Safety precautions when working with electricity
In the 21st century, every person is closely connected with electricity. Household electrical appliances, light, and the operation of any industrial enterprise cannot do without current. If a malfunction occurs in the electrical network, apartment owners often begin troubleshooting on their own. Working with electricity is very dangerous, so you need to know safety precautions when working with electricity. In this article we will look at the dangers when working with electricity, safety precautions, and prevention methods to increase electrical safety in the home.
TB during operation of household electrical appliances
In this case, it is necessary to adhere to the rules and regulations that indicate safety precautions when working with electrical equipment. Following them will minimize the risk of electric shock. We recommend focusing on the following points:
- Do not use faulty household electrical appliances;
- if there are signs of abnormal operation (sparks, smoke, change in noise level, etc.), shutdown should be performed immediately;
- stationary electric heating devices (boilers) must be grounded and connected only through an RCD.
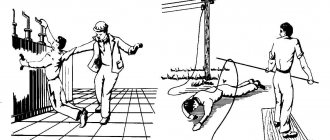
The last point requires a little explanation. The heating elements installed in such devices may lose their tightness over time; the result of this is clearly shown in Figure 8.
Figure 8. The probe shows the presence of phase in the water coming from the boiler
The presence of the phase in water can pose a serious danger to life. Many fatal accidents have been recorded due to this reason. That is why when installing a boiler, special protection based on RCD circuit breakers is required. But for its reliable operation, it is necessary to ensure that the body of the electric heating device is grounded. Actually, this requirement is specified in the instructions for the electrical device, which states that operation without grounding is prohibited.
Source
Electrical Hazards
When an electric shock occurs, the human body suffers harm, often incompatible with life. Every year, 15-20% of electricians suffer due to non-compliance with safety regulations. An electric shock of 35 volts can be fatal. The most common cause of accidents when working with electricity is interaction with exposed wires that are live. The consequence of the effect of current on the human body is uncontrolled muscle contraction, due to which a person cannot tear himself away from the current source, which is the main difficulty and danger of electric shock. All internal systems of human life are stressed. If electrical impulses reach the heart, they can cause it to stop.
Electric shock
This danger is created if safety precautions are violated when operating electrical equipment. Electric shock is possible through direct contact with conductive elements of the unit that are energized. The passage of a discharge through the body is accompanied by biological, electrolytic, and thermal effects. The latter manifests itself in the form of burns in certain areas of the body, heating of blood vessels and blood. Biological effects are accompanied by irritation of body tissues, which, in turn, can lead to the cessation of the functioning of vital systems. The electrolytic effect manifests itself in the decomposition of blood.
Electrical Safety Techniques
To maintain your health, you must follow the following rules for working with electricity :
- It is forbidden to check the presence of current with your hands. Do not operate or touch electrical appliances with damp or wet hands. Also, do not allow water to come into contact with electrical appliances.
- Do not bend or twist live electrical wires.
- When replacing lamps, the surface you are standing on must be dry.
- When troubleshooting the electrical network, you should completely turn it off.
In addition to the listed rules, there are household safety equipment , the knowledge of which is necessary for every person.
- Do not use sparkling electrical appliances. It is also prohibited to use faulty sockets or switches. Monitor their condition, and if they overheat, turn off the power supply. Only then fix the problem. It is not allowed to turn electrical appliances on and off with both hands.
- It is prohibited to connect a large number of devices to the electrical network if the total power exceeds the permissible limit.
- Do not stay near operating power transformers. Stay away from exposed or sagging wires, especially after a hurricane or thunderstorm. A safe distance of at least 10 meters.
- Do not install electrical appliances near flammable objects. Minimum distance 0.5 meters.
- The use of devices that cause a tingling sensation when touched is prohibited.
- Do not insert metal objects into sockets.
- Do not allow children to play near electrical outlets in damp areas.
- A fire that occurs in an electrical network must not be extinguished with water, since it is the best conductor of current.
