Features of SMD LEDs
The main visually noticeable difference between SMD LEDs and conventional ones is the design of their housing:
Conventional with axial leads (left) and SMD LEDs
If a regular diode has leads that are long enough to be mounted through holes in the board, then their SMD analogues have only small contact pads (planar leads) and are mounted directly on the board.
LED mounting in the usual way (left) and surface mounting method
This assembly method is called surface mounting, hence the name of the LEDs: smd (English: Surface Mount Device). This installation is the simplest and can be entrusted to robots.
The assembly of devices using SMD components can be entrusted to a robot
In addition, efficient heat removal from the crystal became possible thanks to the very short but relatively massive pins and the fact that the device practically lies on the board. Indeed, despite their efficiency, super-bright diodes heat up during operation. This design feature made it possible to produce very miniature but powerful SMD LEDs that require good heat dissipation.
Today, the global industry produces many types of SMD LEDs, differing from each other in both dimensions and electrical parameters.
Characteristics of SMD LEDs - DRIVE2
In order not to jump on the internet, I’ll leave this entry here.))) Main characteristics of LEDs
luminous intensity (efficiency) radiation angle, power operating current color (luminescence temperature) LED degradation Indicator LEDs (ILT) (3; 4.8; 5, 8, 10 mm LEDs with lens) SMD (SLT) LEDs (3528, 5050) Powerful (PLT) ) LEDs
RGB LEDs
Efficiency (light output).
Ratio of luminous flux to power consumption (Lm/W). This is the value that first of all comes to the attention of specialists, because it is the efficiency that determines the applicability of LEDs for lighting systems. For comparison: incandescent light bulb: 8-12 lm/W; fluorescent (energy saving) lamps: 30-40 Lm/W modern LEDs: 120-140 Lm/W
gas discharge lamps (DRL): 50-60 Lm/W
The indicators are very good, which allows them to successfully compete with fluorescent, sodium, and halogen lamps. Moreover, LEDs are already superior to gas-discharge lamps in this indicator, because their entire luminous flux goes into one half-plane, so different types of reflectors are not required.
Color temperature23Color temperature of LEDs used: 2500 Kelvin - 9500 Kelvin. -2500-3000 Kelvin: warm white light. (warm white or abbreviated WW) It is closer to incandescent lamps. -4000-5000 Kelvin: neutral white light. (white neutral or abbreviated NW)
-6500-9500 Kelvin: cool white light. (cold white or CW for short)
According to sources of independent research, it is neutral white light that is the most comfortable for office work, and in it objects become clearest. Our company uses LEDs with neutral light. In addition, in lighting devices we use color LEDs (primary colors: red, blue, green, yellow) and RGB LEDs (full-color LED).
LED power.
- low power: up to 0.5 W (20-60 mA) - medium power: 0.5-3 W (100-700 mA)
— high power: more than 3 watts (1000mA or more)
Luminous angle
usually 120-140 degrees, in the indicator 15-45 degrees.
Degradation (resource) of LEDs.
A very important indicator. Many manufacturers declare about 100 thousand hours or even more. What factors influence the lifespan of LEDs? First of all, this is current degradation. If a current greater than that for which it is designed is passed through a diode, then rapid degradation occurs. As a rule: within the first 1000 hours. Unscrupulous manufacturers take advantage of this.
The next factor is temperature degradation. The LED heats up during operation. And, if the heat is not removed, the diode will quickly fade. Many design solutions are used to remove heat. Our luminaires use a board with an aluminum backing.
The substrate, in turn, has mechanical contact with the lamp body, which additionally removes heat. The main thing: at the LED soldering point, maintain a temperature of no more than 65 degrees Celsius. This is achieved in our lamps.
Accordingly, when in operating mode, the service life of the diodes in the proposed luminaires is the declared 40-50 thousand hours.
Indicator LEDs (ILT)
note
Today they are leaders in widespread use. Appearing in the 60s, they quickly gained popularity, displacing incandescent lamps used as lighting and indication.
And the use of crystals with increased brightness in these LEDs allows them to be used in powerful light-emitting devices (lanterns, brake lights, indicator lights, traffic lights, DIP strips, etc.).
Today, almost no household appliance can do without an indicator LED. There are the following standard sizes of indicator LEDs: 3; 5; 4.8; 8 and 10mm.
