Electricity
What is electricity? | SIMPLY PHYSICS with Alexey Ivanchenko
Electricity or electric current is a directionally moving flow of charged particles, such as electrons. Electricity also refers to the energy obtained as a result of such movement of charged particles, and the lighting that is obtained on the basis of this energy. The term “electricity” was introduced by the English scientist William Gilbert in 1600 in his essay “On the Magnet, Magnetic Bodies, and the Great Magnet-Earth.”
Gilbert conducted experiments with amber, which, as a result of friction with cloth, was able to attract other light bodies, that is, it acquired a certain charge. And since amber is translated from Greek as electron, the phenomenon observed by the scientist was called “electricity.”
Electricity
A little theory about electricity
Electricity can create an electric field around conductors of electric current or charged bodies. By means of an electric field it is possible to influence other bodies with an electric charge.fv
Electric charges, as everyone knows, are divided into positive and negative. This choice is conditional, however, due to the fact that it has long been made historically, it is only for this reason that a certain sign is assigned to each charge.
Bodies that are charged with the same type of sign repel each other, and those that have different charges, on the contrary, attract.
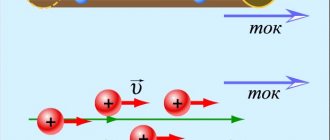
During the movement of charged particles, that is, the existence of electricity, in addition to the electric field, a magnetic field also arises. This allows us to establish the relationship between electricity and magnetism.
It is interesting that there are bodies that conduct electric current or bodies with very high resistance. This was discovered by the English scientist Stephen Gray in 1729.
The study of electricity, most fully and fundamentally, is carried out by such a science as thermodynamics. However, the quantum properties of electromagnetic fields and charged particles are studied by a completely different science - quantum thermodynamics, but some quantum phenomena can be quite simply explained by ordinary quantum theories.
Electricity Basics
History of the discovery of electricity
To begin with, it must be said that there is no such scientist who can be considered the discoverer of electricity, since from ancient times to the present day, many scientists have been studying its properties and learning something new about electricity.
- The first person to become interested in electricity was the ancient Greek philosopher Thales. He discovered that amber, which is rubbed on wool, acquires the property of attracting other light bodies.
- Then another ancient Greek scientist, Aristotle, studied certain eels that struck enemies, as we now know, with an electric discharge.
- In 70 AD, the Roman writer Pliny studied the electrical properties of resin.
- However, then for a long time no knowledge was gained about electricity.
- And only in the 16th century, the court physician of the English Queen Elizabeth 1, William Gilbert, began studying electrical properties and made a number of interesting discoveries. After this, literally “electrical madness” began.
- Only in 1600 did the term “electricity” appear, introduced by the English scientist William Gilbert.
- In 1650, thanks to the burgomaster of Magdeburg, Otto von Guericke, who invented an electrostatic machine, it became possible to observe the effect of repulsion of bodies under the influence of electricity.
- In 1729, the English scientist Stephen Gray, while conducting experiments on transmitting electric current over a distance, accidentally discovered that not all materials have the ability to transmit electricity equally.
- In 1733, the French scientist Charles Dufay discovered the existence of two types of electricity, which he called glass and resin. They received these names due to the fact that they were revealed by rubbing glass on silk and resin on wool.
- The first capacitor, that is, an electricity storage device, was invented by the Dutchman Pieter van Musschenbroek in 1745. This capacitor was called the Leyden jar.
- In 1747, the American B. Franklin created the world's first theory of electricity. According to Franklin, electricity is an immaterial liquid or liquid. Another of Franklin's services to science is that he invented the lightning rod and, with the help of it, proved that lightning has an electrical origin. He also introduced the concepts of positive and negative charges, but did not discover charges. This discovery was made by the scientist Simmer, who proved the existence of charge poles: positive and negative.
- The study of the properties of electricity moved to the exact sciences after in 1785 Coulomb discovered the law about the interaction force occurring between point electric charges, which was called Coulomb's Law.
