Do-it-yourself columnar foundation for a frame house: review
A do-it-yourself columnar foundation for a frame house is easy to do and will cost less. It is constructed from various most affordable building materials.
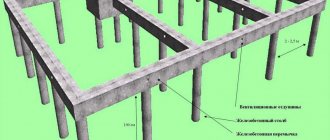
A columnar base is a network of supporting pillars arranged along the perimeter of load-bearing walls, with the lower frame of a building erected using frame technology laid on them.
The supports are placed in areas of the heaviest loads: in corners, when connecting wall ceilings, under spans of 2.5 m or more.
The intersupport distance and cross-section of the supports are calculated in advance and depend on their type, the material of their manufacture, the design of the structure being erected and its weight.
Basically, these parameters are: the intersupport distance is 1.5-2.5 m, and the cross-section for rectangular supports is 25-40x25-40 cm, round – 20-25 cm. Its ground part should protrude by more than 50 cm, and the height underground part – dependent variable on depth.
The upper support bases are located horizontally in the same plane, which is important for the option without a grillage. In this case, the lower trim is mounted along the pillars.
To do this, before the construction of the base begins, the upper mark of each support is marked with a building level, and after they are erected, this condition is checked for compliance and adjusted.
What is a columnar foundation?
This design is a simplified and lightweight version of a pile foundation.
If the piles for the foundation of a brick or reinforced concrete multi-story building are driven close to each other and can go tens of meters into the ground, then a columnar foundation for a frame house is a series of reinforced concrete, metal or wooden supports installed at the corners of the building (required), as well as with at intervals of 1 - 2 meters under external walls and partitions. The lower part of the supports should be in the ground below the depth of its freezing. This indicator depends on the climate zone and ranges from 0.5 to 1.5 meters in most regions of Russia. The posts are driven into the ground, screwed in, or simply dug in. The above-ground part of the supports is aligned in height and connected with a grillage - a kind of tape on which, in fact, the frame house is mounted. The shallow installation depth of piles, their rare location, as well as a wider range of materials used give columnar foundations a confident leadership in terms of price/quality ratio.
Do-it-yourself columnar foundation. Types by depth
Frost heaving is the force that is taken into account first when designing a columnar foundation.
This is a very dangerous pressure, which, if not installed correctly, can tear the foundation of the house.
Therefore, a large number of options for building construction are considered from the point of view of the impact of frost heaving on the foundation structure.
The basic design rule states that the foundation should be laid below the freezing depth of the soil by 30 - 50 cm. And if this indicator is, for example, 1.2 m, then, accordingly, the laying depth will be equal to 1.5 - 1.8 m.
But often a light building cannot exert such pressure on the support posts to contain the forces of frost heaving. That is, even when laid to a great depth, the foundation will be subject to deformation. Therefore, when building a columnar foundation with your own hands, you must take into account that there are two more positions: shallow and surface.
Non-buried
A non-buried columnar foundation or a surface foundation are still the same racks, only their laying depth does not exceed 30 - 40 cm. Often they are simply built on the surface of the soil, having previously made a cushion and waterproofing. Designers classify this type as those foundations whose depth does not exceed a third of the soil freezing level. From our example: 120: 3 = 40 cm.
The construction of a columnar foundation of this type belongs to the category of the cheapest and most rapidly erected structures. As practice shows, they usually use a block modification using blocks, stones or bricks. But since the height of the pillars is not very large, which means their load-bearing capacity is also low, it is therefore recommended to increase the cross-sectional area of the supports. Minimum size – 40 x 40 cm.
Shallow
The name of a shallow foundation suggests that it is buried in the ground, but not to a great depth. In any case, not below the level of its freezing. Designers calculate the depth of their installation at the rate of 0.5 - 0.7 from the depth of freezing of the ground. Again from our example: 120 x 0.5 = 60 cm. The main requirement for this design is not to touch groundwater.
The columnar foundation unit - the grillage - has one single task - to distribute the load from the house evenly across all the pillars. As mentioned above, the grillage can be constructed of concrete, metal (channel or I-beam), wood (beam with a cross-section of 150 x 200 or 200 x 200 mm) or be a log from the first crown of a log house.
Types of columnar foundations
According to the manufacturing option, a column-type foundation can be divided into:
- made;
- monolithic;
- wood.
The prefabricated type includes concrete blocks, bricks, and steel pipes.
