How much mortar is needed for 1m2 of brickwork
As the Russian folk proverb says: “Measure seven times, cut once.” This principle will never become obsolete. Every builder knows that before starting any work, you need to carefully calculate, study and draw up a plan. What is it for? One of the reasons is to find out the required amount of consumable material, calculate how much it will cost, and purchase everything you need. If you are planning to build a house, you may be interested in the question, what is the consumption of mortar per 1 m 2 of brickwork? After all, you need to buy in advance all the components for the mixture, such as sand, cement and other consumables. Please note that the quality of the finished wall is influenced by the following factors: the quality of the material and the quality of the mortar. If the wall is built incorrectly, cold bridges may occur. Therefore, it is important to prepare the solution correctly and apply the right amount. After reading this information, you will find out the consumption of mortar for laying bricks.
Cement consumption for bricklaying
Cement consumption per 1 m2 of brickwork directly depends on the brand of the final mortar and the initial brand of dry mixture. In any case, we recommend buying cement with a reserve, since unexpected solution costs often arise during the work. If rounding down was used during measurements or calculations, it is worth taking into account the large error in the final amount.
The consumption of cement per cubic meter of brickwork is easily calculated, but it depends on the proportion of the mortar:
- if the mixture is 1 to 3, in order to understand the amount of cement consumed, it is enough to divide 1 m3 by 4 (this is the part of the dry mixture). This turns out to be 0.25 m3 of cement per cubic meter;
- to prepare a mixture of 1 to 4, the proportion of cement will be 0.2 m3;
- if a third of lime is used as a binder, that is, the mixture turns out to be 1 part cement, 0.3 parts lime and 3 parts sand, divide 1 by 4.3 and get 0.232 m3.
The consumption of cement per cubic meter of brickwork depends on the proportion of preparation of the mortar.
Similarly, calculations of how much cement per 1 cubic meter of bricklaying are also carried out with other proportions for preparing the mixture. Cement is not calculated in cubic meters; we will have to convert the volume into weight, but this will require knowledge of the standard specific gravity (density). The brand of cement and the degree of compaction (stayed, hardened or fresh cement) have an important influence; let’s take the average number - 1300 kg/m3.
Based on the obtained value, we calculate:
- quantity of materials in a mixture of 1 to 3: 0.25 m3 * 1300 kg/m3 = 325 kg, this is how much cement is required to prepare 1 m3 of solution. To calculate how much cement is needed per 1 cubic meter of masonry, we multiply the number by the cost standard for masonry mortar. For example, we use the consumption for a single wall: 325 * 0.221 = 71.825 kg, round up to 72 kg and add an error of 75 kg. This is how much cement is needed for 1 cubic meter of masonry when using a ratio of 1 to 3;
- to prepare a 1 to 4 solution, less cement will be required. We calculate using the same algorithm: 0.2 * 1300 = 260 kg, now 260 * 0.221 = 57.46, with rounding - 58, adding the error - 60 kg of dry cement.
For convenience of calculations, the concept of a square meter of masonry is usually used. To calculate the solution consumption per 1 m2 we can use a simple formula.
Let’s not resort to calculations of the number of bricks, but rather study the legal norms and calculate the resource costs per 1 m2:
- floor bricks – 51 pcs * 0.0006305 = 0.0321 m3 of mixture per 1 m2 of masonry. We determine the amount of cement 0.0321 / 4 = 0.008025 m3 and multiply by 1300 = 10.43 kg of cement per 1 m2 of stele of 0.5 bricks;
- in brick - 102 pcs * 0.0006305 = 0.0643 m3, then 0.0643 / 4 = 0.0161 m3, now multiply by 1300 kg/m3 and get 20.9 kg of cement per 1 m2;
- 1.5 bricks - 153 pcs * 0.0006305 = 0.0965 m3 / 4 = 0.0241 m3 * 1300 kg/m3 = 31.35 kg/m2;
- in 2 bricks - 204 pcs * 0.0006305 = 0.1286 m3 / 4 = 0.03215 m3 * 1300 kg/m3 = 41.8 kg/m2.
The above calculations are presented for a solution prepared in a ratio of 1 to 3.
A little about the factors affecting consumption
Mortar is the connecting link between bricks. Without it, it is impossible to build a wall. It must be of high quality, properly prepared and have the appropriate consistency. One of the important points that must be taken into account when calculating is its type of composition. The most common are 4 types of solution:
- Cement-sand mixture. It consists of cement, sand and water. This composition can be called the most durable if you strictly adhere to the application technology. Otherwise, there is a danger that it will crack.
- Limestone mixture. There is no cement in its composition; it is replaced by quicklime. The mixture is quite flexible and easy to work with. But there is one drawback - rain will easily wash it out. That is why it is used only for interior work.
- Mixed solution. The composition of this mixture is combined, and combines materials from the first two types. The result is a high-quality solution that is superior to the first two.
- Composition with plasticizer. Sand of 2 mm fraction and cement are additionally mixed with a polymer additive, which increases its plasticity.
These are the most popular mixtures used in construction. But, you should know that they are not the only ones that affect consumption. An important factor is the brick itself. Its size, format, ability to absorb water and the presence of voids directly determine how much mortar will be in 1 m2 of brickwork. In general, the consumption per 1 m 3 of brick is 0.2–0.25 m 3. It all comes down to the fact that the thickness of the wall plays a role, be it half a brick, one, one and a half or two. The greater the thickness, the greater the consumption. The same goes for the shape of the brick. For example, if it is large, then the flow rate is reduced, if it has holes, then the flow rate increases significantly. How is the mortar for bricklaying calculated?
Correct calculation of mortar consumption per 1 m3 of brickwork
The first thing every self-respecting builder does before work is to carefully calculate the consumption of mortar per 1 m3 of brickwork and the cost of all materials used in the work. When building walls, it is especially important to consider the amount of mixture leaving. If the work is done poorly, cold bridges will appear in the wall, which can be dangerous to human health, since mold likes to form there. Also, such bridges can be fraught with poor heat retention, and the amount of energy required to heat the room increases.
