Comparison of technical characteristics
For the convenience of comparing the main technical parameters of conductors and understanding what the difference is between them, we will compile a table comparing the main characteristics.
| Characteristic/Material | PVS wire | VVG cable |
| Core material and design | Copper stranded | Copper stranded or solid |
| Flexibility of the current-carrying core | Flexibility class 5 (high) | 1 – 2 flexibility class (medium) |
| Number of cores in the wire/cable | From 2 to 5 | From 1 to 5 |
| Core cross-sectional area, mm2 | From 0.75 to 6 | From 1.5 to 625 |
| Permissible operating voltage, V | ||
| In AC circuits, at a frequency of 50 Hz | 450 Volt | 0.66 kV or 1 kV |
| In DC circuits | 0.66 kV | 1.6 kV or 2.4 kV |
| Permissible ambient temperature | From -25°С to +40°С | From -50°С to +50°С |
| Permissible long-term core heating temperature | 70°C | 70°C in emergency mode, short-term heating up to 80°C is allowed |
| Standard service life | From 6 years (movable connection) to 10 years (fixed connection) | Up to 30 years old. The manufacturer's operational warranty is 5 years. |
To figure out what is best to use in a given situation, you need to conduct a comparative analysis of individual properties that are decisive.
Properties of the current-carrying conductor. The cores of both conductor products under consideration are made of copper. The PVS wire is produced only in a multi-wire version; the VVG cable can have a solid mono-wire core. The significant difference between them is the flexibility class of the multi-wire versions. In this parameter, PVA is many times superior to VVG. Thanks to this characteristic, the fatigue strength of the wire during repeated bending is significantly higher than that of the cable. That is, when it comes to moving joints, the choice should be made in favor of PVS. Such connections include power supply to non-stationary electrical appliances, as well as electrical wiring with a plug for connecting electrical equipment to the network.
Core cross-section. The table shows that the range of VVG cross sections is much wider towards larger values. In relation to the choice of electrical wiring for a house, apartment or cottage, we can say that the wiring of power circuits supplying power to an oven, hob or air conditioner can only be done using a cable product of the appropriate cross-section. The largest cross-section of PVA is 2.5 mm2, which is not enough for these purposes.
Insulation properties and overall service life. By comparing the operating voltages at which the conductors in question can operate, we will determine how one material differs from another. The fact that the permissible voltages for a cable are higher than for a wire indicates that when operating in the same voltage class, the electrical strength margin of the cable insulation is higher than that of the wire insulation. If we add the fact that the service life of VVG exceeds that of PVA by at least three times, we can draw the following conclusion:
It is more advisable to install stationary electrical wiring, especially hidden wiring, using a VVG cable. In this case, it is better to use a monowire core. Considering that hidden electrical wiring is installed for a very long time, its reliability should be as high as possible. It is better to use the VVGng cable version with non-combustible insulation.
Environmental conditions. The range of permissible ambient air temperatures for VVG is significantly expanded into the zone of negative temperatures in comparison with PVA. This circumstance determines the fact that you should choose a cable product more suitable for this purpose for the street.
Specifications and selection
As already said, all parameters of the PVS wire are described in GOST 7399-97. Everything is regulated there: from the number of cores to their diameter for each section. And, by the way, there is one postscript. Its essence is that if the resistivity matches, deviations in the cross-section are allowed. This makes the choice somewhat difficult. It is not difficult to check the cross-section of a conductor by diameter, but measuring its resistance is more problematic. To do this, you need to have a piece of wire and a measuring device. As a solution, we can advise you to buy a small piece, measure the resistance and cross-section, and then make decisions about whether to buy or not.
Technical characteristics of PVA
When choosing, you should pay attention to insulation. It should have the same thickness, there should be no sagging, especially cracks and other damage. Since the cable is flexible, it can be easily bent without any damage to the insulation. There must also be an accompanying document indicating the manufacturer, brand and parameters of the cable. If you have this minimum, you can buy a cable.
Decoding of PVS cable
PVA wire has a fairly simple decoding, where the letter “P” indicates the name of the product - wire, “B” refers to vinyl insulation, and “C” indicates the type of connection when the cores are in one common sheath. In this case, the cable will have a circular cross-section. The letter “P” in the product name indicates parallel placement of the wires, due to which the wire will have an oval cross-section.
It is worth noting some points here:
- The PVS wire is marked from the outside. In this case, deciphering the cable may be difficult because the name, in addition to letters, also contains numbers.
- After the letters, the first number, as a rule, can be: 2, 3, 4 or 5. This designation indicates the number of cores in the wire.
- Next in the marking is an “x”, followed by a second number, be it: “0.75”, “1.00”, “1.50” or “2.50”. The last digital value indicates the total cross-section of the cores in the cable.
The video below will help you understand digital marking in more detail:
Important point! According to GOST 22483-77, the actual and nominal cross-section between the cores may vary. The main condition is that the electrical resistance of the cable must comply with regulatory standards.
For example, you have a flexible PVA wire 3x1.5. In this case, it must have 3 cores, each with a cross-section of 1.5 mm2.