Basic safety rules at home
- When working in wet areas, you must use a rubber mat and gloves;
- Before connecting a new electrical device to the network, you must carefully study the instructions and strictly follow all instructions for its operation;
- Avoid all dangling power lines, do not touch them under any circumstances, and do not approach transformer installations;
- When operating industrial and household equipment, it is necessary to urgently stop using electrical equipment if sparks appear and a burning smell is felt. It is also prohibited:
- connect several powerful electrical appliances to one outlet at the same time;
- touch wires and electrical equipment with wet hands or while on a wet floor;
- use devices other than for their technical purpose;
- bend equipment cables, both during operation and during storage, so as not to damage the insulation, etc.
- Check for the presence of electricity in cables with bare hands, touch bare wires;
- It is strictly forbidden to use faulty sockets, switches, extension cords;
- Touch live electrical devices with wet hands;
- Leave household appliances (irons, fireplaces and wind blowers, electric stoves) unattended for a long period of time;
- When replacing lighting fixtures, all work is carried out strictly with dry hands, standing on a dry surface;
- In the event of an electrical appliance fire, turn off the circuit breaker; under no circumstances try to unplug the cord from the outlet.
- When carrying out wiring repairs, completely de-energize the entire network.
Methods for preventing and increasing electrical safety at home
To maintain a normal level of electrical safety in everyday life, it is necessary to carry out certain preventive measures aimed at increasing it.
- When installing an electrical appliance, you must follow the operating instructions for the device.
- All equipment must be grounded.
- Once every six months, check all electrical appliances in the room for faults.
- Use fencing protective equipment that is responsible for protecting from live parts (boards, cage fencing, insulating caps).
- To increase electrical safety, it is necessary to use signaling devices that make it clear about any malfunction.
- Safety protective equipment. They include goggles, gas masks and mittens. During preventive measures, they are responsible for the individual protection of the electrician.
- Do not leave lamp sockets hanging from wires as this may cause shorts or sparks.
In this article, I described the rules for working with electricity and ways to increase the level of electrical safety. When working with electricity, remember these rules, and you will not encounter the unpleasant consequences of electrical injuries. Use preventative measures to ensure your family's electrical safety.
Source
Electrical safety rules in everyday life
The insidious feature of electricity is that it is invisible, odorless, colorless, and a person cannot detect it, since he does not have the appropriate senses for this.
Electric current strikes suddenly when a person is included in the current flow circuit. A dangerous situation arises when, on the one hand, it touches faulty insulation or a metal object that is accidentally energized, and, on the other hand, the ground, central heating pipes and other grounded objects.
Below are the rules, the daily observance of which will not only help prevent an accident, but will also be a good prevention of fire in your home.
Basic rules for safe handling of electrical energy.
1. Strictly follow the order of connecting an electrical appliance to the network: first connect the cord to the device, and then to the network. Switching off the device is done in the reverse order.
2. Do not insert the plug into the outlet with wet hands.
3. Warning for music lovers: never place plugged-in electrical equipment on the edge of a bathtub of water or in close proximity to it, so as not to expose yourself to mortal danger.
4. When you wash the refrigerator or other electrical appliances, change a light bulb or fuse, make sure that they are disconnected from the power supply.
5. Do not touch the heated water and the vessel (if it is metal) when the electric heater is plugged in.
6. Do not use electrical appliances with damaged insulation.
7. Do not remove the plug from the outlet by pulling on the cord (it may break, exposing live wires). Do not repair electrical plugs with electrical tape; replace them immediately if they are damaged.
8. Do not use an electric iron, stove, kettle, or soldering iron without special non-flammable stands.
9. Do not use indoor electrical appliances (kettle, iron, table lamp, etc.) in other places where there is no floor that does not conduct electric current. (An earthen floor may cause electrical shock.)
10. Do not plug in more than three electrical appliances. If you connect powerful energy consumers (electric kettle, toaster, iron), try not to use them at the same time.