The operating current of such LEDs is usually 20-40mA; the luminous efficiency for white light can reach 3-5Lm from an LED. The radiation angle of these LEDs is either narrow (15-45 degrees) or wide (110-140 degrees).
SMD surface mounting
Technology for manufacturing electronic products on printed circuit boards, as well as methods for designing printed circuit boards associated with this technology.
Surface mount technology of printed circuit boards is also called TMP (surface mount technology), SMT (surface mount technology) and SMD technology (surface mounted device), and surface mount components are also called chip components.
This technology is the most common method today for designing and assembling electronic components on printed circuit boards.
Its main difference from the “traditional” through-hole mounting technology is that the components are mounted on the surface of a printed circuit board, however, the advantages of surface-mounted printed circuit board technology are manifested due to a set of features of the element base, design methods and technological methods for manufacturing printed circuit assemblies.
The most popular SMD(SLT) LEDs are LED 3528 and 5050.
LED 3528
3528
Main characteristics:
-Operating current 20-25mA -Power 0.07W -Luminous flux 3-7Lm -supply voltage 3-3.2V (for white LED) -colors: all shades of white, red, green, blue, yellow -packing standard - Babina 2000 things.
Use: LED strips, lamps, auto lamps, panels, lamps.
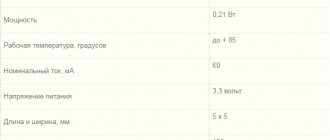
5050 LEDs
5050
The 5050 LEDs use the same type of crystals as the 3528 LED, only in the amount of 3 pieces. And the use of 3 crystals of different colors (red, green and blue) allows you to obtain a low-power RGB LED.
Main characteristics:
-Operating current 60-75mA -Power 0.21W -Luminous flux 10-21Lm -supply voltage 3-3.2V (for white LED) -colors: all shades of white, red, green, blue, yellow, RGB -packing standard – Babina 1000 pieces.
Usage: LED strips, lamps, auto lamps, modules, panels, lamps.
PLT LEDs
For the production of LED equipment, medium and high power LEDs are used. All of them are labeled as PLT LEDs. Comparative characteristics of the LEDs used are presented in the table:
RGB LED
RGB
These are simply three closely spaced LEDs under one lens: red - Red, green - Green and blue - Blue, hence the name. As you know, by combining these three colors you can get any other color.
Typically, these three LEDs have combined positive (with a common anode) or negative (with a common cathode) terminals, respectively, for a total of four RGB terminals, although sometimes it happens that all six terminals are made separately. That is, in fact, RGB control is the control of three LEDs.
The brightness of the LED depends on the current flowing through the LED.
Source: https://www.drive2.ru/b/1516332/
How to decipher the markings
Ultra-bright SMD LEDs are usually labeled with four numbers, and the line of devices produced today looks something like this:
Sizes and appearance of the most popular SMD LEDs
There are, of course, many more types of devices, but these are enough for us to analyze the markings. How to understand this marking and what do the numbers mean? It turns out that there is nothing complicated here: the numbers indicate the horizontal dimensions of the SMD LED housing - length and width in hundredths of a millimeter. For example, the 5050 device has dimensions of 5.0x5.0 mm, and 3528 – 3.5x2.8 mm. The marking does not carry any further information. You can only find out the technical characteristics from the accompanying documentation or take the seller’s word for it.
PHILIPS Lumileds
The most popular of the LEDs from this company - Luxeon Rebel - has the following marking system:
LXML-ABCD-EFGH
- LXML – series designation;
- A – designation of the type of light distribution (P for Lambertian distribution);
- B – color designation (W – white);
- C – shade of white (C – cold, N – neutral, W – warm);
- D – rated current (I for current 350 mA);
- E – the mark is reserved for future versions of this product;
- FGH – luminous flux in lumens.
Thus, white LEDs tested at a current of 350 mA are designated according to the following pattern: LXML-PWxI-0xxx.
Luxeon LEDs of other series have a similar designation system.
This marking, unlike those discussed above, is more informative and allows you to evaluate the general parameters of the LED without even looking at the data sheet.