The monolithic type is reinforced concrete. The building materials used for the production of individual elements must meet all requirements, as well as ensure reliability and high strength. The monolithic type is erected at the construction site by pouring a concrete solution into the completed formwork with reinforcement. The pillars with this option can have a square or rectangular cross-section.
The monolithic reinforced concrete option is the most stable when performing construction work on the construction of a structure.
The depth of burial of this option usually does not exceed one and a half meters. The standard distance between posts should be at least 1.5 meters, but not more than 2.5 meters.
Based on depth, the columnar base can be divided into:
- a recessed version, which is located below the soil freezing level, the depth of which is one meter or more;
- the shallow-depth type is most often buried by 50 centimeters;
- the non-buried version is used only for light buildings; only the top fertile layer of soil is removed.
The lower part of the support should be located 30 centimeters below the freezing level of the soil.
The main requirement for the depth level is that the structure should not touch the groundwater level.
Types of foundation according to section variant:
- Glass-type foundations can be erected under public as well as industrial structures. It can withstand quite heavy loads. This type has a stepped shape. The structure consists of a base, which is erected on a sand base, a glass kneecap, on which support pillars are installed. This option ensures the reliability of the structure, as well as a longer service life of the entire building.
- Pillars of constant cross-section can be used for one-story buildings with a low total weight, which can be made of natural timber or frame options. The base area is not able to withstand heavy loads.
If it is necessary to erect a heavier structure, as well as construction on unstable soils, builders recommend using a combined type - a column-strip foundation.
It combines the advantages of two types of foundations. With this option, the pillars are buried in the ground, and the strip base evenly distributes the total load between the piles. The tape does not exert any pressure on the soil base.
The support-column foundation can be made of brick, steel or asbestos pipes, monolith, concrete blocks, as well as natural wood. This option allows you to complete all the work in a maximum of three days. This figure may vary depending on the area of the future building.
Base structure
In order to competently build a columnar foundation with your own hands for a frame house, it is important to clearly understand the structure and process of its construction.
Work with soil
- To begin work, it is necessary to prepare the site for the construction of the foundation.
- Complete removal of debris and removal of turf by approximately 15-20 cm.
- Leveling the ground surface.
- Marking the area with pegs according to the plan. The pegs are installed at the corner points of the future foundation, connected with a cord, after which the accuracy of the markings is checked along the perimeter.
- The installation points for the pillars are being marked.
- Digging holes.
Support arrangement
1. Brick supports . Some situations make it possible to make support posts from brick, which is advisable to do on stable soils and in places where groundwater is deep.
Laying is possible in two ways:
- laying on a sand bed;
- constructing a concrete shoe, then laying bricks on a hardened base.
The most commonly prepared supports are 25 by 25 cm (a row of 2 bricks). If you plan to build a large building, then you can lay 4 bricks - 38 by 38 cm with additional installation of reinforcement inside the pillar.
It is important to maintain an exclusively vertical position of the supports with regular checking with a plumb line or level.
2. Block . An alternative option is wall or shoe (cushion) rectangular concrete blocks measuring 20 by 20 by 40 cm. The latter should be mounted on top of a sand cushion at the base of the supports, the shape of the posts is trapezoidal. Most often they are erected as shallow or non-buried supports.
The use of concrete pillars is recommended for low groundwater levels and stationary soils.
3. Monolithic . Such supports are made by pouring concrete mortar into pre-installed formwork, round or rectangular in cross-section, additionally reinforced with steel rods.
Columnar foundation for a frame house - useful tips
The first advice can be given regarding the depth of immersion of the pillars. Some recommendations have been given above, but soil freezing should also be taken into account. If we take into account the quality of the soil and its freezing, we can take as a basis the calculations established in various technical reference books.
To prevent the soil from drawing water from the poured concrete, this also applies to creating a substrate; pieces of roofing felt are placed on top of compacted crushed stone or sand.
This is also important for the side surfaces of the well if the filling pillars are made without formwork. In this case, most experts generally recommend making formwork from sheets of roofing material, which are fastened together with tape or an industrial stapler.
All pillars must stand strictly vertically and, accordingly, must be aligned only by level.
As can be seen from this publication, creating a columnar foundation requires certain knowledge. But if everything is done according to the rules, then this is an ideal option for any frame house at minimal cost.