If you calculate incorrectly, there may not be enough material or, conversely, there may be an excess amount left. A lack of materials can lead to the fact that in the midst of work you will have to go for new ones and re-make the mixture, which will slow down the process. It's better to buy everything in advance. The remaining surplus can lie unused for years and eventually deteriorate. Anyone will be sorry for the money spent, so you should calculate everything in advance. For this you will need:
- calculation calculator;
- roulette.
For each type of construction work, different mixtures are used. For brickwork, cement grades M50 or M100 are best suited.
Factors influencing the calculation of mortar consumption per 1m3 of brickwork
The most important factor affecting consumption is the type of masonry mortar used. There are four types:
- Cement-sand. This mixture is made from water, cement, sand. When applied correctly, this solution is very durable and lasts a long time without cracking.
- Limestone mixture is a solution in which quicklime acts as cement. This mixture is not suitable for external work, as it is quickly damaged by moisture.
- Mixed. When properly prepared, this solution will combine all the advantages of the two previous solutions, minimizing the disadvantages.
- Mixture with plasticizer. A special polymer additive is added to the first solution to increase its plastic properties.
To make cement-sand mortars, the strength grade of cement must be 2-3 times higher than the strength of the finished mixture (for example, for a mortar with strength M100, you need to buy cement grade M200 or M300).
Organic and inorganic additives are often added to concrete to improve its properties, mobility, and rigidity.
In addition to the type of mortar, the consumption of mortar for laying bricks also depends on the materials, sizes and properties of the brick itself. The thicker the wall, the greater the consumption. If the brick is not solid, but hollow, more mixture will also be consumed.
Consumption per cubic meter
- for half (120×120×65) it will be 0.189 m3;
- for single (250×120×65) it will be 0.221 m3;
- for one and a half (380 × 120 × 65) it will be 0.234 m3;
- for double (510x120x65) it will be 0.240 m3;
- for double and a half (640x120x65) it will be 0.245 m3.
Thus, one solid brick requires about 0.0006305 m3 of mortar. Therefore, for 1 m2 of brickwork with a width of 120 mm, about 75 liters of mixture will be required.
For modulated bricks (250x120x88) the consumption will be slightly less:
- for half (120x120x88) it will be 0.160 m³;
- for a single (250x120x88) it will be 0.20 m3;
- for one and a half (380x120x88) it will be 0.216 m3;
- for double (510x120x88) it will be 0.222 m3;
- for double and a half (640x120x88) it will be 0.227 m3.
For hollow bricks, the mortar consumption per 1 m2 of masonry will be higher.
To calculate the solution, it is necessary to calculate the total footage of the construction area and multiply it by the consumption per 1 cubic meter.
Cement consumption
After calculating the required amount of the mixture, it remains to find out how much and what brand of cement should be purchased. At the same time, it is always better to buy cement “with a reserve” - in case of unexpected consumption or a large error in the calculations.
If a total of 20.0 m3 of mixture is required, and the proportion of the solution is 1:3, then the resulting value must be divided by 4. The result is 5.0 m3 of cement. However, cement is not measured in cubic meters; you will have to convert it to kilograms. To do this, you need to know the density of the hardener, which can vary greatly between brands. The average value is approximately 1300 kg/m3. Taking into account the knowledge of this indicator, it remains to make simple calculations: multiply the density by the volume. Thus, you get 5.0 * 1300 = 6500 kg, or about 130 bags, taking into account that the weight of each bag is 50 kg.
Brick consumption
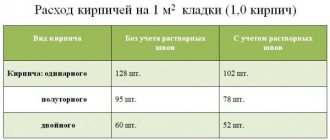
For construction, you need to find out not only the consumption of mortar for brickwork, but also how many bricks are needed. Depending on the size, the indicator of how many bricks are in 1m3 will vary greatly. The calculation results will also be different if you take into account mortar joints.
For 1 cubic meter you will need:
- 512 single bricks excluding mortar joints (394 including);
- 378 (302) one and a half;
- 242 (200) doubles.
For 1 m2 with a thickness of 120 mm you will need:
- 61 single bricks excluding mortar joints (51 including);
- 45 (39) one and a half;
- 30 (26) doubles.
For 1 m2 with a thickness of 250 mm you will need:
- 128 single bricks excluding mortar joints (102 including);
- 95 (78) one and a half;
- 60 (52) doubles.
For 1 m² 380 mm thick you will need:
- 189 single bricks excluding mortar joints (153 including);
- 140 (117) one and a half;
- 90 (78) doubles.
When laying, it is important to take into account the size of the brick, and you must not forget its properties (hollow bricks will require more masonry mortar than solid bricks), as well as the nature of the work performed. For interior work, a mortar with slaked lime instead of cement may be suitable.
In construction, you need to know how much mortar will be used for laying bricks, and how many keys will be needed.
With correct and accurate calculations of brick and mortar consumption, no problems should arise with construction. Just in case, you should take 5-10% more of all materials to eliminate unexpected situations.
In addition to cement and brick, you can also calculate the consumption of various additives, but for this you need to know exactly the parameters of the mixture being produced.
You can also watch a video about calculating bricks and mortar:
Solution consumption per 1 m3
To find out the amount of mortar per 1 m 3 of brickwork, consider the following data. Ordinary brick has dimensions 250×120×65. There are certain standards that show how much mortar is needed per 1 m 3 of brickwork:
- 0.189 m 3 when built in half a brick (120 mm);
- 0.221 m 3 when built in one (250 mm);
- 0.234 m 3 during construction of one and a half (380 mm);
- 0.240 m 3 when built in two, (510 mm);
- 0.245 m 3 when built in two and a half, (640 mm).
It turns out that for 1 standard brick there is 0.0006305 m 3 of mortar. If we convert this into liters, then for 1 m2 with a thickness of 12 cm, there are 75 liters of the finished mixture, and when the thickness is 1.5 bricks (380 mm), the consumption increases to 115 liters.