11. Do not leave electric heating devices plugged in unattended.
12. Do not use paper or fabric as a screen or lampshade for a light bulb.
13. Do not try to repair burnt-out plugs using a homemade bug.
14. When leaving home, turn off the lights and electrical appliances.
Also remember that touching dangling or lying wires on the ground is always dangerous - you can get electrocuted as a result of damage to power lines.
Basic rules of electrical safety at home
To operate household equipment safely, you must adhere to the following basic rules:
- You cannot use electrical appliances in which the wire insulation is damaged or missing, so before starting work you need to carefully inspect all wires regarding their serviceability and possibility of operation;
- It is not recommended to use switches and sockets with damaged housings;
- It is prohibited to operate devices with an open, removed or broken protective casing;
- You cannot start repairing electrical equipment if it is connected to the network; it is also not allowed to repair electrical wiring if it is not disconnected from the network;
- it is prohibited to replace industrial fuses with homemade wire jumpers;
- It is not allowed to place any objects on electrical wires;
- It is not allowed to lay wires from electrical appliances behind gas, water or heating pipes;
- If there are small children in the house, it is recommended to use special plastic plugs for electrical outlets or special outlets in which protection is structurally provided.
In order to avoid problems during the operation of electrical appliances, it is necessary to carry out their maintenance in a timely manner, monitor the grounding and monitor the condition of the insulation on the wires. You also cannot create emergency situations on your own. Electrical appliances must be used strictly for their intended purpose.
Safety precautions when working with electricity
Occupational health and safety is a set of principles relating to occupational safety and health, as well as a separate branch of the science of creating appropriate working conditions. Safety issues in handling electric current are very relevant, especially in production conditions.
The term "safety" has different meanings in practice and can refer to keeping a threat under control, a state in which the risk is at an acceptable level, or a state that meets a safety standard.
Safety precautions when working with electricity
The concept of a household electrical network and its dangers
The electrical network (household electrical) is a set of electrical installations designed to transmit and distribute electricity from the station to the end user.
The main parameters of household electrical networks are voltage, maximum permissible current, wire cross-section, rated currents. The household electrical network is considered as a power source for household electrical appliances and lamps.
The widespread use of electrically powered devices poses various types of risks to people:
- the impact of static electricity on humans and on technological processes;
- electric shock and arc burns;
- danger of fire and explosion;
- negative effects of strong electromagnetic fields.
What current is considered unsafe
Electric current differs in the degree of effect on a person. It is classified as follows:
- tangible;
- not letting go;
- fibrillation.
The voltage of the first type of current is 0.6 mA. When struck by this type of current, the victim feels irritation.
The second type of current can cause convulsive movements of the muscles of the limbs in contact with exposed wires.
The third type of current can cause serious problems in the functioning of the heart. Death from cardiac arrest is possible.
In different situations and under different conditions of the body, the consequences of electric shock can also be different. A current of 15 mA is considered dangerous to humans. In this case, a person cannot free himself from its influence on his own. A current of 50 mA causes serious damage to human health. A current of 100mA for 1-2 seconds can become dangerous and cause cardiac arrest. A current whose frequency is 50-500 Hz is considered dangerous.
Dangerous current for humans
Safety regulations in industrial production
Safety precautions imply a set of technical and organizational measures, the purpose of which is to create safe working conditions at the enterprise, as well as to prevent accidents.
Any enterprise, especially those engaged in production, creates favorable working conditions for its employees in terms of labor safety. For this purpose, financial resources are allocated in the company.
Note! At larger enterprises, a special occupational safety service is created, whose responsibilities include monitoring compliance with safety regulations in the company. Electrical safety rules are central to the security team's work.
Providing protection
Protection against electric shock is a set of technical measures that reduce the risk of electric shock, as well as organizational and legal measures aimed at ensuring the safe operation of equipment, installations and electrical networks. They allow people to work safely.
Technical means of protection against electric shock carried out in production include:
- basic protective equipment (from direct contact);
- protective measures in case of damage (indirect contact);
- protective measures that complement the basic protection.
