When working with station and linear electrical equipment, great importance is attached to protecting the worker from high voltage and electric shock. For these purposes, special electrical protective equipment is used to ensure reliable protection for people working on electrical installations. Complete information on the classification and list of protective equipment for work in electrical installations is contained in the “Instructions for the use and testing of protective equipment used in electrical installations” SO 153-34.03.603-2003.
Electrical protective equipment: types and requirements for them
According to the method of application, all known protective equipment (PE) are conventionally divided into those used by one person - personal protective equipment (PPE) and collective ones - structurally associated with the production process, equipment, premises. According to their functional purpose and the effect they provide, they are:
- isolating or enclosing;
- used for high-altitude operations;
- shielding.
Additional information: Based on voltage, these products are divided for operation in networks up to 1000 V and more than 1000 V.
Insulating electrical protective equipment is usually divided into two types:
- The main ones are the insulation of which withstands the operating voltage of the electrical installation for a long time and allows you to work on live parts that are energized.
- Additional – they complement the main ones, they serve to protect against step voltage and touch voltage, but by themselves they do not provide protection against electric shock.
The requirements placed on them are, as a rule, determined by their intended purpose (ability to withstand the voltage of an electrical installation). In addition, they must be in good working order and have a mark indicating the last test period. Rubber products should not show signs of staleness, as well as cuts and punctures visible to the naked eye.
Insulating protective equipment for electrical installations with voltages above 1000 V
This type of protective equipment and working tools is represented by the following main items:
- insulating rods;
- insulating pliers;
- voltage indicators;
- devices and devices to ensure work safety during measurements and tests in electrical installations;
- special protective equipment, insulating devices and devices for work under voltage in electrical installations with voltages of 110 kV and above.
Basic electrical protective equipment up to 1000 V
The main insulating protective equipment against voltage is largely the same as additional protection equipment over 1000 (V). Basic electrical protective equipment up to 1000 (V) includes:
- Insulating rods. Helps avoid electric shock.
- Seamless dielectric gloves. Protects the electrician's hands from injury.
- Insulated clamps and electrical clamps. They are necessary for safe operation of devices. The second clamp option helps determine the voltage. If an electrician uses pliers, he should be equipped with gloves and goggles.
- Low voltage indicators.
- Hand tools with insulation. It is necessary for various jobs. These include metalworking tools with insulated handles. The thickness of the insulation depends on the type of task being performed.
The considered electrical protective equipment in electrical installations up to 1000 (V) guarantees the necessary safety of the employee.
Means of protection against high-tension electric fields, collective and individual
When work is carried out on overhead lines and outdoor switchgear with voltages of 330 kV and higher with an electric field strength of up to 5 kV/m, the time spent in the work area without protective equipment is not limited. At a voltage value from 5 to 25 kV/m it is limited by the state standard, and at a voltage value above 25 kV/m it is not allowed.
Protective equipment against high-intensity electric fields includes shielding kits used during work operations on overhead power lines (OHL) or at ground level in outdoor switchgear type switchgears. According to the method of arrangement, such protection is divided into the following types:
- removable shielding devices (installed on machines and mechanisms);
- stationary, portable and mobile shielding devices;
- individual shielding kits.
Among the products described, we will highlight individual shielding kits, made in the form of protective equipment worn by a person. Collective shielding systems are designed to protect an entire group of people. They are made of conductive material and are connected to grounded objects (to the protective circuit).
Individual protection means
The last type is electrician’s PPE. Personal protective equipment against electric shock is used by only one employee. Electrician personal protective equipment includes:
- Glasses. Protects eyes from damage from small particles.
- Fencing.
- Mittens.
- Belts and ropes.
- Plastic helmets.
- Respirators and gas masks.
Description of the most common additional and basic protection measures
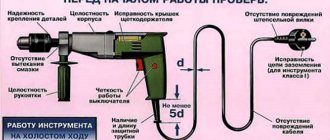
The most common equipment is gloves. They are used for all work. Before testing, they must be checked for leaks. Gloves that have not passed the test are prohibited from being used.
Plumbing tools are used for work at voltages not exceeding 380 V. Their handles are insulated with plastic handles. They perform a protective function.
Voltage indicators are equipped with a special indicator. A luminous indicator indicates the presence of voltage in the equipment.
Insulating pliers are made only of plastic. They are used to mount and dismantle various elements, most often fuses.
Procedure and general rules for using protective equipment
Each worker carrying out work in an electrical installation must be provided with the necessary protective equipment and trained in the rules for their use, and must also use them and comply with the following general requirements:
- use only those products that are marked (indicating the manufacturer, name or type of product, date of manufacture and test stamp);
- before the next use, personnel working on the electrical installation must check the serviceability of the protective agent used, the absence of external damage and contamination and, according to the stamp, the expiration date;
- If the protective equipment is found to be unsuitable for use, it is confiscated, which is recorded in the logbook for recording and maintaining the protective equipment or in operational documentation.
When working, do not touch directly the working area of the product, as well as that part of the insulation that is located behind the limit stop.
Additional electrical protective equipment up to 1000 V
Additional electrical protective equipment in electrical installations up to 1000 (V) is necessary to fully equip and protect the electrician. Technical methods of protection against electric shock include:
- Insulating stand, caps, covers and covers. Stands are placed on the floor where electricians will work.
- Dielectric mat. Can be used like a stand. It is more convenient to use. But the mat is not suitable if there is water on the floor. It must be inspected and checked periodically before use as it may be damaged.
- Insulating fiberglass (dielectric) stepladders and ladders.
- Dielectric galoshes.
- Bars for leveling and transferring potential.
