Types of artificial lighting
Artificial lighting can be general, local, combined and emergency. General lighting
This type of lighting is characterized by a uniform distribution of light throughout a given space. To implement this, light sources are located equidistant from each other.
Chandeliers are also a source of general lighting, however, there is no question of any uniformity of lighting in this case.
Local lighting is in addition to the general one, helping to create additional visibility in certain areas: lighting a desk or cooking area in the kitchen, illuminating a painting in a museum or mirrors at a dressing table.
Most often, room lighting involves the simultaneous use of general and local views, since it solves absolutely all functional problems.
This type of lighting is used as a safety net for others in places where a temporary lack of light can lead to injury to a person.
Emergency lighting, in turn, is divided into safety and evacuation lighting.
Safety lighting is turned on so that the business can continue to operate, and evacuation lighting is turned on so that people can leave the building without risk of injury when normal lighting is turned off.
- Emergency lighting is turned on during non-working hours to provide minor illumination of the room.
- Security lighting is part of the security system; it illuminates the perimeter of the protected facility at night.
There are several types of lighting for houses and apartments that are used, including for highlighting zones in the interior.
Artificial lighting and its classification
Artificial lighting – lighting a room only with artificial light sources.
Artificial lighting according to its intended purpose is divided into the following types:
·working – lighting that provides standardized lighting conditions (illumination, lighting quality) in premises and in places where work is carried out outside buildings;
emergency (Emin ≈ 5% Erab, but not less than 2 lux) – divided into:
Safety lighting (emergency, it is allowed to use incandescent and fluorescent lamps. Safety lighting is provided in cases where the shutdown of working lighting and the associated disruption of maintenance of equipment and mechanisms may cause:
explosion, fire, poisoning of people,
long-term disruption of the technological process, etc.
evacuation (usually with a number of people of more than 50 people, illumination of passages, sites, basements, Eevak is created at least 0.5 lux, open space at least 0.2 lux) lighting;
· special, which in turn is divided into:
security - lighting during non-working hours (out of the total number of lamps, a part will be allocated that must provide lighting of at least 0.2 lux);
duty - lighting during non-working hours.
Artificial lighting can be of two systems (by design):
general lighting - lighting in which lamps are placed in the upper zone of the room evenly (general uniform lighting) or in relation to the location of equipment (general localized lighting);
combined lighting - lighting in which local lighting is added to general lighting; local lighting – lighting, additional to the general one, created by lamps that concentrate the luminous flux directly on the workplace. The use of local lighting alone for production workplaces is not permitted.
Artificial work lighting is intended to create the necessary working conditions and normal operation of buildings and territories. Working lighting should be provided for all areas of buildings, as well as areas of open spaces intended for work, the passage of people and traffic.
Combined lighting is lighting in which natural lighting, insufficient by standards, is supplemented with artificial lighting.
27. Basic lighting units and requirements for industrial lighting.
Organization of rational lighting of workplaces is one of the main issues of labor protection. With unsatisfactory lighting, labor productivity sharply decreases, accidents, myopia, and fatigue are possible.
Lighting is characterized by quantitative and qualitative indicators. quantitative indicators include luminous flux, luminous intensity, illumination, brightness.
Luminous flux Ф is the part of the radiant flux that is perceived by human vision as light (measured in lumens - lm).
Luminous intensity I is a quantity that evaluates the spatial density of the luminous flux and represents the ratio of the luminous flux dФ to the solid angle dw within which the luminous flux propagates:
The unit of luminous intensity is the candela (cd).
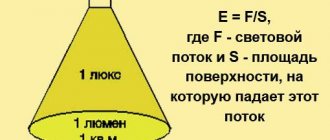
Illumination E - surface luminous flux density, is the ratio of the luminous flux dФ incident on a surface element dS to the area of this element:
3a the unit of illumination is taken to be lux (lx) - with a luminous flux of 1 lm over an area of 1 m2.
