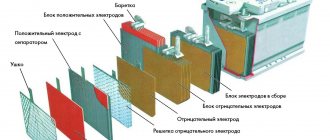
The principle of operation of an acid battery
As you know, a battery consists of a housing divided by partitions into several elements (cans) inside each of which positive and negative electrode plates are placed. They are separated from each other by porous rectangular dielectric sheets (separators) that do not react with the acid of the electrolyte. Separators are necessary to avoid short circuits between the electrodes. Battery electrodes are made in the form of flat lead grids into which powder of either lead dioxide is pressed for the anode plates or metal lead for the cathode plates. In modern lead-acid batteries, the electrode grids are made of an alloy of lead and antimony, this increases their strength and improves other technical characteristics. All cathode plates of the electrodes of each element, as well as the anode plates, are connected to each other in parallel, this is done to increase the electrical capacity and the maximum possible current supplied by the battery. The elements are connected to each other in series, therefore, when the EMF at the terminals of one bank is approximately equal to 2.11 V, the battery voltage is 6 times greater (according to the number of banks), that is, a little more than 12 V.
The operation of lead-acid batteries, which include gel batteries, is based on the electrochemical reactions of lead and its dioxide with an aqueous solution of sulfuric acid.
Discharge
When the load is connected to the battery terminals, an electrochemical reaction between the electrodes and sulfuric acid begins. As a result, the cathode and anode material is converted into lead sulfate. At the same time, an excess of electrons appears at the cathode. At the anode, on the contrary, there is a lack of them, that is, an excess of positively charged ions. Therefore, a potential difference arises between the anode and cathode, under the influence of which a current flows through the external load. In this case, water is formed at the cathode. The consumption of acid, as well as the release of water, leads to a strong drop in the concentration and density of the electrolyte. When most of the electrolyte acid has reacted, the battery becomes completely discharged and needs to be charged.
Charge
When an external source of electric current is connected to the terminals of a discharged battery, the battery charging process begins. It lies in the fact that under the influence of electric current, reverse processes occur in the battery. That is, sulfuric acid is obtained from lead sulfate and water, while the anode material is converted back into lead dioxide, and the cathode material into lead metal. If you do not disconnect the battery from the current source after charging is complete, that is, after the lead sulfate is consumed, the breakdown of water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen begins, called electrolysis. This phenomenon should be avoided, since, firstly, an explosive mixture of hydrogen and oxygen is formed, and secondly, water is irreversibly consumed, and the acid concentration rises significantly above the calculated value - this means that the battery will perform worse.
Maximum permissible characteristics and operating conditions
- Operating temperature range – from -40 to +40 ○C.
- The voltage below which a car battery cannot be discharged is 10.5 V. This limitation exists because with further discharge of a lead-acid battery, intensive sulfation of its electrodes begins. Sulfation is the formation of an insoluble film of lead sulfate on the surface of the electrodes, which significantly reduces the surface of the electrodes in contact with the electrolyte and, as a result, the electrical capacity of the battery.
- Duration of operation up to 500 cycles in 70% discharge and full charge mode.
How to maintain a gel battery
Maintaining gel batteries means restoring the volume of gel electrolyte and the battery charge. Despite the fact that suppliers do not place particular emphasis on the fact that gases are completely regenerated in gel batteries and are not released into the atmosphere, leakage is still present. The battery must be disposed of properly after use.
Charger
A good charger, say Auto Welle AW05-1204, supports charging in several stages, each of which is activated automatically. Multi-studio charging allows you to maintain optimal parameters, which depend on the battery charge. Increased accuracy of output parameters allows you to ensure 100% charge. Simple chargers operate in 2-3 stages; in expensive devices, charging can be carried out in 5 or more stages.
Video: Gel battery. Charging the gel battery
Regular chargers for acid batteries can also charge a gel battery. It is only important to monitor the voltage. Often now chargers are sold with the ability to manually adjust the voltage, so this will not be difficult.
Gel batteries allow rapid charging at significant current levels, although this is not recommended. It is better to set the current at 10% of the battery’s energy capacity and charge it at this current level throughout the day.
It is important to ensure that this gel battery is fully charged. If not fully charged, the gel battery will no longer be able to take a full charge.
Gel batteries are a good source of power for a car network, but some of its disadvantages prevent them from being widely used in vehicles. In addition, they are not cheap, and improper use can quickly ruin it.