Procedure for storing protective equipment
The effectiveness of electrical protective equipment depends on many factors, including compliance with the rules for their storage. In this case, the following mandatory requirements must be met:
- it is necessary to store protective equipment indoors, in conditions that ensure their serviceability and suitability for use;
- protective equipment made of rubber and polymeric materials are stored in cabinets or on racks separately from the tools and be protected from the effects of acids, alkalis, oils, etc., as well as from exposure to sunlight and thermal radiation from heating devices;
- protective equipment is placed in specially equipped places at the entrance to the premises, on control panels.
Equipment check
Each inventory must have appropriate documents, which must indicate the following data: name, manufacturer, date of manufacture and test period. The last point is the most important.
All protection methods are tested upon commissioning. Other checks and their number depend on the type of protective equipment. GOST and TU specify the conditions and time of testing, the frequency of testing and inspections. For example, stepladders are inspected once every six months, and gloves are inspected before each use.
What devices are classified as electrical protective equipment - Fire safety
Insulating protective equipment in electrical installations makes it possible to protect personnel performing maintenance work in existing electrical installations. The danger of electrical installations lies in the increased likelihood of electric shock and thermal effects of an electric arc.
The type and purpose of electrical protective equipment has a direct impact on ensuring safety from voltage exposure. Each electrical protective device, depending on its purpose and the voltage class of the electrical installation (up to 1000 Volts or higher), can provide protection for personnel either completely or be used as an additional means of protection.
A significant percentage of accidents in electrical installations that occur annually are due to the fact that workers ignore labor safety requirements and incompetently use protective equipment during work. Knowledge of the correct use of electrical protection products is invaluable when working with electrical equipment.
Greetings to all readers of the site “Electrician in the House”. Friends, in today’s article I would like to tell you about what is included in the concept of basic and additional means of protection in electrical installations , their list, methods of application and use.
What protection means are used in electrical installations
When performing work in electrical installations, regardless of which area or department they belong to, maintenance personnel must use various protective equipment to prevent electric shock. Any electrical protective agent is divided into two types: basic and additional. What is their difference?
The main means of protection in electrical installations withstand voltage for long working hours and are used during work when the equipment does not need to be disconnected from the network. That is, a worker, using the main means of protection, can safely work on equipment whose live parts are energized.
Additional protective equipment in electrical installations cannot provide 100% protection for personnel from electric shock; it is used in conjunction with basic equipment.
I present a screenshot of what the literal definition sounds like and what a “primary and additional” protective agent is according to the rules.
We should talk in more detail about the essence of electrical protection means in electrical installations with voltages up to and above 1000 Volts and the requirements for them.
Special protective equipment
Special protective equipment that allows you to avoid electric shock includes all kinds of devices and devices, the actions of which are used for narrowly targeted purposes. One of them is various protections designed to automatically turn off the electrical circuit in the event of an emergency:
- Automatic current switches and contactors;
- Differential protections that respond to current leakage during insulation breakdown;
- Insulation control;
- Voltage protection, etc.
Portable grounding connections are installed to connect live parts to the ground. As a result, the residual electrical charge is removed and subsequent control of the lack of potential occurs. In case of accidental occurrence of electric current, a protective shutdown of the electrical installation will occur.
Shunt rods and jumpers - installed when working under voltage. They allow you to equalize the potential and ensure the passage of currents through the insulating sections. If potential equalization is not possible, the protective device will trip.
Isolating towers and hoists – provide electrical resistance to isolate personnel performing live work.
Rice. 3. Insulated towers
To protect the organs of vision from an electric arc or possible sparking, special glasses are used as a protective device, which are mandatory in a number of technological processes.
Means of protection against electric current, list, frequency of inspection, rules of application
Protective equipment against electric shock includes all devices, apparatus and instruments, the purpose of which is to prevent injury to people working with energized equipment.
Damage factors include not only electric shock, but also possible exposure to an electric arc or combustion products of electrical equipment. There are basic and additional means of protection. The first are those whose insulation provides complete protection from the operating voltage of electrical installations. They allow you to work and touch live elements that are energized. For equipment with voltages up to 1 kV, the main means of protection (hereinafter referred to as SZ) are considered to be dielectric gloves, special tools protected with insulated handles, electrical clamps, voltage indicators, insulating rods.
For electrical installations with voltages above 1 kV, the main
means of protection against electric current are the same as in installations up to 1 kV, plus devices that ensure safety during testing or measurements, as well as when carrying out repair work on electrical installations (cable puncture devices, cable damage marks, voltage indicators, insulating ladders , polymer insulators, etc.).
Additional protective equipment is also used (dielectric carpets, boots, galoshes, pads, caps, potential equalization rods, etc.), which are not able to guarantee safety, but reduce the risk of electric shock and the degree of its impact.
Depending on the impact, collective and individual means of protection are distinguished.
For electrical protection equipment, safety conditions must be observed: they must be stored dry and free of mechanical damage. Before use, a thorough inspection should be carried out, during which damaged specimens are rejected. Dielectric gloves, galoshes, carpets and boots should be no closer than half a meter from heating devices. In addition, they should not be exposed to direct sunlight or industrial liquids (oils, kerosene, gasoline, alkalis, acids, etc.).
The means of protection against electric current used must undergo regular testing, and the date of testing is marked on the product. SZ tests are carried out at the enterprise where they are used, or at nearby substations. Dielectric gloves should be checked every six months, insulated tools and voltage indicators should be checked once a year, and dielectric mats should be checked once every 2 years.
General technical means of protection
For rooms with a high degree of electrical hazard (concrete floor, high humidity, etc.), where if the insulation is damaged, the human body will be the only resistance in the current flow circuit, it is necessary to use a reduced supply voltage, a power tool with a reduced voltage or with double insulation of current-carrying elements . The reduction is carried out both through transformers - to obtain alternating current, and with the help of semiconductor power supplies to obtain direct current.