Receiving and sending information in wireless communication lines
In a radio channel, useful information travels from the transmitter to the receiver in the form of electromagnetic waves. In this case, the main parameters of the signal, on which the quality of communication directly depends, will be:
- power;
- frequency (closely related to channel capacity);
- type of modulation used.
In order to ensure good communication quality, it is not enough to simply increase the value of one or all of the above indicators. This is due to the fact that there are certain standards for electromagnetic safety. Therefore, to increase the speed of transmission of data packets within a wireless communication line, various optimizing approaches are used. One of them is a technology that uses a MIMO 3G/4G LTE antenna with resonators that have a low correlation coefficient with each other.
Important! Correlation in its simplest sense is the degree of connection between two quantities under consideration. For example, the amplitude of a local radio signal will correlate with the amount of moisture in the air along its path, but not with the water level in the ocean.
Passing through space, an electromagnetic wave will certainly encounter obstacles made of various materials along its path, experiencing partial or complete reflection and absorption. In this case, the following effects begin to be observed in the channel:
- Intersymbol interference is the superposition of one or more symbols on each other due to multipath signal propagation.
- Frequency selectivity. In the simplest case, the selectivity of the receiver at a given frequency (frequencies).
Thanks to modern and efficient signal processing methods embedded in the mathematical model, using MIMO technology, you can easily separate useful information from emerging artifacts (including noise).
MIMO technology
As mentioned above, the main issues when receiving and transmitting data via a radio channel are ensuring noise immunity and high quality of final processing. To do this, cellular operators use technology in which it is believed that the 4G LTE MIMO antenna is the best available implementation (Multiple Input Multiple Output). Its essence lies in the fact that the exchange of information in the form of electromagnetic waves is carried out not by one pair of transceivers, but by a whole set. In this case, it is important to ensure a low correlation coefficient between them, as well as double (so-called 2x2) polarization.
Healthy! In the simplest case, wave polarization is a characteristic that describes the behavior of the amplitude vector (including its direction); it can be longitudinal, transverse or circular.
From a mathematical point of view, the essence of 4G MIMO technology can be revealed as follows. Let there be N transmitting and M receiving antenna devices, then the properties of each channel (dependence on the features of multipath signal propagation) can be described by specifying a non-stationary (time-varying) complex coefficient hnm, which, when combined, form the so-called channel matrix H. Then, if you have a wave vector of useful data s and wave vector of noise n, then the direction from which the received signal r came can be expressed through the simple formula r = H*s + n.
Healthy! Wave vector is a quantity that determines the direction of wave propagation.
How to properly configure a 3G antenna for a base station?
Posted by DeePole | Reviews (0) | Trackbacks (68)
A lot of people write to me about setting up a 3G antenna from start to full installation. I finally found some time to write an article answering this burning question.
The very beginning:
So, you have a 3G modem, a 3G antenna with cable and an antenna adapter for the 3G modem. I would like to immediately clarify the fact that here I will not describe how to solder a connector for an external antenna into a modem, assemble adapters, and so on. Let's agree that you already have a ready-made installation kit on hand, you already know how to connect the antenna to the modem and all you have to do is configure it to the base station for stable reception.
Preparation:
1) Signal. First, you need to decide on the signal level. Very often, people's reception quality fluctuates greatly, however, many note that a more or less stable signal can be caught on the second floor of the house or on the roof. If you were able to do this, then most likely, by installing the antenna correctly, you will get stable and high-quality reception that can ensure normal and reliable operation of the Internet.
2) Cable. The cable must be at least good , with a braiding density of at least 60%. Ideally, it should be high-frequency with a resistance of 50 ohms, but we assembled cable-antenna paths and on a good RG6 cable with a resistance of 75 ohms, it also worked great, although the SWR was a little higher, but overall it worked great. From me personally, a very good RG6 cable is better than a scorched high-frequency one. And, I want to note, high-frequency will always be more expensive, even the most scorched one.
