How to choose the power of an LED lamp?
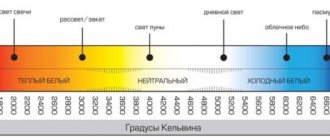
Power: Watt, W (Watt, W) Luminous flux: Lumen, lm (Lumens, lm) Color temperature: K (k). White/yellow, warm/cold... Luminous flux: Lumen, lm (Lumens, lm)
| Incandescent lamp | LED lamp | Light flow |
| 60 W | 8-10 W | ~700 lm |
| 75 W | 10-12 W | ~900 lm |
| 100 W | 12-15 W | ~1200 lm |
| 150 W | 18-20 W | ~1800 lm |
Principle of operation
The source works by emitting wave radiation due to electronic molecular excitation and atoms, as well as due to thermal vibration of the filament molecular nucleus. As the temperature of the filament increases, the translational, vibrational and rotational energy of charged particles increases. As a result, the flux of radiation with average photon energy increases. The radiative wavelength moves into the short-wave infrared and long-wave visible regions. In the future, the body temperature will increase, providing energy that is sufficient to excite molecules and atoms and produce short-wave visible radiation. Therefore, the main factor that determines density with radiation wavelength is temperature.
You might be interested in: Features of a sodium lamp
Operating principle of incandescent lamps
Power of different types of light bulbs
Lamp power and room lighting standards
When choosing a chandelier, ceiling lamp or source of local light for a house or apartment, the buyer thinks in advance about the power of the lamps that will be used there. This is often done on the basis of personal practical experience or, even on a whim. Meanwhile, there are clear lighting criteria that characterize a healthy environment for objects for various purposes. Current regulations and standards recommend following the following illumination indicators for different types of premises (lux):
- Stairs, lobbies, corridors - 20 - 30 lux;
- Bathrooms and toilets - 50 lux;
- Living rooms and bedrooms - 150 lux;
- Children - 200 lux;
- Offices, offices - 300 lux;
- Laboratories, workshops - 400 lux;
- Classrooms - 500 lux.
Regulatory documents operate on two parameters: illumination in lux (lx) and luminous flux emitted by the light source in lumens (Lm). In this case, 1 lux is tied to the area of the illuminated room and is equal to 1 Lm/m2. How can normalized illumination be correlated with the lamp power in watts? To make it clearer, let's look at a simple example. We have a 100 W incandescent lamp installed in a 20 m2 living space. Such a lamp has a luminous flux of approximately 1200 lm, which is equivalent to 1 sq. A meter of area provides 60 lux of illumination, which is clearly not enough for such a room.
So what do we know now? In order to find out whether a room is properly illuminated, you need to know its area, as well as the amount of luminous flux and lamp power, which are indicated on the packaging of the product. Keep in mind that different types of lamps of the same power (W) will have different luminous flux (Lm). Dividing the value of the luminous flux (Lm) by the area of the room (m2), we obtain the actual illumination (lx), which can be compared with the standard one.
Features of the design and operation of different types of lamps
A favorable indoor light environment, necessary for human comfort, is determined by a number of factors that should be taken into account when choosing lamps for lighting an apartment, office, workshop, laboratory, utility room, etc. In addition to the main characteristic - lamp power - the quality of lighting is affected by the color temperature of the spectrum, color rendering coefficient, pulsation, and direction of the light flux. In addition, when operating lamps, one cannot ignore such issues as efficiency, heat dissipation, strength, durability and energy efficiency of lamps. There are several common types of lamps, differing in design and operational characteristics, which we propose to consider in our review.
Incandescent lamps
Incandescent lamps (Il) can definitely be classified as relics of the electric era of lighting. In addition to low cost, lack of pulsation and a pleasant color temperature of about 2700K, close to natural light, the archaic “Ilyich bulbs” have many disadvantages. They have a very fragile glass bulb and are sensitive to mains voltage parameters, which significantly reduce the stated service life of 1000 hours. The low efficiency of light bulbs converts a significant portion of the energy consumed into heat, greatly heating the bulb and base. And the power consumption of incandescent lamps in relation to the luminous efficiency is very high. This is very expensive and wasteful in modern conditions of widespread reduction in energy consumption. But in our review, LNs are interesting because we will use them as a starting point for comparison with other types of light sources.
Halogen lamps
A halogen lamp is an improved version of an incandescent lamp, differing from it in that the filament burns in a protective gas (bromine or iodine). Thanks to this, it was possible to increase the temperature of the coil, which had a positive effect on the increase in luminous flux and increased lamp life up to 4000 hours. The power consumption of halogen lamps, with comparable luminosity to LN, is approximately 30% lower, which allows for slight savings on energy bills. One of the advantages of lamps of this type is the ability to operate in a wide range of ambient temperatures from -60 °C to +100 °C, which makes them similar to conventional incandescent lamps. Halogen lamps also have a good color rendering index of Ra 99-100, which is closest to natural light. But, just like LNs, they get very hot and do not like vibrations. The cost of halogen light sources is significantly higher than traditional lamps, and this makes us think about the advisability of purchasing them for household lighting.
