The monolithic floor slab has always been good because it is manufactured without the use of cranes - all work is carried out right on site. But despite all the obvious advantages, today many refuse this option due to the fact that without special skills and online programs it is quite difficult to accurately determine important parameters such as reinforcement cross-section and load area.
Therefore, in this article we will help you study the calculation of the floor slab and its nuances, and also introduce you to the basic data and documents. Modern online calculators are a good thing, but if we are talking about such an important moment as the roofing of a residential building, we advise you to play it safe and recalculate everything yourself!
Types and advantages of floors
It is important that the floor slab is manufactured in compliance with the hardening time and temperature conditions in the factory. In this case, it will comply with GOST. Today, manufacturers produce not only hollow-core floor slabs, but also solid ones. For this reason, it is important to perform a load calculation or use an example.
Solid slabs have a high cost and weight. They are used only for the construction of the most important objects. Hollow slabs will be sufficient for houses.
Among their advantages are low cost and light weight along with an increased level of reliability. The result is a load-bearing slab. Moreover, it can be multi-hollow.
Note
Note! Voids have a useful function. They are necessary to ensure thermal and sound insulation of the building.
The calculation must take into account the basic parameters of the slabs. For example, the dimensions of the slabs range in length from 1.18 to 9.7 m, while its width can range from 0.99 to 3.5 m. As a rule, in both multi-story and private construction of houses, slabs with a length of 6 are used meters and a width of 1.2 to 1.5 m. For their installation, you will need a crane with a capacity of 3 to 5 tons.
[custom_ads_shortcode3]
Instructions for floor reinforcement
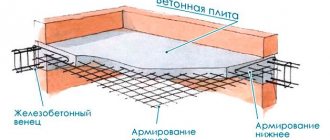
To understand how to properly reinforce a floor slab, you need to consider several important rules. The main materials for completing the task are steel rods with a corrugated surface made of A4 steel and a concrete mixture based on M300 cement, medium-fraction crushed stone and fine sand.
The following will be useful at work:
For formwork - moisture-resistant plywood or boards For bandaging - annealed wire and a special tool Equipment for bending rebar blanks Special pliers or a grinder for cutting rods Everything necessary to create a solution: measuring instruments, tools, containers, etc.
Preparation for the work is simple and includes the following stages: performing calculations, drawing up a drawing and reinforcement diagram, calculating and purchasing building materials, tools, cutting blanks from rods, preparing panels for formwork.
Brief operation algorithm:
Cutting blanks from reinforcement, binding the first layer of mesh. Positioning the mesh with a gap of 3-4 centimeters to the surface of the formwork, securing with vertical rods. Attaching the second layer of mesh, installation on site. Pouring concrete.
Features of monolithic design
- The use of a monolithic structure is possible if it is difficult to organize the work of a crane at a construction site. It is also suitable if the project includes non-traditional parameters and unusual architecture.
- As a result of the special strength of the monolithic
monolithic ceiling structure, all elements acquire special rigidity, in contrast to hollow-core coatings. - Save money on energy costs, welding joints and loading and unloading work. The costs of purchasing construction and consumables are also reduced.
- All the necessary materials are freely available in construction markets and stores.
- The material will not be subject to rotting processes and will not burn.
- There are no joints, which improves the soundproofing properties of the building.
- The lower surface will be flat and smooth, as it will be easier to carry out plastering work.
- This method of constructing buildings makes it possible to construct external structures such as balconies. In this case, their base will be a single slab with interfloor ceilings. As a result, the balcony will be more reliable and durable.
But there is also a drawback. It is associated with high complexity of work if carried out during the cold period. In this case, the required level of strength is achieved in 28 days.
[custom_ads_shortcode1]
Calculation algorithm based on soil bearing capacity
When the dimensions of the foundation slab are determined, it is possible to calculate this structure based on the bearing capacity of the soil. The purpose of this operation is to assess the condition of the soil and its ability to withstand the total weight of all floor walls and other elements inside the building.
Example: Strong pressure on the soil will lead to excessive settlement of the foundation slab and displacement of soil layers. All this together will cause catastrophic consequences.
The foundation area is considered reliable if it exceeds the following condition:
in which S is the base of the house in sq. cm;
Kn – coefficient determining the reliability of the support (assumed equal to 1.2);
F – total mass of all floor slabs (including operational loads) on the foundation in kg;
Kр – coefficient that determines the working conditions;
R – conditional value of the calculated soil resistance in kg/sq.cm.
