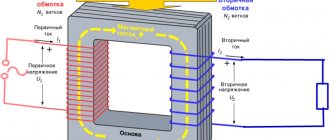
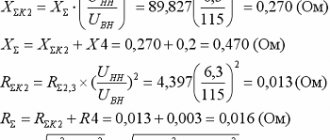What network are our houses and apartments powered from?
Most apartments and private houses use a single-phase electrical connection. At the same time, the total loads
consumers do not exceed 10 kW. Such connections account for about 90% of all electrical receivers.
The remaining 10% use a three-phase connection. It is used if it is necessary to connect a power
more than 10 kW.
For this purpose,
380 Volt AC networks
These include residents of cottages or private houses and owners of apartments where electric stoves or other appliances designed for a 380 V connection are installed.
Elements of a single-phase electric current circuit
Definition 1
Single-phase alternating current is an electric current that varies according to the law of cosine or sine.
The law of change of single-phase current is as follows:
$I(t) = Im * sin(w * t + φ).$
where: Im is the amplitude of electric current oscillations; w is the cyclic frequency of electric current oscillations; f is the initial phase of electric current oscillations.
Sources of single-phase current are alternating current generators, the voltage of which varies according to the same law. Single-phase alternating current circuits connect consumers and sources of electricity. They can be complex or simple, branched or unbranched, as well as with several or one voltage source. The following laws apply to the voltages and currents of such circuits:
Finished works on a similar topic
- Course work Single-phase alternating current circuits 400 rub.
- Abstract Single-phase AC circuits 220 rub.
- Test work Single-phase alternating current circuits 230 rub.
Receive completed work or specialist advice on your educational project Find out the cost
- Kirchhoff's first and second laws.
- Joule-Lenz laws.
- Ohm's laws.
But the physical processes that occur in single-phase circuits are much more complex and varied than in DC circuits. The main elements of these circuits are:
- Inductors.
- Resistors.
- Capacitance capacitors.
- AC voltage sources.
Voltage sources and resistors are used in DC circuits. Capacitors are used to break the circuit and prevent direct current from passing through. Inductors pass direct current, but have zero resistance and do not affect the distribution of voltage and electric current.
If a capacitor is connected to a single-phase alternating current electrical circuit, the measuring instruments will register the presence of current. This is due to the fact that the gap created by the capacitor does not represent an obstacle to the electric field through which the charges on the capacitor plates influence each other. This interaction maintains the electric current because it sets in motion the charges on the other side of the created gap.
— — Do you need help creating a study plan? — Specify a topic and receive a response in 15 minutes — — — — — — get help — —
If a coil is connected to a single-phase circuit, a voltage drop will be recorded by the voltmeter, which is a sign of the appearance of resistance. This is due to a phenomenon called electromagnetic induction. When the electric current changes, the magnetic field of the coil also changes, which causes the appearance of a vortex electric field, and according to Lenz’s rule, a vortex field of electromagnetic induction, which is antiphase to the creating current and resists it. The presence of a capacitor and coils in single-phase circuits changes their properties, which manifests itself in the form of reactive energy consumption and mismatch between voltage and current fluctuations.
Main differences
A common factor is the number of wires and voltage. This is where the differences end. A single-phase connection is characterized by connecting two/three wires (phase, neutral, ground) to the house or apartment. Typically the conductor cross-section is 4-6 mm2. And they use wiring
1.5-2.5 mm2.
However, it is limited in terms of maximum power consumption, which should not exceed ten kW. It may be difficult to connect consumers designed for three-phase voltage. When connecting, additional devices will be required, and you also need to be prepared for a loss of power.
Typically, three phases are supplied to an apartment building, and only one phase is supplied to each apartment. At the same time, they try to distribute the load proportionally, eliminating phase imbalance. They also take into account that 220V voltage is less dangerous than 380V, from a safety point of view.
If the consumer plans to connect to the electrical network
with an allocated power of more than ten kW, it is necessary to use three-phase voltage.
The difference in this case lies in the connection of a cable with four/five cores to the house or cottage. In what
This is
different
from a two-wire connection. In this case, the consumer receives two voltage values: linear will be equal to 380 V, and phase - 220 V.
Measurement is carried out as follows. Phase voltage is measured between the neutral conductor and each phase alternately, linear voltage is measured between phases.
The figure below shows how to measure phase and line voltage.
It should be taken into account that in cottages where the installed power exceeds ten kilowatts, but there is no three-phase load, the active power should be distributed evenly between the phases.
This is the difference
With a single-phase connection, there is no need to distribute power.
The figure below shows the connection diagram for a single-phase load evenly distributed over three phases and the formula
dependence of line voltage on phase voltage.
