- Apartment
The appearance of LED elements (light-emitting diode) marked an evolutionary turn in the development of lighting products. Infrared diode technology was patented in 1961, but a practical LED did not appear until a year later. The first LED lamps cost up to $200; their prices began to fall thirty years later - in the early 90s, when a cheap blue diode was created.
Over the past decade, individuals and business owners have increasingly chosen affordable LED lighting. The serial production of LED elements, demonstrating high growth rates, reflects the brisk demand for them.
What is LED lighting? LED operating principle
An LED is a device based on semiconductor crystals with an electron-hole junction. It produces optical radiation in a narrow range of the spectrum when an electric current is passed through it. Under the influence of the latter, each crystal begins to emit rays in the RGB spectrum, and white color is the result of their mixing. By changing the color ratio, shades of white light from warm to cool are obtained.
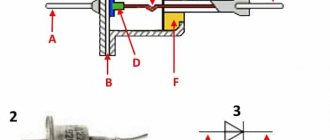
If we talk about modern LED lamps, they consist of the following elements:
- Board with diodes
- Driver for current rectification
- Radiator for heat removal
- Base (E27, E14, E40, GU10, GU5.3, etc.)
- Flask (traditional shape, in the form of a candle, ball, ellipse, “corn”)
- Holders (lower and upper)
The design of standard LED lamps includes:
- Plastic white or colored flask;
- Board with LEDs;
- Driver rectifying alternating current (electronic board);
- Heat sink;
- Base;
- Bottom and top holder.
Bulbs of LED lamps come in different shapes: regular, like an incandescent lamp, and bulbs such as “Candle”, “Ball”, “Ellipse”. There are also “corn” lamps, they are cylindrical in shape, and LEDs are installed on the sides of their body.
The board, depending on the required luminous flux and power consumption, has a different number of LEDs. The lower and upper holders are needed to hold the board with LEDs and the driver, with the elements installed on it. The heat sink removes heat from the lamp body, preventing it from overheating. The base of LED lamps varies, the main types are:
- E27. The classic base is the same as incandescent lamps, so LED bulbs can be safely used in their place;
- E14. Lamps of the “Candle” and “Minion” types are produced with such a base; it looks the same in appearance as the E27 base, only narrower;
- GU10 – rotating pin socket. To fix the lamp in the socket, it must be inserted into it and turned to the side;
- GU5.3. You can distinguish this type of base by its protruding contacts, like an electrical plug. It also belongs to the “pin” type and is connected to the special cartridge using a pin method (similar to a plug with a socket).
Design of LED lamps:
- Frame;
- LEDs located at a certain distance from each other;
- Protective screen;
- Power supply;
- Driver;
- Pay.
Advantages and disadvantages of LED lighting
Like other popular lighting sources - traditional and fluorescent - they also have advantages and disadvantages. The advantages of LED lamps include the following characteristics:
- Life time . They are capable of operating up to 100,000 hours. For an incandescent lamp this figure is up to 1,000 hours, for a halogen lamp - up to 4,000 hours, for a fluorescent lamp - up to 10,000 hours.
- Economical energy consumption . They consume on average 7 times less electricity than an incandescent lamp, 2 times less than a fluorescent lamp and 4 times less than a halogen lamp, provided that they provide the same illumination of the room.
- Light output parameters . The luminous flux power in them is 50-100 lm per 1 W. For halogen lamps this characteristic is up to 22 lm, for fluorescent lamps – up to 60 W, for incandescent lamps – up to 17 lm. In the last three, 40-90% of the power is spent on heating the case.
- Environmental friendliness . The LED lamp contains no toxic components. Incandescent and halogen lamps do not claim to be environmentally friendly due to the amount of energy consumption that is “wasted”. Luminescent products contain mercury vapor and require compliance with strict disposal rules approved at the legislative level.
- Design safety factor . Incandescent and halogen lamps easily break when dropped from a height of up to 1 m and subject to slight mechanical impact. And strong vibration will cause the filaments in them to break. Fluorescent lamp bulbs are more durable, but breaking them is undesirable due to potential harm to health. LED lamps have the most durable housing, since the bulb, the most fragile structural element, is made of plastic.
- Natural light . The spectrum closest to it is produced by LEDs. Their color rendering index is 80-85 units, while natural sunlight has 100 units (absolute value). Among other solutions, only fluorescent lamps with 60-65 units come close to this characteristic.
LED light sources do not require regular maintenance and are suitable for illuminating damp and dusty areas. Their service life is not affected by frequent power switching on and off, unlike halogen, fluorescent and incandescent lamps.
Since their introduction to the market, light sources based on LEDs have continuously become cheaper, but still remain expensive compared to alternative solutions. This is their main and only drawback. But if you consider the service life and reduced energy consumption, installing LED lighting will be preferable from an economic point of view.
