A short circuit (short circuit) is understood as a special case when 2 conductors of electric current of different potentials or phases of an electrical device are connected to each other or to the ground. At the junction of the conductors, there is a sharp increase in the value of the electric current, exceeding the maximum permissible parameter. This leads to a stop in the normal functioning of the device and adjacent elements.
According to a simplified formulation, the presented type of circuit is any abnormal and unplanned connection of electrical conductors having different potential values. These can be, for example, phase and zero, which leads to the formation of destructive currents.
The phenomenon is dangerous to human health and property. A short circuit causes not only equipment failure, but also stops the operation of electrical appliances. If you neglect safety rules, this could potentially result in complete failure of the devices or their individual parts with the impossibility of restoration. Fire may also occur, leading to detrimental consequences for human life, property and the environment.
Short circuit current calculation
To understand why this process occurs, it is necessary to calculate the values of short circuit currents. To do this, you need to know Ohm's law: “The value of the current in a certain gap in the electrical circuit is directly proportional to the voltage value and inversely proportional to the current resistance in this gap.” This is a fundamental law of electricity, which is studied even in the school curriculum. For greater clarity, it should be denoted by the formula: I=U/R, where:
- I - current strength;
- U is the voltage on the circuit section;
- R - resistance.
Any electrical equipment connected to a domestic or industrial electrical circuit is an active resistance. The voltage setting for the household network is 220 V (in some cases 230 V). The value presented is unchanged. The higher the resistance value of a device (conductor or some material) connected to the power supply, the lower the amount of electric current will be.
To calculate short-circuit current, it is better to use a more advanced form of Ohm's law, called Ohm's law for a complete circuit.
This form of Ohm's law is also studied in the school curriculum, but few people remember about it. But it is precisely this that is used to calculate short-circuit current. The fact is that if the resistance of the external elements of the circuit is 0, then a strange division by zero will not appear, but instead the current will be quite specifically and accurately calculated as a result of dividing the emf of the source by the internal resistance of the voltage source:
Ikz=ε / r
Of course, if a short circuit occurs in a house or apartment, the current passes through the wiring from the point of the short circuit to the point at which the EMF occurs. And it doesn’t matter whether the wires are copper or made of aluminum - they have resistance. And in this case R is not equal to zero. What is it equal to - read on.
Example 1. Network with voltage 220–230V
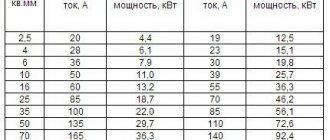
Let's take for a specific example: a wiring length of 100 m and a wire cross-sectional area of 2.5 mm² and then let's see what their resistance will be if they are made of copper.
The formula, also known from the physics textbook of any high school, reads:
R=ρ·L/S,
Where:
ρ is the resistivity of copper, equal to approximately 0.017–0.018 Ohm mm²/m;
L is the length of the conductor, expressed in meters;
S is the area of the conductor, expressed in mm².
Let’s take into account that there are not one, but two wires supplying electricity (the current comes in through one wire and leaves through the second), so the length of the wire L doubles in the calculation:
R =0.018·2·100/2.5= 1.44 Ohm
So, now you can see that the wires have a fairly high resistance. To now estimate the short-circuit current, you can use Ohm's law. We do not know the internal resistance of the power source, but as can be seen from the formula of Ohm’s law for a complete circuit, the greater it is, the less the short-circuit current will be. Therefore, taking r=0 we will find the maximum possible short-circuit current with the calculated R=1.44 Ohm .
We also assume that the supply voltage in the network is also the maximum possible, and is 230 + 10% = 253 V. In this case, the short circuit current will be equal to:
Ikz = 253/1.44 = 175.7 A
So, we carried out the calculation for a specific supply conductor. For postings with other parameters, the calculation can be done in a similar way.
Example 2: Battery
If a short circuit occurs directly at the EMF source (we can encounter this phenomenon in the case of a “short” household or car battery or power battery), then in this case the external resistance R≈0. Therefore, for the calculation we will need to know the internal resistance r as accurately as possible (otherwise, division by zero will occur again and we will not count anything worthwhile). Calculating it is not difficult if you have a resistance (resistor) and a multimeter.
Now let's look at a specific example. Let's say we have a 12V car battery. How to proceed to determine its short-circuit current.
