What is heat shrink tubing and its purpose?
This term refers to a tube made of a special heat-shrinkable material (usually thermopolymers). Such a product can change its size under the influence of a certain temperature, the source of which can be hot water, air, or an open flame.
A characteristic feature of such tubes is a high transverse compression ratio relative to the longitudinal one. That is, the tube can reduce its diameter several times (usually from 2 to 6), while its length will decrease by no more than 20% (for high-quality products 7-10%). This effect is clearly demonstrated below.
An example of changing the diameter of a heat-shrinkable tube (hereinafter HERE) under the influence of temperature
The figure shows a cambric, one part of which was subjected to heat treatment (B), the second, which was not subjected to heating, retained its original diameter (A).
Note that as the diameter decreases, the thickness of the walls of the product increases, which increases its electrical insulation characteristics.
Having dealt with the definition, let’s move on to the purpose, that is, the scope of use of heat-shrinkable materials. The main directions are as follows:
- Insulating material for electrical installation work. At the current time, it can be stated that electrical tape has almost been replaced by heat shrinkage. It is more convenient, more practical and meets the standards of GOST 19034-82.
- Thermal tubes have proven to be excellent protection against corrosion.
- Thanks to this coating, additional mechanical stability is provided for moving mechanisms; an example is the heat-shrink coating of rollers and conveyor rollers.
- Thermal tube casings are widely used in cable marking; for example, you can take any SCS.
Example of digital (A) and color (B) marking using heat shrink for wires - Application in various areas of production where it is necessary to provide protection from an aggressive environment, including the destructive effects of the atmosphere.
Properties of shrink products
When exposed to temperature, heat shrink tubing takes the shape of the object it is placed on.
During use, heat-shrinkable tubes exhibit their individual properties, which can be assessed due to the presence of thermopolymers in the composition. For example, when a heat-shrinkable conductor is exposed to high temperature, it actively and firmly contracts, due to which the quality of the seal will remain high for a long time.
To tighten the switched sections of electricity, a hair dryer or an ordinary lighter can be used. When processing, it is important not to overdo it, otherwise air bubbles will appear inside, due to which the quality of the crimp will be lost.
When heated, the material does not lose its properties, it is only capable of changing shape.
Quality control of electrical wire switching can be carried out using a transparent silicone tube.
Characteristics
The main characteristic of this type of insulation is its ability to shrink, which is measured in the ratio 2:1, 3:1, 6:1 and so on. Heat shrink with glue for wires is quite a convenient material that creates maximum strength after heat treatment. Such means are used to produce secure connections in difficult places.
Shrinkage coefficient
The next criterion is the shrinkage coefficient. What it is? This is the ratio of the original diameter to the diameter after the shrinkage process. That is, depending on the coefficient, the tube is reduced several times. There are odds:
- 2 to 1
- 3 to 1
- 4 to 1
- 6 to 1
The larger it is, the more difficult the product is to manufacture. Accordingly, their prices differ significantly. However, 4 to 1 tubes are considered more versatile than 2 to 1. If you connect two wires of different sections and different thicknesses, without heat shrink with large coefficients. you can't get by.
Wall thickness
Thermal tubes can have different wall thicknesses. According to this criterion they are divided into:
- thin-walled
- mid-range
- thick-walled
In addition, the thermotube can be adhesive - brand TTk. This is the one that has a layer of hot-melt adhesive applied to the inner surface. When heated, the glue melts and fills all microvoids, thereby ensuring complete sealing.
The walls stick to almost any surface. Excess glue should protrude around the edges.
It will not be possible to replace such hot-melt adhesive by first coating the inner walls of a simple tube. It is applied precisely during its manufacture. In addition, the adhesive coefficient of heat shrinkage is greater than that of a regular one - 3 * 1 or 4 * 1 versus 2 to 1. It can also be designed for greater stress due to the thickness of the walls.
Non-flammable
The material from which the product is made is of great importance. It is thanks to the composition of this material that the necessary properties are set in advance. If, for example, fire retardants are added to the composition, the tube acquires self-extinguishing properties and is designated by the NG index.
This does not mean that it does not burn at all. But in the absence of an external source of flame, it will quickly go out. This is achieved by preventing the flow of oxygen to the fire site with fire retardants.
Please note that if you use VVGng cable indoors, then you need to insulate the contacts and connection points with heat shrink only with the NG brand.
In this case, you can no longer use the usual cheaper option.
