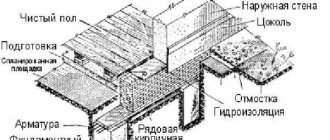
Pile foundation
For a massive residential building made of brick or blocks with a pitched roof and an attic, a pile foundation resting on dense load-bearing layers of soil should be provided. When constructing two-story buildings, such a system is economically justified because it has the best load-bearing capacity.
SVF plan.
The fundamental design of a foundation in a swampy area for a residential building should be based on standard calculations and installation of the required number of concrete, bored or screw piles. Connected by a grillage into a single supporting system, they will ensure reliable support of the entire building structure on solid layers located below the bottom of the swamp.
The cost of a foundation on swampy soil using concrete piles will be significantly higher than that of strip and “floating” slab systems, since special construction equipment will have to be used to complete the work. But, depending on the type and number of installed piles, such a scheme will be able to withstand the weight of a two- or three-story brick residential building without subsidence for many years.
If the depth of the hard soil does not exceed three meters, then metal screw piles can be used to construct the foundation.
Their use reduces the cost of the foundation, but reduces the load-bearing capacity of the structure. In addition, their use is limited by the installation depth.
As a material for the load-bearing walls of a residential building on a screw pile foundation, you will have to use aerated concrete, hollow brick or wood, with additional external insulation made of foam plastic. At the same time, using screw piles, you can make a foundation in a swamp with your own hands, without inviting contractors for this.
To install screw piles in a wetland, the top layer of soil over the entire building area, with the addition of 0.5 meters to each external axis, must be removed to a depth of 50-60 cm. After this, install the piles, screwing them in according to the design scheme. Cover the bottom with geotextile and fill it with crushed stone-sand mixture not below ground level.
Next, it is necessary to connect the screw piles with a powerful reinforced concrete grillage under load-bearing walls and partitions or paired channels No. 18-24 (depending on the weight load).
Estimation of costs for the construction of strip and pile foundations
The estimated cost of a house with a garage using frame technology largely depends on the choice of foundation construction technology. The costs of constructing a strip foundation consist of the following components:
- Cost of materials: concrete or its components, reinforcement, gravel-sand mixtures, roofing felt for waterproofing, boards for formwork and fasteners.
- Payments for the labor of builders and a welder who is hired to strengthen the base.
- In the second part, you can save money and do the work yourself, but it will take a lot of time.
A pile foundation for a garage with a load-bearing wooden frame will cost much less. Material – pipes and channels do not have to be new; used ones are also suitable. To protect against corrosion, they must be treated with special compounds based on petroleum products. The pipes are filled with concrete for strength.
Strip and slab foundations
Strip and slab foundations are shallow foundations, the design of which involves installing the foundation twenty to fifty centimeters deep into the ground.
A non-buried foundation requires fewer consumables, but is in no way inferior in strength to conventional foundations, ensuring the long life of a house, barn or fence.
A strip foundation is one of the most reliable options, along with a columnar foundation. Like a columnar foundation, the base of a strip foundation is laid below the freezing level, which allows it to withstand seasonal expansion of the soil.
Photo:
Device diagram
Among others, there is also a structure called a slot foundation. Its manufacturing technology involves laying concrete without using formwork for trenches.
It is important to remember that the success of the construction of such a foundation directly depends on the extent to which various measures taken depending on several criteria are observed. Important indicators are the degree of deformation and solidity, i.e.
all parts of the foundation must be in clear contact with each other, which will allow the structure to resist stress near the side surface
Important indicators are the degree of deformation and solidity, i.e. all parts of the foundation must be in clear contact with each other, which will allow the structure to resist stress near the side surface.
The structure is strengthened using reinforcement, steel wire or metal rods.
A shallow slab foundation is actually one of the most reliable, along with a columnar one.
However, it is also the most expensive, because its manufacturing technology requires a fairly large amount of materials.
The fact is that the slab itself, on which a shallow foundation for a house, barn or fence is built, is in fact nothing more than a concrete pad covering the entire area of the pit.
Video:
Such a pillow, of course, is able to cope with swelling of any scale, but it also requires colossal infusions of various kinds.
A strip foundation is often attractive because it is quite possible to lay it on your own, which is why it is most often installed for the construction of a house or a fence.