Surface brightness L is the ratio of the intensity of light emitted in the direction under consideration to the area of the luminous surface, cd/m2:
The main qualitative indicators of lighting include: background, contrast of the object with the background, visibility, glare and discomfort indicator, pulsation coefficient.
Background is the surface adjacent directly to the object on which it is viewed.
Visibility is the ability of the human eye to perceive an object at illumination levels from 0.1 to 100,000 lux.
The glare index is a criterion for assessing the glare created by a lighting installation.
The main task of industrial lighting is to create the best conditions for vision. This problem can only be solved with a lighting system that meets the following requirements:
— lighting in the workplace must correspond to the nature of visual work
— it is necessary to ensure a fairly uniform distribution of brightness on the working surface, as well as within the surrounding space;
— there should be no sharp shadows on the working surface;
— there should be no direct or reflected glare in the field of view (increased brightness of luminous surfaces causing glare);
— the amount of illumination must be constant over time;
— you should choose the optimal direction of the light flux and the required spectral composition of the light;
— all elements of lighting installations must be durable, electrical and fireproof;
— the installation must be convenient and easy to use, and meet aesthetic requirements.
What types of lighting are there?
Any human activity is associated with light. There are different types of lighting. The light entering a room can be natural or artificial. There is also the simultaneous use of both types, called combined.
Natural lighting is such lighting in which the luminous flux comes from natural sources. Its intensity depends on the daily movement of the Sun and the geographic location of the area. The flow of light under artificial lighting comes from devices created by man. Different types of lighting fixtures are made using physical processes that produce glow.
Using natural light sources
Natural light is the most beneficial for the eyes. Its main source is the Sun. Daylight is not only good for health, but also economically beneficial. For the fullest use of solar energy, buildings are designed with wide windows and glazed openings are provided in the roofs. Premises intended for housing or industrial activities are designed to ensure maximum solar energy. Depending on the way the light flux enters the room, different types of natural lighting are distinguished. Natural happens:
- entering through the window - side;
- entering through the roof - upper;
- combining both methods - combined.
A separate type can be considered the use of glass atriums, which are hemispheres, domes or pyramids. The solar spectrum is ideal for visual perception, but the uniformity of illumination changes all the time due to the movement of the Sun. Surface illumination is measured in lux (lx). The natural light factor is calculated as the ratio of internal illumination to external illumination. It takes into account the size and type of window glazing, the degree of glass contamination, and determines the effectiveness of insolation systems.
How much light does a person need?
To assess luminescence, the following physical quantities are used:
- Light flow. This is the amount of energy emitted by a source in the visible spectrum per unit time, i.e. power. Measured in lumens (lm).
- Illumination. This is the luminous flux per unit surface area. It is measured in lux (lx). With illumination of 1 lux per 1 sq. m of surface receives a luminous flux of 1 lm.
The second indicator depends on the following factors:
- luminous flux of the source;
- distance from it to the illuminated surface.
The required illumination depends on the type of activity (indicators are given in lux):
- The minimum required for a comfortable state is 200.
- For actions not related to looking at small objects - 300.
- For working with texts or at the computer, in meeting rooms - 500.
- For reading or making technical drawings - 750.
Low light will cause eye strain and quickly cause eye fatigue.
When the reading is less than 200 lux, a person experiences depression and drowsiness.
Artificial light
Natural light is not always able to provide the illumination necessary for human activity. For most types of work, natural light is not enough. Rain, snow, external and internal contamination of windows reduce the intensity of light. Since ancient times, people could not exist without the use of additional devices that increase illumination.
Depending on the direction of action of the artificial light source, lighting can be general, local or combined. The types of artificial lighting are determined by their purpose:
- The work is used to create good visibility on transport and pedestrian routes, in any premises, necessary for the smooth flow of work processes;
- Emergency - used to provide light to places where an emergency situation may occur if the main one is turned off. It is used to prevent dangerous situations and technological disasters. A production process stopped for a long time is also considered an emergency;
- Forced evacuation of people is ensured by evacuation lighting. It should make it possible to distinguish the direction of escape routes (room floor, stairs);
- The boundaries of territories subject to protection are supplied with light sources; this is a security type of lighting;
- Lower lighting compared to the main one, used during non-working periods for visual control of territories and premises, is called duty lighting;
- Façade is used in urban landscape design;
- Parking serves to ensure visibility on traffic routes in green areas and is an element of design.