Brief technical specifications
Although their digital markings do not carry any information about the characteristics of SMD LEDs, there is still some connection between the standard sizes and parameters of the devices. Let's consider the parameters of the most common types of light-emitting SMD semiconductors:
Main technical characteristics of SMD LEDs
| Device type | Case dimensions, mm | Number of crystals | Power, W | Luminous* flux, lm | Operating current, mA | Operating temperature, °C | Solid angle, ° | Glow color |
| 3528 | 3.5x2.8 | 1 or 3 | 0.06 or 0.2 | 0.6 – 5.0* | 20 | -40 … +85 | 120 – 140 | white, neutral, warm, blue, yellow, green, red, RGB |
| 5050 | 5.5x1.6 | 3 or 4 | 0.2 or 0.26 | 2 – 14* | 60 or 80 | -20 … +60 | 120 – 140 | white, warm, blue, yellow, green, red, RGB, RGBW |
| 5630 | 5.6x3.0 | 1 | 0.5 | 57 | 150 | -25 … +85 | 120 | cold, neutral, warm |
| 5730 | 5.7x3.0 | 1 or 2 | 0.5 or 1 | 50 or 158 | 150 or 300 | -40 … +65 | 120 | cold, white, neutral, warm |
| 3014 | 3.0x1.4 | 1 | 0.12 | 9 – 11* | 30 | -40 … +85 | 120 | cold, neutral, warm, blue, yellow, green, red, orange |
| 2835 | 2.8x3.5 | 1 | 0.2 or 0.5 or 1 | 20 or 50 or 100 | 60 or 150 or 300 | -40 … +65 | 120 | cold, neutral, warm |
* – depends on the color of the crystal glow
Now let's look at each of these types in more detail.
Samsung
The LEDs of this electronic giant are indicated by a marking of 18 characters.
Let's decipher this puzzle:
1, 2 – letters SP, meaning “Samsung Package” - this is a constant component of the designation;
3 - LED power: H (high) - high, M (middle) - medium, also in the case of special purposes, there may be other letters in this place (for example, B - for backlight LEDs, F - for camera flashes, etc.) ;
4, 5 – emission color: WH (white) – white;
6 – product version (coded by letter);
7.8 – product designation;
9 – lens type D (dome) – domed;
10 – main parameter, in this case power in watts – 3;
11 – reserved sign, does not mean anything yet – just 0;
12 – color rendering index CRI: 1 – min 68, 3 – min 70, 4 – min 75, 5 – min 80, 7 – min 90;
13,14 – forward voltage drop of the LED, coded by letter and number in accordance with the table below.
An explanation is required here: group E3 includes bins E1, F1, G1, i.e. if the LED is labeled E3, then the voltage drop across it can vary from 2.7 to 3 V. Group E6 already includes the entire range (6 first-order subgroups) from 2.7 to 3.3 V.
15, 16 – correlated light temperature CCT, coded according to the table below.
17,18 – the last two characters determine the nominal luminous flux.
As with voltage drop, there are sets that include multiple bins.
smd 3528
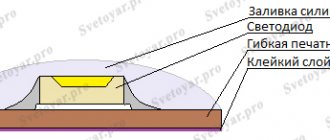
This type of smd LED can be single-chip (white, neutral, warm, blue, yellow, green, red) or three-chip (RGB). In the first case, the device has two terminals for connection, in the second - four: one common (cathodes) and three anodes. To protect them from the environment, the crystals are filled with a transparent compound or a compound with the addition of a phosphor that evens out the color characteristics of the diode.
Appearance of single- and triple-chip LED 3528
As can be seen from the plate, this type of LED has a relatively low luminous flux. But thanks to its small size, moderate cost and ability to illuminate in different colors, including RGB, it has still found wide application in inexpensive lighting and decorative lighting devices.
Very often, 3528 LEDs are included in LCD backlight strips. This strip with SMD LEDs is most often used for decorative purposes.
Car lamps and LED strip assembled on 3528
If you want to learn even more about SMD LEDs 3528, then read our review of it.
LED markings
There are fewer difficulties in identifying LEDs. Each type has characteristic external distinctive features. There are two categories:
- SMD LED color. In turn, they are divided into groups according to radiation: multi-color diodes, neutral, warm and cold white.
- Element size. By analogy with foreign coding, 4 digits are used, which indicate the size in millimeters. 3014 – size 3 x 1.4 mm.
The number in front of the LED type means the quantity per 1 meter of strip. For devices with long leads enclosed in a plastic or glass case, a system of color elements is used, which can be found in the table.
Example of LED color coding
smd 5050
Unlike the 3528, the 5050 is exclusively a three-chip or quad-chip (RGBW) design. If the device is single-color, then all three crystals have the same or close (to equalize the color characteristics) color of light emission. This means that the 5050 diode has three times the brightness of its single-chip counterpart, the smd 3528. As in the first case, the crystals are protected by a compound with or without a phosphor.