Organizational electrical safety practices implemented primarily by users of devices, installations and networks include:
- organization of work (training, instructions);
- qualification requirements;
- protective equipment;
- individual and collective protective measures;
- other measures related to ensuring occupational safety and health.
The implementation of these measures consists, first of all, of ensuring the electrical safety of persons performing work on electrical devices, working on these devices, and near active electrical devices.
Technical and organizational security measures should create a system of coordinated basic protection, damage protection measures and additional measures.
Protection against electric shock
Clothing requirements
Persons working on or near electrical devices must be equipped with appropriate protective equipment against electrical shock, arc hazards, and mechanical damage.
Depending on the purpose, protective equipment in production is divided into:
- insulating equipment that provides protection against the flow of electric current through the human body. This group of insulating equipment includes:
- insulating supports (portable, measuring and installation portable grounding devices);
- pliers and insulation holders for fuses;
- boots, galoshes and electrically insulating gloves, rubber mats and rugs;
- isolated instruments;
- isolation platforms;
- equipment used to determine the presence of voltage: voltage indicators and phase equalizers;
- equipment for protection against voltage occurrence: grounding devices, portable and winding;
- equipment for protection against electric arcs, combustion products and mechanical hazards;
- auxiliary equipment: portable fencing and insulating boards, fencing and cables, insulating gaskets, warning boards and protective nets.
Electrical protection clothing
Personnel protection
The safe execution of production work depends, first of all, on a thorough knowledge of the design and operating principles of electrical devices and installations, the correct sequence of operations and strict adherence to the principles of work organization and the requirements established in the relevant occupational health and safety regulations.
Note! Compliance with health and safety regulations and rules is the primary responsibility of the employee.
In particular, the employee is obliged:
- become familiar with the provisions and principles of occupational health and safety in the workplace, take part in training and instruction in this area and pass the necessary examinations;
- perform work in accordance with the provisions and rules of occupational safety and health at the workplace and adhere to the orders and instructions of superiors;
- take care of the proper condition of machinery, instruments, tools and equipment, as well as the order and order of the work place;
- Each company employee who works with electrical equipment with voltage up to 1000 volts is required to have group 3 safety clearance.
Safety precautions when handling electric current
The life of a modern person is inextricably linked with electricity, because it greatly simplifies and facilitates the solution of current everyday problems, thereby saving time and effort. In everyday life, everyone comes across electricity, without even thinking about observing safety precautions when handling and working with electric current. As for industrial facilities, all employees whose work is directly related to professional electrical installations undergo annual (quarterly) training aimed at complying with safety regulations, passing exams by a specially created commission. All this is regulated by a specialized decree of the Russian Ministry of Energy - “Rules for the technical operation of consumer electrical installations” dated January 13, 2003.
Every year, additions and clarifications are made to the decree. It reveals the basic requirements and basic knowledge that personnel must have regarding safe work with professional equipment; basic first aid skills in case of electric shock; sequence of actions in the event of accidents; the responsibility of managers and team leaders, as well as the frequency of certification and internships. At the end, an exam is taken and the examiners receive a corresponding certificate. This procedure is mandatory and does not imply refusal to undergo it.
Consequences of defeat
Let's consider several situations in which current can pass through the body:
- the man grabbed the exposed live wire with both hands;
- the person is on the ground and touches the exposed wire with his hand;
- a person is standing on the ground in the area of faulty grounding;
- the person touched his head to conductive elements;
- dangerous routes are those that pass through vital organs.
The table below shows the consequences of electric shock.
| Electric current | Type of manifestation | |
| Variable | Constant | |
| Up to 1.5 mA | Minor finger cramps | It is not felt and is safe |
| Up to 3 mA | Increased trembling of the limbs | Not felt |
| Up to 7 mA | Convulsive movements are involuntary | Burning sensations |
| Up to 10 mA | Increased pain sensations | Increased heating |
| Up to 25 mA | Sticking effect. Severe pain | Intense heat. Minor cramps |
| Up to 80 mA | Respiratory and possibly cardiac arrest | The heating is stronger. The movement of the hands is involuntary. Difficulty breathing |
| Up to 100 mA | Stopping breathing. More than 3 s - cardiac arrest | Stopping breathing. |
Note! In any case, the consequences of the lesion may vary depending on the person’s condition and his individuality.