In this case, there is no need to use switching equipment (automatic machines, starters) for high currents. Most often three-phase network
used for industrial enterprises, shops, office premises.
What is the difference between three-phase voltage and single-phase
So, if two wires (phase and zero) enter a house or apartment, then this system is called single-phase and the operating voltage is considered to be 220V (phase), and if there are four wires (three phases and zero), then such a system is called three-phase and the operating voltage is 380V (linear). Let's look at the main differences
So, as can be seen from the above, both there is a common neutral wire. And if you measure the voltage of each phase relative to zero in a three-phase network, then in all cases you will get a value of 220V. And only when you measure the voltage of the phases relative to each other, you will get a value of 380 volts.
So, if two wires (phase and zero) enter a house or apartment, then this system is called single-phase and the operating voltage is considered to be 220V (phase), and if there are four wires (three phases and zero), then such a system is called three-phase and the operating voltage is 380V (linear).
Let's look at the main differences
So, as can be seen from the above, both there is a common neutral wire. And if you measure the voltage of each phase relative to zero in a three-phase network, then in all cases you will get a value of 220V. And only when you measure the voltage of the phases relative to each other, you will get a value of 380 volts.
This is due to the fact that the phase vectors are symmetrically shifted by 120 degrees, and when measuring the voltage between the phases, we see the geometric sum of the two vectors, which is exactly equal to 380 Volts.
From this we can conclude that in a three-phase system there are three single-phase systems to which consumers can be easily connected. The only condition will be to distribute the load evenly across the phases in order to avoid such an unpleasant and even dangerous phenomenon as phase imbalance.
Pros and cons of systems
Each of the presented systems has its own disadvantages and obvious advantages, which directly depend on power consumption, the threshold value of which is 10 kW.
Advantages of one phase
Ultimate simplicity
Low cost
Relatively 380V lower dangerous voltage
Disadvantages of one phase
The power of such a system is limited to just the notorious 10 kW
Advantages of three-phase
The power is limited solely by the selected cross-section of suitable conductors.
Reduced energy consumption.
Possibility to power industrial equipment.
Availability of the option to switch power to a less loaded phase.
Disadvantages of three-phase
The installation cost is higher compared to a single-phase connection.
A voltage of 380 Volts is potentially more dangerous than a setting of 220 Volts.
The voltage of single-phase loads has its own limitation.
Where is 220 V and where is 380 V
Probably, the overwhelming majority of ordinary residents in their apartments and houses have a single-phase network with a voltage of 220 V. And this is due to the fact that up to a power of 10 kW (most apartments and houses have less consumption), it is more advisable to connect a single-phase network.
A three-phase network is used if the planned power consumption exceeds the threshold of 10 kW or there is electrical equipment that requires exactly three phases for correct operation.
Of course, it is possible, for example, to start a three-phase motor from one phase by using capacitors. But remember that this approach will significantly reduce the efficiency of the engine and significantly increase energy consumption.
For example, the maximum power consumption of a private house is 8 kW, which means you can run a two-core copper cable with a cross-section of 6 millimeters at the input, and install a 40A machine at the input.
If the load is 15 kW, then for a single-phase wire the current value will already be 70 A. This means that in this case you will need a wire with a cross-section of 10 millimeters of copper and a power circuit breaker. And they already cost significantly more. In this case, it is much more profitable to use a three-phase system and “spread” the load of 5 kW per phase. That is why most shops, offices and especially enterprises are powered from three-phase systems.
Connection circuits "star" and "triangle" in three-phase
So, in order to obtain the usual phase voltage from a three-phase system, you need to take one of the phases and a zero (which is common to all phases) - such a connection is called “Star”.
If we need a voltage of 380 V, then we use exactly linear voltage - such a connection is called Triangle
That's all I wanted to tell you about the main differences between single-phase and three-phase power supply systems. Thank you for your attention.
Source
Are single-phase networks found in their pure form?
The energy system of our country is designed to use a three-phase network. All generators in power plants produce three phases. This applies to hydroelectric power plants, nuclear power plants, thermal, tidal, etc.
This scheme for transmitting energy over long distances is the most economical. To transmit similar power with a single-phase line, large cross-section wires will be required. Therefore, single-phase networks are not used for electricity transmission.
The figure below shows a diagram of the transmission of electricity from a thermal power plant to a consumer.
However, single-phase electrical networks are widely used as emergency power supplies.
For this purpose, gasoline or diesel power plants are used. Installed at facilities where power outages are unacceptable. For example, for powering hospitals (intensive care units or operating rooms), telephone exchanges, operational warning systems, etc. For powerful consumers, three-phase diesel generators are used. Material taken from the site: https://samelectrik.ru/