3) Cable length. It should be as short as possible, especially if you have a very weak reception. I advise people to use a cable no longer than 7 meters, and if you have 3 or 4 meters, then that is ideal. Never twist excess cable, as we like to do behind TVs or with an Internet cable. Law! If there is an extra cable, cut it off! There are always losses on the cable, so you need to get rid of the extra length. Use WiFi routers to avoid running wires all the way to the computer on the ground floor. The most ideal option is to install the router right in the place where the cable entered the house, and the rest of the space will be filled with a WiFi signal.
4) Installation height. Here, as in all antenna matters, the rule applies - the higher you raise the antenna, the more confident the reception. Remember this. Use sticks, pipes, masts, brackets to raise at least the ridge of the house.
Installation:
To install the antenna correctly, you need to determine which side the signal is coming from. Most likely the signal comes from the nearest populated area. It is in populated areas that the base stations of cellular operators are located. However, there are exceptions. Sometimes these towers are installed in fields to fill gaps in signal coverage. In any case, we will need special software to navigate not by the “sticks” in the modem program, but by normal values.
This instruction will only suit you if your modem is a Huawei brand! Typically, such modems are sold in Russia by Megafon and MTS. Turn your modem over and read the name. It should say something like “Huawei Technologies CO. LTD.”, as well as a model, for example E392, E352 or E173, or others. A lot of them.
If you have a Huawei modem, then let's get started. We do everything in the following sequence:
1) Download the MDMA program (link)
2) Download the plugin for MDMA from Entropiy (link). The plugin can determine the approximate position of the base station and can pronounce the signal level by voice, which is very convenient if you are setting up the antenna alone. We install it immediately after downloading.
3) Turn off the modem’s native program with the operator’s logo. Turn it off completely. Otherwise, it will occupy the port and MDMA will not be able to communicate with the modem.
Now everything is ready to start setting up. We have the modem connected, the wire and antenna are ready and connected to the modem.
Now we launch the MDMA program. At the very bottom of the program there will be an inscription - “Detecting mobile data device”, then “Initializing mobile data device”, and if everything goes well and the program was able to connect to the modem - “Ready”.
Sometimes the program does not work immediately with some modems, for example with Huawei E392 (which has 4G). As practice has shown, MDMA simply does not see the port on which the modem is installed, however, there is a command with which you can force the port to be specified. To do this, you will need to determine which port the modem is on. This can be done through the Windows Device Manager. Go to Device Manager, find the “Modems” section there, select it and find your Huawei there, double-click on it and a window with information about the device will open. In the “Modem” tab you can see the port on which the modem is installed; for me it is COM11.
So, we have identified the port, now we need to force the MDMA program to see the modem on it. This is done as follows:
1) Close the working version of the MDMA program and copy the MDMA.exe file to the root of drive C.
2) Call the command line CMD.EXE (Start-Run) or in later versions of Windows just type cmd.exe in the search and run it. A black window with a command line opens.
3) Enter the following into the command line: C:\mdma.exe /port:COM11 (For me this is COM11, for you it is the one on which the modem hangs) and execute the command.
Let's look at the interface:
At the very top of the program you can see the signal level bar. The signal level in decibels (RSSI) is visible above the bar. Please note that this figure tends to zero, that is, the value -97 is better than -105, for example. Next, we are interested in the “Connection type” parameter, which characterizes your Internet connection. The parameter could be:
a) 3G only - this means that the modem will not look for any other network other than 3G
b) GPRS/EDGE only - this means that the modem will not look for any other network, but will always connect to a slow GSM connection
c) 3G Prefered - this parameter says that even if the 3G signal is almost zero, and slow GSM is a hundred times more confident, the modem will try to connect to 3G, despite the fact that there is almost no signal.
d) GPRS/EDGE Prefered - this parameter exactly the opposite repeats point “c”
In our case, we are hunting for a 3G signal, so I advise you to set the “3G only” parameter.
After selecting this parameter, you should evaluate the quality of reception; if everything is good, then even on the ground, with a connected antenna, we should get several decibels of reception. If this does not happen, then you should climb a little higher and slowly rotate the antenna from side to side.
As soon as some signal is caught, a second program comes to our aid - a plugin for MDMA. Let's launch it and get acquainted with the interface.