Color
Heat shrink tubing comes in a variety of colors, including clear ones. They are mainly used for marking.
They are very convenient for marking the ends of the cable, if you adhere to the old rules of color designation of phases. It is enough to place individual pieces on the end of the core.
For phases A-B-C, buy J (yellow) - G (green) - K (red).
But according to the new GOST, fA-fV-fS correspond to the colors K (brown) - CH (black) - S- (gray). Here you will have to use transparent tubes, or buy them to order.
There is also an original solution using multi-colored tape, on top of which a transparent thermal tube is applied. So the phases will be marked according to the new rules.
This is due to the specifics of the technological process. After each run of the same color, the auger is cleaned of old material. And this is precisely what affects the cost.
There are also two-tone yellow-green products. They are intended for grounding wires.
When you want to see and control the contacts after installation, a transparent tube will help you in this matter. Just be careful. Transparent ones will no longer be non-flammable products. Since the addition of fire retardants always leads to a change in color.
Therefore, self-extinguishing properties and transparency are not compatible here.
True, in this case it is better to heat the transparent heat shrink with a hairdryer rather than with a torch. Otherwise, you may accidentally damage the inscription itself.
Don't miss: Features of the TRONIC LiYY cable
Marking
Using markings you can choose the right insulating material. However, it must be read correctly in order to understand for what purposes the heat-shrinkable material is suitable. On the side of the products, two diameters are written using a black marker using a fraction. The first indicates what diameter is set by the manufacturer, the second indicates what it will become after shrinking at the joint. For example, the following values can be written on the insulation: 8/4, 60/25, 10/4 mm.
Kinds
Products in this group are classified according to the manufacturing method and the materials used for this. Depending on this, the following types are distinguished HERE:
- Polyolefin . They are made on the basis of chemically or radiation-crosslinked polyethylene, to which the addition of plasticizers, dyes, materials that help suppress combustion, etc. is added. Most heat shrink materials are produced using this technology. Operating temperature range from -50°C to 125°C. With special additives it can be expanded to 150°C. Good resistance to benzene and strong oxidizing agents, but with prolonged contact with fuels and lubricants the material is destroyed.
- Elastomers (base - synthetic rubber) . A distinctive feature is resistance to high temperatures (up to 175°C) and the harmful effects of fuels and lubricants. Unfortunately, the high cost of such products negatively affects demand.
- PVC (PVC) tubes made from thermoplastic polyvinyl chloride . This material has excellent insulating properties, but the small operating temperature range (from – 20°C to 80°C) and toxic emissions during fire significantly reduce its demand. It should be noted that rigid PVC is practically non-toxic, but the advent of PET technology (see below) has led to a reduction in the production of PVC materials.
- Heat-shrinkable polyester (PET) , this material has good chemical resistance and physical strength. It is ideal for the production of thin-walled and ultra-thin-walled TUT, replacing PVC materials.
- Fluoropolymer tubes. Due to complex technological processing, these products are used to solve specific problems when it is necessary to obtain unique physical and chemical properties.
Transparent PTFE Heat Shrink Tubing - Silicone based products. It is flexible and non-toxic. In addition, such products are chemically inert and have high electrical strength. Unfortunately, this material is not resistant to organic solvents, which makes it impossible to use silicone tubes for fuels and lubricants.
HERE it is also customary to classify according to the principle of installation; depending on this, the following types of heat shrinkage are distinguished:
- With an adhesive layer applied to the inside of the tube. This ensures the required level of sealing, preventing moisture from penetrating. As a rule, such tubes “shrink” threefold.
Medium-wall adhesive HERE - Without adhesive layer.
In addition, HERE they are distinguished by wall thickness, they can be:
- thin-walled;
- mid-wall;
- thick-walled.
Manufacturers also produce special types of TUT that have certain additional properties. Examples include products with increased electrical density (up to 1000 V), fluorescent additives, corrugated surfaces, etc.
Large Diameter Fluorescent Heat Shrink Tubing Set
Types and sizes of heat-shrinkable tubes. All technical data and characteristics.
Heat-shrinkable tubing (abbreviated HERE) was invented back in the 50s of the last century.
It was obtained by changing the molecular structure of polymers. It is called differently: heat-shrinkable, heat-shrinkable, thermal cambric or simply thermotube. This does not change the essence, since these are all the same products.
