- home
- Useful
- Vertical grounding: its characteristics and installation
»
»
The grounding conductor is an important component of the lightning protection system along with the lightning rod and lightning rod. By grounding, the incoming current is discharged into the ground, and thus about 50% of the charge is neutralized. Grounding electrodes come in different types and shapes, but they are all conventionally divided into vertical and horizontal - according to their location relative to the ground. In central Russia, it is vertical grounding that has become most widespread, since it is quite effective, although in some cases it is relatively difficult to install.
What is vertical grounding?
A typical vertical ground electrode is a metal pin that has a certain diameter and length necessary for reliable fixation in the ground. Metal is a good conductor of electricity, and due to financial feasibility, iron ground electrodes are most widely used (although copper wire can be used along with them).
Vertical grounding is carried out directly next to the construction site. Round or other shaped rods are used as grounding conductors. Since one metal pin may not be enough to discharge a large charge into the ground, several vertical ground electrodes are installed simultaneously. At the same time, they are connected to each other by fittings and electric welding.
Main characteristics of vertical grounding electrodes
When choosing materials for vertical grounding and preparing for installation work, the following parameters should be taken into account:
- number and location of rods;
- diameter and length of pins;
- installation depth;
- soil type, freezing level.
Grounding may consist, as already mentioned, of one or more interconnected rods. In the upper part of the ground electrode, closer to the surface of the earth, a reinforcing strip is welded.
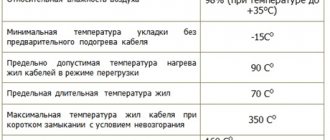
The diameter of each rod should not be less than 16 mm; pins with a thickness of 18-20 mm are usually installed. The length of the ground electrodes can be from 2.5 m; 3-meter rods are most often used. However, this is not the limit - there are rods up to 10 meters long or more.
The minimum permissible installation depth is 1.5 meters. It is important to take into account the type of soil, the level of freezing, as well as its water saturation and the level of groundwater. You also need to take into account the number of grounding rods: for example, one pin 15 meters long corresponds to three interconnected rods, each about 5 meters long.
Materials for the construction of grounding electrodes
Current regulations allow the possibility of manufacturing grounding electrodes from galvanized steel, electrolytically coated copper or pure copper. Copper is often used as a material for protective coatings on steel grounding electrodes. However, none of the standards mention galvanized steel approved materials. The thickness of coatings is also regulated by standards. They are different for different materials, they also depend on how the elements are laid. Others are for horizontal trenches and others are for vertical trenches.
Related article: All about liquid cement
Features of installation of a vertical ground electrode
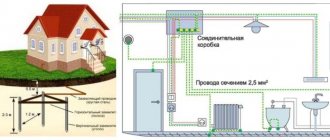
The vertical rod is installed in the ground in a previously prepared trench. Its depth can be 60-70 cm, this is necessary so that the ground electrode is completely immersed in the ground and the connection point of the current conductor is below the surface. At the same level, the connecting strip is welded if there are two or more grounding conductors.
A trench about 60 cm deep can be prepared around the perimeter of the entire building. In this case, the rods are placed at approximately the same distance from each other.
Installation work is carried out manually, using mechanized tools or special equipment. The choice of method depends on the length of the rods, the level of burial, the composition of the soil and the available capabilities. For example, if the depth is shallow and the ground is soft, the ground electrode can be driven in with a regular sledgehammer. In difficult cases, a jackhammer or an excavator with a bucket is used.
Rules for calculating a vertical ground electrode and its installation
In order to ensure electrical safety in a home or business, it is necessary to install a grounding loop. The earth is an excellent conductor that is negatively charged, and if the housing of powerful electrical appliances is connected to this conductor through vertical grounding, then there is no fear of electric shock, even in the event of a phase voltage leak.
In order to install vertical grounding that meets all rules and standards, it is necessary to become familiar with the basic principles of the correct installation of this method of electrical protection.
Materials for vertical grounding
As practice has shown, the best vertical grounding conductor is a steel round rod, which is installed in the ground directly next to the protected object. In addition to a steel rod, it is allowed to use a copper wire as a grounding conductor. But given the high cost of this material, it is not often used as a grounding conductor. One rod is not enough to provide reliable protection against electric shock, so rods placed at some distance from each other are connected using electric welding.