If we talk about thickened products (modulated), then with their dimensions 250x120x88, the consumption is as follows:
- 0.160 m 3 of composition, when working in half a brick (120 mm);
- 0.20 m 3 of composition, when working alone, (250 mm);
- 0.216 m 3 of composition, when working at one and a half, (380 mm);
- 0.222 m 3 of composition, when working in two, (510 mm);
- 0.227 m 3 of composition, when working at two and a half, (640 mm).
Based on these data, it is clear how the size of the material affects the consumption of the mortar per cube of brickwork. There is a certain pattern: the larger the area, the less composition is required. Knowing this data, you can prepare the required amount of mixture for masonry. All you have to do is calculate the total footage and multiply it by the consumption per 1 m 3. Now you are prepared and can purchase materials for work. Below is a table that will help you find out the consumption of cement and additives to obtain the ideal consistency of the composition.
Cement consumption per 1m2 of brickwork
The mixture requirement per 1 m2 is an important indicator; it is advisable to calculate it when planning the process in order to purchase the required number of components. As we already know, it is impossible to accurately plan the amount of consumables for a number of reasons. As a rule, another 10 - 15% is added to the calculated figures. During the calculation process, the future planned area is multiplied by the costs that are prescribed in regulations. It is important to know the type of brick from which load-bearing walls will be built; this is also an important factor. For one standard ceramic block, 0.0006305 m3 of solution is needed, in liters it turns out that for 1 m2 with a thickness of 12 cm, you need 75 liters of cement mixture.
How to know how many bags of cement to buy
Now, let's find out the cement consumption per 1 m 2 of brickwork. To do this, you must take 3 steps:
- Fully calculate the volume of masonry.
- Determine the volume of the required mixture.
- Taking into account the selected ratios of the components, calculate the amount of cement.
For example, you need to calculate how much cement will be needed to build the outer walls of a house measuring 10x12 m. At the same time, the height of such a one-story building is 3.2 m, and standard bricks 250x120x65 are used as the material. The wall thickness is chosen to be 51 cm. So, point 1 states that you need to know the total volume. From school we know the formula for finding volume: the length of the walls is multiplied by its height and thickness. In our case, these are the following indicators: (10+10+12+12) × 3.2 × 0.51 = 71.808 m 3. It turns out that the required number is 71.808 m 3. It's time to find out the total volume of the solution.
Based on the data given above, the consumption of the finished mixture per 1 m 3, with a wall thickness of 51 cm, is 0.240 m 3. You can find out the total quantity by multiplying the volume of masonry by the consumption per 1 m 3. This is what should come out: 71.808 needs to be multiplied by 0.240. Using a calculator, we get 17.233 m3. This number indicates how much cement mortar will be needed for the job. From it you only need to subtract the amount of cement.
If the selected proportion is a component ratio of 1:3, then the following is obtained: 17.233 must be divided by 4. Now you know how much cement you need for a high-quality mortar. This number is 4.308 m3. All that remains is to go to the store and buy as many bags of cement as needed. But cement is not sold in cubic meters. The material is packaged in bags of 25 or 50 kg, so we should convert our figure into kilograms. To do this, you need to know the density of the hardener. As a rule, on average this figure is 1300 kg/m3. Let's do the calculations: 4.308×1300 = 5600 kg. Now, we divide 5600 kg by 50 (the number of kg in one bag) and we get a consumption of 112 bags.
Cement consumption
The consumption of cement per square meter of brick depends on what brand of dry mix is used and what brand of concrete should be obtained in the end. Cement is usually used 1.5-2 grades higher than the required grade of concrete mortar. When making calculations, it is better to round up and add about 5-10% for unforeseen work, nuances, and factors.
Cement consumption in accordance with the proportions of the components of the solution:
- If a mixture of 1 to 3 is prepared, to determine the volume of cement you need to divide 1 m3 by 4 (this is how much dry mixture is consumed). This yields 0.25 m3 of cement per cubic meter.
- When a mixture of 1 to 4 is used, 0.2 m3 of cement is used.
- In a solution where lime is also used as a binder (usually a third is added), the proportions of the mixture look like this: part cement, 0.3 parts lime, 3 parts sand. Then you need to divide 1 m3 by 4.3 - it comes out to 0.232 m3.
Calculations are performed in a similar way to determine how much cement will be needed per 1 m3 of solution, and with other proportions. But you need to remember that cement is not counted in cubic meters, so this value must be converted into mass.
Cement consumption per 1 cubic meter of solution:
- In a mixture of 1 to 3: 0.25 m3 x 1300 kg/m3 - it turns out 325 kilograms. This is exactly how much cement is needed to mix 1 m3 of mortar according to this proportion. To determine the volume of cement per 1 cubic meter of masonry, the number is multiplied by the standard consumption of masonry mortar. If a single wall is placed, it turns out: 325 x 0.221 = 71.823 kilograms = 72 (if rounded) = 75 (if we add an error). It turns out that in a mixture of 1 to 3, 75 kilograms of cement are used per 1 m3 of solution.
- In a 1 to 4 solution, the calculations are as follows: 0.2 m3 x 1300 kg/m3 = 260 kilograms, 260 kg x 0.221 = 57.46 = 58 = 60 kilograms of dry cement needed per cubic meter of masonry.
To make calculations more convenient, you can use a square meter and calculate how much cement is needed per 1 m2 of masonry.
Calculations with a solution of 1 to 3:
- For laying half a brick you will need: 51 brick x 0.0006305 = 0.0321 m3 of mortar. 0.0321 m3 / 4 = 0.008025 m3 of cement x 1300 kg/m3 = 10.43 = 11 kilograms of cement.
- For bricklaying - 102 pieces x 0.0006305 m3 = 0.0643 / 4 = 0.0161 m3 x 1300 kg/m3 = 20.9 = 21 kilograms of cement will be required to lay a square meter of wall one brick thick.
- For one and a half bricks - 153 pieces x 0.0006305 = 0.0965 m3 / 4 = 0.0241 m3 x 1300/m3 = 31.35 = 32 kilograms of cement per square meter of a wall one and a half brick thick.