Its main task is to isolate contacts, but besides this, there are additional ways to use such devices:
- shrinkage onto the butt of a wooden or metal pole of a power transmission line to protect against corrosion and rotting of wood in the ground
- insulation of metal and water pipes from aggressive environments
- improving the ergonomics of tool handles and sports equipment by using ribbed or grooved tubes
- longitudinal sealing of cable bundles. In addition to external insulation, thanks to a special tape, the space between the cores is completely filled and insulated.
- cable protection from high temperatures. There are products for which the operating temperature range is from -65 to +260 degrees. This further helps the cable withstand extreme operating conditions when adjacent to open sources of fire or heat. Such brands are called Teflon or fluoroplastic.
- turning ordinary tools into something like dielectric ones, for example by insulating the tip of a screwdriver
The use of heat shrinkage is based on the shape memory effect. This is achieved through radiation exposure.
If, for example, a polymer is placed in a powerful flow of electrons, then at the molecular level, neighboring macromolecules are connected to each other. This technology is called cross-linking technology.
After this operation, the polymer itself becomes more elastic, and the product, when heated, acquires its original shape and original dimensions.
Theoretically, the same tube can be seated an infinite number of times. If you had a device for heating and inflating it, it would turn into a reusable product. Moreover, its shelf life in its original state is tens of years. All characteristics and quality of the product, subject to certain requirements, do not depend significantly on the date of manufacture.
Today, heat shrink tubing has gained enormous commercial and technical importance throughout the world. However, the main area of application remains in the fields of electronics and electrical engineering.
Thermal tubes are much more efficient than conventional tubes, which are brand TV-40. In addition to technical resistance, they also have chemical resistance. And this allows you to reliably protect insulation and contacts in places with aggressive environments - underground, in wells, cable ducts.
Properties and technical specifications
The main characteristic of HERE is the shrinkage coefficient, it can be from 200% to 600%. Accordingly, an important parameter is the diameter of the product before and after heat treatment. The technical specifications also indicate resistance to a particular operating environment. Depending on this, the product may be:
- oil resistant;
- chemically inert;
- high-voltage (insulation can withstand voltages up to 1000 V);
- petrol resistant;
- light-stabilized, not exposed to solar radiation, in particular UV;
- heat-resistant (non-flammable).
Also important characteristics include the temperature of shrinkage and operating range.
As for the shape HERE, it can be flattened, oval and round. This does not affect the installation in any way, but is made for convenient transportation. As a rule, thin-walled products are supplied in coils, and for this it is more convenient to give them a flattened and oval shape.
High temperature HERE in bays
Adhesive and thick-walled products are transported in cut form to prevent kinks.
Properties of the conduit
The performance characteristics of heat shrinkage are manifested through the use of special thermopolymers in production. The latter can both shrink and expand under the influence of high temperatures. Therefore, it is enough to put the tube on the conductor and then warm it up with a regular lighter or a hair dryer. As a result of such manipulations, the dimensions of the product are reduced, tightly fitting the object, repeating its shape. The main condition is to prevent overheating, otherwise bubbles will form in the tube and it will lose its properties.
During the manufacturing process, the polymer is exposed to radiation, which promotes the release of hydrogen and the joining of molecules of the substance. The result is a durable “cross-linked” material with high heat resistance. Under the influence of temperatures, it becomes elastic, but does not melt, but only changes shape.
No matter how good the material is, it is very important to choose it correctly for a specific situation. Because of this, the main property of heat shrinkage is its ability to change diameter and thickness. A big advantage is the wide range of temperatures, as well as the color palette of products. The latter quality makes it possible to use thermal tubes for marking conductors and cables. To control the quality of electrical switching, a transparent tube is often used.
Marking of heat shrink tubes
In most cases, the markings indicate the main parameters HERE, namely: diameters before and after shrinkage.
Example of heat shrink tube designation
As a rule, these parameters are indicated through a fraction, for example: “4.80/2.40 mm”. It happens that diameters are indicated in inches, most of them on products manufactured in the USA and Europe. But you shouldn’t trust this too much; counterfeit products may also have similar markings.
Some manufacturers indicate the original diameter and shrinkage ratio on the tubes, for example: “20 mm 3:1”. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1DTd9rVJN9Y
Size range of heat shrink tubes
The product range (in our case, size range) depends on manufacturers and suppliers. You can get complete information on this issue on the official websites of manufacturers or their dealers. As an example, we provide information on the size range HERE®.
