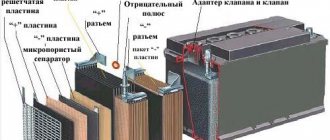
When, how and with what current to charge
As a rule, the degree of charge of a battery is judged by the density of its electrolyte. The density of a fully charged battery should be 1.26-1.28 g/cm³, the voltage should be at least 12.5 V. Everything will depend on what density of the electrolyte was originally installed in the new battery in your region of residence, it can be as high as 12.7 V so 12.9V. The lower the density, the more discharged it is. A decrease in density of 0.01 g/cm3 compared to the nominal value means that the battery has been discharged by approximately 6-8%. The degree of charge must be determined by the jar having the lowest density.
| Charge level (%) | Electrolyte density (g/cm³) | Degree of discharge (%) | Battery voltage (V) | Charge time at 10% capacity (hours) |
| 100 | 1,277 | 12,73 | Not necessary | |
| 90 | 1,258 | 10 | 12,62 | 2 |
| 80 | 1,238 | 20 | 12,50 | 4 |
| 70 | 1,217 | 30 | 12,37 | 6 |
| 60 | 1,195 | 40 | 12,24 | 8 |
| 50 | 1,172 | 50 | 12,10 | 10 |
| 40 | 1,148 | 60 | 11,96 | 13 |
| 30 | 1,124 | 70 | 11,81 | 16 |
| 20 | 1,098 | 80 | 11,66 | 20 |
| 10 | 1,073 | 90 | 11,51 | 24 |
| 1,06 | 100 | 11,4 | Sulfation |
The optimal charging current for a battery is considered to be a current equal to 0.05 of its capacity ( equalizing charge ). So for a battery with a capacity of 55 Am/h this value is 2.75 A, and for 60 Ah it is already 3 amperes. The purpose of this method is to ensure complete restoration of the active masses in all battery plates.
Although they often use the so-called forced charge and take a different ratio - 10% of the capacity . That is, a standard 55Ah passenger car battery is charged with a current of 2.75-5.5A , and for a 60Ah battery the charging current is set in the range from 3A to 6A . But, you need to know that the lower the charging current, the deeper the charge, although it takes more time. The situation is exactly the same with the supplied voltage - the higher the faster , but it should not fall below 13.8 and exceed 14.5 V ). The charging voltage is raised to 16.0-16.5V only when charging a maintenance-free battery .
It should be noted that today there are several methods for recharging the battery:
- At constant current;
- At constant voltage;
- Combining in automatic mode (we will not consider it, since in this case a time calculator is not needed).
Stages of car battery discharge
Battery charging time at constant current
The formula for calculating the charging current is: I=Q*k, where Q is the battery capacity, and k is a certain coefficient of the nominal value (its ideal value is in the range of 0.04...0.06, and the optimal value is up to 0.1). Based on this recommendation, the calculation of the time needed for a fully charged battery looks like this: T = Q/ I. Substituting your values, you will see that it turns out to be quite a lot of time, but since often not a full charge is required, but only restoration of the lost capacity, then this figure will be two or one and a half times less.
To roughly estimate the required time to charge a car battery with direct current , you first need to determine the degree of discharge of the battery (in percent), then determine the lost capacity (in Ah), and then, choosing the value of the charging current, calculate the time for full charging. The formula for calculating how long to recharge a car battery looks like this:
Multiplying this ratio by 2 times is necessary due to the fact that the efficiency of the process is 40-50%, the rest is spent on heating, as well as related electrochemical processes.
When the voltage stops increasing at the battery terminals for an hour while charging, the battery is 100% charged.
The value of the final voltage depends on: the magnitude of the charging current, temperature, internal resistance of the battery, the presence of impurities in the electrolyte and the composition of the alloy of the grids.
Charging the battery at a stable voltage
The charge level, when using this method, depends directly on the voltage that the charger is able to provide. For example, if the highest voltage at the output of the charger is 14.4V, then with continuous charging throughout the day, the battery will be charged to a maximum of 85%, at this voltage value of 15V - up to 90%, at 16V - up to 97%. Full charging can only be achieved when using a charger with an output voltage of 16.4 V.
