How and why lightning occurs
Lightning in most cases forms in cumulonimbus clouds, and sometimes in large nimbostratus clouds. Thunderclouds stand out clearly from the rest due to their rich dark color.
The dark blue hue comes from the thickness of the cloud. Moreover, its lower edge is located at an altitude of about 1 km above the earth’s surface, and the upper edge reaches 6-7 km in height.
As you know, a cloud consists of water vapor. At altitude, the droplets freeze and turn into ice crystals. Due to uneven temperature distribution, heated air rises and carries with it small particles of ice. At the same time, larger frozen floes fall down - particles constantly collide.
Lightning formation
During a collision, the ice floes are electrified (the same phenomenon as during friction of different objects). Smaller particles receive a positive charge, and larger ones receive a negative charge. Different parts of the cloud are charged accordingly. At the top there is a thundercloud with a plus sign, and at the bottom with a minus sign.
The result is a potential difference. Moreover, it is formed both between different parts of the cloud, and between the cloud and the ground. This difference is measured in hundreds of thousands of volts.
Lightning does not appear instantly out of nothing, although it moves quite quickly. The formation of lightning can be divided into initial, middle and final stages.
initial stage
The discharge appears in a certain part of the cloud where a large number of ions are present. An ion is a particle with an electrical charge. It occurs when an atom or molecule gains or loses electrons.
The same thing happens with a thundercloud. Ions are formed due to molecules of water and gases, of which, in fact, the cloud consists. At this stage, the opinions of scientists differ, since it has not yet been possible to thoroughly study the nature of lightning.
Scheme of development of ground lightning
Some experts believe that a high concentration of ions is due to the acceleration of free electrons. They are always present in the air, albeit in a small volume. These electrons then collide with neutrally charged molecules, causing them to ionize.
According to another hypothesis, it's all about cosmic radiation. It also affects the Earth's atmosphere constantly. This is how air is ionized. Ionized gas is a good conductor of electricity, so current passes through it in the cloud.
Middle stage
Then a chain reaction starts. The current passing under high voltage heats the air in a certain area. More and more energetic particles are formed, which convert neighboring regions into ions. Therefore, lightning travels extremely quickly.
Stages of a downward lightning strike
Lightning has a dominant part - the most powerful channel, from which branches spread in different directions. This explains the tortuous shape of the discharges: with each new flash, the lightning seems to move in leaps and bounds further and further by about several tens of meters.
Interesting fact : sometimes the speed of the “main” lightning reaches 50,000 km per second.
At a certain moment, the most powerful discharge reaches the earth's surface or another part of the cloud. But this is not the end. As soon as an electrical discharge breaks through an ionized channel several centimeters thick, charged particles pass through it at high speed. In fact, this is lightning that we can observe.
Due to the high voltage, the temperature inside this channel is measured in thousands of degrees. That's why we see lightning as a very bright flash. Thunder is a consequence of a sharp change in temperature and pressure. During an electrical discharge, a huge amount of energy is released, despite the short duration of the phenomenon.
Final stage
The speed of charge movement along the channel decreases rapidly. However, the voltage and current still remain very high. It is at the final stage that lightning usually reaches the ground and various objects.
Final stage of lightning
If there are people nearby, lightning becomes very dangerous. The final stage takes not even a second, but tenths of it. But this is enough to cause damage, fires, etc. Lightning often strikes the same place several times if this path is the shortest and most “convenient” for the discharge.
How does a lightning strike occur?
We have already determined that lightning is a powerful electrical discharge that occurs when a charge accumulates inside clouds and a large difference in the electrical potentials of objects appears. As a result, lightning can occur between neighboring clouds, between a cloud and the ground, and even inside one cloud, which also happens very often. In any case, the cloud must be electrified. But how is it electrified?
This can be called lightning in miniature. The processes are similar.
This process has been familiar to us since childhood. It is enough to remember how a comb, a balloon or many other things become electrified when rubbed. A similar process occurs in clouds at high altitudes and on a much larger scale.
The fact is that the clouds are a huge ball of water, albeit not quite spherical in shape. Its height can reach several kilometers, but in different states of aggregation there is water in it at all heights. Up to three to four thousand meters these are drops, and above that they are already ice crystals.