PVS wire: decoding and application
It is the best option for domestic conditions, which makes it especially popular. The abbreviation indicates the following characteristics: “P” – wire, “B” – vinyl insulation; “C” – connecting. The cut product is round.
There are options labeled PVSP. In this case, the veins are located parallel, and their shape in the section is oval. It is often called flat. The PVS-T marking can be deciphered as operation in conditions of increased dampness. The PVSN wire means that the product is of the fifth class of flexibility. The absence of the letter “A” at the beginning indicates that the wires are copper.
- connection and repair of household appliances;
- arrangement of temporary electrical wiring in residential and domestic premises;
- as a connecting or extension cable for various needs;
- power supply for small agricultural and gardening equipment;
- in production, for equipment with high energy consumption.
It is an element of the design of almost all household appliances and plumbing tools.
Characteristics
The technical and electromechanical characteristics of the PVS wire are regulated by the requirements of GOST 7399-97. It should be noted that this standard only describes a range of values, and actual parameters may vary from manufacturer to manufacturer. This means that exact data on the size, diameter of cores and wires, as well as the thickness of the insulating sheath should be obtained from the accompanying documentation or directly from the supplier.
- The temperature at which PVA wire retains its operational and technical performance at the highest level is in the range from -25˚C to +40˚C. If the wire marking indicates the “Y” version, the lower limit of the temperature range expands to -40˚C - +40˚C. It should be taken into account that during use the heating of the current-carrying conductors should not exceed +70˚C.
- PVA wire is resistant to combustion and does not spread fire when laid alone.
- The cable is designed for use in rooms with high relative humidity (up to 98%).
- When using PVA wire for laying electrical networks, its working life exceeds 5000 hours. If the cable is used in stationary electrical equipment - at least 12,000 hours.
- The cable's resistance to alternating deformation when bending (with a radius of at least 4 cm for a cross-section up to 1 mm2 and at least 6 cm for a cross-section greater than 1.5 mm2) and rated voltage is 30,000 cycles.
- Climatic cables (PVS-T) are resistant to mold and mildew.
- The PVS wire is intended for use in electrical networks with linear voltage from 380V to 660V.
- The warranty service life of the cable is 2 years and is counted from the moment it is put into operation.
A standard PVA wire can withstand alternating current with a voltage of 2 kW for 5 minutes. After immersion in water for 1 hour - up to 15 minutes. In terms of mechanical strength, it is close to the VVG cable - to break it is necessary to apply a force of more than 10 N/mm2, and before breaking the wire will lengthen by one and a half times.
The standard length of PVA wire on sale ranges from 30 to 200 meters. Most often it is sold in coils and cable drums.
How to choose PVS wire?
First of all, you need to decide on the number of cores; there can be from two to five. In everyday life, as a rule, a three-wire wire (phase, neutral, ground) is sufficient. Having solved this issue, the cross section is selected depending on the power of the connected equipment. In order not to bother with calculations, we present the recommended wire cross-section, depending on the load current:
Table of permissible maximum current for typical cross-sections of PVA wire cores.
| Core cross-section (mm2) | Imax(A) |
| 0,75 | 6,0 |
| 1,00 | 10,0 |
| 1,50 | 14,0 |
| 2,50 | 20,0 |
Given the emergence of a large number of counterfeit products, be sure to check for a certificate of conformity before purchasing.
As for manufacturers' recommendations, it is difficult to give a definite answer to this question without it sounding like advertising. If they comply with GOST, any product will meet the task.
Good afternoon friends
If there is a need to replace electrical wiring, then special attention must be paid to the choice of cable. If you choose the wrong wire, then in the future there may be many problems with wiring and equipment that will burn from power surges, and, as a result, you will need to completely replace the electrical wiring
Experts call the PVS cable the most practical for these purposes. It is also used in many household appliances to connect the device to a power source - the network
This wire is convenient to use because it is not susceptible to breakage due to kinks, which is an important component when repairing several rooms. Read more about all types of PVS cable markings and areas of application later in the article.
Enjoy reading.
PVS wire technical characteristics, structure, application
The widespread use of household electrical appliances, a variety of tools and devices designed to connect to a standard 220/380V network, led to the development of a standard wire specifically for these purposes.
Operating conditions required making it safe, flexible, strong and durable. This problem was successfully solved, and currently Russian companies offer sufficient quantities of PVS wire that fully meets these requirements.
All about PVS wire in GOST 7399-97
Domestic manufacturers of PVS wire working for the Russian and CIS markets strive to comply with the requirements of GOST 7399-97, since it has interstate status. In addition, this facilitates export operations to non-CIS countries, since the content of the document is synchronized with the relevant parts of the international standards IEC 60227-1-93 (97) and IEC 60245-1-94 (97).
Sections of GOST 7399-97 contain all the most important information about the range, mechanical and electrical characteristics of PVA wire, as well as safety requirements, a list of tests, etc.