On heaving soil it is possible to build only a non-buried version of this structure.
But even though this type of foundation is shallow, the foundation still needs to be deep enough to prevent the soil from freezing, making depth a variable depending on climate.
Then you will get a cushion that protects the structure from the influence of heaving from below. On the sides it will be protected by waterproofing. The cushion of sand and crushed stone, in turn, is the basis for a layer of concrete, which is distributed between the sections of reinforcement that limit it.
There is a procedure that must be followed in order to correctly erect a strip foundation.
First of all, you should dig a pit with a depth of half a meter to 70 cm, then trim its edges with waterproofing.
Photo:
Proper laying of the foundation
Then a pillow is poured, each layer of which should be 20 - 30 cm, and their thickness should be the same after compaction.
The top, in turn, is also insulated with waterproofing, and then the entire structure, thus protected from silting and dampness, is surrounded by reinforcement and filled with concrete.
After the concrete is poured, the upper reinforcement is laid, always on wet concrete so that the materials can adhere to each other.
In general, a strip foundation, which is fortunately a rather attractive option when building a house or a fence, requires compliance with a small but important number of rules. As it became clear from the article, even heaving soils cannot prevent the construction of a house, a fence, or any light building in general, and some types of non-buried foundations are even easy to construct, which makes independent construction possible
As it became clear from the article, even heaving soils cannot prevent the construction of a house, a fence, or any light building in general, and some types of non-buried foundations are even easy to construct, which makes independent construction possible.
But, of course, the most important thing is to take into account the type of soil and strictly follow the technology.
Foundation for heaving soil
To make construction on heaving soil reliable and durable, you can use three types of foundations:
- Shallow belt;
- Pile;
- Slab monolithic reinforced concrete.
We will discuss which one to choose below.
Shallow strip foundation
On moving soil, you can install a shallow foundation or not a foundation at all.
On moving soil, you can install a shallow foundation or not a foundation at all. This base is suitable for a wooden or frame house on one floor.
Important: a foundation of this type cannot be used for a stone building. Otherwise, the counteraction of pressure forces from below (from the soil) and from above (from the walls) will be disastrous for the entire building.
The belt-type base for heaving soil has a thickness of 30-50 cm, which makes it possible to make the pressure force of the heaving soil exclusively tangential. In addition, this force will be reduced to almost zero.
In order for a shallow or non-buried base to be even less exposed to the forces of soil heaving, it is necessary to lay a layer of coarse sand or crushed stone under it. The thickness of the layer is at least 20 cm. Such a layer will create a kind of natural drainage of the soil under the foundation and reduce the level of negative impact on the foundation.
Strip foundations for light buildings on heaving soils should only be made of monolithic reinforced concrete. Here the solution is poured into a prepared trench with mandatory reinforcement.
The foundation construction process looks like this:
- According to the design documentation, a trench of a given depth is dug on the ground. Its bottom is covered with waterproofing material and then covered with a sand or gravel cushion. Loose ones compact well.
- The walls of the trench must be carefully insulated. Subsequently, this will be thermal insulation for the foundation.
- Formwork is installed in the prepared pit and reinforcement is installed.
- The concrete solution is poured, treating it with a construction vibrator.
Important: blind areas must be removed from the fully finished foundation to drain rain and melt water.
Advice: a shallow foundation installed in the warm season on heaving soil must be built up. That is, it is forbidden to leave it in this form during the winter. As a result of soil heaving, it will simply break. If it is not possible to build a house right away, then the base should be properly insulated. To do this, you can use a large volume of slag, glass wool, sawdust, straw or other materials that will prevent the foundation from freezing on all sides.
Pile (columnar) foundation
Another option for constructing a foundation on heaving soil is a monolithic columnar (pile) base
Another option for constructing a foundation on heaving soil is a monolithic columnar (pile) base. Due to the fact that the area of each support is relatively small, the soil during heaving seasons cannot have a full negative impact on it. In addition, piles (pillars) can be deepened below the freezing level of the soil without significant financial costs.
Making a foundation for a house with your own hands
Important: a pile (column) foundation can be erected on heaving lands for small and light houses.
Supports for the foundation can be used either factory-made (monolithic reinforced concrete driven piles) or cast independently directly on a concrete site with its mandatory reinforcement. In this case, prefabricated reinforced concrete piles require the use of a special installation.