One less mystery: Scientists have solved the mystery of lightning on Jupiter
These crystals have different sizes and are constantly mixed. Smaller ones fly upward due to rising air currents from the warm earth. As they rise, they constantly collide with larger crystals. As a result, the entire cloud begins to become electrified, similar to the objects in the examples above. Positively charged particles are on top, and negatively charged particles are on the bottom.
This is roughly what the potential difference looks like when lightning forms.
When the potential difference is very high, a discharge occurs. If there are not enough conditions inside the cloud for the formation of a discharge, then the discharge occurs into the ground. At the same time, it is accompanied by a bright flash with the release of heat. Due to the release of a huge amount of energy, the air around the lightning instantly heats up to several tens of thousands of degrees and expands explosively in a small volume. This blast wave is called thunder, spreading out to a distance of up to 20 km from the lightning itself.
In this case, lightning consists of several discharges that occur continuously one after another, but individually last thousandths and millionths of a second.
Types of lightning
Lightning is divided into many types. The main criterion is the nature of the discharge formation, because lightning can occur at different heights. They can also have different shapes, lengths and other parameters.
Types of lightning in the layers of the atmosphere
Linear (cloud-ground)
A common species that occurs due to different charges of the upper and lower parts of the cloud. Linear lightning appears and develops according to the principle described earlier - as a result of active ionization of air. From the main leading channel, flashes diverge stepwise in different directions, reaching the ground at the final stage.
Linear lightning
Earth-cloud
Objects located at high altitudes often attract lightning, accumulating electrostatic charge. Ground-to-cloud discharges occur as a result of the penetration of the atmospheric layer between the bottom of a thundercloud and the charged top.
Ground-to-cloud lightning
Cloud-cloud
Most lightning occurs among clouds. Flashes are formed as a result of different parts of clouds having different charges. Therefore, nearby clouds pierce each other with electrical discharges.
Cloud-to-cloud lightning
Interesting fact : in Venezuela there is a unique place where the Catatumbo River flows into Lake Maracaibo. There is a lot of lightning here all year round (usually at night), which flashes continuously for a long time. The frequency of discharges is 250 per square kilometer per year. The highest peak is May and October.
Horizontal
Similar to cloud-to-ground, but does not reach the earth's surface. The outbreaks spread in different directions. Such lightning is considered extremely powerful. For its formation, one thundercloud in a clear sky is enough.
Horizontal zipper
Tape
Lightning takes on an interesting form, in which several identical channels rush down parallel to each other at a short distance. The reason probably lies in the strong wind, which widens these channels.
Tape zipper
Beaded (dotted)
A rare type of lightning, the nature of which has been little studied. The discharge does not occur in a continuous line, but with frequent small intervals - dotted lines. It is possible that some areas of the lightning cool quickly, giving it this shape. The flash lasts a couple of seconds, and the lightning itself strikes in a wave and only in one trace.
Beaded lightning
Curtain
Occurs above the clouds, and not inside or below them, like previous types. How exactly it is formed is unknown. Externally, it is a wide luminous stripe consisting of a large number of discharges. At the same time, you can hear a low hum. The first time such lightning was captured was in 1994.
Curtain zipper
Sprite
If ordinary lightning occurs at an altitude of about 16 km, then sprites appear much higher - 50-130 km. They are electrical discharges of cold plasma shooting upward from the clouds.
Sprites
It’s difficult to see them, but sprites are formed in groups during every strong thunderstorm, a few seconds after powerful lightning. The average length of flashes is 60 km, diameter is up to 100 km, duration is up to 100 milliseconds.
Elf
Large-scale cone-shaped flares with weak red light (diameter approximately 400 km). Formed in the upper layers of thunderclouds. They reach a height of 100 km and last about 3 milliseconds.
Elf
Jet
Tubular-cone-shaped lightning with a blue glow. The height reaches the lower layers of the ionosphere (from 40 to 70 km). In terms of duration they are slightly ahead of the elves.
Jets
Volcanic
Occurs during a volcanic eruption. This is probably due to the fact that the ash and magma carry an electrical charge when ejected. In addition, these particles constantly collide, which causes discharges.