We will need a 10 Ohm 15W resistor, which will help us perform the necessary experiment:
- We measure the battery supply voltage in idle mode (without load) with a multimeter, let’s say we get a value of 11.85 V.
- Next, we connect a 10 Ohm 15W resistor as a load and measure the current with a multimeter. We got 1.07 A.
- Without disconnecting the 100 Ohm resistor, we measure the voltage drop across the battery terminals. Let it be 10.8 V.
- Now you can calculate the internal resistance: r = 11.85–1.07 10.8 = 0.3 Ohm.
- Now you can determine the short-circuit current: Ikz = 11.85/0.3 = 39.5 A
If you haven’t yet guessed what formulas were used, here are some hints:
r=Uхх–In·Un,
Iкз=Uхх/r,
Where:
Uхх — open-circuit voltage of the power supply;
Iн is the current supplied by the power source under load;
Un is the voltage of the power source under load.
As can be seen from the formulas, the load value itself does not need to be known, however, it is selected in such a way that the measurement error of the device does not give too large a scatter in the result (if the load slightly “drains” the voltage of the power source, that is, Uхх ≈ Un , then the accuracy the result will be extremely low).
ROOM ROOM ROOM
RESPONSIBILITY, RESPONSIBILITY µÐºÑÑиÑеÑкой Ñеп¸, он Ð²Ð¾Ð·Ð½Ð¸ÐºÐ°ÐµÑ ÑолÑко в ÑоР¼ ÑлÑÑае , ROCK ROOM пÑÑжение, ÑÑо Ñо же Ñамое). RESULTS ½Ð° пÑимеÑе водопада: еÑли еÑÑÑ ÑазноÑÑÑ ASSURANCE, RESEARCH, RESEARCH, RESEARCH ¸Ð¸, а когда Ð½ÐµÑ â она ÑÑÐ¾Ð¸Ñ Ð½Ð° меÑÑе. RESULTS SMALL ROOM ени е, и Ñем менÑÑе, Ñем вÑÑе ÑопÑоÑивление, вк RESULTS:
I = U/R,
remark:
I велиÑина Ñока, коÑоÑÑÑ Ð¸Ð½Ð¾Ð³Ð´Ð° назÑваÑÑ Â“Ñ ROOM µÐ²Ð¾Ð´ Ñ Ð½ÐµÐ¼ÐµÑкого ÑзÑка. ROSS (Р).
RESULTS RESEARCH RESULTS ¾Ð³Ð¾ замÑканиÑ. RESULTS Ñ ÑаÑÑо, ÑоÑÑ Ð¿ÑеподаваÑели некоÑоÑÑÑ Ð²Ñзов, Ñ SÑÐ »ÑÑав из ÑÑÑ ÑÑÑденÑа Ñлова «Ñила Ñока» ÑÑÑ Ð¶Ðµ ÑÑ RESULTS. “как же Ð¾Ð³Ð¾Ð½Ñ Ð¸ дÑм, идÑÑÑие Ð¾Ñ Ð¿Ñоводки What's wrong? â ÑпÑоÑÐ¸Ñ Ð½Ð°ÑÑÑÑнÑй оппоненÑ, — ÐÑо ли не Ñила? ÐÑÐ²ÐµÑ ÑÑо замеÑание еÑÑÑ. ROOM SÑеÑÑвÑеÑ, и нагÑев Ð¸Ñ Ð¾Ð±ÑÑловлен именно ÑÑÐ ¸Ð¼ ÑакÑом . R=0, R=0, R=0, R=0, R=0, R=0 ROOM · registry, regurgitation.
We advise you to study POT RM 016 2001 (Occupational Safety and Health Rules)
u registry . RESULTS (S RESTORATION, RESPONSE V). RESULTS ÐС).
R OPTIONAL RESEARCH Ð¸Ñ Ñока. У диÑлекÑÑиков (изолÑÑоÑов) оно болÑÑое, Ñо ÑÑ Ð¸ не беÑконеÑное, Ñ Ñ Ð¿Ñоводников â малоРµ. ROOM ÑделÑной велиÑинÑ. ROOM Ñе пÑÐ¾Ð²Ð¾Ð´Ð¸Ñ Ñок, а Ñем он длиннее, Ñем ÑÑже. RESULTS Ñ Ð² ÐмаÑ, ÑмноженнÑÑ Ð½Ð° квадÑаÑнÑй Ð¼Ð¸Ð»Ð»Ð¸Ð¼ÐµÑ Ñ Ð¸ д ROOM. RESULTS, RESPONSIBILITIES SMALL, SMALL, SMALL µ. 1 1 м ROOM 1 ROOM. 20 years ago 0.024 °.