In order to connect the rods to each other, it is necessary to purchase fittings that are welded to each round steel ground electrode and introduced into the house for connection to electrical appliances and devices.
The price of a steel rod is low, and if you have an electric welding machine, you can do all the work yourself. The cost of consumables when carrying out such work will also not be too high, so grounding, which is done using steel rods and reinforcement, will not require significant financial investments.
Calculation of parameters
Before starting installation work, it is necessary to correctly calculate the grounding parameters. The contact area of the vertical ground electrode with the rock directly depends on the soil resistance.
If grounding installation is carried out in the northern regions of the country, where the soil freezes to a considerable depth, the contact area of the conductor with the soil should be larger than in the south, where the soil does not freeze to a depth of more than 0.5 meters.
When the soil freezes, its resistance increases sharply, which negatively affects the efficiency of the ground loop. Therefore, to ensure the appropriate level of electrical protection in permafrost conditions, installation technologies that differ from the generally accepted ones can be used.
If the ground is completely frozen, then it is necessary to drill to a considerable depth, install metal electrodes and fill the hole with previously removed soil.
The area of contact between soil and soil and the resistivity of the substance also depend on the rock in which it is necessary to ground.
The highest resistance value is in rocky and rocky soil. The length of the vertical ground electrode, in this case, will be maximum in order to ensure the normal passage of electric current in the rock. In such conditions, installation of vertical grounding is the only way to implement electrical protection of the facility. The most optimal option for installing electrical protection in such conditions is the use of a special vibrator, which makes it quite easy to install the rod in rocky or rocky soil.
If grounding is being installed in chernozem and peat, then to ensure normal grounding, immersing the electrode to a depth of 1.5 meters is sufficient.
The diameter of the vertical grounding conductor must be at least 16 mm. Typically, metal reinforcement with a diameter of 18 - 20 mm is used as vertical grounding rods.
Installation of equipment
After the type of soil where the grounding is planned to be installed has been determined, you can begin installing the rods.
Before installing the rods in the ground, it is necessary to remove the top layer of soil to a depth of at least 0.5 meters. Usually such a trench is made along the perimeter of the entire building. The distance between vertical grounding conductors should be no more than 5 meters. The number of vertical grounding conductors is easy to calculate if the total length of the trench is divided by “5”. For example, with a total trench length of 50 meters, the number of vertical ground electrodes will be 10 pieces.
In order to penetrate the rods into the ground to the required depth, you can drive them in with a sledgehammer. If the soil is soft and the length of the rods does not exceed 3 meters, then manual installation will not take much time and effort. For ease of further installation, it is necessary to install vertical rods in the trench so that they rise from the bottom at a height of 10 - 20 cm.
If the ground is quite rocky, you can use a jackhammer with a special attachment to install vertical rods.
The original installation method is used if there is a tractor-excavator of the “Cockerel” type. The hydraulic bucket control drive allows you to exert sufficient force on a vertically placed rod so that the latter completely enters even into rocky soil.
After installing all vertical grounding conductors, they are connected to each other by horizontally located pieces of reinforcement.
The diameter of the horizontally located rods must be at least 10 cm, otherwise the resistance reading at the required level will not be achieved.
The rods can be connected to each other using steel tape. The width of the tape must be at least 48 mm, and the thickness of the metal must be at least 4 mm. Welding must be performed with high quality so that a corrosion process does not form at the joints of the metal, which can be significantly enhanced by currents passing through the weld.
To ensure the unhindered flow of electric current through the conductor, a resistance of vertical grounding conductors of 4 ohms should be provided along the entire perimeter of the electrical circuit. If it is not possible to achieve this ideal resistance value, a deviation of this value up to 10 ohms is permissible, without compromising the protective properties of vertical grounding.
If immediately after installing the electrical protection it is put into operation, then the places where the vertical rods are located must be watered with a significant amount of water. In this way, it is possible to restore the structure of the soil, which will most effectively transfer electrical potential from the metal rods to the ground.
Self-installation
Vertical grounding electrodes can be installed independently. During installation, it is necessary to know the composition of the soil in order to determine the approximate installation depth of the working electrodes. To install grounding, you will need to purchase a welding machine and the required number of electrodes in order to weld vertical and horizontal ground electrodes.