Volcanic lightning
Saint Elmo's Fire
In fact, this is not lightning, but discharges that occur at the pointed ends of towering objects. This includes the tops of rocks, trees, ship masts, towers, etc. They are formed due to high electric field strength. Most often this happens during a thunderstorm or snowstorm in winter.
Saint Elmo's Fire
Ball
Lightning in the form of a spherical plasma clot floating directly in the air. How and why such a discharge is formed has not yet been established by scientists. All we can say for certain is that such lightning behaves unpredictably. Many still doubt its existence.
Ball lightning, 19th century engraving
What is ball lightning and how does it appear?
In addition to ordinary lightning, with which everything is more or less clear, although some questions remain, there are also ball lightning, which have not been properly studied at all and no one can explain where they come from, why and where they disappear.
Initially, ball lightning is a luminous ball (sometimes the shape may be slightly different), which is estimated to have a temperature of 500-1000 degrees Celsius, can move in space, pass through glass and explode a few minutes after its appearance. Nothing more is known for now.
You definitely didn’t know much of this: Interesting and little-known facts about lightning
The first mentions of them date back to BC. True, then it was very allegorical and included talk about birds of fire and the like. Now this is very similar to the description of ball lightning, but one cannot speak about it with certainty.
This is a Phoenix bird, but this is roughly how ball lightning was imagined in the ancient world.
Until recently, many scientists did not believe in the existence of such a phenomenon at all, and eyewitness statements were considered a consequence of damage to the retina after being struck by ordinary lightning. Moreover, everyone was talking about different forms. Now they have begun to believe in it and have started researching, but there is still little information.
Some consider them to be clumps of gas, some to be special particles with a huge amount of energy, and some even talk about higher powers.
However, this does not change the fact that ball lightning can damage objects it comes into contact with. For example, melt glass and metal, set fire to wood and boil water. There are even stories of them shorting out high-voltage transmission lines, creating an arc.
There are several hypotheses for this phenomenon, each of which has not yet been confirmed, but has not been refuted either.
One of them says that ball lightning is a specific interaction of nitrogen with oxygen, as a result of which the energy for its existence is generated. According to another hypothesis, the phenomenon is a spherical vortex of dust particles with active gases. They became this way due to the resulting electrical discharge. As a result, ball lightning is something like a battery. This hypothesis explains the specific smell and trailing glow near ball lightning.
Ball lightning may look one way or another, but this does not make it more studied.
There is a hypothesis that challenges both previous ones, telling us that the existence of ball lightning is impossible without feeding it with energy from the outside. But such a hypothesis is destroyed by the lack of evidence of the existence of waves of the length necessary for power supply.
All this once again proves that ball lightning should be feared, since there are not even clear descriptions of how to act when it appears. The most important recommendation is to immediately leave the area of its action, but without unnecessary haste, so as not to disturb the movement of air and not to carry it along with you.
Lightning color
Lightning can have different shades: bluish, white, yellow, orange, red. The color depends on the composition of the atmosphere. The lightning channel heats up 5 times hotter than the Sun. At this temperature, the air is characterized by blue and violet tones. Therefore, discharges visible nearby in a clear atmosphere acquire a bluish glow.
The bluish glow of lightning is the most common
At a greater distance, the flashes become white, and even further away they turn yellow. This happens because blue tones are scattered in the air. If there is a lot of dust in the atmosphere, the flashes turn orange.
Drops of water “color” the lightning in red shades. The most rare phenomenon is the creation of complex optical effects due to a high concentration of small ice particles in the air.
Development of lightning
The development of lightning begins with the fact that in some place in the cloud a center appears with an increased concentration of ions - water molecules and gases that make up the air, from which electrons have been taken away or to which electrons have been added.
According to one hypothesis, such an ionization center is obtained due to the acceleration in the electric field of free electrons, always present in the air in small quantities, and their collision with neutral molecules, which are immediately ionized.
According to another hypothesis, the initial shock is caused by cosmic rays, which constantly penetrate our atmosphere, ionizing air molecules.
Ionized gas is a good conductor of electricity, so current begins to flow through the ionized areas. Further - more: the passing current heats the ionization area, causing more and more high-energy particles that ionize nearby areas - the lightning channel spreads very quickly.