RESULTS, Ð2 ¾Ð¿ÑоÑивление Ð ¸ÑÑоÑника напÑÑÐ¶ÐµÐ½Ð¸Ñ (ÐÐС).
Causes of short circuit
Now let's briefly look at the possible causes of short circuits.
Common causes of short circuits are as follows:
- outdated wiring;
- mechanical damage inside the circuit;
- improper organization of electrical wires;
- violation of the rules for operating an electrical appliance;
- uncontrolled increase in the power indicator of devices;
- non-compliance with construction standards.
Negative impact of short circuit for a person and his property
A short circuit, depending on the location of its occurrence, leads to detrimental consequences for property and the safety of human life. These include:
- burning and failure of electrical appliances;
- ignition of electrical wiring;
- a decrease in the voltage of the electrical network (in industrial conditions it leads to a shutdown of enterprises);
- decrease in the efficiency of power supply systems;
- the occurrence of electromagnetic influence leads to disruption of the functioning of communications located underground.
Types of short circuit
Electricity is used everywhere in both the domestic and industrial sectors. To reduce the risk of a short circuit to a minimum, a number of measures and devices have been developed to provide protection against short circuits. However, in order to accurately understand in which case and which device to use, you need to know the types of circuits. The main ones are:
- in DC circuits;
- in AC circuits (between: phase and ground, two different phases, three phases, two different phases and ground, three phases and ground).
The share of single-phase short circuits is 65% of damage, 2 phases with earth - 20%, two-phase - 10%, three-phase - 5%. Complex types of damage often occur, accompanied by multiple asymmetries. This means a type of closure of various phases that occurs at several points at the same time.
Sources
The source in everyday life is damaged electrical wiring, an ungrounded cable or a heated damaged wire.
It is worth pointing out that electric current occurs in a one-, two- and three-phase circuit during a phase-to-ground or neutral wire, several phases, or simultaneous phase-to-ground switching. It can be interturn and winding on a metal housing.
To protect against it, you need to install current-limiting electric reactors, parallelize electrical circuits, turn off sectional and busbar switches, use transformers with split windings, and use a switching device that disconnects damaged equipment. You also need to use relay protection along with fuses and circuit breakers.
You may be interested in Calculating the voltage in the electrical network
Sources
Short circuit search methods
Finding the location of this phenomenon in advance is quite difficult. In most cases, neither specialists nor ordinary users care about it. However, this will help neutralize it in time, which will make it impossible for harmful consequences to occur. Thanks to timely response, financial resources and time are saved. There are several methods for determining a short circuit:
- visual inspection of the wiring (there should be no breaks or exposed wires);
- using a multimeter or megohmmeter;
- by sound;
- exception.
Wires that are part of a live cable may come into contact with each other. If they are exposed, then this is the obvious cause of the short circuit. Such damage is usually found in junction boxes and other power supply units (sockets, switches, etc.). Burnt cable insulation is an obvious place where a short circuit could potentially form.
The use of special instruments helps to measure the resistance value of the circuit. They contain 2 wires: one of them is connected to the phase, and the other to zero (hereinafter referred to as ground). If the device display shows 0, then the wiring integrity is normal, if any other value, the contacts are in contact. Please note that the multimeter voltage is quite small. It can be used to measure chains no more than 3 meters long.
Finding the location of a short circuit by sound is a popular method for determining this phenomenon. To do this, you need to listen carefully at all connections. A characteristic cracking sound will be heard at the point of contact. Sometimes there is a smell of burnt plastic and insulation. This method of finding short circuits should be used only as a last resort when other methods are unavailable.
It often happens that the culprit is a connected electrical appliance. Turning it on will immediately trip the fuse. This will lead to an immediate shutdown of the power supply to the area. You can find such a device by elimination, turning on all devices one by one.
Experts strongly recommend not to use outdated methods of searching for short circuits. In most cases, they do not show proper accuracy and efficiency. If there is a need to find a short circuit location, it is necessary to invite professionals who will use high-quality and accurate equipment.
