The modern electrical system of apartments and houses is different from what it was before. If in Soviet times, apart from a TV, an iron and, naturally, more lighting, there were no electrical appliances, then modern housing is full of devices of varying power and purpose that are unsafe. The safety of residents or consumers of electricity now comes to the fore. Nowadays, it is very often possible to see on all devices, in addition to the usual phase and neutral terminals, also a grounding wire or a bolt to which a grounding loop must be connected. Even sockets have a grounding terminal, which, according to the rules, must also be used. Let’s look at why this element is needed and how to organize this type of protection in a private home in more detail.
Why do you need grounding in a private house?
Let's start with the fact that, according to the rules for the construction of electrical installations (PUE), electrical equipment enclosures, which are made of conductive material and, due to an insulation breakdown, may become energized, must be grounded, and a private house is a breeding ground for electrical installations. Electric current is a very dangerous form of energy that cannot be heard, seen, or smelled. It can only be measured using special devices that have been verified and designed for a certain voltage value. During an emergency, namely a breakdown of the insulation of an electrical device, for example, a boiler (water heater), dangerous voltage will appear both on the body and in the water, which can not only harm a person’s health, but also take his life. In general, grounding the boiler is very important, since it contains all the particularly dangerous electrical hazards.
Current, like water, will always flow through less resistance, so if a person’s resistance ranges from 2000 to 5000 Ohms, then the grounding wire and the grounding system itself in a private house should be no higher than 4 Ohms. The current strength in the area of human touch is significantly lower than between the point of insulation breakdown and grounding. With an alternating voltage with a frequency of 50 Hz, the fatal current value for the human body is only 0.1 A; loss of sucking or fainting can occur as early as 0.03 A.
In order for a person to feel the current, he must pass through it, and since the floor in a multi-storey or private house is most often made of conductive material, it is not necessary to even touch some metal object, which will become the closing element of the circuit. The voltage will definitely shock a person, and since its value is 220 or 380 Volts (depending on the power supply), you can easily calculate the current that will pass through the human body. To do this, you need to divide the voltage value by the body resistance. In damp rooms, for example, in the basement, as well as in bathrooms and shower rooms, it will be lower.
Requirements for grounding electrical installations up to 1000 Volts
Equipment grounding is a set of technical measures that make it possible to obtain a reliable electrical connection between the protected enclosures of electrical installations and the ground. It is organized to protect operating personnel and people working on equipment from accidental electric shock.
In accordance with the requirements of GOST 12.1.030-81, protective grounding of the electrical installation should be performed:
- at a rated voltage of 380 V and above alternating current and 440 V and above direct current - in all cases;
- at a rated voltage from 42 V to 380 V AC and from 110 V to 440 V DC when working in conditions with increased danger and especially dangerous conditions according to GOST 12.1.013-78.
Expert opinion
Evgeniy Popov
Electrician, repairman
Important! With a properly equipped grounding system, a dangerous potential that gets onto the machine body, for example, will not cause any harm to the person who touches it.
Protective grounding diagram: 1 - electrical installation, 2 - grounding conductor, 3 - grounding conductor
This is explained by the fact that, when the insulation breaks down, the main part of the current charge flows along the grounding bus into the protective circuit, the resistance of which is an order of magnitude lower than the same indicator for the human body.
Don't miss: Features of the TRONIC LiYY cable
Natural grounding
According to the rules of the PUE, the housings of technological equipment and other devices must be connected to natural or artificial grounding conductors (IZU). When implementing the first of these methods, the following auxiliary elements are traditionally used:
- metal frames of structures laid in the ground that have direct contact with it;
- metal casings for cables laid directly in the ground;
- ordinary metal pipes (except for gas and oil pipelines);
- railroad tracks.
Natural grounding
Expert opinion
Evgeniy Popov
Electrician, repairman
Please note: The use of ready-made structures greatly simplifies the solution to the grounding problem, simplifying the process.
In addition, their use in organizing effective grounding allows one to somewhat reduce the costs of its arrangement.
The importance of current flow resistance
The main requirement for groundings up to 1000 Volts is their ability to create a reliable chain for emergency current charges to flow into the ground. It is estimated by the amount of resistance that ground fault currents have to overcome.
Ground fault current will flow from the damaged phase to the electrical installation body and through the grounding device to the ground
According to regulatory documents (PUE, in particular), the grounding resistance (resistance to the spread of electric current) should be:
- in private homes with a supply voltage of 220 and 380 Volts, it should be no more than 30 Ohms.
- for industrial equipment (substation transformers, in particular, or generators and welding machines) should not exceed 4 ohms.
- in relation to the current source (generator or transformer) no more than 2, 4 and 8 Ohms, respectively, at phase-to-phase voltages of 660, 380 and 220 V three-phase power supply or 380, 220 and 127 V single-phase power supply.