- Then, in 1791, the Italian scientist Galvani published a treatise stating that an electric current arises in the muscles of animals when they move.
- The invention of the battery by another Italian scientist, Volta, in 1800, led to the rapid development of the science of electricity and a subsequent series of important discoveries in this field.
- This was followed by the discoveries of Faraday, Maxwell and Ampere, which occurred in just 20 years.
- In 1874, Russian engineer A.N. Lodygin received a patent for an incandescent lamp with a carbon rod, invented in 1872. Then the lamp began to use a tungsten rod. And in 1906, he sold his patent to Thomas Edison's company.
- In 1888, Hertz recorded electromagnetic waves.
- In 1879, Joseph Thomson discovered the electron, which is the material carrier of electricity.
- In 1911, the Frenchman Georges Claude invented the world's first neon lamp.
- The twentieth century gave the world the theory of Quantum Electrodynamics.
- In 1967, another step was taken towards studying the properties of electricity. This year the theory of electroweak interactions was created.
However, these are only the main discoveries made by scientists that contributed to the use of electricity. But research continues today, and discoveries in the field of electricity occur every year.
Everyone is sure that the greatest and most powerful in terms of discoveries related to electricity was Nikola Tesla. He himself was born in the Austrian Empire, now the territory of Croatia. His baggage of inventions and scientific works includes: alternating current, field theory, ether, radio, resonance and much more. Some admit the possibility that the phenomenon of the “Tunguska meteorite” is nothing more than the work of Nikola Tesla himself, namely an explosion of enormous power in Siberia.
Nikola Tesla
Lord of the World - Nikola Tesla
Electricity in nature
For some time it was believed that electricity did not exist in nature. However, after B. Franklin established that lightning has an electrical origin, this opinion ceased to exist.
The importance of electricity in nature, as well as in human life, is quite enormous. After all, it was lightning that led to the synthesis of amino acids and, consequently, to the emergence of life on earth.
Processes in the nervous system of humans and animals, such as movement and breathing, occur due to nerve impulses that arise from electricity existing in the tissues of living beings.
Electricity in nature
Some types of fish use electricity, or rather electrical discharges, to protect themselves from enemies, search for food under water and obtain it. Such fish are: eels, lampreys, electric rays and even some sharks. All these fish have a special electrical organ that works on the principle of a capacitor, that is, it accumulates a fairly large electrical charge and then discharges it onto the victim who touches such a fish. Also, such an organ operates with a frequency of several hundred hertz and has a voltage of several volts. The current strength of the electric organ of fish changes with age: the older the fish becomes, the greater the current strength. Also, thanks to electric current, fish that live at great depths navigate in the water. The electric field is distorted by the action of objects in the water. And these distortions help fish navigate.
Solar power plant
Deadly experiments. Electricity
Getting electricity
Power plants were specially created to generate electricity. At power plants, with the help of generators, electricity is created, which is then transmitted to places of consumption via power lines. Electric current is created due to the conversion of mechanical or internal energy into electrical energy. Power plants are divided into: hydroelectric power plants or HPPs, thermal nuclear, wind, tidal, solar and other power plants.
In hydroelectric power plants, generator turbines driven by the flow of water produce electric current. In thermal power plants or, in other words, thermal power plants, electric current is also generated, but instead of water, water vapor is used, which arises during the heating of water during the combustion of fuel, for example, coal.
What is electricity - about the nature of electricity - I.P. Kopylov - Yu.N. Ivanov - Global Wave
A very similar operating principle is used in a nuclear power plant or nuclear power plant. Only nuclear power plants use a different type of fuel - radioactive materials, for example, uranium or plutonium. Their nuclei fission, resulting in the release of a very large amount of heat, which is used to heat the water and turn it into water vapor, which then enters a turbine that generates electric current. Such stations require very little fuel to operate. So ten grams of uranium generates the same amount of electricity as a car of coal.
Why is there 220 volts in the outlet?
