating mode, a tungsten filament shines a little better than an incandescent lamp turned on at half the operating voltage. But it’s shining! The second reason for the low efficiency of the DRV lamp is less obvious.
The burner of DRL lamps usually works with an inductive ballast. When the mains voltage passes through the amplitude value, the inductance begins to release the accumulated energy to the load, “pulling” the voltage on the burner. Therefore, the “platform” of the plasma column illumination when powered by an inductive ballast is about 80% of the duration of the half-cycle of the mains voltage.
But when the current is limited by an active ballast (tungsten helix), there is no such energy pumping. Therefore, the duration of the burner glow is reduced by 25-30%. Accordingly, the luminous flux and efficiency of the lamp decreases. The contribution of the glow of the tungsten helix cannot compensate for this drop; it can be completely neglected.
Therefore, DRV lamps, even from leading manufacturers (Philips, OSRAM), have an efficiency of no more than 30 lm/W . For comparison: DRL lamps from these companies have an output of 40-50 lm/W. Relatively low luminous efficiency and short service life, usually no more than 4000 hours, are a characteristic disadvantage of DRV lamps. It is defined by the tungsten filament and makes these hybrid sources unfavorable for outdoor lighting. Replacing such lamps requires the use of towers, which increases operating costs. But the use of DRV lamps for indoor shop lighting will stimulate the demand for these lamps for a long time.
The range of these sources is limited: lamps with a power of 160 with an E27 base and more powerful lamps of 250, 500 W with an E40 base. Some companies offer lamps with a power of 700 and 1000 W, but they have even more limited use.
Design
The design of the DRV lamp is similar to the design of mercury burners. DRV and DRL lamps consist of the following parts:
- Base of standard design. It has 2 points for receiving electricity - in the center and on the side. The base itself is screwed into the cartridge and can be easily changed if it burns out;
- Quartz burner in the form of a tube. This is the main element of the lamps. There are 2 electrons on both sides - the main and the auxiliary; the flask itself is filled with argon and mercury vapor;
- Glass flask. It is “put on” from above and filled with nitrogen; the inside is painted with a white phosphor, which is why the light bulb is opaque.
You may be interested in The problem of light bulbs burning out, how to fix it
The diagram makes it easy to understand the operating principle
Connection
Lamps of the DRV type are connected directly to the electrical network, like a regular incandescent lamp.
To put DRL type lamps into operation, it is necessary to have a ballast (control gear) - a choke that provides adjustment of the operating current values to the specified values. It is necessary to prevent the lighting device from burning out, as well as to create its ignition mode.
The connection diagram for the DRL lamp is shown in the following figure:
A cross-section of a DRL lamp and its connection diagram using a choke
Expert opinion
Alexey Bartosh
Specialist in repair and maintenance of electrical equipment and industrial electronics.
For your information! During operation, the throttle not only ensures ignition of the light source, but also adjusts its operation. It stabilizes the voltage supplied to the contacts of the gas discharge tube.
Chokes used with gas-discharge lamps of this type are available in two versions: independent and built-in. This depends on the design of the luminaire and the location of the ballasts in it.
Appearance of a 150 W independent choke
The main technical characteristics that are the criteria for selecting a ballast model for compliance with the conditions of use with a specific gas-discharge lamp:
- electric power;
- operating current;
- winding temperature in normal operation;
- possible overheating of the winding is acceptable;
- maximum permissible power loss during use;
- Power factor.
Failure of ballasts is the main reason for non-ignition of lamps equipped with gas-discharge lamps during their operation. In this regard, the question of how to check the throttle for DRL is relevant for many owners of such lighting devices.
Using a multimeter is the most correct solution when checking the performance of the throttle
The easiest way to check is to use a multimeter and check the integrity of the windings, as well as the presence of an interturn short circuit.
If you do not have a measuring tool, you can use an incandescent light bulb with a power similar to the power of the inductor and connect it in series to the control gear power circuit.
If the throttle is working properly, the incandescent lamp will burn at half intensity or flicker. The absence of a glow indicates that the winding of the device is damaged; the presence of a bright glow indicates that there is an interturn short circuit in the winding.
The use of gas-discharge lamps in lighting the workshops of industrial enterprises can reduce the cost of paying bills for used electrical energy
Scope of application
DRV light bulbs are used to illuminate large spaces: streets, open spaces (for example, parking lots), industrial facilities (open and closed).
DRLs are used for lighting:
- Streets and roads;
- Squares, courtyards, squares;
- Warehouses, workshops and other large industrial premises;
- Car parks and gas stations.
Lamps are regularly used to illuminate large spaces.
DRVs are used in the following places:
- Boulevards, squares, parks and other city blocks;
- At construction sites;
- Warehouses and industrial facilities;
- DRV 25 is used in greenhouses because it produces a redder color.
Application area
This light source was good in its time, but now there are more effective modern solutions. Technically, DVRs can also be used for street lighting, but they are used very rarely in this capacity. But they are still found in park areas, parking lots, and construction sites. This is due to the initial short service life. The rarity of these lamps in street lamps is also explained by the inconvenience of replacement at a height of six meters or more.
More often they can be found indoors. They mainly illuminate production areas of industrial facilities and warehouses.
Thanks to the emission spectrum, DRV-250 can be successfully used for supplementary lighting of plants in greenhouse conditions. This applies only to the DRV-250 model.
Considering the shortcomings of these illuminators and their imminent removal from production, this lighting technology is losing its relevance.
- Related Posts
- Incandescent lamp: characteristics and features.
- Installation and connection of street road lighting
- IZU: connection diagram, types, which one to choose
Disposal of mercury lamps
Spent and defective mercury-type lamps belong to the first hazard class waste. They must be disposed of using special equipment. During the processing process, one of four methods can be used:
- amalgamation;
- heat treatment;
- firing at high temperature;
- chemical or metallurgical method.
All disposal methods are aimed at separating and sedimenting mercury vapor, its sublimation, followed by burning of organic components. The final products of processing DRV and DRL lamps without chokes are mercuric chloride and sorbent.