Marking example:
PVA 2x0.75+1x0.75 GOST 7399-97
The wire of the PVA brand is designated here; it has two main conductors with a cross-section of 0.75 mm2 and one grounding conductor with a cross-section of 0.75 mm2.
PVA wire structure
The standard defines PVA wire as a flexible wire for voltage up to 380V with twisted copper conductors in polyvinyl chloride insulation, with a polyvinyl chloride sheath. Each core consists of copper conductors; the core class must be at least 5 according to GOST 22483-77.
This standard establishes the thickness of the wires of which the core of each section can be composed. For example, in a standard PVA wire, cores with a cross-section of 1 mm2 cannot consist of wires with a diameter greater than 0.21 mm.
The number of wire cores can be from two to five, the minimum cross-sectional area is 0.75 mm2, the maximum produced by cable factories is 16 mm2, however, it is worth noting that according to GOST 7399-97 standards, the PVA wire must have a cross-section of 0.72 mm, up to 2.5 mm. The twist direction is left, twisting is performed without filler.
Core insulation color: white, grey, blue, blue, green, red, brown and yellow. On top of them there is a sheath of PVC plastic, applied by extrusion and flame retardant when laid individually. It must fill the gaps between the wires, giving the wire a round shape.
PVS transcript
- the absence of the letter A at the beginning of the abbreviation means that the wire is copper;
- P - wire;
- B - PVC insulation;
- C - designation of the purpose of the wire, connecting.
PVC wire technical specifications
Threshold values of basic mechanical and electrical characteristics are standardized by GOST 7399-97; as for specific values for each manufacturer, they may differ within the specified limits.
Therefore, accurate data on diameters, insulation thickness, mass and other indicators must be taken from the documentation accompanying the batch or the manufacturer’s catalogs. As an example, the characteristics of a standard PVS wire from one of the largest Russian manufacturers are shown here.
High-quality dry PVA wire can withstand alternating current voltage of 2000V for 5 minutes, and after an hour in water (tO= 20 ± 5 °C) it can withstand it for 15 minutes. The strength requirements are the same as for the VVG cable, the breaking force must be at least 10 N/mm2, and the elongation before breaking must be at least 150%.
The life of the wire, defined as the number of alternating bending deformations at rated voltage, should not be less than 30,000 cycles.
Application of PVS wire
PVA wire is used in the production of household appliances and electrical tools and devices. In the design of washing machines, televisions, refrigerators, all kinds of plumbing and construction power tools, other machines and devices, it is used to connect to the network. It is also used for the manufacture of network adapters, extension cords, etc.
Other types of PVS wire
- PVSng(A)-LS - the same as PVS, but does not propagate combustion, with reduced gas and smoke formation;
- PVS-Tng(A)-LS - the same as PVSng(A)-LS, but lightweight;
- PVS-TTng(A)-LS - the same as PVSng(A)-LS, but has a thicker insulating layer;
- PVS-TSng(A)-LS - the same as PVSng(A)-LS, but is intended for stationary installation.
Types, cross section
The characteristics and parameters of the PVS wire are described in GOST 7399-97. According to this document, the core cross-section is from 0.75 mm² to 2.5 mm², the number of cores is from two to seven. The maximum permissible voltage is 600 V, works with direct and alternating current. Can be round or flat.
There may be the following modifications:
- PVSm. Frost-resistant with operating temperature range from -40 °C to +40 °C.
- PvSmp. Frost-resistant with an additional sheath - twisted insulated strands are wrapped with synthetic tape. The top is filled with a layer of PVC. More durable modification.
- PVSN - not intended for reinforcement. Only the manufacturer can give the exact difference from the usual one.
- PVSU. Only available from select manufacturers. Sometimes it means a smaller number of cores (compared to GOST). Sometimes the letter "U" denotes a temperate climate. What exactly this marking means must also be clarified with the manufacturer.
If you bought a wire with a plug to connect a washing machine, electric stove, or dishwasher, then most likely it is a PVA wire
- PVSt. Insulated cores are twisted around a supporting cable (usually the number of cores is 5 more). There is another option - where the “t” denotes a tropical version.
- PVSL - tinned round copper core (usually it is polished). This is again from individual manufacturers.
- PVSP - flat.
- PVSPng(A)-LS. Flat wire, non-flammable option. “PN” - reduced flammability, LS - reduced release of harmful substances during combustion.
- PSVL-T.
As you can see, the PVS wire has various modifications. The most useful are frost-resistant PVSm, low-flammability PVSPng(A)-LS, flat PVSP may be useful.
Performance characteristics
Main technical features:
- permissible voltage - 380/660 V;
- maximum heating temperature - +70 degrees;
- resistance to fire when laid alone;
- high strength under mechanical stress;
- service life - six (when installed outdoors) and ten years (indoors);
- Temperature conditions for use: -25...+40 degrees.
The wire also has a modification that is resistant to burning in a group installation. It is designated by the abbreviation PVSng. Such a cable, in turn, is also divided into types depending on the degree of protection, fire properties, and scope of use. The most popular is PVSng-LS. According to GOST 22483-77, it belongs to safety class 5. The letters “ng” mean that the product is non-flammable, and “LS” means that it emits little smoke.