It is not recommended to use various clamps and other threaded connections to connect metals. Over time, such places can significantly degrade the conductivity of a section of the electrical circuit, which will negatively affect the effectiveness of the ground loop. If the soil does not freeze to a depth of more than 0.5 meters in winter, and is not rocky or rocky, then you can use a round rod no more than 1.5 meters long.
Under unfavorable conditions for installing grounding, the depth of the rods should be at least 3 meters, and the distance between them can be reduced to 4 meters. It is not recommended to further reduce the distance between the electrodes, otherwise the total resistance of the grounding installation may increase significantly due to the shielding effect.
If you don’t want to install the grounding yourself, you can contact specialized companies that will install vertical grounding in the area adjacent to the house in the shortest possible time. Although such services will cost money, the time savings can be significant. And if this resource is very important, then it is better to entrust the work to professionals.
evosnab.ru
Calculation of parameters
Before selecting and installing a vertical ground electrode, you should conduct a study of the area. It is important to make sure what kind of soil is at the installation site and to what depth it freezes in winter. In addition, water saturation and groundwater levels are determined.
The fact is that different types of soil have different resistance. The lower the resistance, the higher the grounding efficiency. Conversely, in soils with high resistance, the efficiency of ground electrodes is lower and therefore additional efforts are being made to increase it. In particular, by all means the area of contact between the ground electrode and the soil is increased.
Fertile chernozem soils are characterized by the least resistance. Installation of vertical rods in them is allowed to a depth of 1.5 meters. On the contrary, the maximum resistance is found in rocky soil, where the iron rods are buried as deep as possible, and installation work is associated with significant difficulties.
The level of soil freezing deserves special attention. It may be different in different soils. This is taken into account because when the soil freezes, its resistance increases significantly, and the efficiency of grounding is reduced. Therefore, the area of contact with the metal in this case should also be larger. It is advisable to install grounding below the level to which the ground freezes.
Building ground electrode
The main purpose of grounding a construction site is to comply with the requirements for protection against electric shock when using electrical installations, as well as the functional requirements for installing lightning protection. In particular, these are tasks such as:
- ensuring reliable operation of the electrical installation;
- compliance with all requirements relating to the protection of human life;
- effective equalization of potentials of all objects and removal of overvoltage energy arising in electrical networks, including due to the impact of nearby lightning discharges;
- leading ground fault currents and leakage currents;
- safe dissipation of lightning current discharged from the lightning protection system in the ground.
The design principles of grounding electrodes for lightning protection purposes were included in the GOST R 57190-2016 standard, which distinguishes between two types of grounding electrodes:
- A system of types consisting of horizontal and vertical grounding electrodes made externally. The number of such grounding electrodes must be at least 2
- Type B system, in the form of a base, ring or grid ground electrode.
The effectiveness of a grounding system is determined by its grounding resistance. In general, unless there are special circumstances, the recommendation for normal construction work should not exceed 10 ohms (ohms). However, for single-family homes this is often too restrictive. Sometimes energy companies require this, but this has no basis in legal provisions or technical standards. Private houses are objects with the lowest levels of protection (III and IV), for which the GOST R 57190-2016 standard does not provide the required maximum grounding resistance. Instead, he accepts as acceptable a constant minimum grounding size of 5 m. So whatever grounding resistance comes to us then, that will be accepted.
Article on the topic: Motoblocks and mini tractors: universal assistants for summer residents and farmers
Stages of installation work
There are two possible options for installation work:
- Preliminary study of the area and study of the level of soil resistance with subsequent prompt installation of ground electrodes.
- Sequential installation of rods with resistance measurement until the optimal value is achieved.
In the first case, survey work is required, which involves additional time and money. In the second, it is important to strictly follow the installation technology.
Stages of sequential installation of a vertical ground electrode:
- the pin is buried to the minimum level, after which the resistance is measured;
- a second section is welded to the installed rod and the measurement is taken;
- work continues until the optimal resistance is achieved.
Vertical ground electrodes
Vertical grounding electrodes are made of pipes or specially prepared rods sunk into the ground so that their upper ends are below ground level. It is recommended that the distance between the individual elements of the grounding electrode be at a distance not less than their length. Vertically driven ground electrodes are especially useful when soil resistivity decreases with increasing depth. Their driving depth is usually about 2.5 meters, however there are ground electrodes that are 7 meters long. Further increasing this measurement rarely brings noticeable benefits. If the resistance of the ground electrode is made higher than required, the next one must be immersed and connected to the first in parallel.
