Areas of use of PV-1 wires
All types of this wire have excellent protection from mechanical damage, are resistant to aggressive environmental elements and are insulated from non-flammable materials. Thanks to these qualities, their scope of application is very wide:
- Wires are laid between electrical installations in pipes;
- Over the air and underground;
- In the channels of building structures;
- For power supply of industrial equipment;
- Power supply for electrical outlets and lighting;
Manufacturers make wires of various sections and structures, all of them are designed to operate within an alternating voltage range of up to 450V with a frequency of 400Hz.
An example of connecting an electric motor and wire controls PV-1
Operation with direct current is allowed at voltages up to 1000V. The cable structure is resistant to bending at large angles relative to the size of the wire radius, and to acoustic and vibration loads.
Areas of use
Thanks to the parameters and many cross-section options, PV conductors can be called universal. They have become widespread both in everyday life and in production, helping to create electrical wiring in residential and non-residential premises and various communication systems.
In production, PV can be used even in high voltage equipment, since the improved double polyvinyl chloride insulation does not heat up and ensures safety. There are no special restrictions for it: it is suitable for switching various units, mechanisms, machines, and lighting installations.
Information article from the electrical hypermarket VSE-E.
Main elements of PV-1 wire
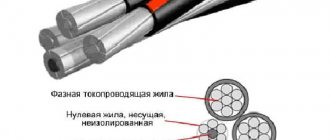
The wire design provides only one current-carrying core; it can be monolithic or consist of several twisted wires of different cross-sections. Manufacturers produce PV-1 wire of the following sections:
The wire with a pink sheath has a solid copper core, the yellow-green wire is flexible with a core of several thin twisted wires.
Cross-sections and weight of wires of PV1 or (PUV) brand:
| Section, S - Ø mm 2 | Weight kg per 1km | outer Ø in mm |
| 2,5 | 15,4 | 3,5 — 4 |
| 4 | 21,2 | 4 – 4,5 |
| 6 | 27,7 | 4,5 — 5 |
| 10 | 45 | 5,5 – 6.5 |
These dimensions are determined by GOST 22483, an insulating sheath around a core of plastic compound of a certain color, the shades of which are also determined by the guest and their purpose when installed in electrical circuits. All these requirements are mandatory for installers in electrical outlet networks with alternating current and voltage of 220 or 380 V. The color of the wire insulation determines its purpose:
- Blue and black are used as neutral conductors;
- Red or white as phase wire;
- Yellow - green as a grounding conductor.
Wires with insulation of different colors
In DC networks, the range of colors can be wider; yellow, green, purple and other shades are used. This is done for convenient tracking of wires passing in the harnesses in order to check the continuity of the circuit and, if necessary, replace them. Please note that the PV brand according to the new identification is called PUV, practically it is one wire, its technical characteristics remain the same, it belongs to the first class of cross-section Ø 0.5 - 10 mm2.
How to choose the right PV-1 cable
Before purchasing, you must rely on the conditions of use and permitted loads during the energy transfer process. If conductors with a smaller cross-section than necessary are used, overheating may occur. Because of this, the outer sheath will melt and the wire will fail. When purchasing cable products, you must visually inspect them and check for damage to the insulation.
You might be interested in Description of the VVGng-LS cable
The same inspection must be carried out after transporting the cable or immediately before installation. This can be done by testing the wire.
Also, before purchasing you must request a certificate of conformity. It must indicate the plant itself, the length of the cable and the date of its production, and a seal about passing the tests. Correct cable products are manufactured in accordance with GOST standards.
The process of laying in a groove
When checking the certificate, you need to pay attention to the name of the manufacturer, which must be written in full, as well as the expiration date of the document.
Important! It is advisable to choose high-quality factories that have been on the market for more than 10 years. Therefore, before purchasing, you can read reviews about the best sellers of cable products.
Operational and technical characteristics of PV-1
The permissible values of individual parameters listed in the table are determined experimentally.