Evacuation and emergency lighting can be divided into 2 options: to function when the working light is on, or to turn on when the main light is turned off.
Artificial
People illuminated their living space with fire torches, torches, candles, and kerosene lamps. And when they learned to produce electrical energy, incandescent lamps, fluorescent lamps, and LEDs became light sources.
Incandescent, fluorescent, LED lamps
Artificial lamps are used:
- for premises and territories for various purposes;
- street decor;
- landscape design;
- creating outdoor advertising;
- The artificial lighting system includes emergency and security lighting.
Street lights
Lamps must meet fire safety standards NPB 249-97. Their type depends on the tasks that are solved by installing lighting devices. Artificial lighting according to the principle of its design is divided into general, local and combined. The combined lighting system, combining the advantages of general and local, is widely used in premises for various purposes.
General lighting of the area
The organization of general light provides a favorable visual environment, allowing a person to freely navigate the surrounding space. Electric light is distributed evenly throughout the entire area. The main lighting is created using stationary lighting fixtures. If ceiling pendant lamps are used, they must be equipped with overhangs of no more than 1.5 m. In high-risk areas, lamps of protection class II or III are used. AC or DC voltage up to 220 V is used for power supply.
Organization of general light
Zonal and local
Zonal and local lighting allows you to create special light conditions in individual areas. Local can be used both in combination with the main one and independently. A dedicated backlight is simulated for a specific area or object. Based on the characteristics of the room and the goals set, diffused and directional lamps and neon lighting are used.
Neon illumination of the auditorium in a cinema, which does not interfere with watching the film
In production workshops, local lighting is created on an individual or group basis. Each workplace is equipped with an individual lamp. Local installations equip several workplaces at once: conveyor lines, machine tools, testing consoles, control tables.
Assembly line
To create local stationary light, a voltage of up to 220 V is used. In case of increased danger, stationary and portable lighting devices up to 50 V are used. The luminaires are powered from autonomous sources or from separating transformer devices.
You may be interested in this Features of a lamp with a motion sensor
Decorative
Decorative lighting, popular in modern design, is optional. Installed in a residential building or public building, it may not perform functional tasks. With the help of lighting effects, a special environment is created that promotes complete rest and relaxation. Decorative lighting can be accent lighting: draw attention to a mirror, painting or artistic composition. Spotlights, LED strips, and directional light flux devices are used.
Decorative lighting of the painting
Architectural, advertising and display
Artificial illumination is used for architectural and artistic illumination of building facades, monuments, sculptural compositions, trees, and green landscapes. With the help of electric lamps, street and shop window illuminated advertising structures are created.
Bolshoi Theater, TSUM
Important! Architectural and advertising lighting is designed in a single complex with the lighting of streets, squares, and roads. Power supply for architectural lighting of buildings, retail displays, illuminated advertising is carried out through independent distribution lines or from the building network. Allowable power, no more than 2 kW per phase with a power reserve.
If the lighting equipment has a protection class of at least 1P54 and is installed at a height of up to 2.5 from the earth's surface (service area), it is permissible to use a voltage of up to 380 V. Retail display lights equipped with incandescent lamps up to 100 W are installed on fireproof bases. They can be installed on wooden bases covered with sheet steel.
Emergency
Emergency lighting is divided into safety and evacuation lighting. Emergency systems are installed in buildings (residential, industrial, public, including shopping malls, business centers, restaurants) and in open areas.
Security Lighting:
- activated in case of emergency shutdown of working lighting;
- allows you to create the minimum necessary conditions for continued work in cases where stopping the production process could disrupt the normal functioning of the enterprise or cause serious consequences for people.
Evacuation:
- used for evacuation in case of emergency power outage;
- Special emergency lamps are used to mark emergency exits.