Popular halogen light bulbs Osram HALOSPOT AR111 35W 3000K G53 from 220 UAH. Osram HALOSTAR STARLITE 50W 3000K GY6.35 from 90 UAH. Osram DECOSTAR 20W 3000K GU5.3 from 36 UAH. Osram HALOLINE ST 1000W 2900K R7s from 2,500 UAH. Osram HALOLUX ECO 60W 2700K E14 from 156 UAH. Osram HALOSTAR 20W 2800K G4 from 40 UAH. Osram DECOSTAR 35W 3000K GU5.3 from 37 UAH.
Fluorescent lamps
Fluorescent lamps using gas-discharge glow of a phosphor layer have a higher luminous efficiency per unit of energy consumption than LN and halogen lamps. Therefore, they are also commonly called energy efficient. They have a long service life of 5 years, subject to rare on-off cycles. The power of a 29 W fluorescent lamp is enough to replace one regular 100 W LN. The disadvantages of such lamps include environmental hazards due to the mercury content in their composition, an unpleasant color spectrum and inevitable flickering during operation. Another disadvantage of energy-efficient lamps for the home is the complex spiral shape of the glass discharge tube, which does not look very aesthetically pleasing in home chandeliers.
Popular fluorescent light bulbs
Philips TL 20W SLV G13 from 350 UAH. Philips MASTER PL-C 26W 4000K G24 2P from 119 UAH. Philips MASTER PL-S 9W 3000K G23 from 131 UAH. Philips MASTER TL5 HE 35W 4000K G13 from 105 UAH. Osram HNS 30W G13 from 317 UAH. Osram LUMILUX T8 58W 6500K G13 from 39 UAH. Osram DULUX S/E 11W 4000K 2G7 from 75 UAH. Osram DULUX S 9W 4000K G23 from 75 UAH. Osram DULUX D 26W 4000K G24d-2 from 111 UAH. Osram T5 8W 6500K G5 from 60 UAH. Wolta 11W 2700K GX53 from 35 UAH. Osram LUMILUX T8 18W Natura G13 from 269 UAH. De Luxe F 18W G13 from 47 UAH. De Luxe T8 36W G13 from 110 UAH. Philips MASTER TL-D Super 80 36W 3000K G13 from 44 UAH. De Luxe PL TUBE PL 9W G23 Ultraviolet from 74 UAH. Osram HNS 36W G13 from 290 UAH. Wolta 4U 65W 6400K E40 from 165 UAH. Philips TUV 75W HO 1SL G13 from 875 UAH. Philips TUV 30W 1SL G13 from 275 UAH.
LED bulbs
Currently, LED lamps have become the leader in consumer preferences. In shape and appearance, they are similar to ordinary lamps, with the only difference being that the electronics with LEDs are covered with a durable plastic bulb. With the same luminous flux, the power consumption of LED lamps is almost an order of magnitude lower than that of LNs, which makes them very economical to operate. The most comfortable lamps for human perception have a luminous flux temperature of 2700 - 3000 K, corresponding to natural sunlight. Temperatures from 4000 to 5000 K are considered white neutral light, and anything higher is white cold light. It should be noted that, according to subjective sensations, LED lamps of the same power seem brighter as they shift towards the cold spectrum of color temperature. But, nevertheless, for home use it is better to buy lamps of a “warm” color spectrum, while neutral and cold ones are more suitable for corridor lighting. Unfortunately, LED light sources containing electronic elements are subject to pulsation, which is reduced to acceptable levels in products from well-known brands.
Popular LED light bulbs
Xiaomi Yeelight Led Bulb 1S Color from 579 UAH. Xiaomi Mi Smart LED Smart Bulb Essential from 429 UAH. Xiaomi Yeelight LED Colorful Smart Bulb from 599 UAH. TP-LINK Tapo L510E from 196 UAH. Osram LED Star Remote A60 9W 2700K E27 2pcs from 199 UAH. Xiaomi Mi LED Smart Bulb Warm White from 324 UAH. Philips Essential LEDBulb A60 5W 6500K E27 from 46 UAH. Eurolamp LED 30W 4000K E27 from 180 UAH. Eurolamp EKO A60 15W 4000K E27 from 53 UAH. Eurolamp LED 40W 6500K E27 from 245 UAH. Nomi LYD003 from 199 UAH. Philips Essential MR16 4.2W 6500K GU5.3 from 53 UAH. Nomi LTW004 from 349 UAH. Osram LED Superstar PAR16 6W 2700K GU10 DIM from 107 UAH. Osram LED Star Remote P45 5.5W 2700K E14 from 190 UAH. Gauss LED ELEMENTARY A60 20W 2700K E27 23219 from 90 UAH. Gauss LED ELEMENTARY MR16 5.5W 3000K GU10 13616 from 55 UAH. Osram LED Superstar Classic A60 10W 2700K E27 from 138 UAH. Electrum LED LR-C 6W 4000K GU5.3 from 62 UAH. Feron LB-10 14LED 2W 2700K E14 from 34 UAH.