Reinforcement of a monolithic base
Working conditions on each soil take on different values. The type of building being constructed also affects the coefficient Kp. For example, it is necessary to build a heavy house on soil whose base is plastic clay. Kp in this case will be equal to 1. Light clay and fine sandy soils - Kp is equal to 1.2. Light construction on coarse sandy soil determines the Kp value to be 1.4. These coefficient values that determine construction conditions can be taken from special tables. The found figure is substituted into the above calculation.
Table 2. Values of coefficients that determine working conditions during the construction of a foundation on soils with organic components
Various load options
In all floors, three main parts can be distinguished:
- The upper part of the slab, consisting of screed, insulation and finishing layer.
- The lower part, including hanging elements and trim, if there is a living space below.
- The structural part that holds the other two parts.
Cut floor slabs have the same load resistance as regular ones.
Floors are represented by special structural elements. For example, the lower and upper parts create a static load. This includes all elements suspended from the ceiling surface.
These can be suspended or suspended ceilings, heavy chandeliers and even swings. This category also includes columns, bathtubs and interior partitions.
Dynamic load can also be distinguished . It is obtained from those objects that can move directly across the floor. These can be not only people, but also pets. Moreover, the latter can weigh quite a lot.
Point and distribution loads . We can highlight the following example: if you hang a punching bag weighing 200 kg on a plate, you get a point load. If you install suspended ceilings, the load will be distribution. If you need to calculate a point or distribution load, more complex situations may arise. When installing a bathtub with an increased capacity of 500 liters, it is important to take into account not only the distribution, but also the point load. The latter is created by each foot of the bath.
[custom_ads_shortcode2]
Drawings and diagrams of reinforcement of a monolithic floor slab
The drawing of the slabs performs an important function - it allows everything to be calculated, planned and done correctly in advance. Using the diagram and drawing, they calculate the consumption of materials, decide which reinforcement to use for the ceiling, determine all the values and indicators, and plan the estimate.
Stages of drawing up:
Carrying out measurements of all rooms, the external perimeter of the house (if there is a project, transferring data from it) Fixing on the diagram all the holes that are not planned to be filled in. Transferring the contours of all load-bearing walls, parts of the intermediate ones, making a detailed diagram of the strapping, mesh, reinforcement with the parameters of the thickness of the rod, places of linking and joining Determining the size of cells, places of installation of the longitudinal outer rod to the edge of the fill Calculation of the dimensions of the corrugated sheet for the lower plane of the slab When planning floor slabs in the drawing, the cells are immediately distributed: usually their number does not have an integer. And the reinforcement is shifted in such a way as to obtain the same dimensions of the reduced cells near the walls. Calculation of consumption and characteristics of materials: multiplying the length of the rod by the quantity, adding a margin for joints (about 2%), rounding up. Calculation of the required diameter for arranging the bottom and top layers Calculation of plastic clamps and rolled products for making inserts between the meshes Determination of the volume of cement composition - based on the area of the room and the thickness of the floor: the top and bottom reinforcement for the floor slab must be covered with at least 20 millimeters of mortar to completely protect the metal from external influences and corrosion. If the total thickness of the floor is more than 15 centimeters, the reinforcement for the floor is laid in 2 layers, with most of the mortar placed on top. The drawing also indicates the number of support columns, formwork, wooden beams for the platform for pouring the floor, etc.
Currently reading: Reinforced concrete power line supports
Calculation of possible loads on the slab
It is important to find out how long they will last. To do this, you need to make a detailed drawing of an apartment or house. After this, it is necessary to calculate the weight of the entire floor.
It is important to consider what material is in front of you. So, it may not just be hollow material. The surface may be multi-hollow.
The mass of all loads is also taken into account. This also includes everything, including the ability to withstand insulation of expanded clay floors, interior partitions and flooring. After this, the resulting calculation is divided by the number of slabs that will carry the load-bearing capacity.
The middle of the slab should not bear the main load of serious elements, even if supporting elements or main walls are located below. It is necessary to begin calculating the total load for the slabs. It is necessary to find out the mass of a particular slab. If you take the PK-60-15-8 slab, its mass will be 2850 kg. The example involves calculating the area for load-bearing slabs. The usable area is calculated according to the following scheme: 1.5 m x 6 m = 9 sq. m.
Floor slabs can have different sizes and different thicknesses, which affects their resistance to loads.
Then you need to understand what the design load will be that the floor can handle. It is necessary to multiply the area by the maximum load of the slabs, which is only per 1 sq. m. The following calculation is made: 800 kg/sq. m. x 9 sq. m. = 7200 kg. It is necessary to calculate from this mass the mass of the slabs themselves: 7200 – 2850 = 4350 kg.
