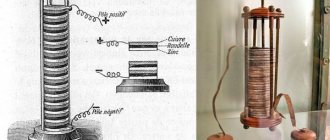
What is a battery
In batteries, electricity is created by the interaction of different chemicals. And the operating principle of these products can easily be found in physics textbooks. All elements are assembled from the same parts.
Battery device
The battery design is simple. The differences between different types of batteries are minimal. Each design is based on:
- The positive pole is the anode.
- The negative pole is the cathode.
- Electrolyte.
Battery operating principle
How does the battery work?
Positively charged particles move towards negative ones. The medium where this movement occurs is the electrolyte. Charged particles are formed during the interaction of different substances. The entire principle of battery operation comes down to a chemical reaction.
The device requires a load in the form of a light bulb or diode, otherwise a short circuit may occur when the “plus” and “minus” contacts occur.
When the cell operates, the anodes oxidize and break down. Over time, the product loses charge and requires replacement. Attempts to restore it will not lead to anything good, because... changes occurring in the battery are irreversible.
If you try to charge the structure, this will lead to an explosion or leak. But scientists, through trial and error, managed to create a rechargeable battery - an accumulator.
Battery operating principle
Current flows from the positive pole to the negative pole. This happens when a load is connected to the battery. If you simply connect the plus and minus wires, a short circuit will occur. As a result, the battery may quickly run out and a fire may occur.
The cathode plays the role of a reducing agent. It acquires electrons from the anode. In an electrolyte environment, ions move well and contribute to good current generation.
What's going on in terms of chemistry?
As a result, when the acid solution and metal come into contact, an electric field is formed at the boundary. At the moment of its appearance, chemical energy is converted into electrical energy. This is the principle of battery operation.
After some time, the battery life will be exhausted. It all depends on where and how the power source is used. For example, if it powers a flashlight, then with moderate use, 2 batteries of 1.5 volts each will last for 1 month. But if you insert these same batteries into an electric machine, it will work for several hours.
As a result of all this, we can conclude that the greater the load, the faster the battery will discharge.
Classification of batteries by electrolyte type (the list is not complete, only the most common ones in everyday life are indicated)
Classification of batteries by type of chemical reaction
| Advantages | Flaws | ||
| Primary | Galvanic elements. The reactions occurring in them are irreversible, so they cannot be recharged. | They are cheaper and have less self-discharge. | Disposable. |
| Secondary | Batteries. The reactions in them are reversible, so they are able not only to release energy, but also to accumulate it. | Multiple uses. More environmentally friendly. | Expensive. Stronger self-discharge. |
Classification of batteries by electrolyte type (the list is not complete, only the most common ones in everyday life are indicated)
Types of batteries by size and their designations
Here we have placed a table that indicates, in addition to dimensions and characteristics, “name” and “labeling”. In essence, this is one and the same thing, and even, as a rule, it is indicated on all elements at the same time. In the USA, a letter designation is accepted (in the “name” column), and it is focused on the physical size of the “battery”.
A car battery is a type of battery that is used in automobiles or motorcycles. Used as a source of electricity to operate the vehicle's on-board network when the engine is not running or to start the engine.
A 12V battery consists of several cans independent of each other - batteries of 2 V each. The batteries are sequentially assembled and connected to each other in one housing.
The active substance contains lead powder with the addition of sulfuric acid. The negative plates contain barium sulfate. During the formation of the battery, the plates are charged, and the active substance turns into lead dioxide, and in negative ones - into sponge lead.
Electrolyte is a special liquid that is poured into battery jars and serves to move charged particles from pole to pole. The electrolyte consists of sulfuric acid and purified distilled water.
Cathodes perform the function of a reducing agent, i.e. accept electrons from the arriving anode. An electrolyte is a medium in which ions that are formed during a chemical reaction move. During the operation of the battery, new substances are gradually formed, and the electrodes are gradually destroyed - the battery runs out.
What types of batteries are there?
Depending on the “filling”, batteries are divided into several types. Salt structures are much cheaper than alkaline ones. They are produced by such companies as Sony and Toshiba. They are descendants of manganese-zinc structures. They are recommended for use in devices with low voltage consumption, such as watches, electronic scales, and control panels.
The most famous are Sony and Toshiba.
A significant disadvantage of these elements is the short charging time. They quickly use up their resources. With prolonged use, elements of this type begin to leak. At subzero temperatures, salt structures do not work.
Alkaline devices appeared relatively recently, in the 60s. last century. They were the first to start producing them. This type of battery is more reliable and has more power.