The technology for installing a pile foundation looks like this:
- Markings are applied to the ground, placing holes for future supports so that they are located at every corner of the house, under all load-bearing walls and at wall joints.
- Now you should prepare the wells using a standard drill.
- Sand 10-15 cm thick is poured into the formed pits and compacted well.
- Next, an asbestos-cement or metal pipe is installed in the pit, which will act as permanent formwork.
Important: steel pipes must be waterproofed on the outside with bitumen mastic.
- Reinforcement is installed in the pipes and ready-made concrete solution is poured.
- After the pillars have completely dried, all the supports are fastened with a monolithic grillage, which looks like a belt. It is on it that the entire mass of the house will rest, thus distributing the load between the columns evenly.
Foundation slab
This base is the most expensive, but it is considered the most optimal foundation option for heaving soils
This type of foundation is the most expensive, but it is considered the most optimal foundation option for heaving soils. The fact is that the slab frame is a reinforced concrete monolithic pad 30-50 cm thick, onto which the entire load of the finished building is evenly distributed. As a result, a house on such a foundation simply maneuvers in the ground, without being subjected to pressure from the heaving soil.
Slab foundations are used for any type of building, including stone ones.
The technology for installing a foundation slab looks like this:
- A pit is being dug along the perimeter of the entire future building, the depth of which will exceed the design by 20 cm. This distance should be filled with coarse sand and compacted well.
- Then a formwork made of strong boards is installed on the sand and a layer of waterproofing is laid so that its edges fall onto the walls of the formwork. All joints are treated with a gas burner to create a sealed layer of material.
- The next stage is summing up all communications. At the same time, they need not only to be installed, but also checked using the spill method. Otherwise it will be too late later.
- Reinforcement is installed on top of the installed communications in the form of steel meshes located on top of each other. The nets are knitted from rods with a cross-section of 12-16 mm and a cross-section of 6-8 mm.
Important: the grids must be completely hidden in the concrete after pouring. The maximum offset on the sides of the foundation can be 1-2 cm, on top and bottom - 5 cm.
- Concrete is poured into the formwork in one go, carefully settling it with a construction vibrator.
- The slab foundation is covered with oilcloth until completely dry. If the weather is hot and dry, it is necessary to moisten the solution periodically to ensure even drying.
Construction of a shallow columnar foundation on piles (bored or cast-in-place)
Another high-speed type of construction of the foundation of a light house is the construction of a columnar foundation on piles. Here, the role of pillars is performed by poured or ready-made factory piles, which, using a special installation, are driven (screwed) into the ground to the required depth. The small amount of time spent on arranging piles compensates for their high cost. Installing this type of foundation is not a cheap procedure, which, if built independently, negates the main idea of savings.
First option
Scheme for preparing a concrete mixture.
A shallow trench is dug along the perimeter of the future house. Wells are drilled in it and piles are poured. The upper part of the piles is covered with waterproofing material. Sand is poured into the bottom of the trench between the ends of the piles. It should be placed flush with the ends of the piles. Then roofing material is laid on top of the sand. Then the formwork is installed, which is lined with glassine or roofing felt from the inside. This is done to prevent concrete from sticking to the formwork panels. Supports are made outside. The outer walls of the formwork are connected by transverse bars. This is due to the need to maintain the integrity of the formwork structure when the concrete solution is poured. Next, a reinforcement cage is installed in the internal space of the formwork. It is tied to the outlets of the reinforcement from the ends of the piles. Once this is done, the concrete is poured. When pouring it, you need to pierce it with a steel bar to release air from the concrete and ensure its density and strength. After the concrete has dried, the formwork is removed and the sand is removed. In this case, a gap of 20 cm remains between the grillage and the ground. The grillage is ready.
Second option
Scheme of a shallow columnar foundation made of reinforced concrete blocks.
At a short distance from the ground, between the ends of the piles, formwork is installed like a box with a bottom. It is into this that the reinforcement frame is mounted and concrete is poured. The rest of the work is the same as in the first option. There remains a distance between the soil and concrete. In order to insulate this structure, you need to make a fence. It will serve to insulate the underground and prevent dirt and snow from entering.