With the advent of filament lamps (on LED filaments), which are a type of LED lamps, the possibilities for decorating antique-style rooms have expanded. They fit perfectly into loft-style interiors with industrial design of the early 20th century. A distinctive feature of the filament lamp is the replacement of the usual set of optical semiconductors with LED filaments, which have a large scattering angle. The glass bulb of the light bulb is filled with a gas mixture, and the electronics with the driver are placed in the base. There is also no radiator cooling, which is usual for LED lamps. During operation, such a light source is externally difficult to distinguish from a conventional incandescent lamp.
Comparison of power and luminous flux
The table below shows the energy efficiency of different types of lamps that produce the same light output. As can be seen from the comparison of power consumption, incandescent lamps are the most “gluttonous”, and LED lamps are the most practical. For example, a 12-15 W LED lamp produces the same amount of light as a 29 W fluorescent lamp, a 72 W halogen lamp, or a 100-watt incandescent lamp. And taking into account the long service life of LED lamps, which is many times greater than other types of light sources, the benefits of purchasing LED lamps become obvious. Despite their high cost, LED lamps quickly pay for themselves due to their economical operation.
Conclusions and recommendations
It makes sense to use conventional incandescent lamps for lighting only in two cases. The first case is if you do not receive electricity bills. The second case is if the light bulbs are used occasionally and for short periods of time. This is the lighting of basements, cellars, garages and other premises where fate brings you for a short time. Regardless of the power of the lamps, such operation will not significantly affect energy consumption and will extend the life of the lamp.
Halogen lamps are bright lamps, resistant to voltage fluctuations, which provide a powerful omnidirectional beam of light over a long distance; they are actively used in car headlights, in the film and photo industries, in ramp lighting of theater and concert halls, in projection and printing equipment. And this specificity suggests that these lamps are quite in demand and should not be written off yet.
Fluorescent lamps, despite their shortcomings, are still actively used in government and public buildings, educational institutions, and medical institutions. But the times when gas-discharge lamps were purchased to illuminate apartments and houses have happily sunk into oblivion, and they have been replaced by LED lamps.
The undisputed leader among modern light sources for household use are LED lamps, which have a long service life of 10 to 25 years. And the main reason for this is high energy saving rates. Traditional products with a plastic bulb are produced in a wide power range from 3 to 50 W, which allows you to use one lamp of the desired rating instead of a whole set. There are also many products of this type of lamps for ceiling lighting on sale. Retro-style Edison light source modifications are limited to a maximum power of 10 W due to cooling difficulties. Advanced products have a dimming function that allows you to adjust the brightness of the lamps, effectively increasing the lighting power.
To summarize the review, we note that of the variety of lamp types available, the most attractive for home lighting are models with semiconductor LEDs.
How to find out the power of an incandescent lamp without markings
One of the main characteristics of any lamp is its power. Its luminosity also depends on this, especially for incandescent lamps. Knowing the power consumption of the lamp, you can calculate the total energy consumption of the lighting system of an apartment or office. Related articles:
- tester, wattmeter, voltmeter, ammeter
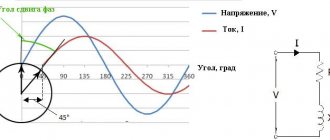
Instruction 1 Most lamps indicate their power consumption and the rated voltage at which the lamp operates. For example, if the lamp says 220 V and 60 W, this means that when connected to a network with a voltage of 220 V, its power will be equal to 60 W. This is the maximum power that this lamp can produce. 2 If the power of the lamp is not indicated on it or it operates in a network with a voltage below the rated voltage (if the voltage is higher than the rated voltage, a short circuit will occur and it will simply burn out), measure its power yourself. Connect the tester in wattmeter mode parallel to the lamp, connect it to a current source, it will show its power.
If you don’t have a wattmeter, you can calculate the power of a working lamp yourself. To do this, connect the lamp to a power source. Connect an ammeter in series to it, and a voltmeter in parallel. Having connected the lamp to the current source, take readings of the current strength from the ammeter in amperes, and the voltage from the voltmeter in volts. For this, you can use a regular tester, only to measure the voltage, connect it in parallel with the lamp, and the current in series. Find the product of current and voltage. The result will be the lamp power in watts. 3 If the resistance of the lamp is known, then it is enough to measure only the current or voltage using a tester. If the voltage is measured, then to determine the lamp power, square its value and divide by the resistance value: P=U²/R. If the current strength is known, then to calculate the power, find the product of the square of the current strength and the resistance value: P=I²•R. When measuring voltage and current on a DC source, be sure to take into account the polarity of the measuring instruments so that they do not get damaged. Connecting devices: Connect the devices when the current source is turned off. Sources:
- lamp power consumption
- Formula for calculating the power of electric current