Do-it-yourself brickwork from A to Z. Expert advice.
Brick has been and remains the most popular building material due to its qualities such as strength, fire resistance, low thermal conductivity, frost resistance, and environmental friendliness.
You can list its advantages endlessly, but the fact is a fact - the most solid buildings are built from brick, which will last for decades.
Is it possible to lay brick walls yourself? This is possible if you follow some rules. SNiP for various conditions of design, architecture and structures provide certain recommendations for the construction of brick houses.
How much does brickwork cost from specialists? They will answer you the same way: prices fluctuate depending on the time of year, complexity and speed of installation. But it has always been like this - the price of one brick will be equal to the cost of working with it. That is, if a brick costs 100 rubles, then the mason will charge 100 rubles per piece for the work (provided that you provide all the building materials and tools).
Types of brickwork
Since bricks are not laid anyhow, but in a certain sequence, the types of brickwork also have their own names.
Masonry depending on material
- Brick (classical) - made from ordinary (ceramic) or silicate bricks;
- Small - and large block - from blocks of various sizes (cinder blocks, aerated concrete, foam concrete, ceramic or cement bricks. Here you should choose more carefully, since the weight of the brickwork will have a significant impact on the foundation of the house);
- Tesovaya - made of processed stone of a certain geometric shape;
- Rubble - made from irregularly shaped stones containing rubble and cement.
How to lay bricks with your own hands correctly
In order to lay bricks with your own hands, you need to master the basics of masonry work. If you have the desire, this is not at all difficult to do. As when mastering any construction business, first of all it is necessary to study the primary source: Construction Norms and Rules - SNiP. Studying the regulatory document is necessary not only to know how to build brick buildings, but also what materials to use for this. In addition, any facility after completion of construction must be officially accepted into operation.
When a house is built not by one’s own hands, but by hired specialists, there is an urgent need for quality control of the work. Knowing the regulatory documents, you will be able to speak the same language with the craftsmen, control their work, and save a lot of money, or even avoid critical mistakes. After all, builders often increase prices for work, demand the purchase of excess materials, and under-finish where this cannot be allowed even under the conditions of safe operation. And all this is only due to the fact that the developer does not understand exactly how the construction of a house should be carried out, and how the construction processes should be carried out.
There are many objects where you can lay bricks with your own hands. Of course, if there are no special skills in this matter, then it is better to entrust the construction of, for example, load-bearing walls of a house (box) to professionals. And, for example, a porch, internal partitions, or small households. buildings can be built with your own hands, which will give you significant material savings.
Now let's look at some of the main points related to laying bricks with your own hands.
When laying bricks, the following basic terms and names are used:
-Poke – the smallest side;
-The bed is the largest side;
-Spoon – the remaining one, medium in size.
The bricks are laid in horizontal rows on their largest side - on the bed. But at the same time, the rows can be either spoon or bonded.
A spoon row is when the bricks are laid lengthwise, so in the masonry of the wall we see their long sides - the spoons.
Studded - the bricks are laid in a row along the width, and in the masonry of the wall, their short sides are visible - the studs.
The simplest laying of a brick wall is when there is an alternation of spoon and butt rows. The bricks are laid on a layer of masonry mortar 10–12 mm thick. Therefore, seams are formed between the rows of brickwork - vertical and horizontal.
Main characteristics of building bricks
Standard brick dimensions: length – 25 cm, width – 12.5 cm, thickness – 6.5 cm.
In addition, the brick can be: one-and-a-half, with a thickness of 8.8 cm, and double, with a thickness of 13.8 cm, while the other sizes remain standard.
There are two main types of bricks – silicate and ceramic. Other subspecies are descended from these two main ones.
Sand-lime brick - made from sand and lime with a small amount of additives. Hence its properties - it is susceptible to the influence of water, not fire-resistant (it cannot be used to build stoves, as well as structures buried in the ground). Used for the construction of walls for use in “dry” conditions.
Ceramic brick - made from clay with various impurities. Excellent resistance to water and fire. Durable.
Bricks can be hollow – i.e. several holes of various shapes can be made in them. Such bricks have slightly lower strength characteristics, but for low-rise construction this is not significant. The main thing is that they have less price, weight and retain heat better.
Based on strength, bricks are divided into the following classes:
weak - M-75, M-100;
medium - M-125, M-175;
durable - M-200, M-250, M-300.
In terms of resistance to negative temperatures in combination with exposure to water (frost resistance):
F15, F25, F35, F50..., the number indicates how many freezing cycles the brick can withstand without consequences.
There is also a distinction between building brick and facing brick. Brick is used in accordance with the building design. For the construction of the basement, only solid bricks (of normal strength) with strength indicators from M200 and above and frost resistance F50 are used. And for walls you can also use hollow building bricks with lower strength indicators.
Masonry mortar
When laying bricks, it is very important that the mortar is sufficiently plastic, but in no case flowing. This speeds up the work and makes the masonry more durable. In construction, a special term is used - mortar mobility. It is determined by a reference cone, which has certain dimensions and a mass of 0.3 kg. If you lower the top of this cone into the solution, it will sink to a certain depth under the influence of its own weight. So, for various types of masonry, a solution is needed, the mobility of which can be within 7 - 12 cm along the reference cone.
The classic mortar for bricklaying consists of water, cement and sand. The ratio of components and their quality in mortar for bricklaying:
- cement brand M500 – 1 part;
-sand of class 1 of medium size with a percentage of impurities of no more than 3 parts;
-technical water – 1 part.