The next stage is waterproofing the grillage. When constructing it, one should not forget about the installation of ventilation holes - vents. Their location, quantity, and dimensions must be planned in advance, before pouring the concrete mixture.
The finished grillage, after the house is completely built, it makes sense to finish it with stone, brick or other material in accordance with the general style of the house facade.
What methods are used to prevent the effects of soil heaving?
The effect of soil heaving can be completely overcome; for this, some construction techniques are used, which will now be listed:
- The base of the concrete foundation is extended, in the shape of a trapezoid. In addition to increased stability, the influence of tangential heaving forces on such a foundation is reduced.
- The walls of the trench, in the case of using a buried and shallow foundation, are lined with waterproofing material. This isolates the foundation walls from the adjacent soil.
- The width of the foundation is increased. Due to this, the heaving of the soil is leveled out.
- The heaving soil is replaced from the bottom and sides of the foundation. Perform sand or gravel backfill.
- Laying thermal insulation along the outer perimeter of the building. Under the heat-insulating layer, the soil does not freeze in winter, so soil heaving does not appear.
- The foundation is deepened so that it is not affected by frozen soil. However, this entails excessive consumption of building materials.
Columnar foundation on heaving soils
A columnar type foundation involves laying pillars to a depth below the soil freezing level. For this purpose, mainly reinforced concrete pillars are used. Also, metal and asbestos-cement pipes filled inside with concrete mortar can be used as supports. An anchor element in the form of a platform is usually attached to the lower part of the supports. This guarantees additional stability and fixation of the supports in the soil.
The pillars are buried in the ground, after which the formwork is installed and a concrete foundation is poured, connecting all the supports with a concrete tape. Metal reinforcement must be used, which is tied with steel wire. The height of the columnar foundation can be different. The concrete strip can go on top of the soil level or be buried in it.
In any case, the design and construction of a foundation on columnar-type heaving soils reduces the effect of soil heaving to almost zero. Therefore, this type of foundation is considered the most reliable for heaving soil.
Arrangement of strip foundation
The strip foundation is one of the most popular foundations that you can make yourself. A strip foundation on a heaving soil has its own characteristics. It can be shallow (discussed below) or deep. Let's consider the second option. A prerequisite is the location of the concrete pour at a depth exceeding the soil freezing level for the given area. For different climatic zones, the depth of the foundation may vary.
A pit is dug, at the bottom of which a layer of crushed stone is poured, and then a layer of sand about 20 cm thick. This protects the foundation from below. To neutralize lateral influences from the soil, the walls of the pit are protected by a layer of waterproofing. In the pit there are pieces of reinforcement connected to each other, after which the concrete solution is poured. On top of the soil level, pouring is done into the prepared formwork.
Pile foundation for heaving soil
For problematic soils, a pile foundation is an excellent option. Moreover, regardless of the size and weight of the structure being built. The construction of a pile-type foundation on heaving soils involves screwing metal screw piles into the ground below the soil freezing level. This foundation is used on sandy, loose, heaving, peaty and swampy soils. The piles can be driven deep enough until they reach solid ground.
A house on a pile foundation can be built almost anywhere, even on a mountainside, without having to do any excavation work.
The durability of such a building is hundreds of years. A small contact area with heaving soil is provided, so it does not affect the structure.
One of the varieties of pile foundation is the so-called bored foundation. Concrete is used instead of metal piles. In certain places, holes are drilled in the soil into which concrete mortar is poured. All wells are pre-reinforced. The depth of pouring depends on the depth of soil freezing. Concrete piles must be at least 30 cm below this level. A reinforced concrete grillage is built on top of the concrete piles, connecting all the piles into a single structure.
Columnar shallow base
A non-buried columnar type foundation is used quite often
A non-buried columnar type foundation is used quite often. It can be installed on slightly heaving and heaving soils, provided that the structure being erected has small overall dimensions and weight. As for rocks, coarse rocks and soils that are not characterized by movement, such foundations can be used under a large house made of timber or logs.
A non-buried foundation on supports can also be used in case of reducing the impact of heaving on the building. To achieve this, the soil under the supports must be replaced with a sand layer.
Pillars can be made from reinforced concrete, rubble concrete, stone, sand concrete and concrete foundation blocks. Typically, blocks of size 0.2x0.2x0.4 m are used. If you decide to use brick, then silicate products and ceramic material with low frost resistance are not suitable for these purposes.