Table: available sizes from the manufacturer HERE®
Selecting Heat Shrink Tube
First of all, you need to decide on the operating conditions, then select HERE with the appropriate characteristics. For example, if contact with fuels and lubricants is possible, then the product must be oil and gasoline resistant. If it is necessary to ensure reliable insulation of the wires of a high-voltage cable, a tube is selected with protection at the connection point up to 1000 V.
Next comes an important point - selection of diameter HERE. In this case, the “-10+20” principle should be used. It is as follows: the minimum shrinkage should be no less than 10% of the original diameter and no more than 20% of the specified shrinkage parameter. A clear example of how this principle works is presented below.
An example of how to choose optimal shrinkage
When choosing the length, it should be taken into account that HERE gives longitudinal shrinkage. In low-quality products from the Land of the Rising Sun, it can be up to 20%. In branded kits, as a rule, longitudinal compression does not exceed 5-7%.
Advantages and disadvantages
When compared to other types of insulation, heat shrink has at least four advantages.
Don't miss: Location of outlets in the bedroom. How to properly place sockets and switches in the bedroom
Firstly, since the heat-shrinkable tube fits very tightly, it does not move due to various mechanical influences. Secondly, installation is a simple and quick process, but you still need to know some rules of use. Thirdly, after shrinking, the insulation material becomes stronger, so the wire becomes even more resistant to mechanical damage and acquires additional rigidity at the junction. And the service life is much longer than that of conventional electrical tape. The fourth plus is a wide range of applications.
The disadvantages of the tube include the following:
- It cannot be reused, because when heated it changes its diameter, so it will definitely be damaged when removed.
- The price of heat-shrinkable tubing is higher than the price of electrical tape, but not so much that it becomes a decisive factor when choosing a protective and insulating material.
If during use some other shortcomings are discovered, then these are shortcomings of the selected manufacturer.
The video below provides a visual comparison of heat shrink and electrical tape:
How to use?
It is advisable to have specialized equipment for this process - a hot air gun or a heat gun. You can set the required shrinkage temperature on them, which greatly simplifies the process. If it is not possible to use special equipment, you can heat the tube with an open flame (a lighter or a match) or place it in boiling water.
Let us describe in detail the algorithm of actions:
- Thick or large cross-sections are recommended to be heated before the process to half the nominal temperature required for shrinkage. The same applies to wide elastic bands. Thin-walled products or small-diameter tubes do not need to be heated in advance.
- Carefully cut off the required length HERE. This can be done with ordinary scissors. Make sure there are no tears or burrs, as tearing may occur during the shrinking process.
- Next, the tube needs to be slightly stretched, and then pulled onto the selected location. You also need to put it on HERE carefully so as not to damage the integrity of the surface.
- Heating is carried out in accordance with the specified temperature. Exceeding it can lead to surface deformation. The hot air flow must be directed from one edge to the other or from the center to the edges.
- Once heating is complete, allow the tube to cool. After this, the procedure is considered completed.
As you can see, using HERE is quite simple, the main thing is to produce uniform heating and not exceed the permissible temperature. If during installation the heat shrink tube bursts or becomes deformed, it must be removed and replaced.
Purpose of products
The main purpose of heat shrink is to insulate current-carrying conductors. Due to the electrical insulating properties and ease of installation of the product, they are increasingly replacing conventional electrical tape.
Today, similar products used to protect the switching of conductors can be easily found on the shelves of electrical goods stores. The demand for thermocambrics as an insulation material lies in the ability to reduce their size under the influence of heat. The required shrinkage temperature is no more than 120 °C. However, in order to do the job correctly, you need to know how to use heat shrink tubing. When exposed to high temperatures, the product is tightly and securely fixed to the conductor, providing insulation and mechanical protection.
Today, manufacturers provide a wide range of colors and sizes of heat shrink tubing. Due to this, they are used not only for insulation, but also for accurately determining in the future the purpose of the insulated conductor.
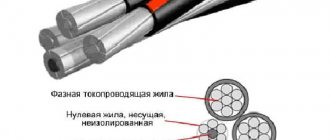
Thus, when processing DC conductors, many electricians use red tubes for the positive and black tubes for the negative. The five-core electrical cable is marked as follows:
- black, brown, and white - phase conductors;
- blue - 0;
- yellow or green - grounding.
Using a heat-shrinkable tube to mark the conductors is very convenient, because it does not need to be placed along the entire length of the conductor. You only need to pull a small piece of the product over the insulating layer onto the end of the wire. This material is very reliable, resistant to external influences and temperature changes. The service life of a thermotube is at least 20 years. These are durable, budget-friendly and easy-to-use products.