Fire Prevention
One of the central measures to prevent fires due to electric shock is the problem of correct selection and operation of electrical equipment, installation of electrical installations and cables to eliminate the possibility of short circuits or overheating.
Other prevention measures include:
- all elements must be correctly selected according to heating conditions;
- all electrical installations must have special protection for disconnecting from the network in the event of danger;
- use of flexible cables;
- Do not place flammable liquids near electrical installations;
- use of energy saving lamps.
Electrical fire
Precise and strict compliance with safety requirements when working with electric current is a reliable guarantee of a high level of fire and electrical safety.
Source
Fundamentals of labor protection organization
The widespread use of electricity in all areas of production, as well as in everyday life, in addition to many advantages, also involves many risks, both for humans and for their work and living environment.
Safety precautions when working with electrical appliances
Labor protection is a system for preserving the life and health of people in the process of carrying out their work activities.
Improperly operating electrical equipment can cause electric shock, breakdown, fire and explosion.
Important! Electrical current used in homes, offices, workshops and shops can also cause serious injury or even death.
Safety precautions when working with electric current
So, if you need to change a light bulb in a lamp that is connected directly to the home electrical network, it is not enough to simply flip the switch button. The main safety rule when working with electric current states that in this case, you need to completely de-energize the electrical network at home.
In addition, when working with electricity, the following safety rules must be observed:
- It is prohibited to repair any electrical appliance if its power cord is connected to an outlet or junction box. It is important that the outlet be de-energized before further work with electricity is carried out.
- When performing repairs or installation of electrical equipment, you should only use tools whose handles are reliably protected by insulating material. If the handles of the tool have an inscription in the form “1000 V”, for example, this means that the tool cannot be used with voltages above 1000 Volts. Of course, you will not find such voltage in a home electrical network, but still, this must be taken into account when performing electrical installation work.
- Having turned off the fuses in the electrical panel, you should, if possible (while carrying out work with electricity), close it and hang a sign on the door stating that repair work is being carried out and that it is prohibited to turn on the fuses of the panel.
- Even after completely de-energizing an apartment or house, you should still make sure that there is no voltage in distribution boxes, sockets, etc. This can be done, for example, with a multimeter, a voltage indicator, or a screwdriver with a special voltage indicator.
- You should know that there are a number of electrical jobs that should only be performed by a qualified electrician. First of all, this is work with electricity meters, input voltage and grounding of the house.
- In addition, you need to remember that couplings, burnt wires and plugs are not subject to further repair, but only to complete replacement.
What should you not do when working with electricity?
When working with electricity, it is strictly forbidden to lean your elbows, lean on, or touch metal parts of an electrical panel, distribution cabinet, etc. with your bare hand. It is best to stand near such electrical equipment on a special rubberized mat or on a dry mat that does not conduct electric current. .
It is often necessary to replace fuses, but it is strictly forbidden to install any metal objects in the socket in place of a blown fuse that could replace it.
Each fuse is designed for a certain current strength, and if you insert a metal nail into the fuse socket, for example, this is fraught with unforeseen consequences, including a fire.
Source
Safety precautions when repairing electrical equipment and electrical networks
3.3 Safety precautions when repairing electrical equipment and electrical networks
All repair work on existing electrical equipment should be carried out only when the voltage is removed from the electrical installation being repaired. In some cases, PTBs allow small-scale troubleshooting work to be carried out without relieving tension. In electrical installations with voltages up to 380 V, such work is permitted (with the exception of particularly dangerous premises) by an electrician with a safety qualification group in the presence of a second person, senior in position, with group IV or V.