Section options
The PVS cable can have several cross-section options (mm2):
- 0,75;
- 1,5;
- 2,5;
- 4.
The cross-section is the size of the cut of the core. If there are several of them, then the total performance of all conductors is taken into account. To determine which cross-section is suitable in a particular case, you need to add up the power of all devices powered by a given cable in the future. It is necessary to provide a small margin so that when connecting an additional device, the wire can withstand the voltage. A product with a cross section of 1 mm2 is capable of passing 2 kW of current. Thus, 4 mm2 will withstand a load of 8 kW.
It is important to consider that according to GOST, a slight deviation of the existing cross-sectional area from the declared one is allowed. However, in this case, the electrical resistance must exactly match that indicated in the technical documents
Number of cores
PVA can have from two to five cores
When choosing a cable, you need to pay attention to this. If there is no grounding in the room (this happens in old houses, for example, in Khrushchev, Stalin, panel buildings, etc.
etc.), then a regular two-wire wire will do.
Newer buildings use TN-CS type power supply. This means that there is a ground connection, so a cable with three or more cores will be needed.
Rice. 3. Options for PVS cables with different numbers of conductors, i.e. cores.
Length of cable
PVA is sold in drums, as well as in coils of 20 meters. If such a long cable length is not needed, then you can purchase 1 or 5 m
However, it is important to take into account that the wires must always be taken with a reserve, because there is a risk of damaging them during installation
VVG cable compared to PVS
Comparison table between VVG cable and PVS wire
VVG cable has good qualities and a relatively low price. Its purpose is alternating current networks: voltage from 660 to 3000 V, operating voltage from 1 kW to 3.5 kW. It can have from 2 to 6 conductors, with a core cross-section of 1.5 - 250 mm2.
They have the same copper conductors and polyvinyl chloride insulation. The main difference is in the flexibility class. PVA is elastic and belongs to class 5. The VVG cable has class 1 or 2. The diameter of the wire and their number in the core depend on this. For example, a VVG cable of class 1 flexibility with a cross-section of 2.5 mm2 may have only one wire 1.78 mm in diameter. The same PVA will consist of 50 wires with a diameter of 0.25 mm.
The product differs in profile type. The veins of small diameter are round, and the large ones are sectorial. Another difference is the thickness of the insulating material and shell. For the cable, the thickness of the inner layer is 0.8 mm, the outer layer is 1.5. For PVA, respectively – 0.8 and 1.1 mm.
There are different modifications of the VVG cable. Hidden wiring in the room is possible. It is used for outdoor installation. An overhead or underground electrical cable requires additional protection with a corrugated sleeve.
PVA cable design
Despite the misleading name "wire", PVA is a cable. That is, each conductor in the structure is protected by insulation, all cable wires are protected by a common sheath.
Both the core insulation and the sheath insulation are made of polyvinyl chloride. It is also flexible, not afraid of frost, virtually does not burn, and is resistant to almost any non-hazardous chemical.
The design of the current-carrying cores is interesting in the design of the PVS cable. These are several thin copper wires twisted into a single core. The number of wires in the core and their cross-section depend on the cross-section of the core; both parameters are standardized. The cable itself is standardized by GOST 7399-97 (interstate).
This feature in the design of PVA cores specializes their connection. The PVS wire is connected through crimp sleeves or special terminals.
Product Description
What is the decoding of the PVA wire being studied?
- The letter “P” means that we have the actual wire in front of us.
- The letter “B” in the abbreviation indicates in this case that this particular wire is enclosed in vinyl insulation.
- The letter “C” indicates that the wire is connecting.
The marking of PVA wire can also include the color designations of the cores. As a rule, white, brown or red colors are used for phase elements. But for the 2000s - blue or dark blue. For “earth” – yellow-green color.
For example, consider the marking of PVA 3x2. What does this mean in this example? What will the decryption be? This is simply deciphered: this is a wire with 3 cores, in addition, the cross-section of each of them is equal to 2 mm².
In the table below you can familiarize yourself with the geometric and weight characteristics of the PVA wire in question.
What can be said about isolation?
The thickness of the actual core insulation is 0.6-0.8 mm, but the outer sheath is already 0.8-1.2 mm.
By design, PVA wire consists of copper cores (which accordingly consist of copper wires) enclosed in a PVC sheath. This entire system is housed in a common flexible polyvinyl chloride shell.
Marking
The general insulation and shell of phase conductors are marked in accordance with the PVA color marking standard:
- The overall insulating sheath is always painted white. Sometimes there are two diametrically located stripes of a different color.
- Black, red, yellow, gray and brown colors are used to mark conductive wires.
- If there is a “zero” phase, it is indicated in blue.
- Green or yellow-green color is reserved for the ground wire, but it is rarely found in PVA.
