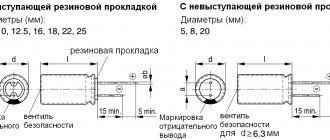
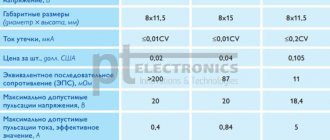
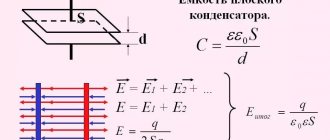
The progenitors of capacitors can be considered a German minister of the Catholic Church named Ewald Jürgen von Kleist and the Dutch physicist Pieter van Musschenbroek, who independently invented a prototype capacitor, the so-called Leyden jar.
More than 250 years have passed since then, designs, shapes and sizes have changed, but the principle of operation and purpose remains the same. Almost no electrical circuit can do without this passive electronic component - this is what Wikipedia and electrical engineering textbooks call a capacitor.
The simplest capacitive device has electrodes called plates. They are separated by a dielectric of very small thickness (relative to the size of the plates). In practice, multilayer capacitors or alternating strips of insulators and electrodes are used.
Classification of capacitors
Capacitors are of the following types:
- electrolytic, for example K50-35 or K50-2;
- ceramic single-layer (K10-7V);
- ceramic multilayer (K10-17);
- tantalum;
- film capacitors.
What a film capacitor is, its functional purpose and scope of application - everything is described in detail in electrical engineering textbooks; brief characteristics will be given here.
A film capacitor is an element in which film serves as a dielectric. It can be made, for example, from fluoroplastic.
Classification
The main parameters of capacitor products are determined by the type of dielectric. The stability of the capacitance, the dielectric loss tangent, the piezoelectric effect and others depend on the material. Based on this, it is advisable to classify models according to the type of dielectric.
Based on this feature, the following types of products are distinguished:
- vacuum;
- with air dielectric;
- radioelements in which the dielectric is liquid;
- with a solid inorganic dielectric (glass, mica, ceramics). Characterized by low leakage current;
- models with paper dielectric and combined, paper-film;
- DC oil capacitors;
- electrolytic;
- category of oxide capacitors, which include oxide semiconductor and tantalum capacitors;
- solid-state, in which an organic polymer or polymerized semiconductor is used instead of a liquid electrolyte.
In solid-state models, the service life is longer than that of liquid electrolytic models and is about 50,000 hours. They have less internal resistance, that is, the ESR is almost independent of temperature, they do not explode.
Products are also classified according to another important parameter - change in capacity. Based on this feature they distinguish:
- permanent capacitors, that is, those that have a constant capacitance;
- variables in which the change in capacitance can be controlled mechanically or using applied voltage (varicaps and variconds), as well as by changing temperature (thermal capacitors);
- a class of tuning capacitors that are used to adjust or equalize working capacitances when setting up circuits, as well as for the purpose of periodically adjusting various circuits.
All existing capacitors can be divided into general and special. General purpose products include the most common low-voltage capacitors (see Fig. 6). There are no special requirements for them.
Rice. 6. General purpose capacitors
All other capacitive radioelements belong to the special purpose class:
- pulse;
- launchers;
- high voltage (see Fig. 7);
- interference suppression
- dosimetric, etc.;
Rice. 7. High voltage capacitors
The devices shown in the photo can operate in high-voltage circuits of relatively low frequency.
Film capacitors
The larger the area of the capacitor plates, the greater its capacity. To increase the area, film devices have been proposed. Due to the large number of layers, an increase in area is achieved, therefore, the capacity is increased.
Film capacitors include K73-17 type capacitors. Designs for different voltage limits make it possible to use them in DC circuits, as well as in various filters and resonant circuits. Capacitive power supplies and rectifier circuits also contain components of this type. The figure shows capacitors for a voltage of 63 V.
Dielectric that can be used for a film capacitor: Teflon, polycarbonate, metallized paper, Mylar, polypropylene. The range of capacitances measured in farads is wide. It ranges from 5 picofarads (this is the smallest possible value) to a maximum size of 100 microfarads. Also, when selecting characteristics, the rated voltage is taken into account, which also has wide limits. Quite often, in various areas, the use of high-voltage capacitors, the voltage of which reaches 2000 volts, is justified.
Various methods of placing dielectric layers and film capacitor plates give the right to classify them into axial and radial. The cases come in both metal and plastic. Shape: rectangular and cylindrical. There is an option without a housing coated with an epoxy compound.
Types of capacitors
A capacitor is two metal plates separated by a dielectric. They are distinguished by the type of dielectric, body material and plate production method. There are these types of capacitors:
- Paper. The plates in it are metal foil, and the dielectric is special paper. They are usually sealed into a metal case, as they are not durable. They behave normally both in low-frequency circuits and in high-frequency ones.
