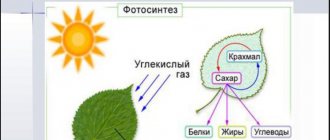
Even children know that plants need light to thrive. Every schoolchild knows that the vital process of photosynthesis occurs in the light. Even an inexperienced indoor plant lover understands that some plants need bright sunlight, others need diffused light, and some grow best in the shade. Light-loving flowers from the subtropics are grown on southern windows, and shade-loving forest inhabitants are best placed on northern ones. Only shade-tolerant plants can develop normally in the depths of the room.
Lighting for indoor plants
In winter, natural light is not enough for almost all house plants. Even on south-facing windows there is little light on short, cloudy days. Some domestic flowers are able to adapt to such conditions and even bloom in winter (Kalanchoe, Saintpaulia, poinsettia, Schlumbergera, chrysanthemum, Erica), but most species lose their decorative effect, stretch out towards the meager light from the window, many simply stop growing (dracaenas, peperomias, many orchids).
It is important to understand that both the intensity of lighting and the length of daylight matter. Many plants are able to bloom only with sufficient daylight (campanula, fuchsia, gardenia, oleander). Almost all orchids that do not have a winter dormant period need additional lighting in winter.
To extend daylight hours and increase the intensity of lighting, I use artificial lighting lamps, and also use some little tricks.
How to make artificial LED lighting yourself
Developing a lighting scheme
LEDs are optimal for creating homemade lighting. These lamps can be placed according to the pattern that, in your opinion, will most effectively solve the problem of additional plant lighting. It is better to arrange them in two lines, this way you can achieve uniform illumination of each sprout in a box or container for seedlings. Please also note that the rays of LEDs diverge in the form of a light cone at an angle of 70-120, so the lamps should be fixed so that the rays of the light cones cover the entire area of the boxes, leaving no unlit areas.
LED lamps are usually chosen by experienced gardeners who have thoroughly studied all the needs of growing seedlings and the capabilities of different types of lamps. LED lighting is a logical and predictable choice of an economical option that consumes a minimum of electricity. In addition, LED lamps give gardeners the opportunity to create their own spectrum, which is, in their opinion, the most effective.
Infrared lamp for plants and animals ERA 250W E27 mirror reflector
To obtain good seedlings with thick, strong stems, it is useful to use different light spectra for different periods and stages of the growing season, namely:
- Before picking the seedlings, optimal results are obtained by using blue and red lamps to produce illumination in a 2:1 ratio. Blue stimulates the growth of the root mass, but somewhat inhibits the development of the stem so that the plant develops not in height, but in width. In this case, the stem will be strong, and the intervals between the leaves will be small.
- Upon completion of picking, it is recommended to reduce the illumination intensity; at this stage, the seedlings are stressed, they need rest and peace after the extreme procedure. Therefore, the sprouts should be illuminated with blue and red lamps for about a month, maintaining a 1:1 ratio.
How to determine that a plant is not getting enough light
Shade-tolerant plants require light levels from 1000 to 5000 lux, and light-loving plants require light levels from 10,000 lux.
You can measure the level with a special device. But if it is not there, and this is usually the case, then the plant itself will tell you when there is not enough light for it. Insufficient lighting affects the appearance of any plant. First, the natural color of the leaves changes: young leaves grow pale and small, leaves with variegated colors (scindapsus, variegated ficus and ivy) lose the brightness of the pattern, sometimes becoming simply green. In many species, the lower leaves turn yellow and sometimes fall off.
In almost all species, shoots are noticeably elongated and bent towards the light. If you compare the distance between leaf nodes that grew in summer and those that appeared in autumn or winter, the difference is very noticeable. For example, in pelargonium, the internodes lengthen by 2-3 times.
An experienced gardener will never wait for his plants to stretch out and begin to lose leaves. First of all, you need to know exactly whether a particular species is shade-loving or needs bright light, which can be found in the encyclopedia of indoor plants. And if there is a suspicion that the house flower is dark, then you should definitely install lamps for illumination.
Many novice flower lovers, having learned about the possibility of using artificial lighting, begin to illuminate plants around the clock. But, contrary to expectations, they languish. In the dark, plants also undergo processes necessary for life. Regular alternation of day and night is important. The flowering of many species depends on changes in these periods.
Which lamps to choose for illuminating plants
When choosing lamps for plants, it is important to know that not only the intensity, but also the spectrum of light radiation is essential. The optimal spectrum for all plants is the spectrum of daylight, which extends from ultraviolet rays, through visible rays, to infrared.
Artificial lighting sources provide light to one degree or another similar to daylight, but not in the entire spectrum. It is known that chlorophyll, which directly transforms light energy into the energy of organic compounds, best absorbs light in the red and blue parts of the spectrum. Blue-violet light promotes the growth of green mass in the first stages of plant development, red light accelerates seed germination and shoot growth.
Various types of lamps can be used as light sources, such as incandescent lamps, fluorescent lamps (FL), gas discharge lamps (HD) and LEDs. Currently, professionals mainly use gas-discharge and fluorescent lamps to illuminate plants.