CSP consumption for bricklaying
50kg - 0.038 m3
in 25kg - 0.019 m3
2. Cement-sand mortar for masonry:
For 1 m2 of brickwork with a masonry thickness of 1 brick, the amount of mortar approaches 75 liters of consumption per 1 m2. If the wall is made of brick with a thickness of 1.5 bricks, then the amount of mortar will correspond to the figure of 115 liters.
3. Proportions of cement mortar:
In order to prepare a mortar, you need: 1 part of a binder (cement) and 4 parts of filler.
4. Proportions of plaster mixture:
You will need 1 part binder (cement) and 3 parts aggregate.
5. Cement mortar for brick:
According to consumption standards, 400 pcs. bricks (more precisely 404) - 1 m3 of masonry. The solution consumption rate per 1 m3 is 0.23 m3 (in practice, 0.25 is accepted).
6. How to calculate the consumption of sand concrete M - 300 per screed?
The approximate density of the sand concrete mixture is 1.7-1.75 kg/cubic dm
For 1m/2 with a thickness of 1cm = 18-20 kg of mixture (sand concrete M300).
7. Tile adhesive:
The consumption of tile adhesive per 1 m2 of laid tiles is 10 kg. dry mixture with a layer thickness of the finished solution of 10 mm.
8. Adhesive for foam concrete blocks and gas silicate blocks:
The consumption of foam concrete adhesive per 1 m3 of laid foam concrete masonry is 40 kg. dry mixture
9. Self-leveling floors:
The consumption of self-leveling floors per 1 m2 of finished mortar is 6 kg. dry mixture, with a recommended layer thickness of 5 mm.
10. Plasters for walls:
The plaster consumption per 1 m2 of finished mortar is 10 kg. dry mixture, with a recommended layer thickness of 10 mm.
11. Wall putties:
The putty consumption per 1 m2 of finished solution is 0.9-1.0 kg. mixtures.
12. Grout (tile joints):
The grout consumption per 1 m2 of laid tiles is 120 g, with a recommended joint thickness of 2 mm.
13. Universal mixture M −150:
The consumption of the universal mixture M-150 per 1 m3 of the finished solution is 450 kg. dry mixture.
14. Masonry mixture M-200:
The consumption of the M-200 masonry mixture per 1 m3 of masonry is 350 kg. dry masonry mixture.
15. Waterproofing material (penetrating layer):
Waterproofing consumption per 1 m2 of surface will require 700 g. dry mixture diluted to a sludge state for application with a brush (roller).
16. Paints:
Paint consumption per 1 m2 of walls or ceilings when first applied to a primed, flat surface is 0.3 liters, the second layer when applied correctly is 0.2 liters per 1 m2.
17. Polyurethane floors:
The consumption of polyurethane self-leveling floor when applied to a dust-removing primer is 1.5 kg per 1 m2 of concrete floor surface, with a thickness of 1 mm.
Amount of cement per masonry (cement consumption per bricklaying):
To prepare 1 m3 of cement mortar you need 8 50 kg bags of cement. and mixed with sand in a ratio of 1:4, where one part of sand is also equal to 50 kg.
19. The consumption of materials (excluding losses) for the construction of 1 m2 of the surface of a brick wall with a thickness of a quarter of a brick is:
cement (for mortar grade M-100) - 5 kg;
cement (for mortar grade M-75) - 4 kg;
cement (for mortar grade M-50) - 2.5 kg.
How much cement, sand, crushed stone in 1 m3 of concrete (how to prepare concrete - proportions):
a) For 1m3 M 150 concrete you will need: 220 kg of cement, 0.6 m3 of sand, 0.8 m3 of crushed stone.
b) For 1m3 M 200 concrete you will need: 280 kg of cement, 0.5 m3 of sand, 0.8 m3 of crushed stone.
c) For 1m3 M 250 concrete you will need: 330 kg of cement, 0.5 m3 of sand, 0.8 m3 of crushed stone.
d) For 1m3 M 300 concrete you will need: 380 kg of cement, 0.5 m3 of sand, 0.8 m3 of crushed stone.
21. Clay-sand mortar. How to cook:
Clay-sand mortar is a 1:3 proportion, where one part clay mortar and three parts vermiculite. The resulting solution is poured in a layer up to 50 mm
To make the clay-sand mortar layer for a warm screed or wall construction even warmer, you need to mix the clay-sand mortar in a 1:1 ratio with sawdust or flooring (finely chopped straw). The prepared solution is poured into a layer 20-30 cm thick.
22. Proportion of concrete and foam chips:
In order to create such a solution, which is mainly used for insulating floors and ceilings of bathhouses, you need to mix 1 part of ordinary cement mortar (or ready-made concrete mortar) and 3 parts of foam chips.
23. How many blocks are there in 1 m3 of masonry?
Size 200×300×600 – 27 blocks per 1m3
Size 200(188)x200(188)x400 - 62 blocks per 1 m3
24. Secrets of brick or block facing masonry, masonry mortar + black seam:
Consumption - 1-1.5 buckets of solution per 1m2. Instead of an expensive plasticizer, 2 caps of cheap shampoo (for plasticity) per batch of 1/4, 1 liter. a jar of black pigment, and in order to avoid efflorescence, 200g. 9% vinegar solution.