Marking of PVS wires is carried out in accordance with the requirements of GOST 7399-97. Decoding the notation is very simple:
- the presence of the letter “l” indicates that the phase wires are made of tinned copper (PVC);
- the capital letter “T” indicates the climatic design of the cable;
- “A” in the marking means that the cable uses aluminum conductors;
- “B” - armored wire;
- PS - the cable insulating sheath is made of a mixture of self-extinguishing polyethylene and polyvinyl chloride;
- G – cable without insulation;
- ШВ – outer insulating shell made of flat polyvinyl chloride;
- PV - the outer insulating shell is made of a mixture of PVC and vulcanized rubber;
- the first number following the letter designations indicates the number of cores inside the cable;
- the number following it is the cross-sectional area of the conductive conductors.
In order to find out the exact physical characteristics of the PVA cable, you should refer to the following table:
| The wire | Number of cores/sectional area of each (mm 2 ) | Number of wires in phase conductors/diameter | Weight of 1km cable (kg) | Outer diameter (mm) | Max Diameter(mm) |
| PVS | 2×0,75 | 24×0,2 | 55,8 | 6,4 | 7,2 |
| 2×1,00 | 32×0,2 | 63,7 | 6,7 | 7,5 | |
| 2×1,50 | 30×0,25 | 85,15 | 7,6 | 8,6 | |
| 2×2,50 | 50×0,25 | 133 | 9,4 | 10,6 | |
| 3×0,75 | 24×0,2 | 66,1 | 6,8 | 7,6 | |
| 3×1,00 | 32×0,2 | 76,5 | 7,1 | 8 | |
| 3×1,50 | 30×0,25 | 107 | 8,3 | 9,4 | |
| 3×2,50 | 50×0,25 | 166,7 | 10,2 | 11,4 | |
| 4×0,75 | 24×0,2 | 79,8 | 7,4 | 8,3 | |
| 4×1,00 | 32×0,2 | 96,5 | 7,9 | 9 | |
| 4×1,50 | 30×0,25 | 134,5 | 9,2 | 10,5 | |
| 4×2,50 | 50×0,25 | 203,8 | 11,1 | 12,5 | |
| 5×0,75 | 24×0,2 | 102 | 8,3 | 9,3 | |
| 5×1,00 | 32×0,2 | 118,4 | 8,7 | 9,8 | |
| 5×1,50 | 30×0,25 | 170,6 | 10,3 | 11,6 | |
| 5×2,50 | 50×0,25 | 257,6 | 12,4 | 13,9 |
Read also: Restoring chrome on a faucet
WIRE PVS
Galla-Cable M LLC sells flexible wire of the PVS brand. These are modern products manufactured by leading manufacturing plants. All PVS wire presented in our catalog has certificates of conformity confirming its high quality. We also guarantee an affordable price.
Scope of application: PVS wires are intended for connecting electrical appliances and power tools, household appliances, small mechanization equipment and other similar machines and devices, and for making extension cords with a voltage of 380 V for 380/660 V systems. They can be used to connect:
- electrical appliances for home care;
- various power tools;
- washing machines and refrigerators;
- small mechanization tools for gardeners and vegetable gardeners.
PVA is also used to make extension cords.
PVA grade wire is suitable for areas with cold climates, which makes it more versatile. Due to this, it is in significant demand. Also, the high demand for these wires is influenced by the affordable price.
Construction: conductor - copper, round, stranded. The insulation of the current-carrying conductors is made of PVC plastic. The insulated cores are twisted. The insulated strands of five-core wires can be twisted around a core. The shell is made of white PVC plastic. The sheathing in the wires is applied to fill the spaces between the wires, giving the wires a round shape. To ensure mobility of the cores during operation and for cutting wires, a layer of talc is applied between the insulation and the sheath.
Characteristics of PVS: Operating temperature: from minus 25°С to plus 40°С Laying and/or rewinding temperature: not lower than minus 15°С. Minimum bending radius: 8 Dн, where Dн is the outer diameter of the cable. Type of climatic version: UHL Fire hazard class: 01.8.2.5.4 according to GOST R53315-2009 amendment 1 Wires do not spread fire when laid alone.
Performance characteristics and scope of application of PVS wire
PVA wire has become widely used due to its performance characteristics. Indeed, unlike wires of other brands, it has a number of significant advantages. And its main disadvantage may be the price, which is much higher in comparison with other similar aluminum products.
- One of the main features of PVS wire is its flexibility. Thanks to the structure of the cores, which are made of a large number of small wires, bending the wire at any angle does not cause any problems.
- The presence of a protective sheath, which is installed by GOST PVA wires, makes the conductors less susceptible to mechanical damage.
Carrying from PVA wire
- Different types of colors for the wire cores make it easier to install. In addition, this increases the ease of repair. After all, even if there is damage in the center of the wire, color marking (see Marking wires and cables according to the rules) will allow you to easily determine the purpose of the damaged core.
- As for the scope of application, the characteristics of PVA wire allow it to be used in a wide range. So it is often used to connect power tools.
- The flexible structure and the presence of an additional shell allow it to be used to create carriers and extension cords.
- Since, according to the PUE, only copper wires have been allowed to be used for lighting residential buildings since 2001, PVS and PVSP wires have found wide application in this area.