So, the signal level received from MDMA is completely duplicated here. If there is at least weak reception, then having a spare Internet connection, you can press the “MAP” button, a browser with Yandex.Maps will open, on which the location of the tower will be marked with a dot. If you do not have the opportunity to access the Internet, then I advise you to activate the option - “Level AS VOICE”. After checking this option, turn on the sound - the program will speak out the current signal level. Remember - the lower the number, the better the signal. However, all values above 100 are pronounced by the program as “ten”. Remember that “ten” is a hundred or worse.
The next step is not tricky. We climb onto the roof or raise the antenna higher or onto a bracket, the program works at this time and dictates the signal level to you. Be careful with the wire - careless movements can break the modem connector or render the antenna adapter unusable.
Setting:
The setting takes place on site, that is, at a high point. You are required to carefully and little by little rotate the antenna on the bracket, about 10-15 degrees at intervals of 3-4 seconds, and listen to the voice telling you the signal level. Start tuning by pointing the antenna towards a populated area, however, try other directions. It should be remembered that a directional antenna, like a flashlight, “shines” only in front of itself, so it won’t catch anything with its back.
Attention! When setting up an antenna, it is worth remembering the fact that 3G operates at a high frequency of 2100 MHZ. Such waves do not have such high penetrating power as, for example, GSM 900 or CDMA 450. They are not able to “pierce” dense objects, especially metal barriers. Metal in the receiving path of your antenna is death to reception. Try to keep as few objects as possible between your antenna and the base station, including the roof of your house. Aim for line of sight to the base station. If there are massive trees on the way, then try to catch the direction between the branches, or, if possible, even cut out some of the branches that clearly interfere with the signal. The swaying of the leaves will have a very negative effect on reception. And wet leaves reflect the signal very strongly, which will certainly lead to instability of the entire antenna path. It is advisable that your trees start no closer than 100-200 meters from the antenna, and preferably from 500 meters. Single trees are not as dangerous as massive stands.
The minimum, almost zero signal is at -113 dB. Ideally, your signal level should be from -65 to -90 dB . In this case, you have a good margin for weather conditions. However, I used it normally even at -99, but in the rain the connection was no longer so “vigorous”.
Having established the best position of the antenna according to the program readings, secure it and go down. Further, returning to the beginning of the article, if you have a lot of excess cable left and you have the opportunity to shorten it, then shorten it. The only contraindication is twisting and electrical tape. If you haven’t come up with anything other than this method and you don’t have a soldering iron at hand, then it’s better to leave the cable unchanged.
Next, you either plug it into your router and get stable Internet via WI-FI, or use a modem in one fixed location as long as the cable lasts.
If the modem remains in your computer, then disable the MDMA program, disable the voice plugin and run the native program from the modem. Where you will already see the “sticks” that are familiar to you and, most likely, there will be 5 of them already at a signal of -90 dB. Operators consider this a chic technique. Using your native program, access the Internet. This can be done, of course, in other ways, but this is the most correct and one hundred percent!
Well, I hope my article will help you save your nerves and money on installation, and of course get stable Internet, wherever you are.
If you still have questions, you can ask them in the comments, and together with you we will update the article to a more informative state.
Did you like the article? You can leave a review or subscribe to RSS to automatically receive information about new articles.
Tags: , antennas, instructions, Internet, Mobile Internet, modems, setup, programs Headings: 3G and 4G technologies, Questions and Answers from DeePole
Trackbacks and pings
There are no trackbacks/pings yet.
Reviews
I have an E392 modem. When mdma.exe is launched, the date counter field remains empty, and it is impossible to set the connection type. When you click the Conect button, you receive an error 623: The system cannot find a phone book entry for this connection. What is the reason, what is wrong???? Otherwise everything is OK. Thanks for the program.
Review from Peter 07/21/2015 at 17:37
from my own experience: the height of the antenna does not always play a role, in the rain the signal may be better, MDMA is not a very good program, an expert is better.
Review by Anonymous 08/01/2015 at 16:04
Hello! My MDMA does not display the parameters “connection tipe” “Unknown”, etc. It shows the decibels, the operator shows that I’m doing something wrong?
Review from Yuri 08/22/2015 at 10:38
The article is fresh from 2009. The MDMA program does not work with ANY modern 3g/4g modem. So don't even load it.
