Step-down voltage transformers are required, and sometimes irreplaceable, in conditions where there is a risk of electric shocks due to an unfavorable environment, for example, in damp rooms. In such situations, models of the indicated devices are used, including 36 Volt ones. This way, if there is contact with the electrical network, the shock will be minor, and it is less likely to damage other devices. There are ready-made modules - YTP (box with a step-down transformer, details later in the article) - for which you do not need to deal with contacts. But the 220/36 V step-down transformer (VT) itself is a device that cannot be immediately plugged into an outlet without preparation; you need to know how to connect it to the wiring. Let's consider the rules, connection options, preparatory steps, and warnings.
What is a current transformer?
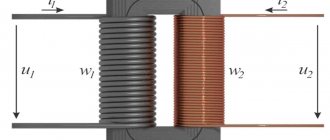
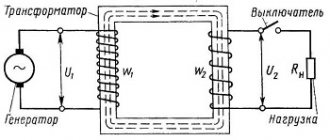
A current transformer (CT) is an inductive device that converts the voltage in the network.
Its primary winding is connected to a source of electricity, and the secondary winding is connected to a protective device with low internal resistance. Current flows through the primary winding, overcoming its resistance. In the process of moving along the turns of the primary winding, a magnetic flux arises, which is captured by the magnetic core. The turns of the secondary winding are located perpendicular to the turns of the primary winding. Under the influence of electromotive force, the current in the secondary winding overcomes the resistance in the coil, as a result of which the voltage at the terminals of the secondary circuit drops.
The transformation ratio is determined at the transformer design stage, so it is important to choose the right device model and order a transformer in Brest, depending on the purpose and operating features.
Making a step-down transformer from 220 to 12 Volts with your own hands
Currently, you can find on sale any step-down transformer that meets all the requirements for this type of technical device. However, for people who have a creative streak and want to make everything with their own hands, it is quite possible to assemble a step-down transformer with their own hands. All work on the independent production of such a product can be divided into several stages: preparatory, execution of work and testing of functionality.
The choice of design and assembled circuit depends on the skills and capabilities of the performer
Preparatory stage
At this stage you should:
- decide on the type of device to be assembled - electromagnetic or electronic;
- determine the technical parameters necessary for further use - power and installation location, permissible overall dimensions and weight;
- calculate the parameters of the primary and secondary windings, in the case of manufacturing an electromagnetic model;
- purchase the necessary materials and components.
When making an electronic device, soldering iron skills and basic knowledge in the field of electronics are required. In this case, the device circuit is initially selected, and, accordingly, electronic components (transistors, capacitors, etc.) are prepared for it. In the case of manufacturing an electromagnetic model, you will first need to calculate the windings of the assembled device, and then perform all other operations.
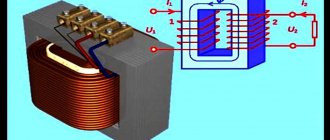
Design of the simplest electromagnetic transformer
To determine the number of turns N1 in the primary winding, you must use the formula:
N1 = (40 – 60) / S , where
- S – cross-section of the magnetic circuit (core) of the transformer, measured in cm2;
- 40–60 is an indicator (constant) that determines the type and quality of the core.
The cross-section of the core is determined based on the geometric dimensions of the blanks used: window, width and thickness of the core jaws. The cross-section of the wire in the primary winding must correspond to the current that will flow in it during operation, which is determined by the size of the connected load, in numerical terms this is defined as:
I1 = P/U , where
- I1 – current flowing in the primary winding;
- P – power of the connected load;
- U – voltage on the primary winding.
Accordingly, knowing the amount of current flowing through the wires, you can select their permissible cross-section, in accordance with the requirements regulated by the Electrical Installation Rules (PUE). The wire cross-section for the secondary winding is determined in a similar way.
When manufactured independently, the core can be selected in various shapes and designs
The number of turns in each winding is determined by the formula:
W = U × (V / 10) where
- W – number of turns in the winding;
- U – voltage in the transformer winding;
- V – frequency of electric current – 50 Hz.
Having decided on the number of turns, and therefore the dimensions of the core, as well as the required length and cross-section of the wire in both windings, you can prepare the necessary materials to complete the work:
- wire for both windings;
- core - you can purchase a new one or use it from used equipment (TV, radio, etc.);
- insulating materials (tape, paper and others).
In addition, it is possible to make a winding machine that facilitates the production of windings, in the case of the option when the windings are made in the form of coils placed on the core.
Execution of work
When all preparatory activities have been completed, you can begin manufacturing and assembling the transformer, in this case the work is performed as follows:
| Illustration | Description of action |
| The coil frames are made from electrical cardboard or other material. | |
| Using a winding machine or manually, wire is wound onto coils; the number of turns on each coil must correspond to the values determined by calculation for each winding. | |
| The coils are placed on the prepared core, their ends are fixed and marked accordingly. |
Functionality check
When the transformer is assembled and all its components are securely fastened and insulated, it is necessary to check its functionality. To do this, a voltage of 220 Volts is supplied to the primary winding, and a load designed to operate at a voltage of 12 Volts is connected to the secondary winding.
If the test is successful, the assembled product is placed in the prepared housing or installed in the location intended for placement.
Scope of application of transformers
Current transformers are installed in many household electrical appliances and industrial electrical equipment that require higher or lower voltages than 220 V or 380 V. To power halogen lamps, a voltage of 12 V is required, that is, almost 20 times lower than the mains, and TT reduces it to the required value.