Fully charging the battery at constant voltage requires at least 24 hours
This method allows you to charge the battery automatically; there is no need to monitor the process. The end of charging is determined by the voltage at the battery terminals; it should be equal to the voltage at the charger output plus 0.1V. But for 95% charge, if charging is done using a charger with an output voltage of 14.4V, it will take more than 24 hours.
How to use the calculator
To find out how long it takes to charge your battery, you don’t need to go into the details of all the processes and calculation formulas, just use this calculator.
For online calculation you must fill in all three fields:
- In the “Nominal capacity” field, enter the capacity of the car battery being charged.
- In the “Degree of discharge” field, you can enter both the percentage calculated from the table and the voltage measured with a voltmeter.
- In the “Charging current” cell you need to indicate exactly what current you plan to charge the battery from the charger.
By clicking the “Calculate” button you will get the required time to fully charge the car battery.
The number of cycles
It is important to remember that the battery life is reduced after each recharge. For nickel-cadmium batteries, the service life is 1000-1500 cycles. Modern products reach up to 4000 full cycles.
It is important that the new battery goes through a full charge cycle 3-4 times. This will allow you to bring it to maximum performance characteristics, which will be maintained throughout its entire service life.
Be sure to read the instructions for the batteries. It tells you how to charge correctly.
Modern rechargeable batteries last on average up to 3 years.
How long does it take to charge rechargeable batteries? So, how long you need to charge rechargeable batteries correctly is easy to find out on your own. In order to understand how much time you need to spend on charging, you should divide the battery capacity by the current of a special charger. It is also important to take into account all the coefficients. Their value ranges from 1.2 – 1.6.
To calculate the charge coefficient, take the ratio of the current and the direct capacity of a particular battery. The greater the difference, the greater the coefficient.
Note: The online calculator works on the same principle.
FAQ
How long does it take to charge the battery to start the car?
To start the car and be able to drive in the summer, it is enough to charge the battery for 30 minutes with a current of 10% of the battery capacity
.
This time is enough for its voltage to rise to 11.8 Volts
and the engine can be started by the starter without external force. In winter, you will need to charge the battery for at least 1 hour to increase its voltage to 12V. Further charging of the battery will occur from the generator when the car is driven at speeds above 1500 rpm.
What determines the speed of battery charging?
Charging speed depends on current strength
. The rate of the chemical reaction will accelerate as the charge current increases. The higher the current from the charger goes to the battery, the faster it will charge, but the stronger and hotter it will be. It is strictly prohibited to charge maintenance-free batteries with high current.
How many amps should I use when charging the battery?
The nominal value of the charging current is 10% of its capacity
. Therefore, when charging the battery you need to set it to 4.5, 5.5, 6.0 or 7.0 amperes. Depending on what battery you had to work with. And to accurately calculate how many amperes you need to set on the charger, in your case, use a calculator by multiplying the battery capacity by 0.1.
How long does it take to charge a 60 amp battery?
To understand how much to charge a 60ah battery, you must first determine the degree of its rarefaction. The average charging time for a dead battery is from 10 to 12 hours
. If battery 60 is charged at 6 amperes, when it has only 11.7 V with an electrolyte density of 1.1 g/cm³, then it will restore its full capacity in 14 hours. The final time depends on the discharge level. The battery is considered fully charged when the voltmeter shows 12.73V at its terminals and the electrolyte is actively boiling.
How many amps should a charged battery show?
To check whether the battery is charged, do not check how many amps the multimeter shows, because a charged battery will no longer take any amps. The voltage is checked at the terminals, which should be at least 12.7V half an hour after charging and about 13.4V if checked immediately after disconnection. Therefore, how many amperes a charged battery should show is not a correct question. If the charger does not have indicator lights, but a built-in ammeter, then the question of how much ampere will be shown on the charger display (which charges with constant voltage) may arise, however, when fully charged, you will also see an arrow at zero (0.1 A). But if charging was carried out with direct current, then it is not the current that needs to be controlled, it will be the same as it was initially installed - look at the voltage. A charged acid battery connected to the device will show 14.4V. A calcium battery fully charged to 100% will produce 16.3V and the current will jump to 0.8A after it initially dropped to 0.4, which will indicate the start of electrolysis.