Speed and length of lightning
On average, lightning moves at a speed of about 56 thousand km/sec. In this case, a thunderstorm atmospheric phenomenon moves at a speed of 40 km/h. The average length of an electric discharge is 9.5 km.
Interesting: Interesting facts about snow, photos and videos
Old photo of lightning in Boston
Interesting fact : the longest lightning strike in the world was recorded in the American state of Oklahoma - 321 km. And the longest discharge in time was observed in the Alps - for 7.74 seconds.
What is a thunderstorm?
A thunderstorm is an atmospheric phenomenon that is accompanied by light and music effects called lightning and thunder. Even during a thunderstorm, the wind often rages and rain pours. In general, everyone has seen everything themselves and knows it all. Rain and wind are more or less clear, but the question arises: where do lightning and thunder come from? Usually people who know that electricity lives in a socket put on a serious face and give the answer: “It’s the clouds colliding, that’s why it sparkles.” Not a bad answer, of course, but let's answer this question from a physical point of view.
Lightning frequency
Early studies showed that lightning strikes approximately 100 times per second across our planet. But satellites make it possible to observe the most remote or hard-to-reach places on Earth.
Lightning frequency (per square kilometer per year)
New data indicates 44 plus or minus 5 lightning strikes per second. This means that about 1.4 billion electrical discharges occur per year. Of these, approximately 25% strike the ground, and the remaining 75% erupt among the clouds.
What types of lightning are there?
Before we talk in detail about the types of lightning, we must say what they generally are. The four main types were given a couple of lines above, namely: linear, zigzag, ball and dry.
Linear lightning is a short sharp discharge that flashes instantly, illuminates the sky and disappears. Sometimes even the lightning itself is not visible, since it passes very quickly and often does not even strike the ground, but between the clouds.
Zigzag lightning is usually called slightly longer lightning, which has a curved trajectory and allows at least a few fractions of a second to be seen. Sometimes you can even notice a slight pulsation of light in them.
Ball lightning is an extremely rare phenomenon. If we encounter ordinary lightning several times a year, and residents of some regions - several times a week, then the chance of seeing ball lightning does not exceed one in ten thousand. This is why the phenomenon is considered very mystical, and if you have seen it, you are very lucky. We need to run for a lottery ticket.
With dry lightning everything is simple. This is usually the name given to lightning that occurs without rain. Not the most common occurrence, but it still happens from time to time. And certainly more often than a ball one.
How to determine the distance to lightning from thunder?
The distance to a thunderstorm can be determined approximately by thunder. To do this, it is recorded how many seconds pass between the sound of thunder and the flash of lightning. It is necessary to take into account the speed of sound - about 300 meters per second. So, 3 seconds is approximately 1 km before a thunderstorm.
Distance to lightning
Taking several measurements allows you to know whether a thunderstorm is approaching or moving away in relation to the observer. It is important to remember that lightning stretches for several kilometers. If lightning strikes are visible in the absence of thunder, it means that a thunderstorm is more than 20 km away.
Why do we hear thunder?
Thunder is the sound accompaniment of lightning, without which it is impossible to achieve the necessary threshold of fear. It is thunder that people fear more than a luminous stripe in the sky.
When an electrical discharge ( lightning ) passes, the ambient temperature rises sharply to several thousand or even millions of degrees. This temperature jump causes the heated air to expand locally ( an explosion ), which causes a shock wave (a thunderclap). If the lightning has many kinks, then we hear several peals of thunder; with each sudden change in direction, a new “ explosion ” occurs.
Since the speed of sound in air is less than the speed of light, we hear thunder a little later than the flash itself. Based on the delay time of thunder, you can approximately calculate the distance to the place where lightning appeared. To do this, you need to calculate how many seconds later thunder is heard after the flash. Every 3 seconds is approximately equal to a distance of 1 kilometer.
That is, if 9 seconds passed after the flash before thunder roared, then lightning flashed at a distance of 3 km.
Are you afraid of thunderstorms??
Consequences of lightning
Lightning leaves behind a large number of different traces, depending on where the discharge strikes and its power. Consider the following manifestations of lightning:
- formation of fulgurites;
- hitting the ground;
- hitting trees, houses and other objects;
- hitting cars;
- hitting a person.