The work is carried out in several stages:
- First, the construction site is cleared of debris, the fertile layer is removed, and the breakdown is carried out.
- Then a hole of the required size and depth is dug under each support.
- A sand cushion is placed at the bottom of each pit.
- After this, you can lay out the supports from the blocks. Usually two rows of 4 blocks each are made. Thick cement mortar is used to hold the blocks together. The open part of the supports is plastered.
- Parts of the supports that will be connected to the house must be waterproofed. For this, bitumen mastic, roofing felt, roofing material or glass insulation are used.
Reinforcement of a columnar base on heaving soils
Reinforcement scheme
For the reinforcement of pillows, A3 reinforcement with a cross section of 10–12 square meters is used. mm, which is cut into rods 35–45 cm long.
Having laid them on a flat surface, they are knitted so as to form a metal lattice with cells 15X15 cm or 10X10 cm.
Then they are placed inside the pits on top of the crushed stone layer, having previously placed several bricks under them.
This is necessary so that when pouring the grate is inside the concrete layer.
Shallow base
This is the most popular type of columnar foundation, since a minimum of money and effort is spent on its construction
This is the most popular type of columnar foundation, since a minimum of money and effort is spent on its construction, and the scope of use is quite wide. Such structures are suitable as a basis for a wooden bathhouse and a frame house.
Typically, a pole is made of pipes, inside which a frame is installed and concrete is poured. Since the main load is carried by the concrete filling, the material of the pipe does not matter much. It acts more as a permanent formwork. Plastic or asbestos sewer pipes are usually used.
The choice of pipe diameter depends on the purpose of the building. For light gazebos, a pipe with a diameter of 100 mm is sufficient, and for log buildings, a pipe with a cross-section of 250-300 mm is suitable. The volume of concrete is calculated taking into account that for every 10 m of a pipe with a diameter of 100 mm, 0.1 cubic meter of concrete is required, and for a product with a diameter of 200 mm, 0.5 cubic meters are consumed, for a pipe with a cross-section of 300 mm, 1 cubic meter of concrete solution is required.
The work order is as follows:
- After preparing the site and completing the stakeout, holes are made in the ground using a hand drill to install the pillars. It is worth remembering that the depth of the hole must be 200 mm greater than the length of the column to make a sand cushion.
- After making the hole, sand is poured into the bottom, watered over it and compacted. To protect the concrete mixture from moisture loss, layers of roofing felt are laid on top of the sand cushion.
- Next, sections of pipes are lowered into the pits, which should have a 10-centimeter headroom. The pipes are leveled and fixed in the well using wooden blocks.
- After this, a little concrete-gravel mixture is poured into the pipe. Immediately after this, the pipe is raised and fixed in this position until the mixture completely hardens at the bottom of the pit. Thus, we will get a solid foundation that will well resist the forces of soil heaving.
- When the concrete hardens, the pipe is wrapped with roofing felt to provide waterproofing.
- The well is filled with sand, poured layer by layer with water and tamped. During this work, the position of the pipe must be checked using a level.
- Then reinforcement is installed inside the pipe and concrete is poured.
- Further work can be carried out after 28 days. In this case, the foundation is isolated from the main part of the structure using a bitumen or polymer solution.
Why reinforcement for a monolithic columnar foundation?
Scheme of reinforcement of columnar foundations
Concrete pillars are strong in compression, but do not tolerate tensile or bending loads. To avoid such deformation, the foundation must be reinforced in areas where tension may occur. For example, when heaving, the upper part of the pillars will be pushed upward, while the lower part will be held in the non-freezing layer of soil, as a result the pillars may crack. This is where vertical reinforcement comes in handy.
The reinforcement frame consists of vertical ribbed bars (class A-3) with a diameter of 1.2 cm. The ribbed bars are selected to provide better contact with the concrete. They are connected using thin, smooth mounting reinforcement (diameter 0.6 cm), which itself does not take the load, but only connects the rods into one structure.
When reinforcing pillars with a diameter of up to 20 cm, 2 rods are required. If the height of the column is about 2 m, the ribbed reinforcement is tied with mounting every 80-100 cm, that is, in 3-4 places.