Source
How to determine if it is a battery or an accumulator
At first glance, the energy sources in question are very similar, but upon closer inspection, you can immediately discern visual differences.
The main indicator of a battery is the inscription on its case with a certain number and mAh mark. These distinctive features indicate that the battery has a capacity that only a battery can have.
REFERENCE: the higher the number in front of the mAh dimension, the greater the capacity of the battery.
You can also find a battery among batteries by the characteristic word present on the label: “rechargeable,” which translated from English means “rechargeable.” If the user gets his hands on a regular battery, it will have a warning on it, that is, “do not recharge.”
REFERENCE: Alkaline batteries are also signed by the English term “Alkaline”, which translates as “alkaline”.
The next point, following which you will be able to select the required battery, is the marking:
- Batteries are divided into types based on materials. Designations may be found: Ni-Mh (nickel-metal hydride), Ni-Cd (nickel-cadmium), Ni-Zn (nickel-zinc), Li-ion (lithium-ion), Li-Pol (lithium-polymer).
- The most common batteries are: R – salt, LR – alkaline, FR – lithium.
The battery and the battery, in addition to differences in markings, differ significantly in price: a battery of the same size will cost up to four times more than a regular battery. That is why the latter are quite popular among users - they can be used in simple household devices, for example, in watches, flashlights or radio-controlled cars, and even inserted into digital devices that have long been collecting dust on a shelf, for example, a camera.
REFERENCE: salt or alkaline batteries and accumulators have similar sizes, for example, in both batteries you can find finger-type (AA) and little-finger (AAA) models. However, the button cell type is found only in batteries (the exception is button cell batteries for hearing aids).
Online calculator for calculating battery charging time (with direct current), how long to charge the battery
The battery plays an important role in the performance of the car. In internal combustion engines, this is the second source of electricity after the generator. Thanks to the battery, the ignition system and starter operate. It also allows you to turn on parking lights, heating, air conditioning, and listen to the radio when the engine is off. To perform its functions properly, the battery must be constantly charged. The battery charging time calculator will help you find out how long it should be charged.
- How long to charge a car battery
- How to use the battery charging time calculator
- How to calculate battery charging time yourself
- 5 questions and answers on battery charging
How long to charge a car battery
It is impossible to drive without a battery. It supplies electricity to the ignition coil, circuits, and starter. This is a DC source that is used when the car is parked with the engine off and when the engine is running. It is constantly recharged while driving from an alternator or from a rectifier.
If you rarely use your car, be prepared for the battery to drain. This happens especially quickly in winter. This is because during idle time, energy is still used to maintain the operation of devices such as a computer, control unit, watch. Therefore, the battery must be connected to a charger every 3-4 weeks.
Three main factors influence how long it takes to charge a battery:
- battery discharge percentage;
- ambient temperature;
- current strength at the output of the charger.
It is optimal when the charging current is from 0.05 to 0.1 battery capacity. For example, if the capacity is 60 Ah, the optimal charging current will be 3 A, and the maximum allowable 6 A.
When using a current of 0.05 of the capacity, charging will take much longer, but the active masses in all plates will be completely restored. The battery will hold a charge longer and its service life will increase.
Using a current greater than 0.1 is harmful for the battery, and less than 0.05 makes no sense, it will not charge.
It should be taken into account that low temperatures reduce battery parameters. If a cell has 100% electrical capacity at 25°C, then at 0°C it drops to 80%, and at -25°C it drops to 60%. Therefore, if the battery is partially discharged or not sufficiently charged, it may stop working at any time.
How to use the battery charging time calculator
It is very important to charge the battery correctly. Since it is impossible to determine by appearance what level the charging is at, it is very important to know how much time is needed for this process.
A battery charging time calculator will help you here. After entering basic data such as
- rated capacity,
- degree of discharge (in percent),
- charging current.
Just click on the “Calculate” button and as a result you will get the time required for charging. For example, if the battery capacity is 60 Ah and it is 80% discharged, then it will take 16 hours to restore its energy reserve (charging current 6A).