Competitive advantages of LED light sources
The increased demand for LED lamps and luminaires arose for a reason. Let's compare LED lamps with other types of lamps and highlight the key advantages:
- Extended operating time
An incandescent lamp (which has already been banned from use) must burn for at least 1000 hours. In fact, it burns out much faster due to voltage fluctuations and the low resistance of tungsten in a cold state at the time of switching on. After 750 hours of lamp operation, its light output decreases noticeably.
The halogen lamp has the best durability, burning from 2000 to 4000 hours.
A compact fluorescent lamp burns for 8000-10000 hours. After half its service life, the luminous flux decreases by 30-35 percent.
In comparison, an LED lamp burns for up to 100,000 hours! If converted into years, this is approximately 11 years. Lighting with LED lamps is the most profitable.
| Comparison parameter | Incandescent lamp | Halogen lamp | Fluorescent Lamp | LED lamp |
| Power consumption, W | 75 | 45 | 15 | 10 |
| Heat | strong | strong | average | Short |
| Structural strength | very fragile | fragile | very fragile | durable |
| Service life, hours, average | 1000 | 2000 – 2500 | 7000 – 10000 | 30000 – 50000 |
| Easy to install, replace | Fine | will satisfy. | Great | Great |
| Environmental friendliness | Fine | Fine | will satisfy. | Great |
- High luminous efficiency and energy saving
90 percent of the power consumed by an incandescent lamp from the network is spent on heating, and only 10 percent on lighting. The luminous output of the Ilyich bulb is 7-17 lumens per watt.
Halogen lamps also get very hot, but their efficiency is 20-50 percent better than that of Ilyich lamps. The luminous efficiency of the lamp is 15-22 lumens/watt, lamps with quartz glass are 24-28 lumens/watt.
Fluorescent lamps produce a luminous flux when consuming 1 watt of power from the network - 40-60 lumens. 1 watt of compact fluorescent lamps (energy saving) is equal to 5 watts of incandescent lamps. This directly affects energy savings.
LED lamps produce a luminous flux of 50-100 lumens per watt. And this is again the best indicator among all lamps. 1 watt of LED lamp power = 3 watts of compact fluorescent lamp (energy saving). But LED lamps also belong to the energy-saving class, but in this regard they are more efficient than compact fluorescent lamps.
| Basic characteristics | Incandescent lamps | Fluorescent lamps | LED lamps |
| Brightness | average | low | high |
| Service life, hours | 1000 | 10000 | 50000 |
| Infrared radiation | very high | minimum | absent |
| Ultraviolet radiation | acceptable | very high | absent |
| Luminous efficacy, lm/W | 7 – 17 | 40 – 60 | 50 – 80 |
| Initial cost | low | average | high |
| Power consumption, W/hour | at least 25 | at least 20 | from 7 to 21 |
- Environmental friendliness
LED lamps have the best environmental performance, since they do not contain harmful components and do not emit infrared and ultraviolet radiation during operation. This is why LED home lighting is so in demand. The most harmful lamps are fluorescent lamps, including compact ones, since they contain mercury and its vapors.
- Structural strength
LED lamps are the most durable. Incandescent and halogen lamps should not be shaken, as their filament will break. Their glass, like the glass of fluorescent compact lamps, is fragile and will easily break if dropped. LED lamps have plastic instead of glass, which can easily withstand the load if dropped, and there is no filament inside the structure.
LED characteristics
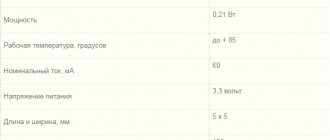
Operating current (mA, milliamps)
LED elements operate from 10-100 mA or more. The more powerful the diode, the higher the current it requires, but the greater the likelihood of the LED burning out. Drivers are used to rectify the current characteristics. The more accurately they work, the longer the diode will last.
Voltage (V, volts)
Depends on the semiconductors and other chemical elements used in the manufacture of the LED element. Their qualitative and quantitative characteristics directly affect the color of the glow.
Power (W, watts)
Determined by current and voltage. The higher the power, the hotter the LED gets, but the faster it fails. To prevent such developments, they are forcibly cooled by installing radiators made of aluminum or other materials with similar characteristics.
Color temperature (K, Kelvin)
It depends on the materials used to make the diode. Temperature determines the hue of the LED. It can be warm yellow (1,800 – 3,500 K), neutral white (3,600 – 5,000 K) or bluish-cold (5,100 K and above).