During long-term storage, unlike salt batteries, they do not lose their charge. Such elements always bear the inscription “alkaline”. But they also have drawbacks. Such elements are more massive. They are installed in children's toys, radios, night lights, in other words, in devices that consume large amounts of energy. Another disadvantage is the high cost.
The third type of mercury products is less popular, because has not become widespread for a number of reasons. First of all, their use had to be abandoned because of the substance by which their work is carried out. Mercury can be harmful to human health.
These elements have 1 significant advantage over other types. There is a possibility of recharging them, but even this did not affect their demand. The advantages of these elements are stable operation at low temperatures and long shelf life without loss of charge.
Home battery charger
The least popular are silver elements. Their electrodes contain silver. This results in longer service life, higher energy density and a constant rated voltage. The big disadvantage is their high cost. A significant advantage is the high capacity, which is many times higher than that of salt and alkaline batteries.
They work equally well at both high and low temperatures. The service life is quite long compared to other types of elements.
Lithium designs were the latest to be developed. They combine the best properties of other types of batteries. They can be used in almost any conditions, and they can be recharged later.
They are the most reliable elements. They are recommended for use in devices with high power consumption.
Differences between different types of batteries
Batteries differ not only in the type of substances involved in the formation of the charge. Batteries are divided into groups according to their shape and size.
According to the form, all elements are divided into 3 groups:
- Disk.
- Cylindrical.
- Square.
Disc batteries are the most popular.
There are 2 ways of marking them: American (less common) and European (more common). Marking helps to accurately select the required battery for the device.
Cylindrical batteries
Cylindrical batteries
The smallest products are marked A23. They are called mini-pinky ones. The next ones on the list are finger ones, their marking is AA. Then come the little fingers - AAA. Rarely, a device may require small pinky fingers - AAAA.
The following 2 types are practically not used: medium - C and large - D.
For cylindrical devices, the voltage indicator reaches 6V.
Square batteries
Square batteries
The highest voltage is produced by square-shaped batteries - up to 9V. But this type is almost not in demand.
Any battery must indicate the type of electrolyte used. The size of each type of battery may vary by 1-2 mm depending on the manufacturer.
The reason for these differences lies in the thickness of the shell, which is used to protect against falls and adverse environmental influences. Most often, it indicates the name of the manufacturer and markings.
Brand designs are of high quality and have a guarantee. Some types of batteries have a special marking - “rechargeable”. This inscription means that the battery can be charged using a special device.
Disc batteries
Disc batteries
Disk designs are produced for very small devices. They, like cylindrical batteries, have their own marking system. The voltage indicator for this type is up to 3V.
Among the variety of batteries, choosing the right one is quite difficult. First of all, you need to focus on the device for which you are purchasing batteries.
For powerful devices there is no point in taking alkaline batteries, because... their charge will quickly run out. In this case, the best solution is lithium. Their service life justifies the high cost.
In addition, device manufacturers often indicate in the instructions what type of batteries are suitable for their equipment.
Chemical processes inside the battery
Briefly about what is happening inside the metal case. Electric batteries consist of two parts, a cathode and an anode, and a liquid or gel that fills a housing that doubles as a housing and a reservoir. The liquid is called an electrolyte and has some chemical activity. The activity is specific - the electrolyte takes electrons from one pole (cathode) and gives them to the other (anode). Where there is an excess of electrons, the result is a “minus” charge, and where there is a deficiency, a “plus” charge.
Based on the type of electrolyte and anode and cathode materials, batteries are divided into:
- Saline. You can recognize them by the R marking. The electrolyte is ammonium chloride. The cathode is zinc, the anode is calcium. These are the cheapest batteries with a small reserve of performance.
- Alkaline. Marking LR. The word Alkaline is also often written. The electrolyte is sodium or potassium hydroxide, the cathode is zinc, the anode is manganese oxide. They have average performance, but are much better than salt ones. Alkaline batteries are capable of creating voltages up to 12 V, but in everyday life they use standard 1.5 V ones. This is more convenient.
- Lithium. CR marking. They differ in that they produce a stable current at different loads. They are used primarily in precision electronics.
- Silver. Marking SR. Zinc anode, silver cathode. They are characterized by high capacity and significant service life. They are used in expensive equipment, for example, good watches.
Mercury batteries are also produced, but due to the toxicity of the liquid metal, they are practically not used in household appliances. They are used mainly in special devices designed for operation at low temperatures.



![Turboloan [CPS] RU March](https://dush-pol.ru/wp-content/uploads/turbozajm-cps-ru-mart-330x140.jpg)