Fulgurite is a substance that is formed when an electrical discharge hits sand or any rock. Essentially, a certain amount of sand simply melts and hardens under short-term exposure to high temperature.
Fulgurite
Fulgurites are not easy to find. They are usually found on mountain tops or in areas where thunderstorms are common. Getting into sand deposits, lightning forms tubes of arbitrary shapes from it, hollow inside. In fact, they turn out to be glass.
There is always moisture and air between sand particles. A powerful blow quickly heats them to high temperatures and expands, as a result of which these tubes of various sizes and shapes appear. They are then instantly cooled.
Very rarely, lightning strikes strike the ground, since the shortest and most accessible path is preferable for them. But in the event of a hit, a depression remains on the surface, from which ornate lines, reminiscent of lightning in shape, go in different directions.
Lightning trace on the ground
Rising above other objects, trees most often attract lightning. In most cases, they burn out, and instantly. If ball lightning hits a tree, it sets it on fire from the inside. When lightning strikes a building, it often damages the roofing part and can also cause a fire.
Lightning struck a tree
If the discharge hits a closed vehicle, such as a car, it will quickly spread throughout the metal body and go into the earth's surface. It is believed that a car is a safe place in which you can wait out bad weather, since lightning does not get inside the cabin. However, the consequences of a direct hit are still serious.
Lightning struck a car
A person being struck by lightning is unpredictable. It is comparable to an electric shock, but the voltage is many times higher. Most often, lightning strikes the chest or head.
Lichtenberg figures
Special marks remain on the body, which resemble lightning in shape - they are called Lichtenberg figures. This mark remains as a result of damage to blood vessels. Being struck by lightning is extremely dangerous, so in the event of a thunderstorm you should take all necessary safety measures.
Following the leader
In practice, the process of lightning development occurs in several stages. First, the leading edge of the conducting channel, called the “leader,” moves in leaps of several tens of meters, each time changing direction slightly (this makes the lightning appear tortuous). Moreover, the speed of advancement of the “leader” can, at some moments, reach 50 thousand kilometers in one single second.
Eventually, the “leader” reaches the ground or another part of the cloud, but this is not yet the main stage of the further development of lightning. After the ionized channel, the thickness of which can reach several centimeters, is “broken,” charged particles rush through it at enormous speed—up to 100 thousand kilometers in just one second—this is lightning itself.
The current in the channel is hundreds and thousands of amperes, and the temperature inside the channel, at the same time, reaches 25 thousand degrees - that is why lightning gives such a bright flash, visible for tens of kilometers. And instantaneous temperature changes of thousands of degrees create enormous differences in air pressure, spreading in the form of a sound wave—thunder. This stage lasts very briefly - thousandths of a second, but the energy that is released is enormous.
Is it possible to use lightning energy?
There is a special term - lightning energy. This is the way in which lightning energy is “harvested” and directed into electrical networks. This energy belongs to the number of alternative renewable sources.
Electrical networks
The potential for using lightning energy is enormous. Its supply is endless - it will solve the problem of expensive electricity and reduce the damage that is currently being caused to the planet’s ecology. Currently, experimental installations for capturing lightning are being developed, and thunderstorm activity is being studied.
But this method of energy consumption also has its disadvantages. It is difficult to predict where and when a thunderstorm will occur. In addition, the flash lasts a fraction of a second, so powerful, expensive equipment is required.
Snow storm
A winter thunderstorm is a rare occurrence in which instead of rain there is snow or ice pellets. The occurrence of a thunderstorm during snowfall is caused by wet and windy weather. During a winter storm, 5–10 cm of solid precipitation may fall per hour.
The term snow or winter thunderstorm is most often used in foreign literature, but in Russia meteorologists talk about a thunderstorm with snow.
Lightning in winter is a rather rare phenomenon:
Thunderstorms are a common, but unpredictable and dangerous phenomenon. The frequency of its recurrence during the warm period increases every year, which is associated with global climatic changes. Forecasters use fairly clear atmospheric signs to determine the onset of a thunderstorm, but it is impossible to calculate where lightning will strike. That’s why every year we hear about disaster victims in the news.
What to do during a thunderstorm?
If you find a thunderstorm outside, you must follow these rules:
- You cannot hide under trees and other tall objects, or stand next to poles or road signs, which are most often struck by lightning. You should move away from them, since the tension diverges in different directions from the center of the impact.