Use of electricity
Nowadays, life without electricity is becoming impossible. It has become quite integrated into the lives of people in the twenty-first century. Electricity is often used for lighting, for example using an electric or neon lamp, and for transmitting all kinds of information using telephone, television and radio, and in the past, telegraph. Also, back in the twentieth century, a new area of application of electricity appeared: a power source for electric motors of trams, subway trains, trolleybuses and electric trains. Electricity is necessary for the operation of various household appliances, which significantly improve the life of a modern person.
Today, electricity is also used to produce quality materials and process them. Electric guitars, powered by electricity, can be used to create music. Electricity also continues to be used as a humane method of killing criminals (the electric chair) in countries that allow the death penalty.
Also, considering that the life of a modern person is becoming almost impossible without computers and cell phones, which require electricity to operate, the importance of electricity will be quite difficult to overestimate.
Electricity in mythology and art
In the mythology of almost all nations there are gods who are capable of throwing lightning, that is, who can use electricity. For example, among the Greeks this god was Zeus, among the Hindus it was Agni, who could turn into lightning, among the Slavs it was Perun, and among the Scandinavian peoples it was Thor.
Cartoons also have electricity. So in the Disney cartoon Black Cape there is an anti-hero Megavolt, who is able to control electricity. In Japanese animation, electricity is wielded by the Pokemon Pikachu.
An ordinary miracle of natural phenomena
It is interesting that the bodies of humans and many living creatures are not only conductors of electrical impulses, but are also capable of generating this energy independently. Illustrative examples are electric stingrays, lampreys and eels, which have special processes in the structure of the body that serve as a kind of accumulative needle, with the help of which they hit the victim with a discharge with a frequency of several hundred hertz.
Most scientists believe that the human body is like a power plant with an autonomous self-regulation system. There have been cases when people not only survived being struck by lightning, but also gained healing from illnesses and new abilities. Each of these lucky people had strong natural immunity, as a result of which the shock of natural electricity only strengthened their innate strength.
There are many phenomena in nature that prove that electricity is an integral part of it and exists everywhere:
- The fire signs of St. Elmo have been familiar to sailors since ancient times. In appearance, they look like brush-shaped candle lights in soft blue and purple shades, and their length can reach one meter. Appear during storms and thunderstorms on the spiers of ship masts. The sailors tried to break off the ends of the masts and go down with the torch, but this was never successful, since the fire spread to other high-lying objects. It's surprising that the fire doesn't burn your hands and feels cold to the touch. The sailors believed that this was a gracious sign from Saint Elmo that the ship was under his protection and would arrive safely at the port. Modern research has shown that the unusual fire is electrical in nature;
- Aurora - many small elements arriving from the depths of space accumulate in the upper layers of the atmosphere. They collide with particles from the lower layers of the air shell and dust particles with different charge poles, resulting in chaotically moving light flashes of different colors. This glow is typical for the polar night period and can last for several days;
- Lightning - changes in atmospheric flows cause the simultaneous formation of ice floes and drops. The frictional force from their collision fills the cumulus clouds with powerful electrical charges. From the contact of clouds with opposite charges, a powerful light emission occurs in thunderclaps. When the lower layers of the atmosphere are filled with electrical charges, they can combine into one whole, and the result is ball lightning, which moves along a rather low trajectory and is very dangerous because it can explode when colliding with a living creature or a static object.
You may be interested in Description of the megohmmeter, purpose of the device and principle of operation
In addition to alternating and direct current, there is also static electricity, which occurs when the balance within atoms is upset. Synthetic fabric has the ability to accumulate it, which is expressed by small sparks when clothing moves while changing clothes and a pricking sensation when touching a person or metal.
This is a very unpleasant sensation, and in large doses it is harmful to health. Static radiation also comes from televisions, computers and household appliances, which electrify dust. Therefore, in order to preserve your health, you need to wear clothes made from natural fabrics, not stay near electrical appliances for a long time and clean more often.