Automatic systems for protecting electrical circuits, which replaced fuses, are widely used not only in extensive networks of industrial enterprises, but also in household electrical wiring. The machines are compact, reliable, and easy to operate. You can protect the electrical wiring of your home network using single-pole circuit breakers. But there are often cases when, in order to fully protect electrical installations, it is necessary to install a two-pole circuit breaker. Sometimes a complex electrical network can be protected solely with the help of group circuit breakers.
The peculiarity of multi-pole circuit breakers is that they disconnect several lines at the same time. This property is very useful in three-phase circuits, since disconnecting only one phase wire can lead to the failure of electric motors and other equipment. Similar problems in a two-wire circuit are solved using two-terminal networks.
Design and principle of operation
The design of a two-pole switch is identical to that of a single-pole circuit breaker. In other words, this device consists of two single-pole circuit breakers combined in one housing. Its peculiarity is that in these protective devices, in emergency situations, both protected lines are automatically switched off simultaneously. In principle, you can make a basic two-pole circuit breaker yourself by tightly connecting the control levers of two single-pole circuits with a bar.
Attention! It is impossible to replace a two-pole circuit breaker with two single switches operating separately! You should also not use single switches connected by a jumper as a two-pole circuit breaker. The design of the two-terminal circuit also includes a locking mechanism, which is not present in the “improved” device of single-pole circuit breakers.
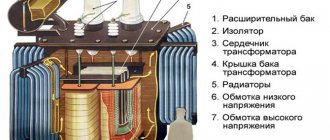
To understand the structure and operating principle of a two-pole circuit breaker, it is enough to understand the structure of a machine with one pole. The simplest such device consists of a bimetallic plate and the design of a charging and releasing mechanism. By the way, the outdated machines looked exactly like this. The design of such a switch is shown in Figure 1.
In situations equivalent to a short circuit or during prolonged overloads in single-phase circuits, the bimetallic plate heats up and, due to deformation, acts on the operating lever of the structure. The protective shutdown mechanism is triggered and the circuit is broken.
Figure 1. Old style circuit breaker
The operating principle of this device is very simple. When the rated currents exceed the permissible parameters, the thermal release actuates the moving contact and the circuit is broken. The power cut-off mechanism can operate in two cases - during an overload or due to a short circuit. To connect the power, it is necessary to eliminate the cause of the operation currents, and then turn on the machine by pressing the control lever.
The operating scheme is simple and reliable. However, it has a significant drawback: the machine does not respond to leakage currents, therefore it cannot protect against electric shock or prevent the wiring from catching fire in the event of sparking. Additional devices are required for complete protection.
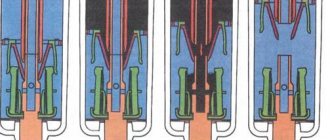
Modern two-pole packages do not have this disadvantage. Figure 2 shows the design of such a circuit breaker. Its design has one important detail - an electromagnetic release. Such two-pole devices combine the functions of conventional differential circuit breakers and a residual current device (RCD).
Figure 2. The structure of a modern machine
Thanks to the electromagnetic release, the charging and tripping mechanism of the two-pole circuit breaker reacts to leakage currents. This is the same blocking device discussed above.
Operating principle of an electromagnetic release.
Along a two-wire line, current flows in two opposite directions - along the phase conductor in one direction, and along the neutral conductor in the other. At the rated voltage, the magnetic fluxes in the solenoid coils, induced by equal counter currents, are compensated. Therefore, the resulting magnetic flux is zero.
But as soon as a leak appears, the balance is disrupted, and the resulting magnetic flux will pull the rod into the solenoid. He, in turn, will activate the levers of the cocking and release mechanism. A two-pole circuit breaker will open 2 poles, regardless of which conductor has a leak or short circuit. The RCD will trip as a reaction to changes in the parameters of the differential currents.
Two-pole machine
Circuit breakers are designed to protect wiring and equipment from overcurrents created by short circuits. They are used everywhere, both to protect household appliances and ensure the safety and safe operation of industrial equipment. However, there is a special type of device that becomes the first obstacle on the way from the substation to the facility. This is a two-pole circuit breaker, or a so-called two-pole circuit breaker.
Device: what are two-pole circuit breakers for?
The design of a two-pole circuit breaker is similar to the mechanism of a single-pole circuit breaker. This device essentially consists of two single-pole modules combined in a housing. Devices of this type are necessary to disconnect two protected lines at once in the event of an accident.
Two-pole circuit breakers are necessary in cases where it is impossible to connect the device to a common network. For example, a transformer has no phase or zero at its output; accordingly, the current flows through both wires, and disconnecting the first wire does not guarantee the neutrality of the second.