Why does a short circuit occur?
Short circuit current occurs in the following cases:
- At high voltage levels. A sharp jump occurs, the voltage level begins to exceed permissible standards, and there is a possibility of an electrical breakdown of the insulating coating of the conductor or electrical type circuit. Current leakage occurs and the arc temperature rises. The short-circuit voltage results in a short-term arcing.
- With old insulating coating. Such a short circuit occurs in residential and industrial buildings in which the wiring has not been replaced. Any insulating coating has its own resource, which is depleted over time under the influence of environmental factors. Untimely replacement of insulation can cause a short circuit.
- Under external mechanical influence. Rubbing the protective sheath of the wire or removing its insulating coating, as well as damage to the wiring, lead to fire and short circuit.
- If foreign objects get into the chain. Dust, debris or other small objects falling on the conductor can cause a short circuit in the mechanism circuit.
- During a lightning strike. The voltage level increases, the insulating coating of the wire or electrical circuit breaks through, which is why a short circuit occurs in the electrical circuit.
Short circuit protection
There are various devices for short circuit protection:
- circuit breakers;
- circuit breakers with automatic return to the on state;
- RCD;
- fuses;
- "traffic jams";
- self-resetting fuses.
The presented circuit involves a zener diode and diodes that protect the LEDs from the effects of reverse currents. 2 resistors are responsible for limiting the current in the protection system. The fuse must be of a self-resetting type; the ratings of the elements must be selected individually depending on the conditions.
An effective way to protect against this phenomenon is to use a current-limiting reactor. It is used in electrical circuit protection systems, where the magnitude of the short circuit can be of such a magnitude that conventional equipment cannot cope with.
The rector has the form of a coil with an inductive type resistance, connected to the network in a series circuit. Acceptable circuit operation allows the reactor voltage drop to be maintained at around 4%. When a short circuit occurs, the main part of the voltage is supplied to this device. Such equipment comes in oil and concrete types. Each of them is used depending on the type of electrical wiring and the equipment it powers.
Total current when a short circuit occurs
The aperiodic component itself cannot be considered, since it is one of the components of the short circuit current. The electrical network contains inductive resistances that prevent the current from changing instantly at the moment a short circuit occurs. The increase in load current does not occur spasmodically, but according to certain laws that require a transition period from normal to emergency values. Calculation and analytical work is greatly simplified when the short-circuit current during a transition is considered as two components - aperiodic and periodic.
The aperiodic part is a component of the current ia with a constant value. It appears immediately at the moment of short circuit and in the shortest possible time drops to zero.
The periodic part of the short-circuit current Iпm is called the initial part, since in time it appears at the very beginning of the process. This indicator is used to select the most suitable setting or check the sensitivity of relay protection. This current is also known as subtransient current, since it is determined using subtransient resistances introduced into the equivalent circuit. The periodic current is considered to be steady when the aperiodic part fades and the transient process itself ends.
Consequently, the total short circuit current will be the sum of both parts - aperiodic and periodic during the entire period of state transition. At a certain moment, the total current reaches its maximum value in the shortest possible time. This condition is known as short-circuit shock current, which is determined when checking the electrodynamic stability of installations and equipment.
The choice of initial or supertransient current for calculations determines the rapid decay of the aperiodic part, which occurs before the protection is triggered. In this case, the periodic component remains unchanged.
We advise you to study the Transformation Ratio
Electrical networks connected to generator sets or a power-limited power system are characterized by significant voltage changes when a fault occurs. In this regard, the currents, initial and steady, will not be equal to each other. In order to calculate relay protection, you can use the initial current indicators. In this case, the error will be insignificant in comparison with the steady-state current exposed to various factors. First of all, this is increased resistance at the damaged point, load currents and other parameters that are most often not taken into account when performing calculations.
Useful short notice
The current arising due to such a phenomenon can bring not only destruction, but also benefit. There are a number of equipment that operate under conditions of increased current. A classic example of such devices is electric arc welding. Its operation is due to the connection of the welding electrode and the ground loop.
Under significant overloads, the functioning of such devices is short-lived. It is provided by a high-power welding transformer. In the place where the 2 electrodes come into contact, a fairly significant current is generated. This leads to the release of a large amount of thermal energy, which is sufficient to melt the metal in the contact area. This process ensures welding operation. The seam is neat, durable and strong.