Lightning protection of buildings and structures is a rare system on the roofs of new and modern houses. This is due to a person’s confidence that a lightning bolt will strike anywhere but nearby.
When lightning strikes the roof, pipes and other elevated structures of adjacent areas, lightning overvoltage and electromagnetic pulses occur, which pose a threat to any electrical devices connected to the AC electrical network.
Features of the lightning protection system
Lightning protection of an object is a set of measures and devices that can protect detached buildings and structures from lightning strikes.
There are three main factors affecting lightning:
- direct lightning strike on the roof of a building;
- impact on nearby communication and technical facilities;
- strike into the ground near a house or into a nearby object with further discharge into the ground.
In the first case, a direct blow can lead to serious damage - a sharp increase in temperature and baking of roofing materials, and in rare cases - even fire of wooden structures and roof slabs. The main destructive factor is hidden in the shock wave generated by lightning.
When a strike occurs on communication objects or power lines, a lightning impulse current is created, which enters the home through electrical wires and pipes. This can lead to electric shock, damage to cable sheaths and cores, equipment failure, and internal system failure.
In the third option, the discharge hits the ground. If the ground resistance is high or due to other factors, the voltage can go through the ground electrode into the neutral wire back into the house. In private houses, the zero is grounded in the village transformer substations. A case may arise when the voltage is both in phase and zero, which will also lead to breakdown of devices and equipment. But this is a rare case: as a rule, the current, entering the ground, spreads evenly.
Important! The most terrible consequences are the destruction or fire of the roof as a result of direct lightning strikes.
Lightning protection of buildings, structures, equipment and communications
Atmospheric phenomena with the formation of lightning, accompanied by bright flashes of light and thunder, are called thunderstorms. Lightning is a thunderstorm discharge of electricity that occurs between clouds and the Earth; inside the clouds.
Lightning strikes a house
Danger to human life, the safety of industrial and public buildings, high-rise engineering structures - chimneys, television antennas, radio communications, including cellular; towers, electrical network supports; technological equipment located on open industrial sites, for example, for distillation columns of oil refining enterprises, lightning is of the first type.
The need for lightning protection is due to the fact that the voltage during lightning discharges reaches 50 million V, and the current strength - up to 100 thousand A; with the release of huge amounts of light, sound and thermal energy. Lightning discharges are electrical explosions, similar to detonation, causing destruction to buildings, breaking trees that served as grounding sources; injure and concuss people, which often leads to their death.
Lightning protection is a set of technical solutions that reliably ensure the safety of people, the protection of buildings for various purposes, and high-rise objects; technological and engineering equipment of production facilities; communications infrastructure of populated areas, power lines, both from direct impacts of lightning discharges, electromagnetic, electrostatic induction, and from the transmission of electric current through metal structures, communications.
Grounding and lightning protection are what, according to the standards, industrial buildings, utility lines, and other facilities must be equipped with. In addition, paragraph 4 of Article 50 of Federal Law of the Russian Federation No. 123-FZ prescribes, as one of the ways to eliminate ignition sources, to arrange lightning protection for buildings and equipment to increase the level of fire safety at facilities.
Standards for lightning protection devices
Considering that buildings, structures, technological installations, communications are quite different in their design and execution, state, departmental, and corporate standards have been developed; standards, design rules for organizing optimal, effective lightning protection for each type of facility - from industrial facilities, where it was first used, to residential buildings.
The standards that regulate the creation of technical protection against lightning are based on experience in organizing the electrical safety of buildings of various types and purposes, taking into account the features inherent in modern buildings, structures and communications infrastructure and communications.
Requirements for lightning protection are set out in many official documents. Design and calculation of lightning protection is carried out on the basis of the following regulatory and technical framework:
- "Rules for electrical installations." Currently, the seventh and some chapters of the sixth edition of this fundamental document are in effect, without knowledge of the requirements of which it is impossible to design any types, types of electrical installations, equipment, equipment for protection against electric shock, including lightning protection. Industrial safety of protected objects with categories of explosion and fire hazard of premises and buildings is also impossible without this type of protection from high-voltage electric discharges. This takes into account the requirements for the organization and implementation of lightning protection for various types of buildings, engineering structures, electrical communications, specified in several chapters of the PUE. Chapters 2.4, 2.5 - for overhead power lines with an operating voltage of less than and more than 1 kV, respectively, including a zoning map of the territory of Russia indicating the duration of thunderstorms per year, which is necessary when designing lightning protection systems and devices. Chapter 4.2 – for switchgears, electrical substations with voltages greater than 1 thousand V. Chapter 4.3 – for converter substations, installations.