If there is a grillage, it is also reinforced. Make 2 belts (lower and upper), each of which includes at least 2 longitudinal rods. For such reinforcement, reinforcement with a diameter of 1.2 cm and a cross section is used. The reinforcement frame is completely immersed in concrete, the level above the surface of the grillage is 3-5 cm.
If you take into account all the engineering and technological features of laying a columnar foundation, know the type of soil, groundwater level and the nature of the future construction, such a foundation will be durable and wear-resistant for decades.
Calculation for a shallow foundation
An example of calculating shallow foundations on heaving soils should be given. For example, a one-story house is being built with the following dimensions:
- height – 4 meters;
- width – 5 meters;
- length – 10 meters.
The structure includes two load-bearing internal walls, each 4 m high and 3 m long. The floor does not rest on the foundation and is filled with concrete. The base will have the shape of a tape with a base width of 40 cm and a depth of 70 cm. The foundation is made of reinforced concrete, for which reinforcement with a diameter of 12 mm is used. The frame will have two belts, each of which consists of five rods, jumpers with a length of 25 cm. Such jumpers are placed in increments of 50 cm.
To find out the mass that the strip foundation will have, you need to determine the following values:
Scheme of a shallow foundation with waterproofing on a printed pad.
- geometric dimensions of the structure;
- density of the building material used.
Geometric dimensions are quite easy to find out. So, the length of the foundation is equal to the perimeter of the future building, that is, you just need to calculate the sum of its sides:
10+10+5+5+3+3=36 meters.
The strip foundation will be poured not only under the external facade walls, but also under the internal load-bearing walls, so they are also taken into account.
Now you can find the volume based on the fact that the height of the tape is 70 cm and the width is 40:
V=36×0.4-0.7=10.08 cubic meters.
But this is the total volume from which the reinforcement must be subtracted to find out the amount of concrete. Knowing that the strip foundation has two belts of five rods with ligation, calculate the length for each:
10-0.5-0.5=9 meters.
The length of all belts will be equal to:
2×(9×2+4×2+2.5×2)=62 m.
Each belt has five rods, which means their total length is: 62×5=310 m.
Now determine the length of the required jumpers for reinforcement:
Scheme of reinforcement of a shallow foundation.
9/0.5+1=19 pcs.,
4/0.5+1=9 pcs.,
2.5/0.5+1=6 pcs.
For one upper chord the number of jumpers is:
19×2+9×2+6×2=68 pieces,
Since the length of one jumper is 0.25 meters, the total length is:
68×0.25=17 meters.
For all horizontal frame lintels, the length is:
17×2=34 meters.
For vertical jumpers, take into account that there are 68 of them on one side and the same number on the other. That is, it turns out 136 pieces with a length of 40 cm. Their total length is:
136×0.4=54.4 m.
Now calculate the total length of reinforcement required by a shallow foundation:
310+34+54.4=388.4 m.
To find out the cross-sectional area for reinforcement, use the formula for the area of a circle:
Scheme for preparing concrete mortar for the foundation.
3.14×0.000036=0.00011 sq. meters.
To obtain the volume, use the formula:
0.00011×388.4=0.04 cubic meters meters.
Now we get the volume only for the reinforcement:
10.08-0.04-0.04=10 cubic meters meters.
The value of 0.04 is taken from the calculation that a shallow foundation will also be reinforced in the corners.
Using this not too complicated calculation, they determine what is required:
- 10 cu. meters of cement (at a density of 2500 kg per cubic meter);
- 0.08 cu. meter of metal reinforcement (with a density of 7800 kg per cubic meter).
That is, the total mass of the entire foundation, which is erected on heaving soils in the form of a strip foundation, will be:
10×2500=25000 kg,
0.08×7800=624 kg,
25000+624=25624 kg.
That is, the strip foundation has a mass of 25624 kg.
Building a house on heaving soils is not the best option. But if there is no other way out, then it is necessary to carefully calculate the future foundation so that after its construction the structure is not pushed out of the soil during winter heaving. This is not so difficult to do, but care must be taken to ensure that during operation there is no deformation of the foundation, and therefore the house itself.
Application of pile foundations
Pile foundations.
Pile foundations in heaving soils are somewhat less popular in private low-rise construction than strip and column foundations. This is due to the increased labor intensity of the work and the need to attract specialized equipment for their construction. Typically, a pile foundation in heaving soils is used when the soil in the region freezes to more than 1.5 m. It is also advisable to use a pile foundation for heaving soils if a frame-type frame is being built.