The photo shows the PSVP wire
- Good characteristics for outdoor use have ensured that the wire is widely used in outdoor electrical networks and gardening.
- The ease of DIY installation has ensured that the wire is widely used in electronics and electrical devices.
How to choose a PVS cable?
Here are the selection criteria to rely on:
- Number and cross-section of cores
. Perhaps this is the most important parameter that determines the area of operation. When choosing, you need to take into account the power of electrical appliances that will be switched to the network through a multi-core wire. - Presence or absence of a grounding conductor
. It provides the opportunity to connect the device and the ground loop. - No defects or damage
. - Correct twisting of wires in a separate core
. It is always carried out in the left direction. - Application area
. There are cables for external and internal use. The former are used in transformers and distribution panels, and the latter - inside residential premises. - Type of cable
. The PVA connecting wire can be copper or aluminum. The first is characterized by high strength and elasticity, low resistance. Its aluminum counterpart loses in these indicators, but costs less.
PVA wire marking
Any product has a letter and number designation. The PVS cable marking used means the following:
- The first digit
indicates the number of cores. - The second number
indicates the cross-sectional area of each individual core.
For example, given a cable marked PVS 3x0.25. From this entry you can understand that we are talking about a wire with three cores with a cross-section of 0.25 sq. mm each. Sometimes you can find more complex markings, for example, PVA 5x0.6 + 1x0.25. This means that the product consists of five cores with a cross-section of 0.6 sq.mm and one additional core with a cross-section of 0.25 sq.mm. The indicated value and actual size may be slightly different from each other. GOST allows this, but states that the value of electrical resistance must correspond to the data specified in the technical data sheet.
PVA cable colors
The general shell can have any color. PVA wire black and white has become widespread. The colors for individual cores are not chosen by chance:
- Red or brown
– phase conductor. - Blue or light blue
– zero. - Yellow-green
– grounding.
PVA is a cable or wire
PVA is one of the most common types, which can be used for networks with voltages up to 380 volts, has from two to five cores. Each core consists of thin twisted wires enclosed in separate insulation. For ease of installation, the insulation of phase wires can be brown, white, red or black. Zero is colored blue or cyan. The insulation of the grounding conductor is yellow-green. The overall shell also comes in a wide range of colors.
Read also: Alternating current parallel connection
There are many options, they differ in the following parameters:
- The outer one has three conductors - phase, neutral, ground. It is convenient for supplying power from an external transformer to an indoor distribution panel.
- The internal wire is arranged in the same way. It has no protection from climatic conditions and dampness. Can be used indoors.
- Copper – high strength, has low resistance and increased current conductivity, and is resistant to corrosion.
- The advantage of aluminum is the price. Aluminum oxide treatment increases service life.
- T – resistance to mold and fungi;
- B – armored cable;
- U – increases the temperature minimum;
- PS – self-extinguishing shell;
- G – without insulation;
- SP – power;
- T – telephone cable.
The wire is also divided into standard sizes according to the number of cores, weight and cross-sectional profile.
Characteristics of PVS wire
The purpose of the PVA wire is to connect electrical equipment installed away from the internal wiring. You can make a carrier (extension) out of it. Another area of application is to use it as a connecting cable to an electric oven, hob, electric stove and any other household appliances. The conductor cross-section is selected depending on the maximum power of the equipment and the type of load (220 V or 380 V).
Diameter of conductors depending on power
It is also suitable as cords for lighting fixtures - lamps, floor lamps, etc. Only the cross-section of the wires in this case is small - 0.5-1.5 mm. The service life of the PVS wire for permanent connection of electrical equipment is 10 years. Not so little. Especially when you consider that we often change household appliances more often.
PVA wire can be used outdoors, but not in northern regions. The upper temperature limit is around +40°C, so summer use is not a problem almost everywhere. But you can only leave it outdoors in winter closer to the south. The lower limit of the temperature range depends on the shell material. Some manufacturers have a lower temperature limit of -15°C, others -25°C. For some regions this is enough, for others it is not. Just one point: outdoor service life is no more than 6 years. Moreover, the warranty period is 2 years.
By the way, there are special frost-resistant modifications. They can be used at temperatures down to -40°C. Such products are labeled with an additional letter “m” - PVSm.
Weight of one meter and maximum permissible current
Long-term permissible heating of the cable cores is up to +70°C, but it is better to avoid this. Cable and wire overheat when the core diameter does not match the load. Therefore, when choosing a section of cores, it is better to take a reserve - it will be more complete. Moreover, we are talking not only about the integrity of the wiring itself, but also your home.
Another important characteristic: flammability. PVA wire is resistant to flame spread, but only in the case of a single installation. That is, installation in cable ducts in fire hazardous areas is not recommended.
Pros and cons of PVS wire
On the positive side
PVS cable has can be classified as:
- flexibility, which allows installation to be laid along cable structures with steep transition radii;
- possibility of use in electrical networks of 220 V and 380 V;
- Despite the fact that the cores are made of copper, the wire as a whole is quite light in weight.