Review from Alexander 09/11/2015 at 18:39
This entire site and “project” is rotten, old, useless junk.
Review from Alexander 09/11/2015 at 18:42
Thank you!!!
Review from Egor 09/14/2015 at 02:25
How to set up a 3g antenna with a Huawey EC 5321 u-2 WiFi router, which program to use because the Huawey EC 5321 u-2 WiFi router has a built-in modem and USB for powering the router.
Review from Alexander 10/28/2015 at 1:41 pm
After the command line it gives the error {an error occurred while initializing the mobile data transfer device}PANTECH UM175AL Intertelecom.
Review from Vladimir Grigorievich 11/15/2015 at 19:21
MDMA does not detect the router, mobile data service detection writes))) question: what does point 3 in the Installation chapter mean - turn off the native program with the operator’s logo?
Review by Anonymous 11/25/2015 at 5:26 pm
Thank you very much, everything is very clear and visual, it helped me a lot
Review by Anonymous 01/03/2016 at 23:30
Thanks for the consistent clear instructions
Review from Nikolay 01/30/2016 at 16:53
Good article on antenna setup https://aizone.com.ua/blog/nastrojka-cdma-antenny/
Review from Evgeniy 02/04/2016 at 16:07
Good afternoon! I ask you to tell me how to determine COM for a connected Novatel Wi-Fi router with an interface for an external antenna or something else. I looked at your instructions for the modem, but it’s clear for the router. Thank you in advance. Christ is Risen!
Review from Nikolay 05/01/2016 at 10:55
What kind of operators think that a -90 signal is very good? Let them spit in the eyes of such operators, let them use the Internet at minus 90.....
A normal network is somewhere around -40, and the Internet speed will be MUCH MORE FUN. BUT few have such opportunities...no knowledge, no money.....
Review from sailor 06/06/2017 at 19:34
I found instructions on the Internet for setting up antennas for 3g-4g Internet, in my opinion it’s clear and intelligible, everything is explained in pictures
Review from Evgeny 07/12/2017 at 19:01
I have a mobile 3G/4G WiFi router ZTE MF93D, it is unlocked, it works with all operators, I can’t set up the antenna, the mdma program does not see the modem, the modem is not recognized as a modem in the device manager. USB connection only: Port_#0001.Hub_#0003.
Review from Mikhail 01/21/2018 at 07:39 pm
Author, please delete this program, it's not working.
Review from Eduard 04/28/2018 at 00:42
Hello! My modem: HUAWET Mobile Broadband E171. I read this article, I hope it will help in installing and configuring the Internet in rural areas. Best regards, Vasily.
Review from Vasily 03/10/2019 at 14:18
your feedback
Paragraphing is automatic, email address will never be published, valid HTML:
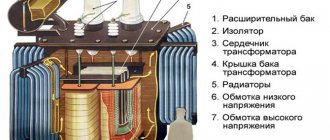
Operating principle of MIMO 3G/4G antennas
How to make a 4G feed for a satellite dish with your own hands
In most cases, since a 2x2 design is preferred, a 4G MIMO antenna is simply two stripline resonators. Their only feature is their location relative to each other; it is designed in such a way that using orthogonal polarization (in the vertical plane the displacement is 45 degrees, and the angle between the antenna planes is 90 degrees) to separate the channels. Thus, when receiving two signals, the difference in their gains will be up to 20 dB.
How 4G works
The new 4G technology, with which modems operate, is an excellent tool for providing high-speed network access. Also, devices with a network with similar coverage will be able to work perfectly even in the absence of an LTE signal. For this reason, your device can pick up an available network in a second, regardless of its generation. For its operation, LTE uses a base of IP technologies. The main distinguishing feature from its predecessor is the increased data transfer speed. In theory, this technology can operate at a speed of 326 MB per second during download, and can send data at a speed of 172 MB per second.
Correctly setting up a 4G antenna will provide a high-quality and productive signal. By itself, it acts as a powerful amplifier, with which you can amplify and stabilize a fuzzy signal, and it can also be received in regions that are located at a great distance from the base communication tower.