How to calculate battery charging time yourself
You can calculate this time using special formulas. First of all, find out how low the battery is. This can be done using a tester by measuring the voltage at the terminals.
Here, be sure to take into account this nuance - the voltage at the terminals is 10% higher than the voltage of the battery itself.
We calculate percentages using the formula x = V*100/v. where x is the charging percentage, V is the actual voltage at the terminals, v is the optimal voltage. Let's calculate using an example. If the battery voltage is 12V, then at the terminals there will be 12+1.2(10%)=13.2V. When measuring, you got a reading of 7V. The charging percentage will be 7*100/13.2=53%, respectively, it will be discharged by 100-53=47%.
The next step is to determine the lost capacity in Ah. Let's look at an example: 60 (battery capacity) * 47/100 = 28.2 Ah. Next, we calculate the battery charging time using the following formula: T = 2*C/I, where T is the charging time, C is the lost capacity, I is the charging current 2 - the charge efficiency is 45-50%, so we multiply by 2.
Such calculations are quite complex, it is much easier to use the Battery Charging Time Calculator, it will do it in a second.
It is assumed that the average battery charge time using a charger is 10–12 hours. It needs to be monitored periodically. When using microprocessor rectifiers, the device automatically goes into standby mode, constantly monitoring the charge level.
Automatic straighteners are the most common and easiest to use. Depending on the degree of battery discharge, they themselves choose the current and charging time.
Before connecting the charger, shake the battery slightly to mix the electrolyte. When using a serviced battery, check the electrolyte level. Add distilled water if necessary.
It is best to charge the battery using a charger outside the car, for example, in a garage or other room where there is an exhaust hood or good ventilation.
Never charge the battery in a residential area.
What batteries can be charged?
Before charging the batteries, let's define the terms. A single cell that can be charged many times is called a battery. Several such elements connected in one way or another constitute a battery. Those cells that cannot be charged are called voltaic cells, and several cells connected are called a battery of voltaic cells.
In the photo on the left is a battery (rechargeable battery), on the right is a galvanic cell (disposable battery)
So, rechargeable batteries or rechargeable batteries can be charged, but galvanic cells or just batteries cannot - they are disposable. We ran out of power and threw it away.
How to distinguish a battery from an accumulator
Before you start charging batteries, you need to make sure that you actually have a rechargeable power source in your hands. It is not difficult. Battery features are presented below.
Capacity _ On batteries, the manufacturer almost always indicates their electrical capacity. You won't find such information on batteries.
Rechargeable batteries of “AA” format have a capacity of 3,000 mAh
Note for reloadability . On the batteries you can find the inscription “Rechargeable”. On galvanic cells there is no such inscription or it says “Do not recharge” (do not recharge).
Above we see the battery, below - the galvanic cell
Type designation . All batteries indicate the technology by which they are made. Batteries come in salt (code R) and alkaline (LR). After the letter there is a number indicating the standard size.
Pen-type batteries, depending on the materials and manufacturing technologies used, are marked as follows:
- Ni-Mh – nickel-metal hydride;
- Ni-Cd – nickel-cadmium;
- Ni-Zn – nickel-zinc.
Calculation of battery charging time
How long does it take to charge a phone, laptop or other device that uses batteries? Would you like to know, but this can be calculated very quickly and simply using an online calculator. How long does it take to charge the battery? The battery capacity is measured in milliamps per hour; its manufacturers write it on the product body, and on the charger there is also data on current generation according to this device (Ml.a). If you divide the capacity by the charging current, you get the time in hours. But this is not yet a final result, because you need to take into account the efficiency of the device, that is, multiply the result of division by 1.4.
The battery charging calculation will look like this: T=1.4 C/I. Here there are indicators of charging time, capacity and current of the charger. In practice, these data may differ by 20 percent, because the charging time of the batteries depends on the quality of the products, correct formatting and ambient temperature.
The easiest way is to use a device with automatic control, but even in this case, additional charging can occur with a slow current, so there is no need to leave the battery on the charger after a full charge.