Work on the repair of electrical equipment is carried out according to an approval order, order or in the order of current operation with an entry in the operational log according to the list of tests in accordance with the list of works performed by electrical personnel in the order of current operation, approved by the chief power engineer.
Inspection, testing and repair work related to the supply of voltage can be carried out by at least two persons, one of whom must have a qualification group of no lower than 4 when working in electrical installations over 1000 V and no lower than 3 in electrical installations up to 1000 V.
In the handles of all disconnecting devices, with the help of which voltage can be supplied to the place of work, warning posters “Do not turn on - people are working” are posted.
Power supply to temporary circuits for repairs, checks and tests of electrical networks must be carried out through a switch, switch, closed circuit breaker with protection and clear indication of the on and off position. To avoid danger that may arise for personnel repairs or erroneous supply of voltage to the section of the electrical network being repaired, all phases of the disconnected part are grounded and short-circuited. Before applying grounding to the area being repaired, check that there is no voltage.
If it is necessary to carry out repairs in an existing electrical network from which it is not possible to remove the voltage, then the work is carried out wearing dielectric gloves, standing on rubber mats. When making measurements using a megger, the area being tested is first disconnected from all sides from where voltage can be applied to it. The person responsible for repair and testing work is responsible for ensuring that all safety measures are implemented.
Repair rooms must be kept clean and tidy and avoid clutter. Waste materials, rags, shavings, sawdust must be regularly removed to specially designated areas. Wiping materials should be stored in metal boxes with lids. The veil is used, has the ability to spontaneously combust, must be removed daily; in the event of a fire or fire, immediate measures are taken to eliminate it and at the same time the fire department is reported
3.4 Fire safety measures
The most common causes of fires and explosions are electric sparks and arcs; overheating of conductors due to short circuit currents and due to overloads, unsatisfactory condition of contacts at the points where wires are connected or connected to the terminals of electrical equipment are unacceptable. The insulation of wires of electrical machines and transformers may catch fire due to damage to the insulation and overload with currents.
To avoid unacceptable overheating of conductors, sparking and the formation of electric arcs in machines and devices, electrical equipment for fire-hazardous and explosive electrical installations must be selected in strict accordance with the requirements of the Electrical Installation Rules. To avoid unacceptable overloads and short circuit currents, electrical protection of wires and electrical receivers should be used.
Electrical equipment used in electrical installations must provide the necessary degree of protection for their insulation from the harmful effects of the environment and safety against fire or explosion due to their malfunction. In this regard, there is the following classification of electrical equipment: open, protected, drop-proof, splash-proof, waterproof, closed, dust-proof, dust-proof, sealed, explosion-proof, explosion-proof, especially explosive and others.
4. PROTECTION OF SUBSOIL AND ENVIRONMENT
4.1 Environmental problems in the oil industry.
Large complexes of the oil and gas industry transform almost all components of nature. More than 3 billion tons of solid industrial waste, 500 km 3 of hazardous wastewater and about 1 billion tons of aerosols, varying in size and chemical composition, are annually released into the atmosphere, water bodies and soil in the world. The main wastewater pollutants include drilling fluids (especially dangerous oil-based ones), chemical reagents, as well as despirated clays, drilled rocks, weighting agents (mechanical impurities), lubricating oils, drill cuttings containing all the chemical compounds used in the preparation of drilling fluids. Pollution generated during well killing remains dangerous. When a spent solution is injected into a well during killing and repair, due to excessively high pressure, open emissions from the wells occur, contaminating the soil with oil, petroleum products, clay solution and highly mineralized waters.
Toxic pollution contains about 800 harmful substances, including mutagens that affect heredity, carcinogens - on the emergence and development of malignant tumors, nerve and blood poisons - on the functions of the nervous system, blood composition. Their content in the air in some cases is 3-10 times higher than the maximum permissible concentrations.
Atmospheric pollution with the appropriate composition and concentration can cause the death of plants and animals, as well as people.
Source