25. Penetrating waterproofing penecrit and penetron:
Penecrete 150-200 grams per seam 25×25 mm per 1 linear meter of grooves
Penetron (for 2 layers according to technology) from 0.8 kg - 1.1 kg per 1 m2 depending on the looseness and unevenness of the surface
How many bricks are needed for 1m2 of masonry:
a) If the wall thickness is half a brick - 120 mm
- single brick - 61 pcs. excluding seam, 51 pcs. with seam
- one-and-a-half brick - 46 pcs. excluding seam, 39 pcs. with seam
- double brick - 30 pcs. excluding seam, 26 pcs. with seam
b) If the wall thickness is one brick - 250 mm
- single brick - 128 pcs. excluding seam, 102 pcs. with seam
- one-and-a-half brick - 95 pcs. excluding seam, 78 pcs. with seam
- double brick - 60 pcs. excluding seam, 52 pcs. with seam
c) If the wall thickness is one and a half bricks - 380 mm
- single brick - 189 pcs. excluding seam, 153 pcs. with seam
- one-and-a-half brick—140 pcs. excluding seam, 117 pcs. with seam
- double brick - 90 pcs. excluding seam, 78 pcs. with seam
Cement consumption for brick laying
A building material such as brick is held together with cement mortar, which is prepared immediately before use. Most individual developers mix it “by eye”, using sand and cement as components. In this case, their share ratio is usually chosen to be 1/3 or 1/4.
However, when constructing brickwork, there are some nuances that must be taken into account. It should be said right away that there cannot be a single recommendation for the preparation of masonry mortar, and here’s why.
What determines cement consumption?
• Type of masonry (wall thickness). It can be 1, one and a half or 2 bricks. • Brand of cement. • Type of bricks – solid or hollow. In the latter case, more solution “goes away”, since it fills the voids in the products. • Mixture preparation technology. Sometimes other components are added to it, for example, lime, clay. • Probably, most of all the consumption of mortar, and, consequently, cement, is influenced by the degree of professionalism of the master. After all, the layer can be made of different thicknesses. If there is not enough practical experience in carrying out masonry work, then the seams are thicker, which significantly increases the amount of binder used to prepare the mortar.
Cement consumption for bricklaying is calculated in different ways. Some are interested in 1 m 2 of surface, others – in 1 m 3 of the prepared mixture. Let us present some averaged data depending on the brand of solution.
Cement consumption per 1 cubic meter of solution
The amount of cement for the construction of masonry in ¼ brick (in “kg”): • M50 – 2.5; • M75 – 4; • M100 – 5.
There are other examples. When laying 1 brick, you will need about 75 liters of cement mortar for each “square”. If the wall is built with 1.5 bricks, then the consumption increases to 110 l/m2.
Consumption 1 m3 (cube)
Sometimes they operate with such measures, since the proportional ratio is calculated specifically in relation to volume. On average, to prepare 1 “cube” of solution you will need 400 kg (8 standard packages of 50 kg each) of cement. This ratio is valid if the mixture is prepared at the rate of 1 part binder and 4 parts filler (sand).
The average rate is approximately ¼ m3 of solution for 1 “cube” of masonry. It is this ratio that is used in practice. If the brick is silicate, then per 1 m3 of masonry you will need less mortar - about 0.22 m3.
On various sites devoted to this issue, you can find data that differs somewhat. It is necessary to take into account that consumption depends on the specifics of masonry operations. We have provided approximate figures that can only be taken as a basis when calculating the required amount of cement for independent work.
It's a matter of the date of its manufacture. Although cement is not a food product, it also loses some of its qualities after a certain time. Any specialist will say that, depending on storage conditions, this building material can reduce its characteristics by up to 40% in six months. In other words, you can buy M400 cement, and when used after some period of time, it will actually correspond in its “parameters” to the 200th or 100th grade. But all proportions are calculated based on the fact that the cement is “fresh”.
Therefore, if it has been stored for some time, then its share in the mixture should be increased. Consequently, one must proceed from the fact that its consumption will be higher than calculated.
Practical advice
• In the process of preparing the mortar for the construction of load-bearing structural elements, cement of a higher grade is taken than for others (self-supporting). • To simplify calculations, experts advise using a ratio of 1 to 4. • When introducing various additives into the prepared mixture (lime, marble chips, clay and some others), the proportion may change and reach 1 to 9. • You should not purchase the material in “simple » double-layer packaging. They poorly protect cement from moisture, so its quality will be lower than that declared by the Manufacturer. Consequently, consumption will have to increase, and this will lead to higher construction costs.
Consumption of dry mixture per 1 m3 of solution: weight, volume
When building a house, it becomes necessary to use a material such as a cement-sand mixture. Thanks to this combination of ingredients, it is possible to obtain a reliable coating for the wall, make a strong floor screed, or even lay a brick wall. You can purchase this composition in a ready-made form in the store or prepare it yourself. If you choose the second option, then it is considered the most economical; in addition, you yourself will be able to regulate the concentration of the flow of your mixture.
Amount of solution consumption per square meter
Today in construction stores the range of building mixtures is huge, thanks to this you can choose your composition for specific work. When choosing a building material, it is important to know its consumption. In this case, you can purchase the exact amount of the mixture and save on buying unnecessary material. But each type of work has its own expense. DSP is quite convenient and popular material.
For floor screed
How to calculate the consumption of CSP per 1 m2 of screed? The process of calculating the mixture for floor screed is simple, so all these manipulations can be performed in your head. No complex mathematical formulas are used here. Let's look at the whole process using a specific example. For a screed of 10 cm per 1 m2 you will need 50 kg of M400 mixture.
If you need to get highly accurate results, then you need to apply the following formula: multiply the area by the height of the screed. As a result, you should get a number that will indicate the required amount of solution.
For example, the area under the screed is 50 m2, and its height is 8 cm. The above formula takes the following form: 50 m2 × 0.08 m = 4 m3. But grains of cement and sand play a very important role here. When preparing a solution, they reduce their volume under the influence of liquid. Consequently, the total volume of the prepared solution will be less than the amount of materials spent on it. When choosing a material, it is important to consider not only the brand, but also the GOST of the cement for the job.
Consumption per 1 liter is approximately 1.4 kg of dry mixture. To put it another way, from 50 kg of composition you can get 36 liters of solution. As a result, the resulting volume of the mixture will be equal to 2/3 of the volume of materials involved.
This indicator can be calculated only with accurate knowledge of the quality characteristics of the sand used. Often this information is not included on the packaging. For this reason, it is best to calculate the necessary data without taking into account shrinkage, and then add the approximate amount of materials used to eliminate it.