The distance between these elements should be:
- equal to at least their length in the case of two vertical elements;
- greater spacing with more vertical elements.
If there is a risk of freezing or drying out of the soil, the length of the vertical elements should be increased by 1 or 2 meters.
Related article: Drinking water for office and home
The elements connecting the individual parts of the vertical ground electrode must have the same mechanical strength as the rods or pipes of the ground electrode, and must also be resistant to mechanical stress during impact.
Methods for deepening electrodes
Depending on the type of soil and the depth of the electrode, one or another installation method is selected. It was already noted above that both manual and mechanized installation is possible (using a tool or a special machine). In this case, various methods of introducing rods are applicable.
What deepening methods are applicable:
- driving;
- indentation;
- screwing in;
- vibration immersion;
- drilling a well with subsequent installation of an electrode.
In soft soils, methods such as pressing and screwing are applicable. Clogging can also be used, and several methods are often combined. If the soil is more dense and complex, only driving can be used (screwing and pressing are no longer applicable).
Vibration immersion using special equipment has shown its effectiveness in frozen soils. This technology is often used in winter.
In the most difficult - rocky - areas, as well as in frozen soil, if it is necessary to immerse the pins deeply, a rational way is to pre-drill a well into which the electrode is then placed.
The installation of vertical grounding is clearly presented in the following video:
What is a deep ground electrode and why is it needed?
A traditional ground loop requires a lot of site space. When creating a contour of this type, the volume of excavation work is large.
These two factors - a lot of space, an abundance of excavation work - are a big disadvantage of the classical grounding system.
Most of the listed disadvantages are devoid of a vertical, deep grounding system or, scientifically speaking, a modular-pin grounding system. Deep grounding electrodes are manufactured in industrial conditions from copper-plated steel and are a set of elements. The service life of a similar ground electrode reaches 30 years.
It provides stable values of resistance to current spreading at any time of the year due to the driving of vertical electrodes to a great depth - up to 30 m.
Everything is not so simple in this system at first glance. This system is more expensive - this is its main drawback. The cost of materials and labor for constructing such a grounding system is higher than that of a traditional one.
But if you compare the service life, high reliability, and the absence of the need for regular monitoring, it turns out that the costs are completely worth it.
Construction of the ground electrode.
Consists of individual rods d = 016 mm, connected via threaded couplings.
Special hardened steel allows them to be used as deep ones, with the possibility of immersion to a depth of about 20 m, while using deep layers of soil with low resistivity. This helps to quickly achieve the normalized resistance values of grounding devices.
The material and design of the grounding device are resistant to corrosion thanks to a protective zinc coating obtained by hot-dip galvanizing, which ensures the durability of the grounding device throughout the entire life of the electrical installation.
The assembled grounding rod is a set of individual rods connected to each other by means of couplings, immersed to a depth of 1.5 m to 20 m, depending on the required value of grounding resistance.
Corrosion resistance is ensured by protecting the rods with a zinc coating obtained by hot-dip galvanizing with a thickness of at least 80 microns. To drive the rods into the ground, a vibrating impact tool with an impact energy of 25–50 J is used.
Installation of deep, vertical grounding.
- Prepare a pit. A small hole - 50-70 cm deep,
- Take out the first rod, screw the tips (top and bottom), the sharp ones into the ground, the second one is needed for the impact tool, treat it with a special paste (anti-corrosion, conductive).
- Place the assembled first part of the rod vertically on the bottom of the dug pit.
- Using a hammer drill and strong hands, immerse the first part of the rod into the ground to such a depth that a part of it 250 mm long remains above the ground surface.
- pull the next rod out of the box and perform the same actions as from the first.
- We work until the set runs out.
What needs to be done after installing the ground loop.
After completing work on the circuit installation, it is necessary to take measurements.
Using instruments, make sure that the circuit fits within the parameters established by the regulatory documentation.
Such measurements are carried out by a licensed electrical laboratory.
The circuit is issued:
- passport;
- test report;
- act of hidden work;
- certificate of acceptance into operation.