Each similar product has its own lifetime, which is determined by the number of recharge cycles. This value depends on the battery type. Therefore, if you constantly underload the device, you can significantly reduce the operating time of the product. To keep it intact and use it for a long time, you need to make the correct calculation of the battery charging time
Timing
How long it takes to charge a 60 Ah car battery can be calculated using a special formula. To measure battery capacity, milliamps per hour or mAh is used. Information about its size is always indicated by manufacturers on the battery case. The charger always contains information about what generates the current of the device. This indicator is expressed in milliamps.
If you divide the battery capacity by the charging current of the charger, you get the time expressed in hours. But you also need to take into account charging efficiency. To determine the time more accurately, the division result should be multiplied by 1.4.
To calculate the time required to charge the battery, use the following formula:
Т=1.4C/I
In it:
- T is the time required to fully charge the battery. It is indicated on the device.
- C is the size of the battery capacity in milliamps per hour.
- I – charging charging current.
When making calculations, it is important to take into account that the time required to charge the battery is affected by its quality, correct formatting, and ambient temperature. This means that real data may differ by 20% from the calculation results.
How long does it take to charge rechargeable batteries after purchase?
When purchasing a new device, the charge is half done, and therefore the first three times you need to completely discharge the device until it turns off completely, and then charge it at full power for about 12 hours, following the included instructions from the manufacturer. The battery is fully charged in 3-4 hours, and subsequently recharged with slow current to its full capacity. After three full recharge cycles, the device enters operating mode, and there is no need to wait for it to be completely discharged or charged.
An online calculation of battery charging time on our website will help you very quickly get the required result, which will tell each user how much to charge the batteries so that they function uninterruptedly for a long time.
Source
How long does it take to charge batteries?
The charging time can be determined by dividing the battery capacity by the charger current. In this case, it is important to take into account the coefficients of conversion of electricity into heat, energy dissipation coefficients, which take values from 1.2 to 1.6.
The charge coefficient can be taken from the calculation of the ratio of the charge current to the battery capacity. The greater this difference, the larger the coefficient should be used.
Note: the online calculator “how long to charge batteries”, located above this article on our website battery.rf, works in a similar way.
Safety rules when charging a car battery.
It is not recommended to charge in a residential area due to the fact that explosive gases are released from the battery. This is true for serviced batteries with plugs.
For the same reason, it is prohibited to smoke or perform any other work with open fire or sparks.
First, the charger is connected to the battery terminals, and then it is connected to the network. Disabling is done in reverse order. First, disconnect the charger (charger) from the network, then disconnect the terminals. This procedure will avoid the formation of a spark when connecting the charger.
Be sure to unscrew all plugs in batteries being serviced. This can be conveniently done using a regular coin of 2 or 5 rubles. After unscrewing, the plugs must be put back into the holes, but not tightened. This position of the plugs will allow gases to escape freely and at the same time protect the battery from possible dust and dirt getting into it. This will also reduce the loss of electrolyte during evaporation.
The plugs are unscrewed and inserted into their sockets.
Before unscrewing the plugs, be sure to wipe off all dust and dirt from the working surface of the battery. This will also prevent dirt from getting inside the battery.
If charging is done in an apartment, then it must be done on a balcony with an open window or in a room where there is an exhaust hood, for example, a toilet.
How to determine whether a battery is charged or discharged
This can be determined by the voltage at the contacts and the density of the electrolyte.
In a fully charged battery (100% charge), the voltage at the terminals should be 12.7V. When discharged, 11.7V (0% charge). Therefore, every 0.1V is 10% charge. These values are relevant for a battery temperature of 20-25 degrees.
For example, the voltage at the contacts is 12.2V, therefore the charge is 50%.
Table - dependence of the battery charge level on voltage.
The second, more accurate way to determine the degree of charge is by determining the density of the electrolyte. This method is only suitable for serviceable batteries in which it is possible to unscrew the plugs and get to the electrolyte.
A sulfuric acid solution is used as an electrolyte in batteries, the density of which is measured in g/cm3. During discharge, the density of the electrolyte decreases. Knowing this property, you can determine the degree of battery discharge. Density is determined using a special device - a hydrometer.
The density of a fully charged battery (100%) at 25 °C is 1.27-1.28 g/cm3.