Tri-chip LED 5050
This is perhaps the most popular device used for decorative lighting and illumination. It has an optimal cost/power ratio and can provide any backlight color (if using rgb5050), including high-brightness white (four-crystal version), by simply changing the power on each of the crystals.
Most often, such LEDs are built into LED decorative strips such as:
- single-channel, where three crystals are connected in parallel and powered by the same voltage;
- RGB and RGBW, having three and four channels respectively.
Thanks to the sufficiently high power of the diodes, even at their density of 60 pcs. per 1 meter of LED strip it can be successfully used not only for decorative lighting, but also for interior lighting. At the same time, the user can change the color temperature and even the color of the lighting independently; to do this, it is enough to install the appropriate controller.
LED strips 5050 single color (left), RGB and RGBW
Marking of domestic diodes
Russian-made diodes were marked in their own way in different periods. The standard was constantly changing; three versions were developed before the modern system was approved. Low and high power diodes were labeled differently. Combinations of letters and numbers correspond to color symbols, according to the table.
Marking of Russian diodes
Old notation system
What is a diode - operating principle and design
The least informative, from the point of view of the modern variety of diodes, marking was used until 1964. It included only three elements:
- letter “D” – semiconductor diode;
- a number indicating the design features of the diode and its purpose;
- letter identifying the variety (if any).
All useful information was encoded in the second part - the serial number. For example, a number up to 200 meant that the diode was a point diode, from 200 to 400 - a planar diode; Zener diodes were assigned a value from 801 to 900 and so on. It was difficult to navigate such a system.
In 1964, the system was improved. At the beginning of the code, an indication of the material of manufacture was placed: 1, 2, 3 or G, K, A - for germanium, silicon and gallium arsenide, respectively. The next letter indicated the type of device:
- varicap – B;
- Zener diode - C;
- diodes with high operating frequencies - A;
- rectifiers and diode bridges - D.
Then came the serial number, but it already belonged to a specific subclass. This made it possible to divide, for example, a tunnel diode into several groups: generator (up to 299), switching (up to 399) and reverse (up to 499). At the same time, for zener diodes the number indicated the stabilization voltage. For example, 1C273 can be deciphered as follows:
- 1 – germanium;
- C – zener diode;
- 273 – low power, stabilization voltage – 73 V.
At the end there could be a letter indicating the type of device, as in the first version. This marking was more convenient, but technological progress and the emergence of new types of diodes required further refinement.
New notation system
For modern models of domestic diodes, a new marking principle is used, based on several industry standards. The designation of the semiconductor material and diode category remained unchanged. The changes affected the three-digit number that determines the operating principle.
It cannot be considered separately, since each type of diode requires a special division according to technical parameters. For example:
- pulse diodes - the first digit indicates the recovery time (from less than 1 ns to 500 or more);
- rectifiers – average value of forward current;
- Zener diodes - different power (from 1 to 3 - less than 0.3 W, from 4 to 6 - up to 5 W) and stabilization voltage (less than 10 V, up to 100, more than 100).
The following numbers, unlike the old system, indicate the development number - the characteristics of a particular diode are not included in them. If there is a further division within the diode class, the corresponding letter appears after the number.
Important! Depending on the purpose of the diode, the marking may contain additional elements, for example, a number on a packaged device that determines the design features.
smd 5630 and 5730
The smd 5630 is a single-chip powerful device (see table above) capable of creating a luminous flux of up to 57 lumens. Thanks to the built-in protection assembled on two stabistors, the device is able to withstand pulse current up to 400 mA and polarity reversal. The LED has 4 pins, but only two are involved in the operation of the crystal. The remaining two and the metal substrate are used for better heat dissipation. The LED glow color is white with different color temperatures.
Appearance and internal circuit of the 5630 LED
5730 devices can be either single or dual chip. The former have characteristics similar to the 5630, the latter are twice as powerful (1 W) and are able to create a luminous flux of up to 158 lm.
Appearance of LED 5730
Both types of devices emit white light of different color temperatures and can be used to make powerful LED strips, lamps, and spotlights.
Car lamp at 5630 and a hundred-watt spotlight at 5730
You can find more detailed information on smd 5630 devices here, and on smd 5730 here.