To ensure security during operation, a device of this type is used, which is guaranteed to disconnect both lines.
Most often, two-pole circuit breakers are used for:
- Quick shutdown of a circuit section in case of overvoltage.
- Power control of household appliances - they are necessary for washing machines, electric stoves, refrigerators.
- Protection of wiring in overcurrent rooms.
- Convenient and easy network branches.
- Structuring wiring.
The difference between two-pole machines
The greatest difference between such machines and single-pole ones is that the latter monitor the parameters of both lines simultaneously and guarantee that both are turned off when the current parameters change significantly, while a pole circuit breaker controls only one line.
It is impossible to make an equivalent replacement of a two-pole circuit breaker with two single-pole ones, because the two-pole ones have in their design not only a common shutdown lever, but also a special locking mechanism that allows you to quickly de-energize both lines and quickly find problems that have arisen on any of them.
If you install two single-pole circuit breakers, if a malfunction occurs, only the phase will be disconnected. This will not allow you to turn off the zero at the same time, ensuring the safety of the device, because the zero will continue to flow using the second mechanism, which can lead to breakdown or fire of the device.
It is imperative to install a two-pole circuit breaker as an input circuit protecting the line. If you need to provide additional protection to any individual circuits of the network, you can safely use both double-pole and single-pole ones - in this case, both will cope with their role equally well.
Between themselves, two-phase circuit breakers differ in the rated current that can pass through them. For example, a machine with a power of 6A will turn off at a load four times less than 32A. Therefore, a more powerful machine is usually installed on a common apartment network, and options with a power of 5a, 6a and the like are connected separately to household appliances.
Application of two-pole circuit breakers
The scope of application of two-terminal circuits is very wide. Most often they are used in old apartments where single-phase two-wire wiring is installed, that is, where phase and zero are two absolutely identical wires. When connecting in a common switchboard, reversing the phase and zero is not an error, which is why in apartments it became necessary to disconnect both wires in the circuit. When installing a circuit breaker in a three-phase network, grounding wires must not be passed through it.
For the machine to operate correctly, a connection is required in the transformer panel, since it does not have a constant phase and zero. Therefore, when working with it, both lines must be turned off simultaneously.
Two-pole circuit breakers are also necessary to protect against burnout or breakdown of washing machines, refrigerators and other complex equipment, as they absorb sudden changes in network load and help reduce losses from overcurrents that occur during a short circuit to a minimum.
How to connect a two-pole machine
Connecting a two-pole circuit breaker yourself should not cause any particular difficulties, but entrust the matter to an electrician and do not risk working with potentially dangerous devices yourself. Of course, it’s easy to figure out how to connect everything with your own hands, but it is extremely undesirable to install such a mechanism alone - usually even electricians work on the connection in pairs. Therefore, it makes sense to ask someone to help and make sure nothing happens.
The installation of any mechanism of this type is carried out with permission. The procedure for obtaining it is simple; you only need to contact the housing and communal services or management company. If you don't do this, you risk getting a fine.
Attaching the device to a special metal rail is not difficult; just use a regular flat-head screwdriver to pull out the latch located on the back of the object’s body, place it on the special fasteners located on the rail, and release the fastener. The mechanism will latch itself, ensuring reliable fastening to the desired location. The wires are connected to the terminals with special clamping bolts. As a rule, the input wires of zero and phase are connected at the top, and the cores that need to be routed into the circuit are connected at the bottom.
The main thing is not to mix up the places where the wires are connected, otherwise the machine will simply fail.
Machine connection diagram
The general connection diagram is extremely simple:
- An input switch AB is installed in front of the meter.
- A two-pole AV is installed after a meter with a single-phase input.
- It may be necessary to install two or three switches. This depends on the complexity of the circuit in a single-phase network.
Operating principle
According to the principle of operation, a two-pole circuit breaker is not particularly disconnected from single-pole or three-pole versions of the device. In an emergency, the circuit breaker instantly cuts off the electrical current, shutting down the device connected to it and protecting it from damage.
The main feature of a two-pole circuit breaker is that both circuit lines pass through it.
If a fault occurs on any of the lines, regardless of whether it is zero or phase, the device turns off both at the same time, which simultaneously ensures the safety of the unit, since the circuit is instantly broken, cutting off the power completely, and greater convenience when troubleshooting.
Thus, a two-pole circuit breaker is the most important element of protecting the network from overcurrents. If you are not sure of a constant phase or you need to power complex equipment with high energy consumption, you should not hesitate to install a two-pole circuit breaker, otherwise repair costs may be high. And also, do not forget that the device does not protect devices connected to a given network, but only saves the network itself from overcurrents that occur during a short circuit. And it is better to trust any connections of machines to a professional electrician.