| Humidity (at 35°C) | 100% |
| Guarantee of trouble-free operation subject to all safety requirements | 2 years. |
| Tested (at an alternating voltage of 50 Hz) for 15 minutes. after 24 hours. Keeping under water | 2.5 kV |
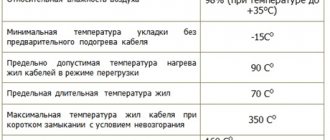
| Critical operating temperature of the conductor. | 70°C |
| Maximum negative temperature for installation without heating, | -15°С |
| Acceptable voltage for AC current | 450 V. |
| Bending radius when installing wire | 10 outer Ø |
| Temperature range during operation. | +35°С -50°С |
| Resistance of the insulating layer, per 1 km. | 1.0 MOhm. |
Comparative characteristics of PUV with other wires
In many respects, other wires are not inferior to the option under consideration, and some are even better according to the stated parameters. But in practice, sometimes it turns out differently, the PUNP wire, for example, has a large assortment of wire cross-sections, several cores 2,3 and even 5 in double insulation, at first glance it is more practical to use it. It turns out that many parameters of PUNP do not correspond to the declared characteristics:
- Smaller wire cross-section;
- Wire alloy composition, reduced percentage of copper;
- The composition of the insulating layer must be made of non-combustible materials;
- The thickness of the insulation layer can be reduced to 20%.
Tip #1. If possible, try not to buy PUNP, take wires with similar characteristics. It is not possible to check all the parameters on site; the composition of the alloy and insulation can only be assessed at a glance, and this can only be done by an electrician with extensive experience.
Let's compare the parameters of other brands summarized in the table:
| Wire type | Number of cores | Produced sections, mm2 | Core cross-section class |
| Automatic reclosing | one | 2,5…1625-120 | First second |
| PV-1 | 0,5…1016-95 | First second | |
| PV-2 | 2,5…95 | Second | |
| PV-Z | one | 0,5…1,5 2,5; 4,0 6,0-95 | Second, third, fourth |
| PV-4 | one | 0,5; 0,751,0; 1,52,5; 4,06,0; 10 | Fourth fifth |
| APPV | Two - three | 2,5…6,0 | First grade |
| PPV | 0,75…4,0 | ||
| APBPP | two | 2,5; 4,0 | |
| PBPP | Two - three | 15…25 | |
| PBPPz | Three | 1,0…2,5 | |
| PUNP | Two - three | 1,01,5…6,0 | |
| PRKA | one | 0,5…2,5 |
Wires with a cross section of 0.75 mm2 are ideal for laying a lighting network in apartments and private houses. Based on the data in the table, it can be seen that some brands do not produce such a section, while others do not inspire confidence in quality, so consumers prefer to purchase PV-1.
Conditions for storage and transportation of PUV wires
In factories, wires are wound into coils or onto wooden drums; the coils can have different lengths and weights, this depends on the cross-section of the wire, the norms determined by the standards and the manufacturers:
Designation of passages
|
Coil of wire PV-1 in plastic packaging
Length of wire PV (PUV) in meters for various drum designs:
| Operating voltage 0.66 kV | One core and cross-section in mm2 | External Ø of drum structure mm | ||||
| Brand | 800mm | 1000mm | 1200mm | 1400mm | 1600mm | |
| PUV | 1x10 | 3200m | 7300m | 14500m | 22400m | 36600m |
| 1x16 | 2000m | 4400m | 8800m | 13700m | 22400m | |
| 1x25 | 1200m | 2800m | 5600m | 8700m | 14200m | |
| 1x35 | 1000m | 2200m | 4400m | 6800m | 11100m | |
| 1x50 | 700m | 1600m | 3150m | 4900m | 8000m | |
| 1x70 | 500m | 1100m | 2300m | 3600m | 5900m | |
| PUV | 1x95 | 300m | 800m | 1600m | 2600m | 4200m |
Packing wires with a thick section on the structure of wooden drums is associated with the large weight of the wire, a coil of which requires a rigid, more durable structure. This makes it more convenient to transport and unwind wires at work sites.
Specifications
Mechanical
Mechanical parameters mean the resistance of the cores and the insulating layer of the wire to atmospheric influences, flexibility, compression and rupture.
- One of the main features of all brands of wires is their ability to bend. PV-1 cannot be called flexible. The bending radius is no more than 10 outer diameters of this wire.
- The operating temperature range ranges from -50 to +70 degrees Celsius.
- A significant advantage of this brand is moisture resistance. Test results showed that at a temperature of +30 degrees the wire does not lose its functionality even at a relative humidity of 100%.
- It has good resistance to acoustic, vibration, mechanical, thermal, chemical and other influences.
Another advantage of the modification is that it does not propagate combustion. Thanks to this feature, the wire was taken as the basis for high-voltage PVV-1, which is actively used in the automotive industry.
Electrical
Grounding device
It is the electrical characteristics that are most often fundamental. In this case, PV-1 shows its best side.
- The electrical design is intended for use in AC electrical networks with voltages up to 450 V and a frequency of no more than 400 Hz. If we are talking about DC networks, the voltage should be no more than 1 kV.