- In an open area, you need to sit down and press your head to your knees, taking the lowest possible place.
- Move your umbrella and all metal and long objects away from you - they attract lightning.
- Turn off your phone and other devices.
- If possible, take shelter in the car.
- Do not approach the reservoir, especially do not swim.
What to do during a thunderstorm
While indoors, you should also turn off your telephone, electrical appliances, and gas supply. It is recommended to close all windows. There is a version that even the beam of a laser pointer aimed at the sky can attract a discharge.
Interesting fact : there is a concept of step voltage. It occurs between two points on the surface, and the greater the distance between these points, the higher the current strength. For example, cattle and horses are at greater risk because their front and rear legs are located far away.
Types of lightning and facts about lightning
Lightning between sky and earth is not the most common lightning. Most often, lightning occurs between clouds and does not pose a threat. In addition to ground-based and intra-cloud lightning, there is lightning that forms in the upper layers of the atmosphere. What types of lightning are there in nature?
- Ground lightning;
- Intracloud lightning;
- Ball lightning;
- "Elves";
- Jets;
- Sprites.
The last three types of lightning cannot be observed without special instruments, since they are formed at an altitude of 40 kilometers and above.
Here are some facts about lightning:
- The length of the longest recorded lightning on Earth was 321 km. This lightning was seen in Oklahoma, 2007 .
- The longest lightning lasted 7.74 seconds and was recorded in the Alps.
- Lightning does not only form on Earth . It is known for sure about lightning on Venus , Jupiter , Saturn and Uranus . Saturn's lightning is millions of times more powerful than Earth's.
- The current strength in lightning can reach hundreds of thousands of amperes, and the voltage can reach billions of volts.
- The temperature of the lightning channel can reach 30,000 degrees Celsius - this is 6 times the temperature of the surface of the Sun.
How are planes protected from lightning?
The entire aircraft body is protected by a special shell, which contains a metal shielding mesh inside. Thus, when struck by lightning, the shell conducts current, but prevents the electrical discharge from penetrating into the aircraft. People and equipment inside remain safe.
Arresters on the wing of an airplane
Also, all technical equipment of the aircraft is equipped with additional protection against electrical discharges. A lightning strike occurs on the nose of the aircraft, the discharge moves towards the wings and tail. Passengers and crew may hear a loud sound during an impact, but this does not always happen.
Interesting fact : before the aircraft is put into operation, it undergoes a thorough check. One of its stages is the simulation of a lightning strike.
Where do thunder and lightning come from?
Everyone knows what a thunderstorm is - the flash of lightning and the roar of thunder. Many people (especially children) are even very afraid of her. But where do thunder and lightning come from? And in general, what kind of phenomenon is this?
A thunderstorm is indeed a rather unpleasant and even eerie natural phenomenon, when dark, heavy clouds cover the sun, lightning flashes, thunder rumbles, and rain pours from the sky in torrents...
And the sound that arises is nothing more than a wave caused by strong air vibrations. In most cases, the volume increases towards the end of the roll. This occurs due to the reflection of sound from clouds. This is thunder.
Lightning is a very powerful electrical discharge of energy. It occurs as a result of strong electrification of clouds or the earth's surface. Electrical discharges occur either in the clouds themselves, or between two adjacent clouds, or between a cloud and the ground. The process of lightning occurrence is divided into the first strike and all subsequent strikes. The reason is that the very first lightning strike creates a path for electrical discharge. A negative electrical discharge accumulates at the bottom of the cloud. And the earth's surface has a positive charge. Therefore, electrons (negatively charged particles, one of the basic units of matter) located in a cloud are attracted to the ground like a magnet and rush down. As soon as the first electrons reach the surface of the earth, a channel (a kind of passage) free for the passage of electrical discharges is created, through which the remaining electrons rush down. Electrons near the ground are the first to leave the channel. Others are rushing to take their place. As a result, a condition is created in which all the negative energy discharge comes out of the cloud, creating a powerful flow of electricity directed into the ground.
It is at such a moment that a flash of lightning occurs, which is accompanied by peals of thunder. Electrified clouds create lightning. But not every cloud contains enough power to penetrate the atmospheric layer. Certain circumstances are necessary for the manifestation of force and elements.