Evacuation exit
It is recommended to use lighting devices with incandescent or fluorescent lamps. Lamps and light indicators should not be connected to a common electrical network. They turn on automatically in the event of an emergency shutdown of a worker.
Outdoor and security
Lanterns and spotlights installed above the roadway, on embankments, along sidewalks, squares, park alleys, squares, illuminate:
- transport routes;
- pedestrian areas;
- public transport stops;
- bike paths;
- courtyards and playgrounds;
- ponds and landscape compositions.
You may be interested in Features of spot lighting
With the help of outdoor (street) lighting, a safe, comfortable environment for people is created. The system includes illuminated information boards and pedestrian direction indicators, which must be turned on 24 hours a day.
Moscow at night
The streets are illuminated with high-pressure sodium discharge lamps, LEDs and metal halide lamps are used. The lamps are mounted on special supports, suspended on cables, and secured using brackets. Objects that should be illuminated in cities, towns, and villages are determined by local executive committees. External lighting is designed in accordance with current GOSTs and SNiPs.
The installation height of lighting devices above the roadway must be no lower than 6.5 m, above the tram overhead contact network - no lower than 8 m to the rail head, above the trolleybus overhead contact network - no lower than 9 m from the roadway level, above pedestrian areas and boulevards - not below 3 m.
Important! Lighting networks are powered via independent lines, created by SIP wires or cables with protection against overloads and short circuits. In open areas, in low-rise buildings, air networks are protected from lightning strikes.
Security systems are used to protect the perimeters and areas around buildings. They are autonomous and turn on automatically. The security system can operate in the following modes:
- permanent work (on duty);
- activation upon activation of alarm systems (alarm).
Security lighting system for the territory
Lamps should form a continuous chain of light 3-4 meters wide around the protected area. Devices are used that provide instant access to the nominal parameters of the luminous flux. It is recommended to use incandescent lamps. Infrared lamps with a constant or modulated wavelength are used for hidden protection. In open warehouses, floodlights are used that are installed on metal masts. Lamps can be suspended from ropes stretched over the platform, mounted on supports made of metal or reinforced concrete.
Railroad tracks, highways, stations, and parking lots are equipped with security lighting. For transport tunnels, it is recommended to use lighting devices with a degree of protection of IP65.
Lighting systems
All types of lighting used in everyday life and in production are created using special systems. General lighting can be provided by a traditional light source - a ceiling lamp or chandelier. At home, the role of light source is most often played by incandescent lamps, energy-saving or LED devices.
Local lighting is designed to provide high illumination to individual areas, such as workplaces. A feature of local lighting systems is that the light is concentrated on a specific area, rather than distributed evenly throughout the room. The apartment contains several areas that require additional lighting. In addition to the desktop, it needs a food preparation area, a place for reading, and a mirror in the bathroom.
A functional approach to providing the required light intensity allows you to select the appropriate lamp for each zone. To organize local lighting, traditional lighting devices, as well as track systems, are used. The latter are distinguished by increased power and the ability to change the position of the light source. With the help of track (bus) models, industrial premises, studios, and offices are illuminated.
Most often in everyday life and in production there are systems that include both types - combined. The need to combine general and local light sources arises when the main, overhead light is not enough.
Street lighting
According to the intended purpose, street lighting is:
- General. Designed for safe movement around the yard (illumination of paths, porch of a private house, steps, etc.)
- Security. It is used to protect a personal plot, as well as the country house itself.
- Decorative. Most often used in landscape design to decorate the appearance of the territory.
All types of lighting used today are presented here.
If you need lighting items, you can look in our catalog. Share post
Typical division
Based on the direction of the light rays, the following types of lighting are distinguished:
- general - for uniform distribution of light in the space as a whole;
- directional - to achieve the required illumination of a specific area;
- indirect (reflected) - when light rays are directed at the walls and ceiling, and uniformity of lighting is achieved due to reflection;
- diffused - occurs due to the passage of light through a lampshade made of translucent material;
- mixed - combines the last few types; it can be obtained using modern table lamps and some models of pendant lamps.