In private construction, piles with a depth of no more than 3-4 m are usually used. Driven piles made of wood, concrete or reinforced concrete are most often used. They come in the following types:
- driven reinforced concrete;
- cast-in-place reinforced concrete or concrete;
- screw.
When constructing a pile foundation on heaving soil, it is important to ensure that water drainage is done as efficiently as possible. For this purpose, drainage systems are used, and waterproofing is installed along both axes of the foundation.
Construction of a shallow columnar foundation made of pipes
Diagram of the causes of foundation failure.
With this method, permanent formwork is made to form pillars - a steel or asbestos pipe of the required diameter (20, 40 cm, etc.). If the soil has a standard load-bearing capacity (4 kg per 1 cm²), then it is assumed to simply dig a round depression and insert a pipe of the appropriate cross-section into it. Concrete mixture is poured into the prepared recess to a third of the height. In this case, the pipe will slowly rise, and the solution will flow out onto the previously overlapped waterproofing layer. In this way, a widened base is created - a hydraulic cushion. After the concrete has hardened, work continues. The solution is gradually poured into the pipe to a distance of 15 cm to the level of the zero boundary (20 cm at a time and vibrocompressed). From the outside, the “form” is fixed with compacted soil in order to prevent its distortion. The subsequent stages of work on creating a columnar foundation from pipes are carried out by analogy with the previous methods.
DIY columnar foundation on heaving soils
To build such a foundation, the following materials and tools may be required:
- reinforced concrete pillars;
- concrete mixture;
- metal pipes;
- shovel;
- waterproofing materials;
- sand, crushed stone;
- drilling rig, etc.
Scheme of a shallow, economical strip foundation for heaving soils (clays and loams).
A columnar foundation can be an excellent solution for the construction of low-rise buildings in heaving soil conditions. The correct columnar foundation should be installed below the freezing level. This method allows you to save a large amount of money. To avoid stress acting on the support pillars, reinforced concrete pillars should be selected. Columnar foundations made using reinforced concrete are an excellent solution for laying a foundation in soil characterized by heaving phenomena. This technology is convenient and highly manufacturable, so they can be erected in swampy, damp areas and soils with a high level of groundwater.
On these soils, a columnar foundation can have a type of construction in which an anchor platform is firmly tied to the supporting frame, which serves as a support for the building. The following products can be used as load-bearing pillars for such a foundation: reinforced concrete pillars, asbestos-cement pipes with reinforced internal walls, metal pipes reinforced on the inside with cement-sand mortar and on the outside with epoxy resin. The fittings can be wire with a diameter of 6-12 mm, metal rods or parts of water and gas pipes. The concrete mixture should be prepared only using high grade cement. Crushed stone or sand are suitable as fillers. The stiffer the concrete, the stronger the structure will be.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=hI8oietMmho
Pouring monolithic pillars
Pouring pillars for the foundation
The next phase of production ends with pouring the pillows, their thickness is about 10 cm. M250 grade concrete is used. During the pouring process, rods protrude from the cushions to further attach the pillar frame. The time for complete hardening of the pillows is 7–10 days, after which the formwork of the pillars is installed.
The formwork is a wooden box without a bottom, made of edged boards. Professional builders have various boxes for arranging different foundations, so they will perform this type of work most efficiently.
Pouring of pillars for shallow foundations on heaving soils is also carried out with concrete grade M250. A deep vibrator is lowered inside a wooden box filled with concrete mixture, which creates vibrations, thereby compacting the entire concrete mass. I begin to compact the concrete mass from the bottom of the box, gradually raising the vibrator to the top.
Tamping is completed by adding the required amount of concrete mortar, on top of which a bent corner or metal plate is laid to perform subsequent tying. The end result is a monolithic structure. After the pillar has completely cooled down, after 5–7 days, the wooden formwork is removed, which helps speed up the setting process.
Three weeks later, the pillars are tied using a channel, and after a month the structure is ready for waterproofing work. The best way: covering the entire plane of concrete pillars with bitumen mastic, followed by installation of roofing felt. After waterproofing is completed, the columns are sprinkled with earth from below and compacted.