- RD 34.21.122-87 “Instructions for the installation of lightning protection of buildings and structures.” Its purpose is clear from the name. Despite the fact that the document was approved by the Ministry of Energy of the Soviet Union, in agreement with the State Construction Committee, it is still in force today.
- Some of its provisions have inevitably become outdated, not keeping up with scientific and technological progress, therefore, when designing modern technical systems and lightning protection devices, they use Russian GOSTs, which are identical to the standards of the International Electrotechnical Commission; as well as domestic instructions on lightning protection, published later.
- One of these documents SO 153-34.21.122-2003, developed by the same team of scientists, regulates the design of lightning protection for both buildings and infrastructure communications.
- GOST R IEC 62305-1-2010, GOST R IEC 62305-2-2010, which are two parts of one national standard on risk management when protecting facilities from lightning. The first part formulates general principles, the second – methods for assessing the risks of death and injury from electric shock to people; complete/partial destruction of objects, public communications; economic losses from lightning strikes.
- It is important that such factors as fire safety are considered, since the calculations take into account spaces with a flammable environment - an air mixture of vapors of flammable liquids, gases, and dust.
- GOST R IEC 62561.1-2014. This is the first part of the national standard on elements of lightning protection systems, concerning requirements for their parts and connections.
- GOST R IEC 62561.2-2014 – to conductors, grounding electrodes.
- GOST R IEC 62561.3-2014 – for distribution arresters.
- GOST R IEC 62561.4-2014 – for fastening elements.
- GOST R IEC 62561.5-2014 – for inspection wells, seals of grounding electrodes.
Requirements for the design, grounding, lightning protection of electrical installations, building equipment, power lines in the USSR were also established by SNiP 3.05.06-85 on electrical devices. Today there is a set of rules in force, issued as its updated version - SP 76.13330.2016.
In addition to the standards in force on the territory of the Russian Federation, similar requirements for lightning protection systems applied in the allied states should be mentioned. In the Republic of Kazakhstan, this is SP RK 2.04-103-2013 on the design of lightning protection of objects, issued to replace a similar instruction SN RK 2.04-29-2005; in the Republic of Belarus - technical code TKP 336-2011 on lightning protection of objects and utilities.
Type of lightning protection zones
Lightning protection systems for objects, engineering, communications and technological equipment are understood as external and internal technical devices that allow them to be protected both from the direct impact of lightning strikes and from secondary impacts - electric, electromagnetic fields that accompany a lightning discharge.
There are active and passive lightning protection systems.
Passive , capable of intercepting lightning before it discharges on the structure of a construction site, equipment body or part of an engineering, communications structure, and discharging the charge into the ground, consists of the following elements:
- Lightning receiver.
- Lightning rods.
- Grounding devices.
In an active system, these integral elements are supplemented by devices that generate an upward flow of ions that attracts a lightning discharge.
Several types of lightning protection systems are designed and installed - rod, cable, which, based on the results of calculations, depending on the number of rods/cables, their arrangement/location, configuration of the protection area, can create two types of lightning protection zones:
- A. The degree of protection reliability is from 99.5%.
- B – from 95%.
Types of lightning protection systems
In practice, if a construction site, technological installation, tower, pole, utility antenna is completely located in the zone of protection from lightning strikes, the probability of them being damaged by a lightning electric discharge tends to zero.
Classification of buildings and structures by lightning protection device
There are the following categories of lightning protection for construction sites , depending on the purpose, significance, fire hazard class and the possibility of explosion; fire load – presence, quantity, type of explosive and fire hazardous materials; regional frequency of lightning discharges; recorded lightning strikes:
- Category I , which has the highest level of protection against a possible direct lightning strike on an object. These are production facilities with explosive zones of hazard classes B-I, II. Protection zone type – A.
- II category . These are industrial and warehouse buildings, open areas for storing flammable liquids, flammable liquids, and with technological equipment installed on them, where they are circulated; as well as explosive production, outdoor installations with hazard class below B-Ia. Type of protection zone for process equipment installed on open industrial sites – B; for objects - A or B, depending on the predicted number of lightning discharges per year.
- III category . This includes construction projects for various purposes with III–V degrees of fire resistance in areas where the annual duration of thunderstorms is more than 20 hours. The main type of lightning protection is B.