The main types of artificial lighting, distinguished by the direction of the luminous flux:
1) Directional or direct. Involves directing a light source towards a specific surface or object. As a result of directional lighting, an object is visually enlarged by emphasizing its volume and shape. In a living room, table lamps, spotlights, built-in lamps, floor lamps with shades, etc. are used for this.
2) Indirect. This type of artificial lighting is also called reflected, as it is obtained by directing the light flux to the ceiling or walls, from which it is reflected and illuminates the room. In a living room it can be implemented using lamps with a luminous flux directed upward or onto the walls. Reflected light visually increases the area of the room and is most effective in a bright interior.
3) Diffuse lighting is obtained as a result of the passage of light through a translucent or matte lampshade and is scattered throughout the room. One ceiling lamp with diffused light can illuminate a small room.
4) Mixed. It is obtained by combining the above types of artificial lighting. A lamp with mixed lighting can distribute the luminous flux in different directions and through a translucent shade or lampshade.
By light source
First of all, lighting is divided into artificial and natural, which in our opinion is the most important indicator. The natural source of light is, of course, the sun's rays that penetrate the room through window openings and other design solutions. In turn, natural lighting can be divided into the following systems:
- Lateral, when light passes through the windows in the walls.
- Top – light passes through glazed coverings or technological openings.
- Combined - the room is illuminated by windows and upper openings.
It should be noted that this type of lighting is the main one and in rooms where people spend most of their time, natural light must necessarily prevail. If for some reason it is not possible to create openings for the penetration of sunlight, artificial lighting is additionally organized, which is divided into the following systems:
- General – the lamps evenly illuminate the entire area of the room.
- Local – additional illumination of important objects, for example, a workplace.
- Combined - a combination of general + local or natural + artificial can be used.
Also, according to the light source, lighting can be divided into such special types as fluorescent, LED and halogen. You can learn more about light sources in our corresponding section of the site.
By purpose
If we talk about how the types of electric lighting are divided according to their functional purpose, then first of all it is necessary to conditionally include such a nuance as the scope of application. Today it is customary to consider types of lighting in production, indoors and outdoors. It is in relation to these objects that we will perform the division.
Production
In a production environment, lighting can be:
- Working – used to ensure normal, and most importantly safe, working conditions for personnel at the enterprise.
- Emergency - designed to maintain minimum illumination at the time of an emergency, if turning off the light could lead to dangerous situations (explosion, fire, etc.). According to the standards, the illumination created by emergency lamps should not be lower than 5% or 2 Lux in the building or 1 Lux on the street.
- Evacuation - the name of the type speaks for itself; evacuation lighting is used to evacuate personnel to a safe area. Illumination in this case should not be less than 0.5 Lux indoors and 0.2 Lux in open areas.
- Security - used to protect the territory, should not be less than 0.5 Lux.
- Duty is a subtype of security system. For the operation of emergency lighting, some of the lamps used for working or emergency lighting are used to ensure minimal illumination in the protected area, as well as in places where duty is carried out at the enterprise.
All these points are briefly but clearly discussed in the presentation:
House and apartment
As for the interior, there are two main types of lighting in a house and apartment: natural and artificial. Natural light in residential premises can be side, top or combined, we have already talked about this. But as for the artificial, in this case it is customary to divide it into the following systems:
- General or as it is also called – basic. This is accomplished by installing ceiling lights that evenly illuminate the entire room.
- Local (functional) – used for local illumination of certain objects, for example, a work area in the kitchen, a desk in a nursery, or a mirror in a bathroom. For local lighting, wall sconces, floor lamps, table lamps and spotlights are used, which emit bright directional light.
- Decorative. This type of interior lighting is intended for additional decoration of rooms and individual objects. As an option - illumination of paintings, the perimeter of the ceiling (LED strip), etc. Decorative also includes festive.