The video shows a recipe for a floor screed solution with a consumption of cement-sand mixture per 1 m2:
Plastering the surface
If you decide to level your walls or simply remove defects such as depressions and cracks, then using sand-cement plaster would be an excellent option. Its consumption will vary with different laying thicknesses. If the layer thickness is 5 mm, then the consumption will be 7 kg per m2.
Here you can watch a video about the disadvantages of a house built on screw piles.
In terms of volume, the amount of solution per 1 m2 with a thickness of 5 mm will be 5-6 liters. The layer thickness can reach from 5 mm to 30 mm. Most often in practice, a bag of cement is used, slaked lime - 40 kg, sand - 550 kg, water - 100 liters. If the process of preparing the plaster was carried out correctly, then it is possible to achieve high-quality wall cladding. In addition, it is quite possible to reduce the consumption of cement for repairs and cladding of the house several times.
Cement consumption when laying bricks
- Wholesale prices
- Delivery
- Call
- Wholesale prices
- Delivery
- Call
Count your expenses. All rates and costs are below:
How many cubes in a bag of dry cement or building mixture:
50kg - 0.038 m3
in 25kg - 0.019 m3
2. Cement-sand mortar for masonry:
For 1 m2 of brickwork with a masonry thickness of 1 brick, the amount of mortar approaches 75 liters of consumption per 1 m2. If the wall is made of brick with a thickness of 1.5 bricks, then the amount of mortar will correspond to the figure of 115 liters.
3. Proportions of cement mortar:
In order to prepare a mortar, you need: 1 part of a binder (cement) and 4 parts of filler.
4. Proportions of plaster mixture:
You will need 1 part binder (cement) and 3 parts aggregate.
5. Cement mortar for brick:
According to consumption standards, 400 pcs. bricks (more precisely 404) - 1 m3 of masonry. The solution consumption rate per 1 m3 is 0.23 m3 (in practice, 0.25 is accepted).
6. How to calculate the consumption of sand concrete M - 300 per screed?
The approximate density of the sand concrete mixture is 1.7-1.75 kg/cubic dm
For 1m/2 with a thickness of 1cm = 18-20 kg of mixture (sand concrete M300).
7. Tile adhesive:
The consumption of tile adhesive per 1 m2 of laid tiles is 10 kg. dry mixture with a layer thickness of the finished solution of 10 mm.
8. Adhesive for foam concrete blocks and gas silicate blocks:
The consumption of foam concrete adhesive per 1 m3 of laid foam concrete masonry is 40 kg. dry mixture
9. Self-leveling floors:
The consumption of self-leveling floors per 1 m2 of finished mortar is 6 kg. dry mixture, with a recommended layer thickness of 5 mm.
10. Plasters for walls:
The plaster consumption per 1 m2 of finished mortar is 10 kg. dry mixture, with a recommended layer thickness of 10 mm.
11. Wall putties:
The putty consumption per 1 m2 of finished solution is 0.9-1.0 kg. mixtures.
12. Grout (tile joints):
The grout consumption per 1 m2 of laid tiles is 120 g, with a recommended joint thickness of 2 mm.
13. Universal mixture M −150:
The consumption of the universal mixture M-150 per 1 m3 of the finished solution is 450 kg. dry mixture.
14. Masonry mixture M-200:
The consumption of the M-200 masonry mixture per 1 m3 of masonry is 350 kg. dry masonry mixture.
15. Waterproofing material (penetrating layer):
Waterproofing consumption per 1 m2 of surface will require 700 g. dry mixture diluted to a sludge state for application with a brush (roller).
16. Paints:
Paint consumption per 1 m2 of walls or ceilings when first applied to a primed, flat surface is 0.3 liters, the second layer when applied correctly is 0.2 liters per 1 m2.
17. Polyurethane floors:
The consumption of polyurethane self-leveling floor when applied to a dust-removing primer is 1.5 kg per 1 m2 of concrete floor surface, with a thickness of 1 mm.
Amount of cement per masonry (cement consumption per bricklaying):
To prepare 1 m3 of cement mortar you need 8 50 kg bags of cement. and mixed with sand in a ratio of 1:4, where one part of sand is also equal to 50 kg.
19. The consumption of materials (excluding losses) for the construction of 1 m2 of the surface of a brick wall with a thickness of a quarter of a brick is:
cement (for mortar grade M-100) - 5 kg;
cement (for mortar grade M-75) - 4 kg;
cement (for mortar grade M-50) - 2.5 kg.
How much cement, sand, crushed stone in 1 m3 of concrete (how to prepare concrete - proportions):
a) For 1m3 M 150 concrete you will need: 220 kg of cement, 0.6 m3 of sand, 0.8 m3 of crushed stone.
b) For 1m3 M 200 concrete you will need: 280 kg of cement, 0.5 m3 of sand, 0.8 m3 of crushed stone.
c) For 1m3 M 250 concrete you will need: 330 kg of cement, 0.5 m3 of sand, 0.8 m3 of crushed stone.
d) For 1m3 M 300 concrete you will need: 380 kg of cement, 0.5 m3 of sand, 0.8 m3 of crushed stone.
21. Clay-sand mortar. How to cook:
Clay-sand mortar is a 1:3 proportion, where one part clay mortar and three parts vermiculite. The resulting solution is poured in a layer up to 50 mm
To make the clay-sand mortar layer for a warm screed or wall construction even warmer, you need to mix the clay-sand mortar in a 1:1 ratio with sawdust or flooring (finely chopped straw). The prepared solution is poured into a layer 20-30 cm thick.
22. Proportion of concrete and foam chips:
In order to create such a solution, which is mainly used for insulating floors and ceilings of bathhouses, you need to mix 1 part of ordinary cement mortar (or ready-made concrete mortar) and 3 parts of foam chips.
23. How many blocks are there in 1 m3 of masonry?
Size 200×300×600 – 27 blocks per 1m3
Size 200(188)x200(188)x400 - 62 blocks per 1 m3
24. Secrets of brick or block facing masonry, masonry mortar + black seam:
Consumption - 1-1.5 buckets of solution per 1m2. Instead of an expensive plasticizer, 2 caps of cheap shampoo (for plasticity) per batch of 1/4, 1 liter. a jar of black pigment, and in order to avoid efflorescence, 200g. 9% vinegar solution.