CREE
Powerful lighting LEDs have the following marking system:
SSSCCC-BD-0000-NNNNN
- the first three letters indicate the LED series, such as XPG for the XP-G series;
- then come three letters of color designation, encoded using the English abbreviations of the corresponding colors: WHT - white;
- HEW – high efficiency white;
- BWT – second generation white (we are talking about the second generation of white LEDs, for example, if the XP-G series was designated XPGWHT..., then the XP-G2 series will be designated XPGBWT...);
- ROY – royal (bright) blue;
- BLU – blue;
- GRN – green;
- AMB – orange;
- RED – red, etc.
- 01 – white for outdoor lighting;
An example of the designation of an XP-E2 series LED with a color rendering index of at least 80, a color temperature of 4300 K, and a luminous flux of at least 87.4 lm at a current of 350 mA: XPEBWT-H1-0000-00AE7.
smd 3014
A single-chip compact device of moderate (0.12 W) power and a luminous flux of up to 11 lm. Depending on the version, it can emit white light of different color temperatures, as well as blue, yellow, green, red and orange. To protect from the environment and correct color temperature, the crystal is coated with a compound containing a phosphor.
LED smd 3014
The main area of application of smd 3014: LED strips and modules for decorative lighting, spotlights and lamps for them. Often used to make car lamps.
Car lamp, table and recessed lamps, strip based on SMD 3014 diodes
If you are interested in type 3014 LEDs, you can read more about them in this article.
SMD 5630 LED: technical specifications and reviews
Technologies January 22, 2018
Since the advent of the first LEDs, they have been actively used in various spheres of human life. These include flashlights, household lighting, and, of course, TV screens and various gadgets that have a screen or display area. This article will focus on the SMD 5630 LED.
A little history
Emissions from a solid-state diode were first noticed in 1907 by Henry Round. He discovered that when current passes through metal and silicon carbide, electroluminescence is observed. And then the Russian scientist Losev noticed similar phenomena.
Who even published his discovery, but due to the fact that the science of that time did not allow a complete explanation for the phenomenon, it went virtually unnoticed.
smd 2835
High power single-chip LED. Available in three versions: 0.2, 0.5 and 1 W. It emits white light of different color temperatures, the body size is the same as the 3528 device, but differs from the latter in the rectangular lens (the 3528 has a round lens).
smd 2835 (left) and smd 3528
Due to the high popularity of devices, a lot of fakes are produced, in which crystals of lower power are installed. So, although the Chinese smd 2835 is officially produced, it is equipped with a crystal of only 0.09 W. Externally, it can be impossible to distinguish it from a one-watt one due to the phosphor added to the compound, since it is opaque, and accordingly, it will not be possible to estimate the dimensions of the crystal by eye.
The device is used in powerful lighting lamps, household and street lamps, spotlights, and LED strips.
Light bulb, lamps and tape on SMD 2835
If you are interested in the smd 2835 LED, you can get more detailed information from this article.
Differences between SMD 5050, 2835 and 3528
| Appearance of matrices | |||
| SMD 5050 | SMD 5630 | SMD 3528 | SMD 2835 |
2835 is a compact version of the 5050, which is used to create high-brightness sources. The only difference between the 2835 and 5050 LEDs is the size of the light-emitting layer and the heat sink area; the 2835 has a larger one. 3528 and 2835 diodes are often confused. Despite the same dimensions, these are different classes of products.
High-brightness LED strips have found application in advertising to create luminous structures when high brightness is required with minimal dimensions.
This type is not suitable for household lighting. The smaller size of the light emitter gives a narrower beam, which will result in differences in illumination zones, which is not observed with diodes with standard size 5050.
Please rate the article. We tried our best:)
Did you like the article? Tell us about her! You will help us a lot :)
Application
It is easier to list those areas of our life where there are no SMD LEDs than those where they are used. White diodes can be found:
- in tactical and pocket flashlights;
- in car lamps;
- in household light bulbs of various wattages;
- in decorative indoor and outdoor lighting.
Multi-colored RGB and RGBW are used no less widely:
- in signs, road signs, traffic lights, signs, advertising;
- in lighting lamps with variable color temperature;
- in landscape design;
- in decorative indoor and outdoor lighting;
- in display devices.
Examples of using SMD LEDs
That's all about SMD LEDs in a nutshell. Now you know why they are called that, what they are and where they are used.