You can learn more about light in the interior from this video:
In the garden, the types of lighting are very similar to those that are usually organized in the interior. So, according to purpose, street lighting is divided into the following types:
- General (functional). Designed for safe movement around the yard. This includes illumination of paths, the porch of a private house, steps, as well as garden buildings (chicken coop, garage, outbuilding).
- Security. Used to protect the garden plot and the country house itself from ill-wishers. For external security of the territory, illumination of the entire perimeter of the site, parking lot, main entrance to the home and other important areas is organized.
- Decorative. Most often they are used in landscape design to decorate the appearance of the area. For decorative lighting on the street, artificial ponds, small architectural forms, fountains, etc. are illuminated. This also includes architectural lighting of building facades, which is a modern and very popular solution today.
- Festive. With the help of electric garlands and hanging lanterns, trees, the façade of a house, and even a fence are temporarily decorated. As a rule, holiday lighting is used for the New Year and other holidays.
And, of course, we provide you with a useful video on the topic:
These are all types and lighting systems that are used today. As you can see, the classification is quite extensive, so it increasingly depends on the purpose and area of application of the lamps!
Interior
There are two types of interior design: artificial and natural. Artificial lighting is divided into the following systems:
- Main lighting is carried out by installing ceiling lamps that evenly illuminate the entire room.
- Local - used for local illumination of certain objects. For local lighting, wall sconces, floor lamps, and table lamps are used.
- Decorative lighting is intended for additional decoration of rooms and individual objects.
Daylight
Natural lighting is taken to be the light emanating from the Sun during the daytime and penetrating into the room. In this case, the methods of entering the premises are as follows:
- through window openings in the side parts of the building (side type);
- through window openings in the upper parts of the building (upper type);
- combination of top and side type (combined type).
With the first and third options, the positive side is that the light spreads evenly in the room, but with the second option, the distribution occurs unevenly.
Artificial lighting
Artificial lighting is considered to be light distributed when there is insufficient illumination or at night in a room. The organization of light is carried out by special devices (incandescent lamps or gas-discharge lamps). Types of artificial lighting: combined and general. Other subtypes: work, emergency (such lighting is divided into safe and evacuation), security and duty. The classification of artificial light with details is given below.
General lighting
Scope of application: for interior spaces. General lighting: uniform or localized. The uniform option leads to effective work on the illuminated area. The localized option installs lighting fixtures near the equipment, making a larger area of the territory suitable for work both during the day and at night.
Points that must be observed when organizing this lighting option:
- if citizens over 40 years of age work in the rooms, then SNiP 05/23/95 obliges them to increase the level of brightness supplied to them;
- When calculating, the degree of reflection from the walls is taken into account.
Zonal and local lighting
Local lighting is used to highlight objects or areas. With this approach, the light source is fixed to a selected area (part of a wall, table, ceiling or other area).
Local lighting is a factor worth considering in interior design. It is important to note that when local lighting is used, the use of the first option is excluded, since when combining options the result will not meet expectations.
Consider the disadvantages of these options. First: it is impossible to change the direction of the main flow of light, increased degree of scattering. Second: illumination of only the selected area, excessively bright light.
When organizing the first or second option, it is worth remembering the following:
- the zonal type provides an extended degree of illumination. It is recommended to use this type in the kitchen, workplace or in a room intended for relaxation from work;
- depending on the specifics of the room, as well as the purpose, it is necessary to determine the lamps that will be used in the room;
- the local type is suitable for a separate area of the workplace, reading room or place with a computer device;
- The local type will be effective if you use directional lighting devices for it.
Decorative lighting
This option is used for private, public or commercial houses.
Task: to place accents appropriately, set the mood for the atmosphere, zone the room, making the object attractive in appearance. Additional types of decorative lighting: static (on-off) or dynamic (wired or wireless control), monochrome or color.
When choosing this option, keep the following in mind:
- since this option is aimed at improving the appearance of the object, there are no specific requirements for brightness or saturation for it, it is recommended to proceed from the specifics of the object in order to achieve favorable parameters for it;
- It is worth distributing light taking into account how it will affect human health. The distribution zones do not need to be made too aggressive in pulsation.