All the main parameters of the lightning protection system for any specific facility can be determined using Table 1 of RD 34.21.122.
Types of lightning protection
Depending on the category of objects, the lightning protection system can be of several types:
- Protects against direct impacts. The devices used for this are called lightning rods, consisting of a load-bearing support, which can be the building itself, a discharge receiver, a down conductor and a grounding conductor. Both rod and cable lightning rods and metal mesh laid on the roof of the protected object are used. For overhead power lines, lightning protection cables are used to absorb lightning strikes.
- From electrostatic induction. This is done by connecting all electrical equipment to the facility’s grounding system.
- From electromagnetic induction. To do this, conductive jumpers are installed at the junction points between sections of pipelines and overpasses.
- From the drift of electric potential caused by a lightning discharge. To do this, all communications entering buildings and structures, including the metal sheath of electrical cables with voltages up to 1 thousand V, are grounded. Overhead power lines at the approaches to the facility are equipped with lightning protection cables, and arresters and surge suppressors are mounted on the supports.
Means and methods of lightning protection
The means of protection against electrical lightning discharges include:
- rod lightning receivers;
- lightning protection cables;
- mesh lightning rods;
- down conductors;
- grounding contours of construction sites.
There are two types of lightning protection options:
- External, protecting from the direct impact of a high-potential electrical discharge that can cause destruction, explosions and fires, due to its discharge into the ground to dissipate energy.
- Interior. For protection against secondary factors of direct or close to the protected object lightning strike. For this purpose, various types of special devices are used, called SPDs - surge protection devices.
Lightning protection of a building
Installation of lightning protection and testing of lightning protection upon completion of installation work is carried out by organizations performing electrical work.
Operation of lightning protection does not require additional costs and is designed for a long period. But inspection of lightning protection for detection of mechanical damage to discharge receivers, current-carrying, grounding elements, and connections between them is still required.
Checking lightning protection allows facility owners, management of enterprises, and organizations to be confident that it will not fail during a dangerous thunderstorm period.
Types of lightning protection
According to the design of the protection system, there are:
- external;
- internal.
Each system has its own purpose, and they must be used in combination to eliminate all three factors of lightning damage.
An external lightning protection device for buildings and structures is mounted on roofs, nearby extensions, structures and consists of an air terminal, a down conductor and a grounding conductor. Their main function is to divert the current discharge into the ground, preventing it from reaching the roof surface. The discharge enters the ground electrode through the down conductor and then spreads into the ground.
The internal type of lightning protection system consists of installing a device inside a building and serves to protect against surge voltages.
There are the following types of internal devices:
- Voltage control relay with the ability to manually adjust the minimum and maximum voltage levels in the network. If critical points are violated, the device turns off the voltage. Can be installed throughout the house or separately for each device. The simplest and cheapest option.
- Voltage regulator.
- Phase control relay (for three-phase voltage). Refers to microprocessor devices.
Active and passive lightning protection
Different types of external lightning protection are a system consisting of conductive structures, some of which are installed in the upper part of objects. They intercept a lightning bolt and then release its high energy into the ground. The effect of such protection depends on the number of components and the coverage density of the hazardous area, and on the architectural features of a particular building. All processes here occur naturally, therefore such standard systems represent passive lightning protection.
Typically, it includes the following components:
- Lightning rod. Attracts to itself and receives electrostatic atmospheric discharge. Structurally, the design options come in the form of metal rods, cables stretched between supports or a receiving mesh with a set cell pitch. The latter option is used mainly on flat roofs with large areas.
- Down conductors. They seem to play a secondary role, but without them it is completely impossible to remove high currents that enter the lightning rod. They are made of thick steel wire with a diameter of 8 mm or more. This cross-section ensures the safe passage of large potentials within a short period of time.
- Grounding and lightning protection. They are used together and consist of individual grounding electrodes or an entire system that combines several electrodes into a single grounding loop. Down conductors can be connected to an existing grounding, but for this you will need to connect special arresters to the circuit.
Types of lightning rods
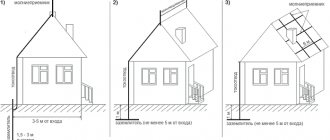
According to design and material, lightning rods are:
- rod - separately located and on the roof;
- cable;
- mesh - on the roof.
The most common and frequently encountered are rod and cable roofs, which are used on simple and complex gable roofs. If the roof structure is multi-level, it is recommended to use a combined system using two different types of receivers.