Design features of MIMO antennas
Antenna for a computer to strengthen the Wi-Fi signal
In addition to the rather complex theoretical part regarding the operating principle of MIMO technology, the antennas used in it also have some design features that are of great importance during proper installation:
- Antenna type. If we talk about the 3G/4G signal, such a device will definitely be a street type; it should be installed at the optimal point in space, directed towards the nearest cell tower and with a minimum of obstacles in the path of the electromagnetic wave.
- Mounting type. The basis for the installation should be a mast, fixed by means of its own foundation (up to 4 meters in height) and guy wires (cable from 4 mm) or on a building (roof, facade). The bracket itself, to which the antenna device is directly mounted, must have three degrees of freedom (in other words, rotate in three planes: X, Y and Z), which will allow you to adjust the polarization.
- Weather resistance. The antenna must be reliably protected from precipitation; this is achieved by placing it in a plastic case, and in some cases by applying a layer of varnish or paint (PF type) to the metal parts. Also, connections (connectors) with a coaxial cable are coated with sealants.
Important! Additional sealing is necessary even for purchased devices; it would be a good idea to place a hydrophilic substance (silica gel sorbent in bags) in the housing and replace it periodically.
- Lightning protection measures. Of course, commercial antennas provide such a function; it is provided by short-circuiting the DC outputs. However, if the device is installed by mounting it on a mast, then a lightning strike can simply evaporate the entire structure, so in this case it is advisable to have a lightning rod.
- Additional details. During installation, additional materials may be required, such as coaxial cable (usually with a characteristic impedance of 50 Ohms), connectors and adapters.
Characteristics of external antennas
Antennas operating in MIMO technology are manufactured in several modifications. Their common difference is the place where the device is used:
Based on antenna design, they are divided into:
- to circular ones;
- to universal ones;
- to omnidirectional;
- for panel ones;
- to multistandard;
- to directed;
- to sectoral, etc.
These include:
- Operating frequency range (measured in megahertz and denoted mHz). This is a definition of the antenna bandwidth requirements, for example 1700-2700 MHz.
- Gain. For example, MIMO 2×2 panel antennas are available with a gain of 15-17.5 dBi.
- Input impedance. This is the ratio of the direction at the terminals to the electricity at the feeder input. The value of this resistance must be known, since it is necessary to correctly connect the antenna and cable. The antenna input impedance has active and reactive parts.
- Data transmission standard, for example 2G (EDGE, GPRS at GSM1800 frequencies), 3G (UMTS 2100), 4G (WIMAX, LTE1800, LTE2600), WI-FI (IEEE 802.11b, g, n), LTE800, UMTS900, GSM900, etc. .
Panel antenna
Equipment for strengthening cellular and Internet signals
Today, this type of antenna is most widespread in the commercial niche (it is believed that this 4G panel antenna is one of the best) and is used by all cellular operators to achieve optimal coverage in the required area. Structurally, such devices consist of two matrices of dipoles (in common parlance - “patches”), which are arranged in vertical rows and spaced apart by placing them in different housings (in the custom version of the receiving equipment, often in one housing with four patches for each segment).
The connection is made using different connectors to two different feeders, respectively, to two independent inputs of the emitter/receiver. In accordance with the theoretical part outlined above, the relative position of the planes of stripline resonators can be set either 45 degrees with respect to the vertical vector, or orthogonal to each other.
Selecting a device to configure a 4G antenna
If a modem with built-in WiFi is used for setup, we recommend using a Powerbank. This approach to business will allow you to not be tied to an outlet. Our many years of experience and field conditions have shown a device that has proven itself well. Many of our technicians use a Huawei E8372 modem to set up a 4G antenna. It’s another matter when you don’t have such a modem at hand, in which case we’ll consider a couple more options. The ready-made kits presented in our catalog include a combination of Huawei E3372 and Zyxel KN-1210 4G router. Both devices are presented in the mid-range price range. However, in terms of functionality and quality they can compete with professional equipment. This fact has been confirmed and tested by time. With such advantages, both devices are reasonably priced, which makes them more than attractive.