Emergency lighting
This option is used in case of problems with the standard light or other equipment.
This type helps to avoid aggravation of the situation (fire, etc.) and facilitates the prompt evacuation of people from a dangerous building. The minimum light with this option is 5% of the normalized values, but not less than 1 lux. When organizing, it is recommended to consider the following:
- This option is a mandatory measure for industrial premises, for which the lack of light will become critical for normal functioning and will lead to loss of profit, as well as the risk of a fire or other negative phenomenon;
- minimum illumination of not less than 5% and not less than 10 lux for incandescent lamps, 30 lux for fluorescent lamps;
- It is recommended to select diffused type lamps;
- power sources must be independent in nature, since only they will provide emergency operation in a critical situation, and will not be turned off along with other devices if a failure occurs in the building;
- The level of illumination in the rooms must be at least 0.5 lux. This value allows you to install devices at a distance of at least 25 m relative to each other. At the same time, some of the devices are installed at turns, this eliminates the formation of “blind” zones;
- It is recommended to use lamps with diffused light. In addition, it is recommended to place special signs that will direct you to the nearest exit from the premises.
Outdoor and security lighting
The external type is used to illuminate the external perimeter of the territory of an object that needs to be protected. In this case, the same devices are used to perform the task that work in the interior. This allows you to reduce energy consumption.
Security lighting is a complex structure; in its case, the lighting fixtures are arranged so that there are no “blind” areas in the room. It is important to observe this, since the lives and health of people and the safety of property at the enterprise depend on it. When organizing this option, the following must be taken into account:
- the degree of brightness that will need to be provided largely depends on traffic congestion and the number of residents in the city. For example, central highways with traffic of more than 500 cars require lighting of at least 20 lux, local roads with traffic of less than 500 cars on roads - at least 4 lux;
- objects that are heavily located in the shadow should receive at least 0.35 of the total light;
- It is important to consider that when lighting crossings and roads for pedestrians, the time of day also has an impact. In the daytime, the illumination is higher, at night - lower;
- It is best to use diffused type lamps. They provide sufficient brightness and do not hit people’s eyes; this type of light also allows you to increase the distance between devices;
- the duty regime in the premises must function on a permanent basis, since the lives and health of citizens depend on it. It must provide at least 0.5 lux (the exact figure depends on the characteristics of the enterprise where this work is carried out);
- The use of both diffused and directional lamps is allowed. The decision should be determined by the feasibility of application, as well as the solution of the assigned tasks within a particular enterprise, taking into account its characteristics.
Types and systems of artificial lighting
Electrical laboratory » Designer's textbook » Types and systems of artificial lighting
The topic of choosing the right lighting is always relevant in everything, be it a luxurious shopping and entertainment center equipped with the latest innovations, or an ordinary utility room. Only a competent and rational approach to the selection of lighting devices (OU), subject to the required standards, will help design specialists create harmonious interiors and ensure effective lighting of the space. The electrical laboratory will help you determine the standards and also perform all the necessary measurements.
Traditionally, in residential interiors and public buildings, i.e. where there are no special requirements due to working or living conditions, a general lighting system .
Combined lighting is necessary in places where, in addition to common op amps, additional ones are also required. For example, workrooms, offices, library reading room. Each table is equipped with an additional table lamp (SNiP 23-05 visual work of A-B categories). Otherwise, the conditions of staying in such a place will not be comfortable, and sometimes even harmful to health. The same system works in rooms where work of I-IV categories is performed, requiring extreme accuracy and good visibility. For example, watch repair, household appliances, cutting and sewing jobs, etc.
To ensure the life and health of citizens, a number of facilities must use security lighting . We are talking about the dispatcher’s or computer center operator’s room, communication and server rooms, electrical switchboards, fire duty stations, security posts, main cash registers, etc.
In order to ensure the safety of a large flow of people, this type of lighting is necessary in self-service stores and children's rooms. Places such as restaurant halls, hotel lobby, rescue centers of hotels and tourist resorts also require safety lighting .