25. Penetrating waterproofing penecrit and penetron:
Penecrete 150-200 grams per seam 25×25 mm per 1 linear meter of grooves
Penetron (for 2 layers according to technology) from 0.8 kg - 1.1 kg per 1 m2 depending on the looseness and unevenness of the surface
How many bricks are needed for 1m2 of masonry:
a) If the wall thickness is half a brick - 120 mm
- single brick - 61 pcs. excluding seam, 51 pcs. with seam
- one-and-a-half brick - 46 pcs. excluding seam, 39 pcs. with seam
- double brick - 30 pcs. excluding seam, 26 pcs. with seam
b) If the wall thickness is one brick - 250 mm
- single brick - 128 pcs. excluding seam, 102 pcs. with seam
- one-and-a-half brick - 95 pcs. excluding seam, 78 pcs. with seam
- double brick - 60 pcs. excluding seam, 52 pcs. with seam
Calculation of how much mixture is needed per 1 m3
Intuitively, every person should understand that the consumption of the presented mixture will depend on the strength of the structure that will be erected. For example, to build a foundation you need M300 concrete and no lower, but for a screed, a solution with a strength of 150 kg/cm2 is quite suitable. Each brand of mixture has its own properties and scope of application.
The higher it is, the less material is needed. Knowing the consumption of the mixture per meter cubed is very important, because in this way you can purchase the exact amount of material and not worry that you will need to bribe it. In addition, when purchasing, you can even purchase material in a larger volume, since its consumption is greatly influenced by the type of structure being built. It will also be interesting to read about how many bricks are in 1 m3 of masonry.
Plastering walls
When performing such work, a classic plaster mortar is most often used. It contains components such as sand, cement, taken in a ratio of 1:3.
When leveling the surface, material consumption will be directly related to the thickness of the applied layer. If this parameter does not exceed 12 mm, then for 1 m3 of plaster you will need to stock up on 1.6 kg of M40 mixture or 1.4 kg of M500 mixture. The volume of solution per m2 is easy to calculate. To do this, we use the above formula: 1m2x0.012 m = 0.012 m2 or 12 liters.
Here you can see photos of the base panels.
Wall masonry
When laying a brick wall, it is very important to ensure its strength. In this case, it is necessary to take into account not only the quality and strength characteristics of the brick, but also the mortar that will be used in this case. If you decide to buy a ready-made composition for masonry, then you need to take into account that to build 1 m3 of wall in 1 brick, you need to use 75 liters of M100 mortar.
Mortar consumption for brick laying
Every builder, before starting the construction of a building, thinks about how much necessary materials should be purchased in order to avoid the fact that after the completion of construction, he will be left with stocks of cement or bricks. To do this, you need to clearly calculate the amount of all materials that will be used in construction.
In our article we will focus on how to determine the consumption of mortar for laying bricks.
Correct calculations
To correctly perform all the calculations, you will need a tape measure and calculation skills. When performing calculations, you should determine what type of work will be performed, because the quality characteristics of the solution depend on this. solutions can be: concrete, slag cement, sand cement, and others. The strength of these solutions will depend on the brand of cement and quantitative composition. For example, for concrete screed, when pouring floors, concrete of the M200 grade is most often used; to prepare a mortar for brick or cinder block masonry, a mixture with a hardness of M50 to M100 should be used. To prepare the mixture from which the cinder blocks themselves will be molded, you should use a solution with a hardness grade also from M50 to M100. For plastering walls, you should take a solution with a hardness of M50 to M100. Once you have determined what kind of concrete mortar you will work with, you can begin to calculate what kind of cement, what brand you will need to purchase.
Mortar proportions for bricklaying
The strength and durability of brickwork depends not only on the quality of the blocks, but also on the quality of the binding mortar. Depending on the type of brick used and the characteristics of the masonry, different types of binders can be used.
The article will analyze the main types of mortars for bricklaying, determine the scope of their application, and discuss the composition and methodology for preparing various mixtures. Particular attention will be paid to operational properties and application features.
Calculator for calculating mortar for bricklaying
The strength and durability of the structure depends on the quality characteristics of the cement mortar. Therefore, it is important to purchase in advance all the necessary components for its preparation. The calculation of the mortar for masonry is carried out based on determining the consumption of cement, the hygroscopic properties of which require accuracy and efficiency of preparation in order to avoid the unsuitability of the mixture.
The calculation of mortar for brickwork depends on the project, the type of brick and the brand of cement. As a rule, for the construction of brick walls, a mixture is used, the hardness of which varies within the range of M50, M100.
Scheme for calculating mortar for bricklaying
Initially, the preparation of cement-sand essence involves determining the required cement grade, the choice of which directly depends on the expected strength of the finished composition. Its class should be two or three times the hardness of the mixture. So, to obtain a cement mortar with a hardness of M100, it is necessary to purchase cement of grade M200 or M300. The most rational solution would be to use the M400 brand. A certain percentage of it in the preparation of the mixture allows you to achieve the required strength coefficient.
The next stage involves calculating the amount of mortar for masonry, which is determined based on a consumption of 0.25 m3 per square meter. m. of brickwork.
As practice shows, to lay a wall one brick thick, you will need 0.21 cubic meters. solution. Laying two bricks requires the consumption of 0.23 m3 of cement-sand mixture. It is important to consider that regardless of the type of mortar used (standard three-component, lime or with an admixture of plasticizers), the volumetric flow rate will be the same. At the same time, the amount of the mixture depends on the structural features of the brick. Its hollow version will significantly increase the consumption of cement mortar.
The calculator for calculating mortar for masonry will allow you to make calculations regarding the total volume of the cement mixture. The reliability of the result obtained is determined by the accuracy of the measurements of the size of walls, window and door openings. The presence of concrete wall belts involves calculating their height from general measurements.