Then it is calculated how much mass will be spent on screed and insulation of floors, as well as on the finishing layer. As a rule, all this takes no more than 150 kg per 1 sq. m. m. An example calculation will be as follows: 150 kg/sq. m. x 9 sq. m. = 1350 kg. Then the following calculations are made: 4350-1350 = 3000 kg. In terms of per square meter, this amounts to 333 kg/sq. m.
What will this number mean? The mass of the floor covering and the slab itself has already been determined. Therefore, this figure indicates a payload suitable for slabs. It is important that at least 150 kg be accounted for by the loads that will be introduced in the future. They can be not only static, but also dynamic.
The remaining mass of the slabs can be used for installing interior partitions or decorative elements. If the calculated weight exceeds the specified parameter, give preference to a lightweight floor covering.
[custom_ads_shortcode3]
Why do you need a monolithic floor calculation?
The reliability of the entire building structure depends on the strength of the walls, and this fact is undeniable, but floors are no less important for the safety of those living in a private house (as well as in an apartment building).
A strong floor underfoot is very important in order to feel comfortable in the premises. But, if concrete slabs at the design stage are forced to adhere to certain frameworks, since their parameters are constant, then the calculation of a monolithic floor, on the contrary, has to be done based on the desired layout of the house
And mistakes are extremely undesirable.
Any ceiling can withstand only a strictly defined (expressed in kilograms) load per square meter. Not knowing this value, and exceeding it, for example, by changing the layout by installing partitions, can provoke the appearance of cracks in the concrete structure. As a result, the poured monolithic base of the floor will be weakened and may subsequently collapse
To avoid this, the calculation must be done in such a way as to have a margin of safety for the floor, taking into account the characteristics of the concrete grade used, the diameter and number of bars for the reinforcement, and their total weight
In some cases, to strengthen a monolithic self-leveling base, horizontal reinforced concrete beams under the ceiling can be made in a similar way, which will act as stiffeners. To calculate them, you only need to determine in advance the dimensions, which consist of height, width and length. This is the main difference between a beam and a floor, for the calculation of which you need to use parameters such as the area and thickness of the concrete pour. Next, we will look at the basic standards that should be followed when pouring slabs so that their strength is high enough.
Features of determining point load
Calculation of loads on the floor slab is done for each linear meter of it.
This load case must be calculated with extreme care and caution. The service life of the ceiling itself largely depends on how you load a certain point. It is not so important whether your floor is monolithic. The design can also be multi-hollow.
An example of calculating point loads for slabs is as follows: 800 kg/sq. m. x 2 = 1600 kg. As a result, each point accounts for no more than 1600 kg of load. But it is more important to calculate point loads using a reliability factor.
The example is as follows. In residential spaces the coefficient is 1-1.2. The result is the following calculations: 800 kg/sq.
m x 1.2 = 960 kg. This example is safer, because we are talking about a prolonged load on a specific point.
[custom_ads_shortcode1]
Calculation of hollow-core floor slabs
Save the link in one of the networks:
2
Introduction 3
1. Calculation of the floor slab based on limit states of group I. 4
1.1. Determination of standard and design forces acting on the floor slab. 4
1.2. Determination of the parameters of the design section of the floor slab. 6
1.3. Determination of strength and deformation characteristics of concrete and reinforcement. 7
1.4. Calculation of a hollow-core slab for strength along inclined sections. 8
2. Calculation of a hollow-core slab using limit states of group II. eleven
2.1. Calculation of a hollow-core slab based on deformations. eleven
2.2. Calculation of a hollow-core slab based on crack opening. 12
Calculation of short-term crack opening. 14
2.3.Calculation of the opening of cracks inclined to the longitudinal axis of element 15
Advantages and disadvantages
The main advantage of a slab foundation is its large support area, which reduces the pressure on the ground and reduces the possibility of deformation of walls and other load-bearing structures of the building. Other advantages of this type of foundation undoubtedly include long service life, safety of use, quick and easy installation, resistance to ground and surface water, as well as the possibility of building a basement and simultaneous use of slabs as the basis for the floor of the first floor. But all this is possible only if the correct calculation of the foundation slab has been made.
A monolithic foundation is also the floor of the first floor. Source domsumom72.ru
The only important drawback of a slab foundation is its high cost. However, the high price is usually justified - after all, it is a highly reliable, durable, durable design with excellent technical and operational properties.