A cloud whose height reaches several thousand meters can be considered a thunderstorm. The bottom of the cloud is located near the earth's surface, the temperature regime there is higher than in the upper part of the cloud, where water droplets can freeze. Air masses are in constant motion. Warm air goes up, and cold air goes down. When particles move, they become electrified, that is, they are saturated with electricity. Different parts of the cloud accumulate different amounts of energy. When there is too much of it, a flash occurs, accompanied by peals of thunder. This is a thunderstorm. What types of lightning are there? Someone might think that lightning is all the same, that a thunderstorm is a thunderstorm. However, there are several types of lightning that are very different from each other. Linear lightning is the most common type. It looks like an overgrown tree upside down. Several thinner and shorter “shoots” extend from the main canal (trunk).
The length of such lightning can reach up to 20 kilometers, and the current strength can be 20,000 amperes. Its speed is 150 kilometers per second. The temperature of the plasma filling the lightning channel reaches 10,000 degrees. Intracloud lightning - the occurrence of this type is accompanied by changes in electric and magnetic fields, and the emission of radio waves. Such lightning is most likely to be found closer to the equator. In temperate climates it appears extremely rarely. If there is lightning in the cloud, then a foreign object that violates the integrity of the shell, for example, an electrified aircraft, can force it to come out. Its length can vary from 1 to 150 kilometers. Ground lightning - This is the longest-lasting type of lightning, so its consequences can be devastating.
Since there are obstacles on its way, in order to get around them, the lightning is forced to change its direction. Therefore, it reaches the ground in the form of a small staircase. Its speed is approximately 50 thousand kilometers per second. After the lightning has completed its path, it stops moving for several tens of microseconds, and its light weakens. Then the next stage begins: repeating the traversed path.
The most recent discharge is brighter than all previous ones, and the current in it can reach hundreds of thousands of amperes. The temperature inside the lightning fluctuates around 25,000 degrees. Sprite lightning. This variety was discovered by scientists relatively recently - in 1989. This lightning is very rare and was discovered completely by accident. Moreover, it lasts only some tenths of 1 second. What distinguishes Sprite from other electrical discharges is the height at which it appears - approximately 50-130 kilometers, while other types do not overcome the 15-kilometer mark. In addition, sprite lightning is distinguished by its huge diameter, which can reach 100 km. Such lightning looks like a vertical column of light and flashes not individually, but in groups. Its color can be different and depends on the composition of the air: closer to the ground, where there is more oxygen, it is green, yellow or white. And under the influence of nitrogen, at an altitude of more than 70 km, it acquires a bright red hue.
Pearl lightning. This lightning, like the previous one, is a rare natural phenomenon. Most often, it appears after the linear one and completely repeats its trajectory. It consists of balls located at a distance from each other and resembling beads. Ball lightning. This is a special variety. A natural phenomenon where lightning is in the form of a ball, shining and floating across the sky. In this case, the trajectory of its flight becomes unpredictable, which makes it even more dangerous for humans.
In most cases, ball lightning occurs in combination with other types. However, there are cases when it appeared even in sunny weather. The size of the ball can be from ten to twenty centimeters.
Its color can be blue, orange or white. And the temperature is so high that if the ball unexpectedly ruptures, the liquid surrounding it evaporates, and metal or glass objects melt. A ball of such lightning can exist for quite a long time. When moving, it can unexpectedly change its direction, hover in the air for several seconds, or sharply deviate to one side. It appears in one copy, but always unexpectedly. The ball may descend from the clouds, or suddenly appear in the air from behind a pole or tree. And if ordinary lightning can only strike something - a house, a tree, etc., then ball lightning can penetrate into a closed space (for example, a room) through an outlet, or turned on household appliances - a TV, etc.
How do you protect equipment from lightning?
You need to understand that there is no protection against direct lightning strikes on equipment. We are talking about lightning protection - this is special equipment that allows you to protect equipment from damage caused by thunderstorms. Lightning rods are also installed and equipment is protected from overvoltage.
Lightning protection
The main purpose of lightning protection is to protect equipment from static electricity. It has a certain protection indicator, designated as ESD Protection. This indicator is measured in kilovolts and is indicated as a numerical value.