The density of a completely discharged battery (0%) at 25 °C is approximately 1.1 g/cm3.
Knowing these data, it can be calculated that approximately every hundredth unit of density is equal to 6% charge (0.01 g/cm3 = 6% charge).
For example, the density is 1.24 g/cm3, therefore the degree of charge is 76%.
Graph showing the dependence of electrolyte density on temperature.
Table - dependence of electrolyte density on temperature.
Before checking the electrolyte density, be sure to turn off the charger and wait a few minutes. Density is more accurately determined when no gas is released from the electrolyte.
How to determine the battery charge level
The classic way to calculate the condition of a battery is to measure the density of the electrolyte. But in modern conditions, few people want to carry a hydrometer and electrodes of a maintenance-free battery coated with a solution of sulfuric acid. It is much easier to measure voltage using an accurate digital voltmeter.
After first making sure that the electrolyte level is normal, that is, the battery banks have not lost water. This often occurs during overcharging, intensive use and high temperatures. It is difficult to lose acid; to do this, the battery must be turned over, allowing the electrolyte to flow out, and the water easily evaporates with the intense release of gases on the surface of the plates.
Battery voltage should be measured under strictly defined conditions. Information is provided by EMF (electromotive force), and it is numerically equal to the voltage at the terminals only when the battery has not been charged or discharged for some time, that is, all chemical processes in the active zone have been completed.
On the subject: 4 ways to restore a battery at home
The norm, that is, 100% charge, corresponds to a voltage on six series-connected lead-acid elements (banks) of approximately 12.7 Volts .
With reasonable accuracy, we can assume that a drop in this value for every 100 milliVolt (0.1 V) means a loss of 10% of the charge. That is, for example, if you intend to use 12.0 Volts, you should not come to the conclusion that everything is fine, because the car network is called 12-Volt. This is quite arbitrary, but in reality the battery is discharged by about 70%.
Naturally, you need to use a trustworthy and accurate, tested voltmeter. Otherwise, using erroneous information, you can bring a perfectly good battery to a dying state.
What current and voltage should the battery be charged with?
The charging voltage for batteries manufactured using different technologies is different. But there are general requirements that apply to most batteries.
The most optimal and safest charging is to set the voltage limit to 14.7V and the current to 1/10 of the battery capacity. Let's say the capacity is 70 (A*h), then the current set during charging should be 7 amperes.
The quality of the battery charge and the current strength have an inverse relationship, that is, the lower the current strength, the better the battery will be charged and the slower its charging will occur. If you have time, it is better to choose an even lower current strength in the amount of 1/20 of the battery capacity. For example, for a battery with a capacity of 70 (Ah) this will be a current of 3.5A.
For maintenance-free batteries, the current should be no more than 1/20 of the battery capacity. In other words, if the capacity is 60 Ampere hour, then the current should be 3A. This low current is due to the design of the battery itself. Since the battery is maintenance-free, when the electrolyte boils, the gas released will have nowhere to escape and the battery can be ruptured by gas pressure. To avoid boiling of the electrolyte, choose small currents for charging.
As it charges, the voltage will rise to 14.7 V, and the current will remain constant until the voltage reaches this value. After the voltage reaches 14.7V, it will stop growing as it is limited by the memory settings. As the charge continues, the voltage is now limited, and as the charge continues, the current will decrease until it reaches a value indicating the end of the charge (approximately 1-0.5A). If the current does not decrease within two to three hours, then we can assume that the battery is fully charged in this charging mode.
After charging is complete, turn off the charger and let the battery stand for a few minutes so that the electrolyte stops releasing gas. We take density measurements.
If the electrolyte density has not reached its optimal values of 1.27-1.28 g/cm3, then you can try to increase it by charging at a higher voltage. To do this, we set the voltage limit to 16.3V, and the current to no more than 1/20 of the battery capacity. The current strength can be set even lower to the level of 0.5A. This way the battery will charge more slowly, but in this way we reduce the likelihood of the electrolyte boiling, which means the risk of destruction of the battery plates. In this charging mode we can withstand from one to four hours. The time depends on how quickly the electrolyte density returns to normal.
If an automatic charger is used for charging, it automatically selects the voltage and current.