- The resistance force primarily depends on the cross-section of the wire. For example, 0.5 mm kV resistance is not more than 0.015 Mohm, otherwise there will be problems.
- The peculiarity of PV-1 is its stable parameters. Even during use, the electrical resistance does not differ from the nominal parameters by more than 120%.
All studies are carried out on a 1 km long wire and at an operating temperature in the range of +70-90 degrees.
Approximate prices for wires
The price of wires depends on many parameters, mainly on the cross-section of the wire and the region in which it is sold. In Moscow and the region prices are approximately the following:
| Price in rub. | Section mm2 |
| from 3.5. | 05 |
| from 4.5. | 075 |
| from 6. | 1 |
| from 8.5. | 1.5 |
| from 51.5. | 10 |
| from 34 | 6 |
In most cases, prices in other regions of Russia and CIS countries do not differ significantly. Prices for PV-1 wires in Novosibirsk:
| Cross section of one PV-1 core in mm2 | Price in rub. |
| 0,5 | 2.39 |
| 0,75 | 3.59 |
| 1 | 4.86 |
| 1.5 | 6.58 |
| 2.5 | 10.24 |
| 4 | 15.98 |
| 6 | 24.35 |
| 10 | 40.56 |
The terms of sale are the same in almost all companies; payment by non-cash or bank transfers is possible. Delivery within the city is free to other regions, taking into account the carrier's prices; wholesale customers receive significant discounts. The tables show that in provincial regions remote from the capital, prices are slightly more expensive. Apparently, this is due to transportation costs, data taken as of 08/08/2017.
Explanation of the name and nomenclature of PV1 wires
Even without certificates and other accompanying documents, you can obtain information about the main parameters from a standardized designation. A detailed study of the nomenclature will help you find a product that is suitable for current and other operating conditions. Careful preparation eliminates mistakes when purchasing.
Decoding the name of the wires PV1
Typical markings indicate the following features:
- P – wire;
- B – protective shell material (polyvinyl chloride);
- 1 – flexibility class, indicating resistance to deformation;
- the absence of the letter “A” (aluminum) at the beginning of the abbreviation indicates that the conductor is made of electrical copper.
This digital symbol corresponds to a relatively large permissible bending radius. PV 1 wires are installation wires. This category assumes the possibility of installation in a stationary position.
For your information. Installation modifications of wires (class 3) are created in a multi-core design. This engineering solution significantly increases flexibility. These products are used to create power cords and connect moving drives.
Nomenclature of wires PV1
Domestic enterprises produce these products in accordance with industry GOST 6323-79. Subject to compliance with the standards established by the standard, products must comply with the following indicators (part of the nomenclature):
- for a cross-sectional area of 0.5 mm square. the maximum diameter along the outer surface is 2.4 mm, the weight of one kilometer is 8 kg (0.5 / 2.4 / 8);
- 0,75/ 2,6/ 10;
- 1/ 2,8/ 13;
- 1,5/ 3,3/ 19;
- 2,5/ 3,9/ 30;
- 6/ 4,9/ 65;
- 25/ 9,8/ 260.
Typical errors when working with these and other wires
- When purchasing a wire, visually check the integrity of the insulation; if possible, test the coil with a multimeter to ensure the integrity of the core. Look for a tag that should indicate the wire brand, cross-section, coil length and weight;
- Often wooden drums or coils are stacked for storage in open ground; this is strictly prohibited. Coils should be stored on racks in a dry place;
- It is not recommended to use the PUV for grounding by connecting the equipment frame to a common ground loop. In this case, the wire must have a cross-section of at least 16 mm2; for this purpose, PV-2 and a larger cross-section class are installed.
Sometimes PUVs with monolithic copper conductors are installed on household appliances or industrial equipment with moving elements. This could be a lawn mower, a moving part of technological equipment, a winch for a crane beam and others. This is strictly prohibited; during operation, the wires often bend and break off at the joints. For these purposes, only flexible stranded wires are used, preferably with double rubber insulation.
- When laying PUV through walls as socket and lighting networks, it must be passed through plastic or metal pipes;
- Sometimes inexperienced installers unwind the wires from the outside of the coil; this periodically requires lifting and turning the coil over, which ultimately results in the wire getting tangled. The end of the wire must be removed from the inside of the coil and pulled out sequentially, so that it will evenly come out in rings without getting tangled.
There are special devices on which the coil is placed and the wire is unwound
Tip #2. To pull the wire through the casing or pipes, use stiff steel wire. First, a steel cable is threaded, the wires are tied to it, then they are pulled through the pipe to the other side.