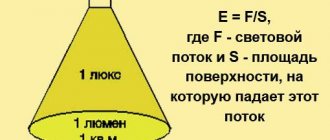
Luminous flux (lx, lux)
Determines the light intensity. It means the number of lumens (units of luminous flux) per unit of power equal to 1 W.
Scattering Angle (°, degree)
It depends on the characteristics of the diverging lens. For a single diode, the dispersion angle ranges from 50 to 120°. If accent (spot) lighting is required, use a collective lens. If the dispersion angle needs to be increased to 270-360°, modular structures are made.
Conclusion
Despite some disadvantages, LED lighting has significant advantages:
- efficiency;
- long service life;
- good quality of light;
- variety of colors and shades of light.
Manufacturers strive for unification, so they produce models that can easily replace other types of light bulbs, both in everyday life and in industry.
Despite the high price of high-quality light bulbs, they will pay for themselves in 1-1.5 years by reducing electricity bills.
- Related Posts
- Decorative lighting at home: variety of ideas
- LED warehouse lighting: selection, calculation and installation
- LED dimmer 220V
How can LED lighting help you save money?
We looked at how much more profitable LED solutions are compared to halogen, fluorescent and incandescent lamps. The main advantages of LEDs in economic terms are determined by their service life and reduced energy consumption. We suggest you verify this with an example.
| Light flow | LED lamp | Energy saving lamp | Incandescent lamp |
| 50 lm. | 1 tu. | 4 tu. | 20 tu. |
| 100 lm. | 2 tu. | 5 tu. | 25 tu. |
| 100-200 lm. | 2.5-3 W. | 6-7 tu. | 30-35 tu. |
| 300 lm. | 4 tu. | 8-9 tu. | 40 watts |
| 400 lm. | 5 tu. | 10 watts | 50 watts |
Let's take a popular 60 W incandescent lamp. The closest power characteristic to it will be a 9 W LED lamp. Here you can see a sevenfold saving in energy consumption, which will be reflected in the bills for consumed electricity. We add to this the advantage in light output (78 lm/W versus 13 lm/W) and service life, which differs by 50-100 times (up to 100,000 hours of continuous operation versus 1,000 hours). We take away the need for special disposal (this is not a free service for enterprises) and the need to replace lamps as a result of damage - and the result is an economically sound solution.
Are LEDs harmful to eyesight?
The properties of the light emitted by an LED are very similar to the characteristics of light from a fluorescent lamp. This means that LED light is similar to monochromatic light, which is the main difference from solar or incandescent lighting. At the moment, there is no in-depth research in this area, so it is difficult to say whether it is good or bad. There is also no data on the harm of light emitted by LEDs.
Types of LED lighting
Apartment
Such lamps are installed in chandeliers, table lamps, sconces and spotlights. They are purchased complete with lamps or separately, in order to switch to economical energy consumption.
Office
For offices and classrooms, LEDs are used as part of recessed or ceiling mounted lamps. They provide a uniform diffused light flux with similar characteristics at each workplace.
Trade
In this case, LED lighting plays an important role in generating profit from sales, as it presents the product from a favorable angle. For this purpose, downlights, cardan and modular models, track lamps on a busbar and other types are installed.
Industrial
LEDs are used in production workshops, warehouse complexes, and livestock farms. Such light sources are able to withstand aggressive operating conditions: temperatures over 35° and humidity over 80%, excessive dust, regular mechanical impact.
Emergency
As a backup option, when the main lighting is turned off, LED lamps are used at industrial facilities, in medical and entertainment institutions, and in retail chains. There are completely autonomous models and those that are designed to be connected to a centralized power supply. There is also a category of emergency evacuation lamps that indicate exit routes in emergency situations (for example, when a fire alarm is activated).
Cantilever (street) and architectural
Street and architectural lamps with LEDs are installed on highways and city streets, parks and along pedestrian paths.
LED elements as part of strips and individual lighting sources are used to illuminate the facades of buildings and sculptures. To obtain various effects, optical systems, reflectors, and lamps with a scattering angle of up to 180 ° are used. Garlands are used to highlight architectural objects, and media facades made on the basis of modular grids are used to broadcast advertising and other content.
Spotlight
LEDs are components of modern floodlights - long-range devices with large coverage: sports complexes, parking lots, train stations. The number of LED elements in them ranges from 30 or more, and the power varies from 20 to 100 W. This achieves a high concentration of light flux, allowing you to visually highlight objects located at a distance of tens of meters.
Where is it most beneficial to use LED lighting?
The area where LEDs are used is quite extensive. They can be used almost anywhere, you can only exclude industrial premises in which they can be used as emergency lighting.
Designers widely use LEDs in their designs because of their pure color. LED lighting will also be indispensable in conditions of severe energy savings or high requirements for electrical safety.
LED apartment lighting
use of LEDs for lighting