To achieve the resistance values standardized by the PUE, special measures will need to be taken. Usually they come down to the following standard procedures:
- increasing the area of contact between the components of grounding devices and the ground;
- improving the quality of contacts at the junctions of individual elements and copper connecting bars;
- improving the conductivity of the soil itself (due to constant moistening or adding saline solution, for example).
The same requirements prescribe periodically (at least once every 6 years) checking the resistance of the grounding circuit to ensure its value corresponds to the approved standards.
Grounding operation in case of violation of the protective insulation of live parts
The most common malfunction encountered during the operation of electrical equipment is a phase short circuit to the metal casing due to the destruction of the protective insulation.
Expert opinion
Evgeniy Popov
Electrician, repairman
Additional information: In modern household appliances equipped with switching power supplies with a Euro standard plug, a dangerous potential may be constantly present on the metal housing.
Depending on what protective measures are taken when working with the equipment, the following degrees of user safety are possible:
- The most dangerous option is when the metal body of the device is not grounded and the RCD is not installed at all. The contact of a phase with current-carrying parts does not manifest itself in any way, except for a noticeable shock upon accidental touch.
- In the absence of an RCD, the housing is connected to the established grounding circuit, and the leakage current along the drain circuit is very high. In this case, the device will work instantly and turn off the supply line or a separate circuit of it.
- In the presence of an RCD, the housing is not grounded, which is detected only when a leakage current flows, which will trigger the protection device. In a time of about 200-300 milliseconds, a person who touches the device will feel only a light electric shock.
- And finally, the safest option involves grounding the housing and simultaneously installing a separate RCD in this branch.
There is nothing to say about the first case, associated with the lack of special protective equipment, but the second option is not entirely safe. This is explained by the fact that with high transition resistance and significant fuse ratings, the residual potential on the device body is very dangerous for a working person. So, with a grounding structure resistance of 4 Ohms and a 25 Ampere fuse, it can reach 100 Volts.
Expert opinion
Evgeniy Popov
Electrician, repairman
Important! In the latter case, two protective devices complement each other and eliminate possible problems in one of them.
When a phase hits the housing, and through it to the grounding conductor, the current safely flows into the ground. At the same time, the RCD instantly reacts to a leak and turns off the line and electrical installation, eliminating the possibility of injury to personnel working on it.
Scheme of grounding operation in case of insulation failure of live parts of electrical equipment
In addition, if the leakage current significantly exceeds the operating threshold of the fuse installed in the circuit, the protective element itself may also operate, duplicating the action of the RCD. Which of these two devices will turn off the circuit first depends on their speed and the magnitude of the current flowing to the ground (their simultaneous operation cannot be ruled out).
How to make grounding correctly
Grounding of PUE
In order to properly ground a country house, it is not enough to connect the wire to the heating or water supply pipes, which, as it would seem, are also reliably connected to the ground. In the event of an unexpected breakdown, in this case, not just one person, but several may suffer, that is, all those who, when voltage appears on the body, and therefore on the water pipes, touch them. This also leads to the destruction of the metal products themselves. The main task of grounding is to ensure safety.
In power supply, there are two types of grounding:
- Working. This is when the conductor is used as a neutral wire and is necessary to create the required voltage, such as standard 220 V, for which the majority of electrical appliances are designed. With a three-phase voltage system, the value between one phase and ground will be exactly 220 Volts. The cross-section of the phase and neutral conductors should be selected according to the power of the load that will be connected to the network. Sockets with such power supply may not have an additional output;
- Protective. This is a completely different type of grounding device, which is connected only for the purpose of protecting a person in the event of an insulation breakdown.
It is much easier to organize protective grounding in a private house, country house or cottage than in an apartment building, especially when you do not live on the ground floor.
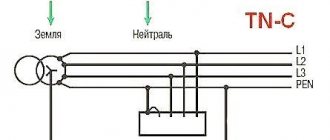
The most effective is the so-called TT grounding system, in which the protective wire PE is in no case connected to the neutral working conductor N. This is clearly visible from the figure below.
Why ground yourself?
Greetings from Khabrovsk.
Who is this post for?
Those who know and understand why grounding is needed will not discover anything new. When I made this discovery for myself, I was surprised to discover that many of my friends (connected with the IT sphere) have little understanding of why they need to be grounded at all. That is why you are actually seeing this post now.
Background
Having bought new headphones with a microphone, and coming home, I was sad to discover that the microphone was creating extraneous noise.