This type of lighting is a mandatory attribute for premises where activity is continuous or can occur at any time. Such facilities include operating rooms and delivery rooms in hospitals, urgent testing laboratories, duty doctor posts and emergency departments. In the premises of strategic life support facilities for the population, such as boiler houses, pumping facilities, boiler rooms, fire extinguishing stations, safety lighting is provided provided that personnel are constantly on duty on the premises. Also, if the electrical receivers of these premises belong to the loads of the first category in terms of reliability of power supply (PUE 1.2.17-1.2.21).
Each owner of a particular premises must be familiar with the requirements of the relevant departments in terms of technical equipment that must be implemented for public use. Particular attention in this aspect is paid to evacuation lighting , which is provided in case of an unforeseen situation requiring the immediate removal of people from the building.
As a rule, evacuation lighting is installed in corridors, halls and lobbies, and staircases of public buildings where 50 or more people are simultaneously present. In addition, there are facilities that require its presence without fail, regardless of the number of personnel. These include:
— swimming pools, sports and assembly halls;
— locker rooms and kitchens of preschool and school institutions;
— premises…bath departments;
— health centers, medical and preventive premises, archive rooms, preschool institutions;
— classrooms in universities, assembly halls and conference halls;
— trading floors with an area of more than 90 square meters and exit routes from them;
— transport tunnels of trading floors;
- premises where people are constantly present, if due to the switching off of working lighting, subject to continued work, there is a danger of injury (industrial premises of enterprises, repair shops, laundries, etc.).
From a legislative point of view, lighting of public facilities is regulated by SNiP 23-05 and Chapter 6.1 of the PUE.
Equally important is the light sign Exit , which is installed, accordingly, at the exits from the premises.
Canteens; assembly and conference halls; premises where more than 100 people can be present at the same time; any premises in which 50 or more people are present at the same time require the presence of this sign at the exits from the premises and corridors.
If this is the hall of a building, then if the corridor is more than 25 meters long, the illuminated Exit sign must be installed without fail. At the same time, for good visibility, the light indicator is mounted at a height of 2 m and a distance of 25 meters from each other, as well as at bends in corridors. The same rule applies to exits of shopping centers with an area of more than 180 square meters. m and supermarkets – 110 sq. m or more. The facility's power supply is provided by an emergency lighting , and if it is autonomously powered, from any network. Signs are also installed at a height of 2 m.
If there is a need for emergency ( night ) lighting of individual areas of premises, such as lobbies, corridors, assembly and sales rooms..., lamps from evacuation lighting sources are used. In the case of power supply from an independent group line, you should use part of the luminaires of the work lighting . For emergency lighting of treatment and prophylactic premises, special lamps are used, which are mounted near the entrance in niches, at a height of 0.3 m from the floor, powered by evacuation lighting.
In hospital wards of psychiatric and children's departments, sleeping quarters, isolation wards of preschool institutions and boarding schools, night lighting units are installed above the doorway, at a height from the floor level of at least 2.2 m.
In areas north of 65 degrees latitude, vital installations for ultraviolet preventive irradiation are provided. When designing them, the Guidelines for the design and operation of artificial ultraviolet irradiation installations should be taken into account.
In rooms where children are located, the requirement for installing emergency lighting at a distance of 0.3 meters from the floor is determined by limiting the voltage to 50 V.
The locations of fire paraphernalia, entrances to buildings and waste collection chambers must be illuminated by the fire control units connected to the emergency network.
For OU light fencing, the standards are regulated by the Operation Manual for Civil Airfields (REGA RF-94), Chapter 3.3.
Standard separation
Another division of light source types is made according to the direction of the beam:
- general plan - when the direction is uniform across space;
- directional plan - when the direction is set artificially to illuminate the selected area, the rays are distributed evenly;
- indirect (reflected) plan - when the direction goes to the wall and ceiling, and the uniformity of distribution is obtained due to the reflection that occurs;
- diffuse plan - when the direction passes through a lampshade made of material of a translucent shade;
- mixed plan - when several of the above types are implemented simultaneously.