- Metal and paper. They differ in that metal coating is applied to the paper. They are more reliable, and have the same size as paper ones and have a larger capacity.
- Electrolytic. An oxide is applied to metal foil (tantalum or aluminum), which acts as a dielectric. The second layer of dielectric is the electrolyte. It can be dry or liquid. Usually electrolytic is called with a liquid electrolyte. Electrolytic capacitors are almost always polarized. And when connecting them, be sure to observe polarity. Otherwise they will simply fail. There are such subtypes: Although dry electrolyte capacitors are of the same type, they are usually called tantalum. It is with tantalum that dry electrolyte is usually used.
- Aluminum electrolytic capacitors. This is when aluminum trioxide is coated on aluminum foil. They have a large capacity with small sizes, but can only be used in low-frequency circuits. And another drawback is the high leakage current.
- It is correct to call tantalum capacitors made of tantalum foil, in which the dielectric is tantalum pentoxide. They are as compact as aluminum but have lower leakage current. And yet - they are more durable mechanically.
These are all types of capacitors that can now be found on sale and on boards. As you can see, there are a lot of them and they look completely different. Since some of the problems with equipment are related to their failure, it would be nice to understand their markings. This will take less time to find a replacement.
Advantages
A very important property of a film capacitor is its ability to self-heal, which makes it possible to protect the radio element from premature failure. This ensures its high reliability when compared with other types. Another remarkable property is great thermal stability and good electrochemical properties. They also have low series resistance and sufficient AC load capacity, which reduces heating during operation. All of these advantages allow these types to be widely used in radio electronics, computer and electrical equipment, and in many other industries related to the use of circuitry. Disadvantages: low dielectric constant.
Parasitic parameters of capacitors
Capacitors, in addition to their main characteristics, have so-called “parasitic parameters” that distort the operating properties of the oscillating circuit. They must be taken into account when designing the circuit.
These parameters include their own resistance and inductance, which are divided into the following components:
- Electrical insulation resistance (r), which is determined by the formula: r = U/Iout, in which U is the power source voltage, Iout is the leakage current.
- Equivalent series resistance (ESR). This value depends on the electrical resistance of the material of the plates, leads, contacts between them, and losses in the dielectric layer. The ESR increases with increasing frequency of the current supplied to the storage device. In most cases, this characteristic is not important. The exception is electrolytic storage devices installed in the filters of switching power supplies.
- Equivalent series inductance - L. At low frequencies, this parameter, due to the self-inductance of the plates and leads, is not taken into account.
Parasitic parameters also include Vloss - an insignificant value expressed as a percentage, which shows how much the voltage drops immediately after the capacitor stops charging.
Checking the functionality of the capacitor
The easiest way to check the serviceability of the radio element is with a multimeter. In the capacity testing mode, which is available on modern digital devices, you can quickly determine whether the radio element is suitable for further use. Using a pointer tester, it is necessary to monitor the deviation of the pointer. After a small jump, it returns to position “0” or there is a slight deviation. This indicates a malfunction (breakdown). Such a component cannot be used due to the risk of a short circuit in the circuit. If the arrow deviates slightly, but does not reach infinity, there is a so-called leakage current, and the capacity is too small. When using such an element, ineffective operation will result in the functions not being implemented 100%. The use of such a capacitor is impractical.
How to check a film capacitor if it is sealed on the board? By connecting a serviceable element similar to the one being tested into the circuit in parallel, one can conclude that replacement is necessary and understand whether the previous component is operational.
Marking
The capacitance of the capacitor is usually indicated on the housing. The manufacturer has the right to decide for himself what to include in the labeling. To understand, you should carefully study the technical conditions or other technical documentation for the film capacitor. In the international system, it is customary to measure it in farads (on behalf of the famous physicist Michael Faraday). But 1 farad is a large capacitance. To make the task easier, it is customary to use particles: pico-, micro-, nano-, for example, the capacitance of a film capacitor of 100 nf will be equal to 10-7 F.
If the marking of the film capacitor is unclear due to abrasions, you can find out the value of this characteristic using a multimeter with a capacitance measurement function. Typically, a multimeter has five limits. When testing, the probes are connected to special plugs for measuring capacitance with the designation Cx. Polarity must be strictly observed. Sometimes instead of sockets on the panel there are metal plates to which you need to connect the capacitor leads, not forgetting the polarity.
Film capacitors are widely used for operation in various DC and AC circuits, in household equipment and radio electronics, and in designs on printed circuit boards. Many modifications and a variety of overall dimensions allow them to be used with virtually no restrictions in any design.