Ordinary incandescent lamps with tungsten filament are not suitable for these purposes - their light intensity is low, they heat up very much, their spectrum contains too many red, orange and infrared rays, which accelerate vertical growth, so plants stretch out under incandescent lamps.
Fluorescent lamps are closest to the daylight spectrum; they are also much more economical than incandescent lamps. Many plants develop best under such lamps. Saintpaulias and balsams illuminated by fluorescent lamps bloom all winter without ceasing.
Recently, quite efficient and economical LED-based lamps have appeared on the market. By combining LEDs of different colors, lamps are obtained that emit in the desired areas of the spectrum and are useful at different stages of the growing season.
Special phytolamps are also sold. At first glance, they do not differ from ordinary lamps, but they generate a luminous flux in the blue and red spectrum, designed to activate photochemical processes and have a beneficial effect on the pace of development. When you mix red and blue light, you get a magenta (pink) hue of light. But such light is often unpleasant for humans.
When choosing a lamp, you should avoid options with a lamp shutter, because ordinary glass can also be an obstacle to the light. Even windows block up to 80% of sunlight! Lamp bulbs are usually made of special grades of glass that transmit maximum light. But from time to time, do not forget to wipe off the dust from them, after turning them off.
How to choose?
It is recommended to approach the choice of additional lighting very wisely. A universal option for most varieties is ultraviolet radiation.
The main thing in this matter is to choose the most suitable intensity of light rays for most species.
In specialized departments, there is a huge selection of LED strips with changing light beams. Here the maximum imitation of solar radiation is created. The operation of such a lamp can take quite a long period of time.
If such a backlight malfunctions, the inoperative element can be easily replaced. This applies to both the whole segment and its individual parts. The LED strip is tightly fixed to any surface.
To save electrical energy, fluorescent lamps were developed. They have minimal weight and simple design.
An incandescent lamp is also suitable for lighting indoor plants. The only drawback of such a device is its excessive energy consumption.
The most budget option is still an LED strip or a table lamp with an energy-saving light bulb. These types of designs are able to maintain optimal light supply in the dark.
How to increase illumination
When looking for a place for a lamp, remember an important rule: illumination decreases greatly with distance. By doubling the distance between the lamp and the plant, we will give it only a quarter of the original amount of light. Lighting is most effective if the rays fall on the illuminated object perpendicular to the surface. Since the leaves of most indoor flowers are located horizontally, the source should shine as strictly from top to bottom as possible.
There is a way to significantly increase the illumination of a surface while maintaining all the parameters of the light source. Using a reflector allows you to increase light output by up to 50%. The principle of operation of this device is to reflect upward and sideways light from the lamp down to the plants. Point light sources (incandescent, energy-saving and gas-discharge lamps) are most often equipped with a conical or elliptical reflector, and fluorescent tubes are U-shaped. White matte surfaces reflect light best, not mirrors, as we used to think.
Often reflectors are provided with lamps in which a light source is installed. For halogen incandescent lamps and high-pressure discharge lamps, the reflectors may be contained in the bulb itself. You can make a simple reflector yourself from foil and tin. But remember that it must be fireproof and provide for heat removal from the lamp.
You can complete the creation of a home artificial light system using electric timers, designed in the form of an adapter: the device is plugged into an outlet, and the lamp cord is connected to it. A timer with a mechanical programmer is much cheaper than an electronic one, but is not as easy to use. The latter's microcomputer allows you to program the lamp on/off with an accuracy of up to a minute for a week or month in advance, and you can set different lighting modes on different days.
When choosing a light source, pay attention to the type and electrical power of the lamp - they determine the intensity of the glow. The color richness of the spectrum is also very important: for successful growth and flowering, plants need the red and blue components of sunlight. The human eye is adapted to perceive yellow and green rays. A bright lamp, from our point of view, may well turn out to be dim for an indoor flower or seedling.
Lighting characteristics are presented in the table below (
e)
Which lamps will be most effective for illuminating seedlings?
Diode phytolamps are considered the most effective. Their use can improve seed germination and growth. They are also used for additional lighting in greenhouses.
Before the first shoots appear, the ground where the seeds are located is constantly illuminated. They don't turn it off even during the day. When the plants have sprouted, the intensity is reduced by turning it off at night for 6 hours.
To increase the efficiency of such lamps, a reflective screen is installed. Another option is to combine lamps with different color spectrums. Diode phytolamps emit a pink-violet spectrum. Red and blue rays have a beneficial effect on the development of vegetable and flower crops. But it should be noted that pink-violet radiation is unnatural for the human eye. If sprouts grow and develop better under the influence of this spectrum, then it can cause headaches and other ailments in humans. Therefore, it is preferable to use them in greenhouses, especially since their energy consumption is minimal.
If you grow on the windowsill at home, it is recommended to install reflectors. They will prevent the rays from spreading throughout the room. Reflectors can be made from white cardboard, cutting it to the desired size, or from foil.
To ensure that the lighting for seedlings at home fully satisfies your wishes, you can make it yourself.