To calculate, it is necessary to set the parameters of the length and height of the walls in meters, the thickness of the masonry, which is determined based on the thickness of the brick.
The online construction calculator provides the ability to quickly and conveniently calculate the norm of cement mortar. Among other things, determining the consumption of brickwork will allow you to navigate the cost of masonry and set the required budget for the construction of the building.
Types of masonry mortar
Masonry mortar allows for reliable bonding of bricks into monolithic masonry. The strength and durability of the brickwork depends on the quality of the binder mixture. There are several types of masonry mortar:
- cement;
- cement-clay;
- cement-lime;
- lime.
Each of these mixtures has its own area of application and characteristic features.
Cement masonry mortar
Due to the ease of preparation and the minimum number of ingredients, the cement mixture is often used for bricklaying, plaster and in the construction of floor screeds. Before mixing, it is recommended to sift the sand and cement to avoid foreign inclusions. This type of masonry mortar is characterized by high strength, rigidity and low mobility.
Cement-clay
This type of masonry mixture has the ability to retain moisture longer than cement mortar, which allows it to be used at lower temperatures. The clay included in the composition is finely ground and cleaned of unwanted impurities. Before adding this component, it is thoroughly mixed until a homogeneous dough is obtained.
Cement-lime
The strength and ductility of the cement-lime mixture allows it to be used for laying any brick. The presence of lime paste greatly simplifies the application of the solution and promotes good adhesion to the surface of the blocks. To prepare the cement-sand mixture, mix it with lime milk, and the resulting mixture is thoroughly mixed.
Mortar
The low strength and fragility of lime masonry mixtures limit their scope of application to plastering work and the construction of one-story buildings. The ingredients used are sifted sand and ground quicklime. The ratio of lime and sand is determined by the fat content of the latter and can be from 1:2 to 1:5.
Currently, on the building materials market you can purchase ready-made dry mixtures for preparing various types of masonry mortars. In order to obtain a ready-to-use composition, it is enough to mix the contents of the package with the specified amount of water and mix thoroughly.
Cement consumption rate per 1m2 of masonry
The rate of consumption of cement mortar per 1 m2 of brickwork directly depends on the thickness of the latter: the thicker the wall, the more material is required. For walls with a thickness of a quarter of a brick per 1 m2 of masonry you will need:
- 5 kg of cement in a solution of grade M100;
- 4 kg for brand M75;
- 2.5 kg for brand M50.
Brickwork diagram.
Cement mortar is consumed approximately the same for brickwork, about 300 kg per 1 m3 (0.25-0.3 cubic meters of mortar per 1 cubic meter of surface). A cement to sand ratio of 1:4 allows for optimal rigidity, mobility and adhesion. If other components are added to the batch, such as clay, limestone, marble, synthetic additives, etc., the ratio decreases down to 1:9. To prepare concrete, cement consumption should not exceed 500 kg per 1 m3. The exact characteristics of concrete are fixed by GOST, but it is allowed to change the proportions for the production of concrete to obtain certain characteristics of viscosity, density and drying time of concrete. To prepare a masonry batch, you will need the following tools:
- container for mixing and measuring (you can use a bucket or trough);
- mortar mixer or hammer drill with a mixer attachment;
- shovel.
To make a batch, dry sand and cement are first mixed, then water is gradually added in small portions. The solution should become homogeneous, solid, and not spread much. Brickwork will last longer and concrete will be stronger if the cement mixture is prepared correctly. Such designs can provide high reliability and durability.
The ratio of cement and sand in the solution
Cement and sand are the main components of any masonry mortar; its strength and service life depend on their ratio. The masonry mortar must contain cement and sand in a strictly defined ratio, determined by the brand of cement, the type of brick used and the mechanical strength of the masonry. In addition, the amount of sand in the finished mixture depends on the presence of additional components, in particular lime.
The table shows the ratio of ingredients depending on the brand of cement.
M400 (with added lime)
M500 (with added lime)
Compliance with the proportions indicated in the table will ensure a long service life and high strength characteristics of the brickwork.
Requirements for masonry mixture
The requirements for masonry mortars are described in detail in GOST 28013-98. According to this document, the following requirements apply to mortar mixtures:
- the composition must have a high degree of adhesion to brick and other substrates;
- withstand large amounts of freezing and defrosting;
- to ensure that the masonry does not collapse under the influence of atmospheric influences and temperature changes, the masonry mixtures must have high water resistance;
- due to the plasticity of the mortar, during the laying process, it becomes possible to timely adjust the position of the masonry material, which significantly increases the quality and productivity of the work;
- water-retaining properties prevent decomposition of the mixture and precipitation of heavy fractions;
- the strength characteristics of the composition are decisive in the calculation of building structures. This parameter shows what maximum loads the material can withstand. The brand of the solution reflects its strength in kgf/cm2.
Failure to comply with these requirements leads to the formation of cracks in the brickwork, increased consumption of the mortar mixture, increased thickness of the joints and reduces work productivity.
Determination of solution mobility
The mobility of a masonry mixture means its ability to spread under the influence of its own weight. To determine the mobility of the finished solution, an Abrams cone is used. This device is a cone weighing 0.3 kg, the height of which is 150 mm, and the angle at the apex is 30 0.
Determination of solution mobility is carried out as follows:
- Working container 1 is filled with the finished mixture so that the distance from the edge of the vessel to the surface of the solution is 10 - 15 mm.
- The laid mixture is bayoneted 25 - 30 times and shaken by light tapping.
- The cone is installed so that its top touches the surface of the mixture and is fixed using the clamping screw 3, after which the location of the pointer on the scale 4 is noted.
- Locking screw 3 is released, as a result of which the cone begins to freely sink into the solution. As soon as the cone stops sinking, the locking screw is tightened again and the pointer reading on scale 4 is again noted in the laboratory notebook.
- The immersion depth of the cone is determined as the difference between the primary and secondary measurements, and the mobility of the composition is determined as the arithmetic mean of the results of two experiments.
Recommended mobility values of the solution depending on the purpose are given in the table.