Transformers are also used for electricity metering. Measuring CTs are widely used, which are connected to measuring instruments (voltmeters, ammeters, etc.) and transmit currents to them. Both compact models are produced that fit into the housing of household appliances, and models for installation outdoors on power lines.
Technical specifications: what you should pay attention to
There are 3 main parameters that you should pay attention to. This:
- input voltage value (220 or 380 V). In the case of household lighting, you should choose a device with an indicator of 220 V;
- output voltage – must correspond to 12 V;
- power. This indicator is calculated from the total load that the lamps will create. For example, if you plan to connect 9 lamps of 15 W, then the power of the transformer should be 150 W.
Expert opinion
Igor Marmazov
ES, EM, EO design engineer (power supply, electrical equipment, interior lighting) ASP North-West LLC
Ask a specialist
“You should not purchase a step-down device with a large power reserve. This will lead not only to unnecessary purchase costs, but also to a shorter service life. A margin of 10-15% is considered optimal.”
Related article: 12V power supply for LED strip. Types of devices, pros and cons of use, connection options, overview of models, recommendations - read the publication.
Main advantages of the products
The use of current transformers provides the following advantages:
- Unification of measuring instruments, calibration of their scales in accordance with the measured primary current;
- The level of safety when working with various relays and measuring instruments increases due to the separation of high and low voltage circuits;
- The maximum voltage range and measurement limits for various measuring instruments are increasing;
- Provides power to the current windings of protection relays and measuring instruments;
- Reliable insulation against high primary voltage.
How much does it cost and where to buy a 220/12 Volt step-down transformer - price review
The price of 220 to 12 Volt transformers depends on their technical characteristics, purpose and degree of protection, as well as the place of their sale. These products can be purchased in lighting and electrical stores, retail chains of various equipment and building materials, as well as on the Internet.
In the departments of lighting and electrical products, step-down transformers of various brands and designs are always on sale
The following table shows the cost of various models of step-down transformers when selling them through Internet resources, as of the second quarter of 2021.
| Model | Specifications | Average cost (as of May 2021), rubles |
| TDM SQ0360-0011 | Electromagnetic 220/12V 35−105W | 529 |
| TDM SQ0360-0010 | Electromagnetic 220/12V 20−60W | 389 |
| YaTP-0.25 | Electromagnetic 0.25 kW, 220/12V, IP30 | 1500 |
| GALS ET-190K | Electronic 220/12V 105W | 550 |
| GALS ET-190T | Electronic 220/12V 250W | 1469 |
| SVETOZAR SV-44955 | Electronic 220/12V, 1 input−2 outputs | 215 |
| SVETOZAR SV-44965 | Electronic 220/12V 2 inputs-3 outputs | 649 |
| NT-EH-060-EN Navigator | Electronic 220−12V 60W | 200 |
| NT-EH-105-EN Navigator | Electronic 220−12V 105W | 270 |
transformer TDM SQ0360-0010
YaTP-0.25
GALS ET-190K
GALS ET-190T
NT-EH-060-EN Navigator
NT-EH-105-EN Navigator
The presence of various models that differ in technical characteristics, sizes and operating conditions allows you to select a step-down transformer in accordance with the requirements for it in different price ranges.
Nowadays, it is not difficult to buy a voltage converter; the main thing is to make the right choice from the variety of offers on the electrical products market
Options for selecting a connection scheme
It is not difficult to connect a transformer intended for household use yourself - just strictly follow the connection diagram. But for the efficient and safe operation of electrical appliances, it is necessary to choose the right circuit. When choosing, you need to consider:
- Number of phases in the network - three-phase models have 4 outputs, and single-phase models only 2, so the connection diagram for a three-phase transformer has a number of differences;
- Type of current transformer - step-up or step-down;
- What current parameter is needed by the consumer - for the operation of household appliances, direct current is needed, and in the network - alternating current, and to convert it, it is necessary to connect the secondary winding of the current transformer through a rectifier.
Popular connection schemes
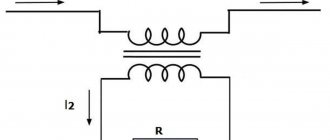
If CTs are used to connect voltmeters, ammeters and other highly sensitive instruments through them that measure low current, the current transformers are connected according to the following scheme:
The primary winding L1-L2 is connected to the linear wire, and the secondary winding of the CT I1-I2 is connected to the current winding of the measuring device. Terminals L1, I1 are connected by a jumper and connected to the phase wire. The third clamp is connected to the neutral wire.
For a three-phase power supply, three single-phase transformers are most often used, which are connected according to the following diagram:
If you need to connect a step-down device, you should follow the diagram:
Most often it is used to create lighting systems. The small size of CTs makes it possible to mount them directly in the ceiling frame. The transformer is located between the switch and the lamps. The lamps are connected in parallel.
What is important to consider when connecting?
To facilitate installation, manufacturers mark them with the following markings: TAa, TA1, KA1, which allows the elements to be connected without errors.
When installing a transformer on three-phase lines, it must be taken into account that if the network voltage is from 6 to 35 kV, transformers can only be installed on two phases, since in such networks there is no neutral wire.
To order current transformers and other electrical equipment, to consult on issues of their selection, connection and operation, call: +375 (162) 44-66-60 or +375 (29) 978-35-00.
Source: viva-el.by