Formula for calculating charging time by capacity and current
And now you can answer the question of how to properly charge batteries. The general charging time formula will look like this:
t = C / I * k,
Where:
- t – charging time in hours;
- C – element capacity in A*h;
- I – charging current in amperes;
- k – coefficient equal to 1.2-1.4.
The coefficient is needed to correct for the efficiency of the element. Since part of the energy during charging is spent on heat and creating chemical reactions, the battery will need to receive more energy than its electrical capacity itself to fully gain capacity.
Important! This formula is valid only for completely discharged batteries. Usually we do not discharge the element “to zero” (this will quickly destroy it), so the possibility of using it is very doubtful without some amendments. About them below. But as a rule, the end of charging is judged by the voltage on the element, and not by the estimated time. This is exactly how an automatic charger works.
What current can you charge?
Now about the current. We all know that, for example, lead-acid car batteries are charged with a current of 0.1C, where C is the battery capacity. Is this true for the types of elements we are talking about? Fair, but only partly. If we choose such a current, we will definitely not overheat any type of battery and damage it. However, the manufacturer allows the following charging currents:
- Ni-Mh – optimally 0.1 C-0.5 C, perhaps less often 1 C. The number of charge/discharge cycles is 300-500 (some manufacturers, in particular the GP company, indicate 1,000);
- Ni-Cd – 0.1С-0.5С, number of charge/discharge cycles – from 100 to 900;
- Ni-Zn – optimally 0.1C-0.5C, occasionally they can be charged with a current of 1C. Number of charge/discharge cycles – from 250 to 370;
- Li-ion – optimally up to 1C with constant control of the body temperature. Number of charge/discharge cycles until 20% capacity is lost – 600;
Examples of calculations
Now, as an example, let’s do a little calculation and find out how long it takes to charge specific batteries. Suppose we have a completely discharged Ni-Cd battery with a capacity of 1,000 mAh. The manufacturer of this type of battery allows for deep discharge, and we took advantage of this. The charging current will be 200 mAh (0.2C). Let’s take the average coefficient – 1.4. Let's try to calculate the charging time using the formula given above:
1/0.2*1.4 = 7 hours
Now let's charge the lithium-ion battery with a capacity of 3,000 mAh. It will be 90% discharged. We choose a charge current of 0.5C, the coefficient is the same. Since the element is not completely discharged, we amend the formula by subtracting 10% from the total electrical capacity.
(3 – 0.3)/1.5*1.4 = 2.67 hours
As we can see, the calculation is extremely simple, but, unfortunately, not always correct. The true time depends on many factors: ambient temperature, the actual capacity of the element (it falls over time), and the degree of discharge. But the real degree of discharge cannot always be accurately determined.
The consequences of a deeply discharged battery and how to properly charge it after that
During a deep discharge, sulfation of the plates occurs. Large crystals of lead sulfate (PbSO4) are deposited on the positively charged battery plates, thereby clogging them. In this case, the surface area of the plates free from lead sulfate crystals is greatly reduced. As a result, the battery capacity decreases. Three or four full discharges and almost all the plates will be clogged, and the battery can be thrown away.
Battery plates clogged with lead sulfate crystals.
Under normal operating modes (charge - discharge), small crystals are formed and during charging they dissolve in the electrolyte. This way the plates are cleaned and the battery capacity is restored. This does not happen if a deep discharge occurs, since during normal charging large lead sulfate crystals practically do not dissolve in the electrolyte. In this case, to dissolve them, you need to use a different charging mode.
A deeply discharged battery should be charged with a voltage of 16.2 - 16.3V and a low current of 1-0.5A. In this charging mode, it is possible to partially restore its capacity. In one cycle, it will not be possible to restore the capacity and increase the density of the electrolyte to 1.27 g/cm3. Therefore, when the electrolyte begins to boil at low currents, the charge must be stopped and allowed to stand for 2-3 hours. After this, we repeat the charging again. We repeat this process several times. In this way, it is possible to increase the density of the electrolyte to the state of a fully charged battery.
But we should not forget that voltages above 14.5V are not suitable for all batteries. These include helium and hybrid.