Negative side of the PVS cable
is that it is inconvenient when installing hidden wiring, since it has a round shape. This design parameter creates inconvenience when laying it under plaster. Despite this, this type of cable is in great demand among buyers who use it for installing electrical networks. Such widespread use does not depend on the place of its implementation, be it Moscow or another city in our country.
Design
Modern PVA wire consists of several intertwined copper wires with separate insulation made of high-quality polyvinyl chloride. Additionally, all conductors are protected by a PVC sheath. The standard cable has a round cross-section, although the PVSP model, as described above, will have an oval cross-section. Insulating materials may include various additives that give them additional protective functions (for example, the product does not support the combustion process).
Each copper core contains a large number of copper wires. When twisting each one, a dense rope is formed. In accordance with GOST, the class of lived in PVA must be at least fifth. Such a standard automatically regulates the minimum thickness of the wires from which a separate core is formed.
If the cross-section of each core in the cable is 1 sq. mm, then the diameter of the wires used should not be lower than 0.21 mm.
Analyzing GOST, you can discover another important rule: in PVA, the cores are twisted in the left direction, but the density is so high that filler is not used. When choosing an insulating shell, manufacturers try to use materials of different colors, which simplifies installation tasks. Individual wires can be colored blue, brown, red, yellow or even yellow-green
The phase conductor is usually marked brown or red, the neutral conductor is blue or cyan, the ground conductor is double, yellow-green. The common sheath, under which all the cores are located, can have an arbitrary color (for example, black)
Individual wires can be colored blue, brown, red, yellow or even yellow-green. The phase conductor is usually marked brown or red, the neutral conductor is blue or cyan, the ground conductor is double, yellow-green. The common sheath, under which all the cores are located, can have an arbitrary color (for example, black)
When choosing an insulating shell, manufacturers try to use materials of different colors, which simplifies installation tasks. Individual wires can be colored blue, brown, red, yellow or even yellow-green. The phase conductor is usually marked brown or red, the neutral conductor is blue or cyan, the ground conductor is double, yellow-green. The common sheath, under which all the cores are located, can have an arbitrary color (for example, black).
The top, outer layer is a polyvinyl chloride shell, which is applied using the extrusion method. During the single installation process, the protective layer does not support combustion. Due to its plasticity, the sheath fills any gaps formed between the cores, making the wire round in shape. The maximum eccentricity value is 10%.
Operating conditions and technical specifications
An important condition for the operation of PVA wires of any model is maintenance in the operating temperature range, which ranges from -35 to +40 degrees. Celsius. If you follow this rule and exclude mechanical damage, the cable will last for ten years.
Due to its high technical and operational characteristics, PVS is significantly superior to wires of other brands. However, there is only one drawback - the price. However, the reasons for the higher cost are quite obvious.
We list the main technical parameters prescribed in GOST:
For production, cores with a flexibility class of at least five are used. In accordance with this requirement, the cross-section of the wires used to form the core is selected. For example, 0.21 sq. mm each for a cable with cores of 1.0 sq. mm or 0.26 sq. mm for 2.5 sq. mm. The specific thickness of the insulating layer for an individual core and the entire wire as a whole depends on their cross-section. For cores, the thickness range is 0.6-0.8 mm, for sheath - 0.8-1.2 mm. When choosing this value, you need to focus on the electrical resistance specified in GOST. The operating temperature range of PVA wire is from -35 to +45 degrees. Celsius (for some versions below - from -25 to +40). The maximum permissible value when heating the cable is +70 deg. Celsius, and installation must be carried out at a temperature of at least -20 degrees. Celsius. The polyvinyl chloride shell is flame retardant but may crack when exposed to extreme cold or heat. The service life in accordance with GOST, subject to strict compliance with the conditions, is at least six years. The wire sheath must not have any visible defects, including bulges or dents.
It is important to ensure that there is no free space between the cable cores, and if necessary, use additional materials as filler. In this case, the sheath is removed from the cores easily, without any difficulty.
Application of PVS cable
The positioned purpose of the PVA as a connecting cable is the main one, but not the only one. PVA with sections ranging from 0.75 to 2.5 sq. mm, you can connect household appliances and power plants with current loads from 6 to 20 Amperes. PVA 4 and 6 mm will withstand load currents of 24 and 32 A, respectively.
Related articles: What types of pebbles are used for landscape design?
According to GOST, PVA is used for connection (connection):
- Household electrical appliances;
- Electrical tools for home repairs;
- Electric stove connections;
- Washing machines;
- Refrigerators and air conditioners;
- Garden equipment;
- Manufacturing of extension cords and carriers.
Can be used in lighting.
Basic properties of wire
Next, let's look at the main properties of the PVA cable; after all, for the most part, its installation location and choice depend on them.