Rod lightning rods
The main feature is a long vertical pin, the main function of which is to receive a lightning strike. The device must be highly durable, resistant to precipitation and aggressive environments, but be light and easy to install.
Depending on the roof area, several such masts can be installed. Such structures must be installed on the highest point of the roof or wall. It is necessary that the pin rises at least 1.5 m.
You can install such a system separately from your home. In the second case, the mast can reach several tens of meters. The rod structure forms an imaginary cone around the housing - a zone of protected space. The size of the mast can be determined from the diameter of the cone and its height.
Cable lightning rods
The horizontal installation system consists of a tensioned steel cable along the entire length of the ridge. The lightning strike is absorbed by the cable. You can install pins at different ends of the roof and stretch a cable between them, resulting in a combined type of protection. This is suitable for roofs where the length is many times greater than the width. The diameter of the cable must be at least 12 mm. The thickness of the cable is determined by the length of the installation span.
The system has special requirements for the strength of the tension element, which is associated with wind loads and icing. To avoid damage to the system, it is recommended to install several intermediate fasteners along the entire length of the roof.
An economical and simple option is obtained by using steel wire rod instead of a cable, which is easy to install (can be welded to structures and to each other) and is quite durable. To fasten the wire, you can use special bolt clamps - terminals.
Mesh lightning rods
The system is horizontal, mounted on flat roofs. The mesh is made from rolled wire with a diameter of 10 mm or steel strip of any diameter. Such receivers are mounted by welding and require a large consumption of material, so the system is considered very labor-intensive to install.
It can also be installed on pitched roofs. In this case, the mesh is mounted around the perimeter of the plane. This is the main reason why cheaper, simpler and safer systems are installed on pitched roofs. This type of protection is suitable for installation on the roofs of schools and kindergartens, institutes and government agencies. Considered the most reliable.
Lightning protection of enterprises: a set of measures
Depending on the type, height and purpose of the industrial building, various protective measures are taken:
- Grounding of at least two points of the metal frame on high-rise buildings or structures with a metal frame (towers, water pumps).
- Installation of rod lightning rods for open objects with the possibility of an explosion when struck by lightning (filling and pumping stations, various types of tanks, etc.). It is also possible to install a lightning rod directly into the tank itself.
- Installation of lightning rods of different types at substations with distribution equipment.
- Installation of rod lightning rods with a rod diameter of at least 25 mm to protect factory and plant pipes.
All protective systems are calculated and installed in full compliance with the requirements of the relevant regulatory documents.
has its own electrical laboratory (for measuring grounding resistance during installation).
Down conductors
This element connects the lightning rod to the ground electrode. For manufacturing, steel wire with a diameter of 6–10 mm is used; a steel strip or a half-inch water pipe is also suitable.
It is very important to make a strong and reliable connection between down conductors and lightning rods with grounding conductors. The strongest connection is considered to be a welded or bolted connection. To make the down conductor invisible on the facade, it can be painted in the color of the cladding or finishing of the house. Along the entire length of the descent it is necessary to make intermediate fastenings at a distance of 1.5 - 2 meters.
Lightning protection of industrial buildings (industrial lightning protection)
Let's consider lightning protection of an industrial building , or any other large structure with a straight roof.
A significant difference is the presence of a straight roof; in this case, the method of placing the conductor is used (usually a galvanized circle Ø8 mm is used) in the form of a grid. This creates a kind of shielded barrier that prevents lightning from entering the roof of the building.
In this case, roof holders with or without concrete are used.
The holders are placed over the entire roof surface at a distance of 0.8 to 1.2 meters from each other.
The main requirement, in addition to the relative position of the holders (according to TKP 366-2011), is maintaining the height. The conductor should not be closer than 110 mm. to the roof surface.
This requirement is met by the overall dimensions of the roof holder (code: 30000 or code: 30001) TerraZinc.
It is worth noting that this requirement (to maintain a height of 110 mm) is specified only in the technical requirements of the Belarusian standards and in the requirements specified in the technical documentation of the countries of the former CIS. And yet, knowing the requirements, Polish and German manufacturers continue to produce holders of a much smaller height.
Under these conditions, when using such holders, when installing a galvanized conductor in a lightning protection system, it is necessary to use additional pads and extensions, which greatly increases the cost of industrial lightning protection .