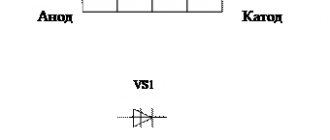
Lightning protection standard is 15-20 kV. It is a diode bridge. When a voltage difference of 6 V or more is detected in the wires, a protective diode is triggered, which grounds the wires.
Origin of lightning
The weather has prepared all the conditions that will help all its effects appear. She created the clouds from which thunder and lightning come.
A roof charged with negative electricity attracts the positive charge of the most exalted object. Its negative electricity will go into the ground.
Both of these opposites tend to attract each other. The more electricity there is in a cloud, the more it is in the most elevated object.
Accumulating in a cloud, electricity can break through the layer of air located between it and the object, and sparkling lightning will appear and thunder will thunder.
History of the study
People have been able to observe lightning since ancient times, but for a long time there was no explanation for this phenomenon. Initially, it was believed that flashes in the sky were the result of the activities of the gods. Even ancient Greek philosophers noticed that lightning strikes tall objects.
Mariners made a significant contribution to the study of lightning. On the open sea, electrical discharges turned out to be even more powerful. The connection between lightning and electricity was put forward in the 17th and 18th centuries, during the development of physics.
Lightning in the sea
Benjamin Franklin described this hypothesis in most detail in his studies. In 1750, he presented a scientific work in which the now famous experiment to determine the electrical nature of lightning was described.
The essence of the experiment was to fly a kite during a thunderstorm. At the same time, a copper rod was attached to the kite, and a metal key was attached to the cable. The purpose of the experiment is to prove the electrical nature of lightning.
The Benjamin Franklin Experience, illustration
To confirm the hypothesis, lightning must strike the kite, travel along the cable and leave a mark on the key. Franklin carried out the experiment in June, taking care of the lightning rod. It is worth saying that it was successful and confirmed all the physicist’s guesses.
In the 20th century, scientists discovered unusual types of lightning (sprites, jets, elves) that occur in the upper atmosphere. Currently, lightning research is carried out using satellites.
Physical nature of lightning
How is the origin of lightning explained? cloud-ground or cloud-cloud system is a kind of capacitor. The air plays the role of a dielectric between the clouds. The bottom of the cloud has a negative charge. When there is a sufficient potential difference between the cloud and the ground, conditions arise in which lightning occurs in nature.
Step leader
Before the main flash of lightning, a small spot can be observed moving from the cloud to the ground. This is the so-called stepped leader. Electrons, under the influence of a potential difference, begin to move towards the ground. As they move, they collide with air molecules, ionizing them. From the cloud to the ground, an ionized channel is laid, as it were. Due to the ionization of air by free electrons, the electrical conductivity in the leader’s trajectory zone increases significantly. The leader, as it were, paves the way for the main discharge, moving from one electrode (cloud) to another (ground). Ionization occurs unevenly, so the leader can branch.
Backfire
The moment the leader approaches the ground, the tension at his end increases. A response streamer (channel) is thrown out from the ground or from objects protruding above the surface (trees, roofs of buildings) towards the leader. This property of lightning is used to protect against it by installing a lightning rod. Why does lightning strike a person or a tree? In fact, she doesn't care where to hit. After all, lightning seeks the shortest path between earth and sky. This is why it is dangerous to be on the plain or on the surface of the water during a thunderstorm.
When the leader reaches the ground, current begins to flow through the laid channel. It is at this moment that the main lightning flash is observed, accompanied by a sharp increase in current strength and energy release. The relevant question here is where does the lightning come from? It is interesting that the leader spreads from the cloud to the ground, but the opposite bright flash, which we are used to seeing, spreads from the ground to the cloud. It is more correct to say that lightning does not come from heaven to earth, but occurs between them.
Why does lightning thunder?
Thunder results from a shock wave generated by the rapid expansion of ionized channels. Why do we first see lightning and then hear thunder? It's all about the difference between the speeds of sound (340.29 m/s) and light (299,792,458 m/s). By counting the seconds between thunder and lightning and multiplying them by the speed of sound, you can find out at what distance from you the lightning struck.
Need a paper on atmospheric physics? For our readers there is now a 10% discount on any type of work