According to GOST, the service life of the wire is 6 years. However, as a rule, the service life is significantly longer if the product is not exposed to negative external influences. According to the instructions, the cable sheath is not subject to combustion, however, this does not exclude exposure to high temperatures. Based on the previous point, it is worth saying that the most favorable temperature range for PVA wire is considered to be the border between – 25 and + 40 degrees. At the same time, you should not install the cable at temperatures less than minus 20 degrees and more than plus 70. According to GOST 22483-77, the cores of the PVS cable correspond to class 5
This is worth paying attention to when choosing a section! For example, for a wire whose core has a nominal cross-section of 1.0 mm2, a single wire should be no more than 0.26 mm2.
According to GOST 7399-97, insulation depends on the cross-section of the cores and varies within 0.6-0.8 mm. In this case, the thickness of the shell can vary within 0.8-1.2 millimeters, providing a resistance not lower than that proposed in GOST.
Important! Pay attention to paragraph 4.1.1.6 of GOST 7399-97, according to which there should be no visible dents or bulges on the surface of the PVA cable. At the same time, the wire sheath is made in such a way that there are no voids between the veins. To achieve this, it is permissible to use additional materials
With any approach, separation of the cores from the sheath should occur without difficulty
To achieve this, it is permissible to use additional materials. With any approach, separation of the cores from the sheath should occur without difficulty.
Accepted colors
The above GOST does not impose any special requirements for the coloring of external insulation; 10 color options are allowed: white, black, gray, etc.
As for the color of the core insulation, it must correspond to the table below.
The color chart for insulation is live depending on their purpose and quantity:
| Number of cores | Accepted color standard | |
| there is a grounding conductor | No grounding conductor | |
| 2 | brown, blue | |
| 3 | yellow-green, brown, blue | black, brown and blue |
| 4 | yellow-green, black, brown, blue | blue, black, brown, black or brown |
| 5 | yellow-green, blue, black, brown and black or brown | blue, black, brown, black or brown, black or brown |
The purpose depending on the color of the insulation is shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3. Colors according to GOST for neutral, protective and phase conductors
Please note that sometimes the insulation of the phase conductor is also white, which is acceptable according to the international standard. Having finished with the design features and color designation, let's move on to the description of the main parameters
Having finished with the design features and color designation, let's move on to the description of the main parameters.
Advantages and disadvantages of wire
PVA has the following positive qualities:
- reliable insulation that protects the wire from damage and electric shock;
- good conductivity;
- resistance to corrosive wear;
- a large selection of characteristics, depending on the intended use;
- flexibility, facilitating installation;
- Availability of colors for easy installation.
Disadvantages include its inability to be used outdoors.
Additional designations
The PVS cable may be marked with a number of additional letters and/or numbers indicating individual design features or functional properties. First of all, this is a 3x2.5 format code - a standard designation of the number of cores and their total (since they are multi-wire) cross-section.
Other possible designations:
- T - “tropical” version, increased resistance to humidity.
- Y - increased temperature range (up to –40 degrees).
- L - conductors made of tinned copper.
- A - conductors are made of aluminum, not copper.
- B - presence of armor.
- G - no insulation.
- PS is a shell made of a mixture of polyethylene and polyvinyl chloride.
- PV - shell and mixture of PVC with rubber mass.
Related Posts
- Cable current cross-section
- Pugnp and punp wires: characteristics, differences, prohibition of use
- Pvs cable. pugsp, pugnp: alphanumeric marking and decoding
- Screw wire area of application
- Wire cross-section for home wiring: how to calculate correctly
- Which wire is better: single-core or stranded
- Wiring diagram and installation of electrical wiring in the kitchen
- Repair of electrical equipment on ships - cable termination
- Wire pv-1: description and characteristics
- Technical parameters and scope of application of heat-resistant wire RKGM
- Which cable to choose for installation outdoors (over the air and in the ground)
- How is SIP cable deciphered: its types and features
- What is the difference between a cable and a wire?
- Installation, connection of the rj 45 socket. pinout of the internet socket
- Heating concrete with PNSV wire: goals and technology
- Explanation of markings, areas of application and installation of VVG PNG (a) cable
- Connecting the hob to the electrical network: diagrams, selection of cables, sockets, machines
- Choosing a cable for installing video surveillance systems
- Heat-resistant cable channel for baths
- How to move a socket with your own hands: advice from professionals, a guide to action and 110 photos of transfer options
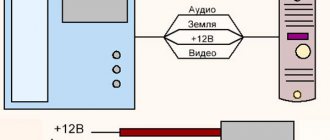
- Video intercom cable
- Decoding the alphanumeric markings of electrical cables and wires
- How to install a socket
- Open wiring: installation, types of fittings
- Copper installation wire pugv (pv-3)
Read with this
- Cable current cross-section
- Pugnp and punp wires: characteristics, differences, prohibition of use
- Pvs cable. pugsp, pugnp: alphanumeric marking and decoding
- Screw wire area of application
- Wire cross-section for home wiring: how to calculate correctly
- Which wire is better: single-core or stranded
- Wiring diagram and installation of electrical wiring in the kitchen
- Repair of electrical equipment on ships - cable termination
- Wire pv-1: description and characteristics
- Technical parameters and scope of application of heat-resistant wire RKGM