Belorusskaya proposed a way out of this situation. The enterprise for the production of lightning protection and grounding systems, in April 2015, began producing roofing holders of its own production that meet all the requirements specified in the technical documentation.
Similar roof holders made in Poland:
All other lightning protection elements: lightning rods; fastening elements and clamps used for mounting the conductor to the facade of a building, etc., are similar to the lightning protection elements used for a residential building.
Grounding
The device is a metal structure buried or driven into the ground and ensuring good contact of the system with the ground. In wet soils, there is no point in equipping a ground electrode deeper than 80 cm. As a rule, a steel rod 18–20 mm or an angle 40–50 mm, or a steel strip 40 mm wide is used. The length of the ground electrode must be at least 3 meters.
The design may have the shape of a triangle or resemble an inverted letter “W”. The connection of the grounding elements is carried out by welding or bolting. The design must be reliable for many years, not weaken and have no backlash.
Important! If there is a ready-made grounding loop near the house, lightning protection for buildings can be connected to it.
Lightning protection grounding device
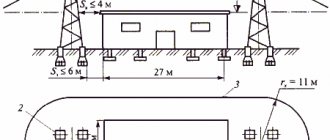
Grounding loops are located at a distance of at least 1 meter from the object itself, paths and other places where people frequently appear. This requirement allows us to avoid the step voltage that arises during the process of spreading the charge over the ground.
If the facility has a massive reinforced concrete foundation, the grounding should be located even further, and lightning arresters should be installed inside the building to protect electronic equipment. This requirement is mandatory, since part of the lightning charge falls on the foundation and other elements in contact with it - utility networks, equipment housings.
The main indicator of grounding is its resistance. If two separate circuits are used, they are connected to each other by steel conductors by welding. The circuit resistance should be minimal so that the current can easily flow to the ground. If the soil resistivity is 500 Ohms, then the standard resistance of the ground electrode will be 10 Ohms. At higher soil resistances, the following formula is used for calculations: Rз = 10 + 0.0022 (ρ – 500) Ohm, where Rз is the resistance of the ground electrode, ρ is the soil resistivity indicator.
Standard values can be obtained by replacing the soil. The old soil is removed, and soil with other parameters and characteristics is placed in a hole or trench. After this, grounding is installed in the renewed soil. In another case, chemical reagents are added to the soil that can change its performance in the desired direction.
Once the grounding is established, regular measurements of its resistance are subsequently carried out. If its performance is outside the standard range, you should install an additional pin or replace the inappropriate element. Particular attention is paid to the connections between all components of the grounding device.
Installation of lightning protection
Installation should begin with the installation of lightning rods. When working at height, follow safety rules. If you plan to do the installation yourself, start with a primitive project. When you are going to connect to a finished ground loop, plan the installation taking into account this connection location.
Always follow the rule: down conductors should be as short and straight as possible. Select the shortest distance from the lightning rod to the ground electrode.
Note! If you are not confident in your abilities, entrust the installation of lightning protection to professionals. Specialists will complete the project and conduct pre-operational tests.
Lightning protection price
To determine the cost of a lightning protection system, we need information:
- building design;
- photographs of the building from 4 sides;
- overall dimensions of the building (length, width, height of the wall to the beginning of the roof, length of the slope, length of the ridge);
- roof covering material;
- ridge shape (semicircular/angular);
- the presence of elements (dormer window, chimney, ventilation pipe, antenna, etc.) protruding above the roof (specify the distance);
- material and size of pipes on the roof (diameter or perimeter, height);
- presence of storm drains; location and diameter of drainpipes;
- facade material (main wall material; insulation material and thickness);
- the presence of snow retention, roof fencing and ladders for maintenance;
- type of soil.
Use our service for online calculation of lightning protection.
It is necessary to refer to the accompanying documentation to answer what the price of lightning protection depends on, or more precisely to TKR 366-2011:
For buildings of the 1st level of lightning protection, the number of elements used in the lightning protection system will be greater and, accordingly, the price of lightning protection will be higher. And for Level 4 structures, the number of elements used is smaller and the price of lightning protection is correspondingly lower.
At the same time, regardless of the level of lightning protection, a large object requires a large amount of galvanized conductor (galvanized circle or galvanized strip).
And in the presence of a complex roof structure (broken roof, the presence of a large number of output pipes and receiving antennas and other protruding elements located above the roof), the number of lightning masts increases.
All these conditions will influence the formation of the price for lightning protection.
The price of lightning protection will depend on the number of elements required to provide lightning protection and grounding of the facility.