Do-it-yourself bricklaying
The solution can be prepared using classical technology, using cement, sand and water, or with additives, mainly plasticizing or frost-resistant. To build internal partitions, clay or lime is added to the solution. For external work, waterproof polymers can be added to the solution.
For hollow bricks in unloaded areas, you can use a cheaper and weaker mortar with a cement to sand ratio of 1/4. The solution must be used within 1.5 hours after preparation. Therefore, you cannot prepare a lot of solution at once. Usually they make as much as they intend to use within the next hour.
Bricklaying Tools
1. Container for mixing the solution. Usually - an old metal basin, a trough. But a little solution can also be mixed on a moisture-proof surface - a sheet of metal, a piece of linoleum.
2. Trowel, which is more often called “trowel”. The main tool of a mason. Using a trowel, stir and apply the solution.
3. Hammer-pick. Necessary for breaking bricks.
4. Rubber hammer, with the help of it they upset and level the bricks in a row. True, experienced craftsmen do this with the help of a trowel handle.
5. Construction level. It is clear that the horizontality and verticality of the masonry must be constantly monitored.
7. Rule. A long, up to 2 meters long and even strip, with the help of which the wall is checked and the plaster (screed) is leveled along the beacons.
8. Ordering - a long ruler with marks, which is used to verify the row of masonry.
9. Stretched horizontal cords (moorings), plumb lines. They control the execution of work.
Rules for laying bricks
The rules for laying bricks are prescribed in the regulatory documents discussed above. It is worth paying special attention to the following. The surface of the brick being laid must be strictly horizontal (for walls), so that the brickwork evenly bears the load. Otherwise, overstress may occur in certain places of the wall, which can lead to cracking.
The seams in the masonry must be bandaged. This means that the vertical and horizontal seams of adjacent rows should not be on the same line. If this is not done, the wall simply will not take the load and will collapse into separate fragments and columns.
The external load-bearing walls of the building are laid out simultaneously. One adjacent wall should not be allowed to outstrip the number of rows of laid bricks.
The thickness of masonry joints must be maintained within 10 - 12 mm. You cannot increase it, as this will reduce the strength of the wall. It is also impossible to reduce the thickness, otherwise the solution layer will lose its binding properties.
Methods of laying mortar and bricks.
Now let's look at the methods of laying bricks.
Suck it. In this case, a very mobile mortar with a thickness of 11 - 12 cm is used. The mortar is laid on the underlying layer of bricks so that it does not reach the edges of the wall by 2 - 3 cm. The brick being laid moves along the mortar, partially scooping it up with its end. Then it is pressed against the already laid brick. With this method of laying, the seams remain unfilled at the edges. It is believed that such masonry was made “in a wasteland.” It is used if the wall will be plastered in the future. Since in this case the plaster will hold stronger.
Press it in. With this method, the mortar is applied with a trowel to the vertical surface of the adjacent brick. The solution used is quite rigid, with a mobility of about 8 - 9 cm.
Types of bricklaying. There are a huge number of types of masonry. Let's first consider the laying of walls, depending on the number of rows of bricks being laid.
Half a brick . We get the thickness of the unplastered wall (without finishing) equal to 12.5 cm.
One brick - thickness 25 cm or 26 cm (depending on the type of masonry - either one whole brick, or two halves of a brick with a vertical seam of 1 cm).
One and a half bricks - thickness 38 cm (1 cm - vertical seam between bricks.).
Two bricks - thickness 51 cm (1 cm - vertical seam between bricks).
A wall of more than two bricks is very rarely used today. Previously, similar masonry was used in the construction of walls of high-rise buildings.
In general, when building wide walls, when not one, but one and a half, or two or three bricks are placed in one plane, a huge number of combinations of seam dressings and types of masonry arise.
The knowledge about proper bricklaying is very extensive, and this can only be learned gradually through constant practice of bricklaying. So there is the laying of a wall under plaster with the laying of facing bricks (read - facade), different types of bricks are laid in different ways - hollow, solid, red and silicate. Different techniques are used when laying dry and wet bricks, and different types of masonry mortars are also used.
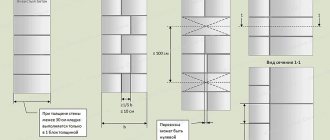
Dressing sutures
In thick walls, as already noted, a large number of seam dressing options can be used. All suture dressings are divided into two types - single-row and multi-row.
Single-row dressing means that in each new row all seams (internal and external) will overlap by a quarter or half of a brick. With this bandaging of seams, the greatest strength of the wall is achieved. In fact, the spoon and butt rows constantly alternate. It is used in the construction of high-rise buildings. But such a dressing is also more expensive. Here the complexity of execution is higher, there is more brick breaking, since many parts of a whole brick are required.
Multilayer dressing is more economical, but the strength of the wall is reduced by 10 percent. But for one or two-story houses this is not critical. With multi-layer dressing, one splice row is laid, and then 5–6 spoon rows in a row. Material consumption is reduced, and masonry work is simplified and completed faster.
If the simplest thin partition is built from brick - half a brick, then naturally there will be a simple ligation of the vertical seams, by moving each row to the side by half a brick. At the same time, so that the vertical seam between bricks in one row is opposite the middle of the brick in the lower and upper rows.
To strengthen the masonry walls, they need to be reinforced. Every 4 - 5 rows, a metal mesh or reinforcing bars should be laid between the rows.