Application of panel antennas for operation in 4G networks
Today the market offers many antennas, the design of which varies significantly depending on parameters such as radiation pattern and operating frequency range. Regarding the first: the opening angle of the main lobe varies from 30 to 90 degrees, for cellular antennas - usually from 60 to 75 degrees. The tilt angle also contributes to the directivity, which can be either mechanically adjustable (vertical plane) or stationary, set by the manufacturer (horizontal plane).
The second parameter just determines the frequency selectivity of the antenna (as mentioned earlier) and for 4G networks the range can be very different (from 800 MHz and above), some cell towers operate at several values at once, for example, for LTE it can be 700 MHz lines , 800 MHz, 2600 MHz. If 3G is required, the 2100 MHz band is additionally used. Naturally, this requires separation both in the planes of polarization and spatial, as well as different directions. This will inevitably lead to a huge variety of devices, which can be observed on the market.
How to Install a MIMO Antenna
To improve communications outside the city, you don’t need to wait for the arrival of 4 G communications in the countryside, let alone the speed of 5 G (the practical universal implementation of which is still very far away). Service specialists will select an antenna with support for MIMO 2×2 as part of the wireless data transmission system equipment. The system will support all existing and implemented standards for the people:
Such equipment is an excellent option for installing a communication system “reception point – output point”, “reception point – many output points”. A 3G, 4G antenna that supports MIMO technology is usually equipped with a plastic housing that protects it from precipitation and UV rays. It can be mounted on a vertical surface and the angle of inclination can be adjusted, which is especially important when you need to “catch” a signal in the country.
Contact Lan Center! We have adopted the latest technologies so that communication outside the city and in the country will be a joy for you.
Source
Installing antennas for a modem yourself
After the choice has been made, and the antenna has been purchased, and additional connectors have been purchased, it must be installed. It is strongly recommended that before carrying out work, make at least a rough sketch (preferably a drawing to scale), which will indicate the lines of the coaxial cable, its length, calculate signal losses, and show the locations of nearby towers and possible obstacles. The search for cellular emitters and their characteristics can be done using special mobile applications, and OpenStreetMap (https://openstreetmap.ru) can be used as a basis for maps. After this, you need to collect the necessary tools, materials and carry out installation:
- Tools and materials. Depending on the type of installation, you may need: crushed stone, sand, cement mixture, anchors, cables, turnbuckles, screws, dowels, metal corners, sealants, weather-resistant paint. To work, you need pliers, a hammer drill, a screwdriver with a set of bits and drills, a multimeter, a hammer, a shovel, a stepladder, and buckets.
- The basis. If the installation is carried out on a mast, first of all you need to determine the place where it will be mounted. After this, a hole is dug, the bottom of which is filled with a small amount of sand. If the location for placing the antenna is the façade of a building or the roof, the bracket is simply attached using anchors or self-tapping screws.
- Installation of the mast. It is very important to remember that the mast is installed only when all the equipment is mounted on it. To do this, an antenna is attached to the upper end, in accordance with the instructions, on a bracket, feeders are connected, and the connections are sealed. Cables (usually 3 pieces) of the required length and with turnbuckles at the other end are attached to the rings. After this, the mast is raised and placed in the pit with the lower ring base, filled with medium crushed stone up to half the height of the walls. After this, without pouring the foundation, proceed to setting up the antenna.
- Setup. This stage involves (regardless of the type of installation) turning the resonators in the desired direction (according to the drawing) and monitoring the quality of communication. After this, you can move on to the final stage.
- Final activities. Once the antenna is positioned in the desired direction, all accessible screw connections are tightened with locknuts. The foundation of the mast is poured with a cement mixture, the cables are strengthened in the ground using pins (you can also strengthen them with crushed stone and cement backfill/pouring), tension is carried out by rotating the turnbuckles. Coaxial cables are installed on an overhead communication line, or secured with clamps along the wall.
Important! There is also a method of indirectly attaching the antenna to the facade of the building, namely by installing a short mast.
It is used when the device needs to be moved higher, for example, above the ridge of a roof truss. In this case, equipment is also mounted on the mast, and it is fastened to the wall with clamps.