Specialists will quickly and free of charge carry out calculations and draw up a list of necessary elements for installing a lightning protection and grounding system for your building. They will also explain why these particular elements were chosen for lightning protection of your structure. And they will answer the question: lightning protection price.
If necessary, we will refer you to a friendly design organization (with a good discount), where they will draw up a project and issue the necessary set of accompanying documentation, in accordance with the legislation of the Republic of Belarus.
Test and inspection
Before using lightning protection, you must check the following system elements:
- Welding joints for strength. This is done visually or by tapping with a hammer.
- Bolted connections and ties. It is necessary to tighten all connections, especially those that will be in the ground or on the roof.
- Ground resistance. It is measured with a special device - an insulation resistance meter.
- The transition resistance of contacts and joints is measured with an insulation resistance meter or an ohmmeter.
- Measuring current flow resistance with an insulation resistance meter.
- Check for compliance with project documentation.
- Reliability of fastening the lightning rod and intermediate clamps.
It is recommended that before the spring-summer period, an annual visual check of the system for damage and breaks after winter icing and winds is carried out.
It is not worth saving money on protecting people from electric shock and the safety of housing and electrical appliances. The best option is a set of measures to prevent the consequences and destruction from lightning strikes.
Lightning protection from "Aleph-EM" is:
- Optimal solutions: we use modern materials and innovative developments to create safe, economical and reliable protective systems.
- Staff of specialized specialists: the company employs qualified employees, each of whom has extensive experience and impeccable professional skills in their industry.
- Improvement of services: the company monitors all the latest trends in the field of lightning protection, promptly introducing technical innovations.
- Reliable high-quality materials (see Catalog) from the best world-class manufacturers. Delivery to all regions of Russia.
- A full range of services in a short time.
For all types of work performed, clients are provided with a guarantee of quality and safety:
- warranty on materials – from 1 to 5 years (depending on materials),
- for completed work – up to 3 years.
Questionnaire for preparing technical specifications for the lightning protection system
(Download the questionnaire and send by email)
There are three types of current collectors:
Clause 6 of Appendix 1 RD 34.21.122-87.
Structurally, lightning rods are divided into the following types:
- rod - vertical arrangement of the lightning rod;
- cable (extended) - with a horizontal lightning rod mounted on two grounded supports;
- meshes are multiple horizontal lightning rods intersecting at right angles and laid on the protected building.
Rod - a metal pin with a length of 30 to 150 cm, which is mounted vertically. The installation location can be a roof ridge, a chimney, or a television antenna. It is desirable that the pin be made of a material that is not prone to oxidation - copper or galvanized steel. The diameter of the pin is approximately 12 mm. If a metal tube is used, its upper end must be welded. Most often, such devices are used on metal roofs.
Cable - the system is used for lightning protection of low buildings, cottages and private houses. The base is a metal conductor cable stretched between lightning rods, to which down conductors are connected.
Mesh lightning rod is a mesh consisting of round galvanized steel rods. It is located along the ridge of the roof. This is a good option for protecting tile roofs. The down conductor is a steel wire with a diameter of at least 6 mm, connected by welding or bolted connections to an air terminal. It must be able to withstand a current of 200,000 amperes.
It is very important that the fastening of the lightning rod and down conductor is strong; it must not be loosened or broken. The down conductor is lowered from the roof to the ground electrode or ground loop so that its length is as short as possible. . They need to be laid as far as possible from window and door openings. If the house is large and there are several down conductors, then the distance between them should not be less than 25 m.
I would like to draw attention to the fact that in the absence of practice in using factory-ready elements, it is almost impossible to implement effective lightning protection on your own. Therefore, for safety reasons, you should contact specialized organizations
Home safety is not limited to installing lightning protection. In order for it to work as intended, you need to constantly monitor its serviceability: The metal pin of the lightning rod must be cleaned, removing the oxide layer. The reliability of all connections must be constantly monitored. If you find rust or metal deterioration anywhere, that item must be replaced immediately.
The devastating effects of lightning
If lightning hits a person, it results in death or serious injury, and if it hits a building that is not protected by an external lightning rod system, it results in a fire. Hundreds of such cases are recorded in Russia every year. At the same time, much more often due to atmospheric electricity discharges, overvoltages occur in the electrical network, as a result of which electrical appliances fail.
To protect yourself from disastrous consequences during a thunderstorm, you should think about installing a lightning rod system in a timely manner.