Source: https://pauk.top/dvuhpolyusnyy-avtomat.html
Purpose
In the case of a single-circuit electrical circuit, often used in the electrification of houses, it is not advisable to use two-pole circuit breakers to protect the network. This problem is successfully solved by single-pole switches, since there is no particular need to simultaneously disconnect different segments of the circuit. In single-phase wiring with a grounded neutral, when all neutral conductors are short-circuited to neutral busbars, you can also get by with single switches.
A completely different situation arises in cases where some equipment cannot be connected to one common circuit. For example, if a transformer is used to power a group of electrical appliances, then you can’t do without a two-pole circuit breaker. The explanation is simple - there is no phase and zero at the output of the transformer. Cutting off the electric current on one of the wires does not exclude the presence of voltage on the other. Only the simultaneous disconnection of two poles ensures the safety of the equipment.
Installing a two-terminal network allows you to combine the tasks of differential protection and RCD in one device. In this case, it is no longer necessary to install separate discrete residual current devices.
Four-pole circuit breakers operating in three-phase networks using neutral wires operate on a similar principle. Three-pole circuit breakers protect three-phase loads from short circuits.
By the way, the PUE does not prohibit the use of two-pole switches as input circuit breakers. They can also be used to protect group and individual loads. But, under no circumstances should ground wires be connected through this device. Remember that breaking the PE wire is only allowed when removing the plug from the socket.
Application area
- As introductory circuit breakers. This is the most popular method of application. By simultaneously disconnecting the phase and zero, maximum safety is ensured when working in the circuit, because a complete de-energization occurs. In addition, according to the new rules of Electrical Installations (clause 6.6.28, clause 3.1.18), the operation of single-pole circuit breakers at the input is prohibited.
- To protect a separate group of electricity consumers. Disabling the two-pole circuit breaker will prevent the operation of the RCD (Residual Current Device - designed for protection against differential currents) in the event of erroneous contact between zero and phase during repair work in circuits under load. It also makes it easier to find a branch with a fault when an RCD is triggered by a current leak to the ground.
- For protecting and controlling circuits with simultaneous power supply. For example, when connecting a heat gun, a phase is supplied through one pole of the machine to the heating elements, and through the other pole, a phase is supplied to the fan motor. If one equipment turns off, the other will also turn off, which will prevent the possibility of the heating elements operating without cooling.
Advantages and disadvantages
Two-pole circuit breakers provide control of lines with single-phase power supply, as well as protection of equipment operating in three-phase circuits.
The advantages of these devices include:
- reliable protection of homes, offices and industrial premises from network surges;
- the ability to control the power of individual electrical appliances and installations;
- ease of installation and maintenance. Two-pole AVs are ideal for branching and structuring wiring in the electrical supply of premises.
Of course, the main advantage is that a two-pole circuit breaker simultaneously de-energizes two conductors, regardless of which of them the accident occurred. This guarantees a complete absence of voltage in the protective conductors.
Disadvantages include:
- there is a possibility of cable breakdown when two loaded lines are turned on simultaneously;
- in rare cases, if the thermal release fails, an arbitrary power outage is possible even in the rated voltage mode;
- the need to select two-pole circuit breakers in accordance with the design parameters of the network. If the sensitivity of the switch is too high, it will often trip without good reason, and if the speed of reaction to an unusual situation is too low, the machine will not notice the network overload.
Thanks to the unique advantages, the use of two-pole switches is justified even taking into account the existing likelihood of the manifestation of these disadvantages.
Installation and connection diagrams
Mounting devices on a DIN rail is very simple. For this purpose, special grips (latches) are provided on the back side of the machine (Fig. 3). Connecting wires to the device terminal is also not difficult: the wires are easily clamped with bolts on the device terminals. By default, input wires are connected to the upper terminals, and output wires are connected to the lower terminals.
Figure 3. Mounting the machines
The generally accepted connection diagram is as follows:
- An input switch AB is installed in front of the meter.
- After the meter with a single-phase input, a two-pole AB is mounted.
- If a three-phase input is provided, then use a three-pole or four-pole circuit breaker, depending on the connection diagram of the neutral conductors.
In complex branched circuits there may be several two-terminal circuits, after which another single-pole circuit breaker is installed on each branch. An example of such a circuit with a common zero bus is shown in Figure 4. Please note that a two-pole machine is used for phase input. There are no other input devices in this diagram.
Rice. 4. An example of a circuit diagram for switching on circuit breakers
Installation
How to properly install circuit breakers in an electrical panel? First, DIN rails are screwed into it with self-tapping screws - these are metal plates, onto which all automatic devices and RCDs are then attached. The length of the DIN rail can be adjusted using a hacksaw. In addition, distribution terminal strips are attached to the shield. They can be for neutral wires and separately for ground wires. The modern configuration of the tires allows them to be mounted directly on a DIN rail.