Charging Features
Poorly charged batteries can be dangerous. For example, exceeding the charging current can lead to “drying out” of the battery. According to the standard, gel batteries are considered self-sufficient (do not require maintenance), since they hold water in their capsules. However, with an increased charging current, evaporation may pass through the protection valves. A used battery greatly loses its characteristics.
Functionality check
It is recommended to perform a test run at 30-40 percent of the planned load. To make sure that the choice of load for the test is rational, it is better to refer to the instructions and clarify the data there.
Keeping the case clean
In the case of traditional batteries with liquid electrolyte, this point is considered not just important, but even critical. Accumulating dust and dirt on the surface of the case, combined with acid vapor, over time turns into a substance that perfectly conducts current. As a result, a closed circuit appears between the terminals and battery compartments. This is the root cause of increased battery self-discharge.
There is no liquid electrolyte in gel batteries, and, as the manufacturer assures, there is no acid evaporation either. However, this does not mean that it is beneficial for the battery to be in a dirty state. Dust and dirt may contain salts and other components that convert fine dielectrics into conductive substances.
Accordingly, a pure gel battery is a healthy and durable battery .
To remove dust and dirt from the surface of the case, it is recommended to use ordinary warm water with soda previously dissolved in it. Such a solution neutralizes almost all components capable of turning pilus into a current conductor.
Do not use household chemicals for cleaning. Also pay attention to the water. It should contain as little salt as possible. To achieve the best results, it is better to take distilled water of proven quality.
It's interesting and useful! You can test the water for salt content in a garage. To do this, connect a regular incandescent lamp to a power source, and one of the wires is cut and the ends are lowered into a container with test water. If the lamp does not glow, the water does not conduct current. Glows - the water contains salt. So, by the way, motorists test distilled water, which is often sold from the tap.
Cleaning the terminals
Over time, white salt deposits appear on the terminals. As a result, contact deteriorates, which often leads to a break in the circuit between the battery and the vehicle's on-board network. To avoid such problems, terminals and fastenings must be promptly cleaned of salts and deposits.
Fine-grained sandpaper is optimal for these purposes (clean without fanaticism). For prevention, after removing plaque and connecting the battery back to the wires, the terminals and fastenings can be treated with Vaseline or grease (also without fanaticism). The goal is to limit the access of moisture and oxygen to lead.
Remember acid batteries
To begin with, it won’t hurt to briefly remember how a lead-acid battery works. Inside it there is a package of plates with negative and positive poles, and between the plates there is a plastic spacer that prevents them from shorting with each other. Total - 6 standard “cans” and 6 packages of plates filled with liquid electrolyte.
The electrolyte has the following composition: 35% sulfuric acid and 65% distilled water. It is the electrolyte, interacting with the lead plates, that allows the charge to accumulate. Water is absorbed, the density of the acid increases.. Thus, charge accumulates inside acid batteries with an output voltage of 12 volts.
When such a battery discharges, sulfuric acid settles on the lead plates, and more water appears in the battery. If it is in the serviceable category, fresh electrolyte can be added to it to restore performance.
Pros and cons of acid battery
Pros:
- Moderate price , up to 5000 rubles.
- Service life 5-6 years (provided good capacity performance).
- Among lead-acid batteries, there are more advanced, maintenance-free options , where there are no plugs on top, and the electrolyte is “sealed” inside. It evaporates, since there is water inside, but cannot leave the jar, condensing downwards.
- Resistant to medium overcharges . It can be charged from 14.4 to 16 V and will hold up despite the high load. The main thing is not to give it a high amperage at such a voltage.
However, they have more disadvantages:
- If the batteries are serviceable, you need to constantly monitor the level and density of the electrolyte . Without constant monitoring, the acid tank will quickly fail, and restoring the battery will become impossible.
- May freeze in cold conditions . For example, if it is discharged to zero, and frosts hit 20-30°C.
- It may explode when overloaded . If the electrolyte is boiling strongly, only one spark is enough for an explosion to occur, releasing volatile hydrogen gas.
- The plates may crumble and the container immediately falls . In this case, it will also be impossible to “reanimate” the battery.
- not allowed to turn the battery upside down or on its side (the plates will be exposed and overheat, and the electrolyte may leak). Store and operate only in a vertical position.
- Cannot be used inside a car due to the release of hydrogen sulfide gas, which is poisonous and hazardous to health.
Gel batteries with an output voltage of 12 V have undeniable advantages over lead-acid ones. Especially in terms of safety. Let us first consider their main features and chemical structure.