How to make a 4g lte MIMO antenna with your own hands
Existing mobile networks are used for more than just making calls and sending messages. Thanks to the digital transmission method, data transmission is also possible using existing networks. These technologies, depending on the level of development, are designated 3G and 4G. 4G technology is supported by the LTE standard. The data transfer speed depends on some network features (determined by the operator), theoretically reaching up to 2 Mb/s for a 3G network and up to 1 Gb/s for a 4G network. All of these technologies work more efficiently if there is a strong and stable signal. For these purposes, most modems provide for connecting external antennas.
3G antenna type “wave channel”
How to make an antenna yourself
So, antenna arrays allow you to receive and amplify the signal to the desired value. They are divided into three types:
- narrowly targeted, receiving radio waves of a clearly defined direction;
- sectoral, the radiation pattern of which can highlight a specific reception area;
- omnidirectional, having a circular radiation pattern.
The latter are the easiest to manufacture and, in fact, all other antennas are their advanced modifications. There are many options for devices for self-production; several proven types that have proven themselves will be discussed here.
Simple sector antenna
In the store you can find a device that is a focusing reflector, on the rod of which you need to install a modem. Typically, such models are expensive, and making them yourself is not the most difficult task. The best material for the reflector will be a cover from an old PC case; the only tools you will need are a marker (pencil), metal scissors, a file and sandpaper. The procedure is as follows:
- transfer the drawing of the antenna parts onto a sheet of iron;
- cut out, process all sharp edges with a file and sandpaper, preferably paint over it;
- form the antenna along the fold line, insert the 4G modem into the rod and connect it to the router or computer via a USB cable;
- Screw the antenna assembly onto something heavy with its base for stability.
By the way, if you need to perform a temporary (indoor) option, you can use any available material, starting from foil cardboard.
Panel antenna
To make such an outdoor 4G MIMO antenna, you will need the following set of materials:
- sheet iron (galvanized), the size of the main panel is 33.4 cm by 29 cm (1 piece), and the dipoles are 11.8 cm by 7.05 cm (4 pieces);
- copper wire with a diameter of 2 mm;
- some copper foil for a connecting element in the form of a circle with a diameter of 2.1 cm;
- dielectric for spacers under dipole plates (foam plastic is suitable), glue for it.
Attention! Remember that dipole plates are the same thing as patches!
First of all, you need to collect the patches into a segment. To do this, you need to take a sheet of paper the size of the antenna reflector, lay out the patches on it according to the drawing and solder them together on a copper connector.
It is necessary to drill a hole in the main reflector plate for a coaxial cable (characteristic impedance 50 Ohms). Glue the dielectric plates and a segment of dipole plates to it, the result should be an antenna, as shown in the figure.
The central core of the cable must be soldered to a copper nickel, and the screen to the reflector.
By the way! If you make two such antennas and space them in space at an angle of 90 degrees to each other, you will get a full-fledged device with polarization selection. You can also experiment with the shape of the reflector, for example, it can be parabolic.
Kharchenko directional antenna
There is constant debate on this type of receiving device on the World Wide Web, but it really is a working model. The only nuance in its manufacture is that it is necessary to familiarize yourself with a certain theoretical minimum, and during practical implementation, observe a high degree of accuracy. The procedure is as follows:
- First, copper wire with a diameter of 1.6 mm (or, in other words, a cross-section of 2 mm2) is taken, a frame is bent from it in the form of two rhombuses with a side length of 53 mm, the angle between the outer arms should be 120 degrees, and the gap in the central part should be 5 mm. It is important to remember that a displacement of even 1 mm will significantly affect the antenna parameters.
- A square with a side length of 14 cm is cut out of sheet aluminum 2 mm thick, and a hole with a diameter slightly smaller than the existing 50 Ohm coaxial cable is drilled in its center.
- A frame is installed exactly in the center, on dielectric stands, above the reflector at a height of 36 mm.
- A cable is threaded into the hole, the central core is soldered to the bottom corner in a gap of 5 mm, and the screen is soldered to the top.
- After this, the antenna is fixed to a bracket (possibly from a satellite dish) and adjusted by rotating in three planes.
Attention! The location of the frame relative to the reflector (parallel or perpendicular) will affect how the antenna is polarized, i.e., when assembling two devices, a full-fledged MIMO receiver will be obtained.