How to place lighting lamps
When placing lamps, it is useful to know that if the distance to the lamp is doubled, the light intensity on the plant will decrease by four times.
If burn marks appear on the leaves, then the lamps are hung too low, elongated stems and pale leaves indicate that the light source is too far away.
With side artificial lighting, plants can bend their stems towards the light; it is better to add light from above.
The actual issue of landscaping a living space is not complicated. There are more than 500 species and varieties of indoor ornamental plants available for sale. Many books, magazine articles, and instructions have been written on this topic. However, almost all of them consider keeping plants in natural light, even in partial shade rooms. Based on this, plants are divided into light-loving and shade-tolerant.
In practice, as a rule, they do not think about this. When purchasing living plants, people treat them as floor lamps, vases or coffee tables, caring only about where they will look best. But this “ideal” place may not be suitable for the chosen plant. Then there it will be suppressed over time and die, primarily because lack of lighting is the main factor limiting its growth.
It is light that provides plants with the energy necessary for the synthesis of organic compounds.
With a lack of lighting, plants experience the disease chlorosis, which in the initial stages is tested for the following signs: leaves turn pale and become smaller, or grow in length but not in width; stems stretch; the water content of living tissues (turgor) decreases, the leaves droop; plants do not bloom or bloom with small pale flowers. In addition, plants become sensitive to all factors of external conditions: from the hardness of the water used for irrigation to drafts.
The main way to treat chlorosis is to increase lighting. And this is where artificial lighting comes to the rescue.
Artificial lighting of violets
The first official information about the use of artificial lighting dates back to the time of Louis XIV, under whom the Versailles greenhouse was built. For us, this time is comparable to the reign of Peter I’s elder brother, Tsar Fyodor Alekseevich. In France, the creator of the landscape park and garden of Versailles, A. Le Nôtre, used wax candles to illuminate the citrus trees in the greenhouse in winter.
According to chroniclers, oranges, oranges and tangerines bloomed there. In Russia, during the time of Catherine II, it was popular to build greenhouses and orange houses in parks and estates, the plants in which were also illuminated with numerous wax candles.
In English gardening literature there is a mention that plants in winter gardens were illuminated with gas lamps - lighting devices using gas.
So artificial lighting has been known for a long time. But, of course, a huge breakthrough in this area came with the discovery of electricity. Artificial electric lighting is the easiest and cheapest way to provide sufficient light to plants that do not receive the required amount of sunlight.
How to place lighting fixtures?
It is possible that initially some mistakes were made when placing the devices. It's never too late to fix them. It is necessary to change the arrangement in the following cases:
- Plant leaves are covered with burn marks. This means that the nearest lamp is too close.
- The leaves of the seedlings turn pale and the stems stretch out. The reason is that the light source is far away.
- If side lighting is used, the stems may bend towards the lamp. The lamp should be moved upward.
Little tricks for lighting plants
Ordinary mirrors will help to slightly increase the intensity of the most useful natural light. They are installed on the side slopes of window openings. As a result, the light reflected in the side mirrors and plants is much lighter. When only slanting rays of the sun enter the window for a short time, such a little trick helps to extend the daylight hours. And, besides, a little sun in the room in winter will not be superfluous. And such a window looks quite beautiful, and the flowers are reflected in the mirrors and there are “more of them.”
To make illumination of potted plants more effective, reflectors (reflectors) and reflective surfaces are used. They are positioned so that they reflect artificial light towards the plants. As a reflector, you can use foil, white glossy fabric or special reflectors for lamps. Traditional tulle curtains on the windows also partially reflect light, including daylight. If they separate the plants on the windowsill from the room, then the reflected and diffused light from the curtain hits the plants. If the tulle is located in the path of sunlight to the plant, then the light intensity decreases.
The length of daylight hours and the correct alternation of day and night are extremely important for all types of plants. It is not at all useful to shine light irregularly, from time to time, disrupting the biorhythms to which all living things obey. To maintain the optimal regime, a timer is indispensable! Having a timer is also important in order to safely leave powerful lamps on at home when leaving early in the morning for work. They will turn off after half an hour, even if you forget to do so before leaving.
It is useful to regularly monitor the condition of windows and reflective surfaces and clean them of dust and dirt. The window appears clean and transparent, but a thin layer of dust greatly reduces the intensity of daylight.
About the “necessary” and “unnecessary” spectrum
As for the “usefulness” of the spectrum, the biggest misconception is that seedlings do not need green light at all - after all, they reflect it. In fact, it is needed in another way - for many important processes. Don't experiment with it!
The fullest spectrum is that of sunlight. These are full of different colors and different lengths. So,
- Blue and purple are designed to regulate cell growth so that the shoots are short and strong.
- Red influences seed germination and stimulates flowering.
- Yellow and green - reflected from the leaf plate, but necessary.
Of course, artificial light sources, with all the achievements of modern science, are still far from the sun - they still have shifts in one direction or another of some colors. Therefore, it is better to use a matte screen as a reflector - it not only increases the efficiency of the backlight, but also makes the light “diffuse” - scattered. This is much better absorbed by plants than straight and hot.