Installing a two-pole circuit breaker on a DIN rail is very simple. Using a flat-head screwdriver, you need to pull out the snap-on bracket on the top of the case, attach the machine to the DIN rail and release the fastener. Removal is also carried out. According to the rules, the introductory machine is installed in the upper left corner.
Next you need to connect the wires. The scheme must be strictly adhered to. The phase and neutral input wires are connected to the two-pole circuit breaker from above, and the wires from below are discharged into the circuit. It is important not to confuse: the entrance is from above, the exit is from below, otherwise the machine may fail and will not perform its functions.
You can connect machines using jumpers made of copper wire of the same cross-section as the circuit wire. Jumpers are required to connect two-pole circuit breakers in a row. And also with the help of combs - these are insulated buses, used to connect single-pole circuit breakers.
The ends of the wires are stripped using a special stripper tool or a sharp knife. Then they crimp the cable lugs with a hand tool using a crimper. If there is no such equipment, then you can simply tin the ends with a soldering iron using rosin and tin. When connecting wires to machines, it is necessary to tighten the bolts firmly with a screwdriver so that weak contact does not cause heating and damage to conductive materials.
The grounding wire always passes past the machines directly to the grounding bus. The neutral wires are connected to the neutral bus.
How to choose a two-terminal network?
In order for a circuit breaker to fully provide the necessary protection, it is necessary to carefully select it. The main thing is not to make a mistake with the denomination. To do this, you need to know the rated load that you plan to connect to the device.
The current in the circuit protected by the circuit breaker is calculated using the formula: I = P / U, where P is the rated load, and U is the network voltage.
For example: if a 400 W refrigerator, a 1500 W electric kettle and two 100 W light bulbs are connected to the device, then P = 400 W + 1500 W + 2 × 100 = 2100 W. At a voltage of 220 V, the maximum current in the circuit will be equal to: I = 2100/220 = 9.55 A. The rating of the machine closest to this current is 10 A. But in the calculations, we have not yet taken into account the wiring resistance, which depends on the type of wires and their cross-section. Therefore, we buy a switch with an operating current of 16 amperes.
We provide a table that helps determine the network power to be taken into account when calculating current strength.
| Current strength | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 16 | 20 | 25 | 32 | 40 | 50 | 63 | 80 | 100 | |
| Single-phase network power | 02 | 04 | 07 | 09 | 1,1 | 1,3 | 1,7 | 2,2 | 3,5 | 4,4 | 5,5 | 7 | 8,8 | 11 | 13,9 | 17,6 | 22 | |
| Wire sizes | copper | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1,5 | 1,5 | 1,5 | 2,5 | 4 | 6 | 10 | 10 | 16 | 25 | 35 |
| aluminum | 2,5 | 2,5 | 2,5 | 2,5 | 2,5 | 2,5 | 2,5 | 2,5 | 2,5 | 4 | 6 | 10 | 16 | 16 | 25 | 35 | 50 | |
Using the table, you can accurately calculate the necessary parameters of a two-pole circuit breaker.
As for the stores where you can buy them, focus on prices and product range. From the list of manufacturers we can recommend, for example, the Legrand brand.
Frequently asked questions from readers
Is a two-pole input circuit breaker allowed in a TN-C system?
Yes, it is completely permitted; moreover, I recommend installing it at the entrance to a house or apartment.
A two-pole switch is an excellent switch, as it provides simultaneous interruption of both the phase and neutral conductors, unlike a single-pole one. This is convenient because voltage cannot be supplied from the network through any of the terminals. The fact is that in practice there are often cases when, due to the willfulness of neighbors or the grief of electricians, the conclusions in your house can change places. In such a situation, a single-pole circuit breaker at the input will disconnect not the phase, but the neutral conductor. Which significantly increases the likelihood of electric shock; as you already understand, a system with a two-pole circuit breaker at the input does not have this drawback.
If you are considering this problem from the point of view of the PUE, then here I would like to draw your attention to clause 6.6.28, which reads:
In three- or two-wire single-phase lines of networks with a grounded neutral, single-pole switches can be used, which must be installed in the phase wire circuit, or two-pole ones, and the possibility of disconnecting one neutral working conductor without disconnecting the phase conductor must be excluded.
The design of a two-pole circuit breaker fully complies with this requirement, since both the phase and neutral conductors are broken simultaneously. But it is definitely impossible to replace one double-pole with two single-pole ones, since such a scheme will allow breaking the neutral conductor without disconnecting the phase conductor, contrary to the requirements of clause 6.6.28 of the Electrical Installation Code.