Directional MIMO antenna from KREOSAN
This is an acclaimed design that takes full advantage of dual polarization and claims to be the best 4G antenna. Moreover, it is easy to set up, since it only needs to be adjusted in two planes. There are several models for MIMO 3G network and 4G network (for different frequencies), but the manufacturing principle is the same. To assemble the antenna you will need:
- Sheet copper or aluminum, discs with a diameter of the required frequency are cut from it.
- M8 hairpin 14 cm long and a set of nuts in the amount of 12 pieces. The disks are secured to it in the manner shown in the pictures.
- Coaxial cable. Two segments are needed, one is soldered (or riveted) to the central conductor to the second largest disk at a specified distance from the edge, the second - in the same place, only at an angle of 90 degrees relative to the first. The screens are mounted on the largest disk.
After assembly, the antenna is installed on a bracket that can be mounted on a mast and all that remains is to point it at the nearest mobile operator tower. By the way, regarding all the antennas listed above, it is most convenient to use a modem with two existing Pigtail connectors as a receiver, and a corresponding adapter on the coaxial cable.
Step-by-step instructions for assembling a simple external 4G amplifier with your own hands
Based on the fact that a factory repeater is not cheap, many decide to make it themselves. To make a simple device, the user will need the following materials:
- plastic;
- copper wire: 38-40 cm;
- connection block;
- coaxial cable: 8-10 m;
- fastening hardware;
- polymer pipe: 20 cm.
Work order:
- The wire is bent 90° in the middle.
- Next, the “whiskers” are folded on both sides at a distance of 9 cm from the center at 90°: you should get a rhombus (gravitating towards the volume of the square).
- The ends (2-2.5 cm) must be bent inward.
- A connecting block is connected to them.
- One side of the polymer pipe is cut lengthwise, and a hole is made on the opposite side.
- The pipe is attached to the connecting block.
- Next, the cable is connected.
- On one side, the outer insulation is removed.
- Conductors (external and internal) are connected to the contacts of the connecting block.
- Then the device is installed on a pole or on the roof of the house (dacha). It must be directed towards the nearest mobile operator station.
- The second end of the cable must be connected to the plastic plate.
- Testing is carried out: the turned on mobile phone is brought to the amplifier - the cellular signal strength indicator should increase by 1-3 divisions.
Other homemade antenna options
Ideas for homemade antennas could be the following:
- Colander 4G. Everyone has a simple aluminum colander in their home. You need to fix the USB extension cord on the handle of the cookware. Connect a modem to it - it should ultimately be within the circle of the bowl. We direct the colander to the base station and catch the signal.
- 3G/4G satellite dish. If you have an old satellite dish, use it. The signal will be amplified significantly, since the antenna will be outdoor. Remove the converter from the boom. Secure the modem at this location. Naturally, you will need a USB extension cable - carefully stretch it to the modem and connect it. Now point the dish at the operator tower. To adjust, you will need to rotate the plate slowly to achieve maximum effect.
- Antenna "Double Ring". The method is similar to the Kharchenko antenna. It is just as effective, but here you also have to work hard to make the antenna.
How I did it in a village (100 km from the city) Internet based on MTS Unlimited
Hi all! I decided to share with you how I set up the Internet for myself in the village. Brief background. The house is located a hundred kilometers from the city. I really wanted to set up good internet so that parents could communicate via Skype, and for themselves as well. I decided to act.
I bought this gadget on the used market, it cost me about two thousand rubles.
But the speed was sad, about 1mb/s for downloading and 100kb/s for downloading. After some time, I decided to correct the situation and bought another set.
Firstly, we needed a normal router that worked well with modems. I chose the Zyxel Keenetic 4G III (Not an advertisement, I got it before anyone else in the store).
It had good WiFi coverage, so the signal penetrated all the wooden walls and there was WiFi throughout the whole house, even outside. It has USB with a good list of natively supported modems.
But, as you already guessed, you don’t need to catch good Internet on its own. You need a good external antenna. Since I was looking for everything in stores in our country, I found a cool Connect 3G Street Mini antenna in DNS.
It picks up the signal well from the village, located behind a dense forest at a distance of about 10 km.
After full setup I got about 20Mbps download and 1Mbps upload. Very good result on 3G.