I returned to the store, where we checked on the laptop, there was no extraneous noise from the microphone. When I got home I started looking for the reason. I connected old headphones, they don’t make any noise. I connected new headphones again, they are noisy. After some time, I accidentally touched the system unit with my foot, and lo and behold, the noise decreased significantly. So, I came to the conclusion that there is some kind of interference on the system unit case. I immediately thought about grounding, and I started measuring the voltage of the case relative to the ground. I first took the neutral wire as the ground, and was surprised to find that the potential difference was about 100V. I decided to measure the voltage relative to the heating battery, still the same ~100V. I became curious and decided to Google it, and as it turned out, I was far from the first:
Where does the tension come from?
I will not go into detail about where the voltage on the housings of refrigerators/washing machines comes from. Let me just say that the reason in 99% of cases is the same as on the system unit case. You can find a more detailed description and explanation on Google. In short, the reason is this: The computer’s power supply contains a filter that dampens high-frequency interference and dumps it into the ground. And here is the filter itself:
Thus, we have 110V going to the ground (if the socket has 220V), but the current is only interference current, which means that the current strength will be insignificant. But this device is probably familiar to everyone:
The pitfall of this device is that it connects the grounding of all devices included in it. If you have N system units included in it, then the current filtered by each filter in the power supply will add up, and the sum will be on the body of each system unit. In addition, as my “ground measurements” showed, exactly the same filters are in monitors (at least At least this is exactly the case in both of my monitors).
If you have N system units included in it, then the current filtered by each filter in the power supply will add up, and the sum will be on the body of each system unit. In addition, as my “ground measurements” showed, exactly the same filters are in monitors (at least At least this is exactly the case in both of my monitors).
What does this threaten?
Even adding up the current from 5-6 devices connected to the above-mentioned surge protector, it is unlikely to be strong enough to kill a person. But there are other pitfalls here. What happens if one of the filter capacitors suddenly breaks? You can easily get the full 220 on the case of your system unit. Of course, capacitors are selected with such a rated voltage that breakdown does not occur even from strong surges (in the diagram above, 2kV, for example), but as they say, once a year the bast shoots. But that's not the worst thing. The main beauty is that devices designed for grounding are designed as if you have a ground. the device rightfully believes that in the event of an emergency it can dump excess current into the ground. In the diagram above you can see that the land I circled is not the only one. And it is unknown how many such potential places you have. Thus, without an existing grounding, life-threatening voltage can easily form on the body of your electrical appliance.
And the worst thing
It is especially dangerous to use devices that somehow work with water in this way. For example, washing machines or dishwashers. In a washing machine, for example, the heating element may leak, and there will be a full 220V on the body, and since the washing machine is often located in the bathroom, where there are tiles and moisture, you will be an excellent conductor, and an electric shock will most likely be fatal
conclusions
I hope I convinced those who still do not have grounding to do it.
Finally, I’ll just say, don’t do the grounding the simpler and faster way (to the battery, grounding, etc.), do it the right way, because this is not only your personal safety, but also the safety of others. There are articles on Habré on how to do grounding correctly. You can also google a lot of information on this matter. Well, thank you for your attention. UPD. Through the efforts of TolTol, vertu77, juray, I realized that you can significantly protect yourself by using an RCD, because it can be connected to a circuit without grounding. However, not without its drawbacks
UPD. Through the efforts of TolTol, vertu77, juray, I realized that you can significantly protect yourself by using an RCD, because it can be connected to a circuit without grounding. However, not without its drawbacks
So, what does the grounding circuit in a private house consist of?
Ground electrode
What is the difference: grounding and grounding
These are pins buried in the ground, which should be located at a depth of no less than 0.5 meters, however, as practice shows in cold winters and low temperatures, the best, and therefore minimal, grounding resistance is obtained if the grounding loop pins are driven to a depth of 2-3 m. It is necessary Note that this separates two types of contour:
- Closed. Driven metal pins or stakes at a distance of 1-2 m from each other form a triangle. After which they are welded together with a strip of metal. This type of circuit is a good functional element, and even if during operation under the influence of moisture and rust the sides of the triangle break, the protective grounding will deteriorate slightly, but will not disappear, and will still protect in unfavorable situations.
- Linear. In this case, the pins are driven or dug into one line and connected to each other in a sequential manner, the dimensions are indicated below. The negative side of this connection is that if the jumper breaks at the beginning of the first pin, then the grounding in the entire private house will deteriorate, which means it will become more than 4 Ohms. And it will not provide reliable protection. However, sometimes this method is used.
Here are a few more ways to install grounding pins, but there is no point in talking about them in detail, since they are used extremely rarely.
Connecting ground conductor
The metal structure connecting the upper end of the ground loop and the busbar input is made of a strip of metal or round timber. If it is necessary to change the angle or direction of this structure, then the elements must be welded; bolted connections are not allowed here.
Internal main ground bus
It is made of a copper busbar with bolted connections assembled on it, to which the grounding wire from any electrical equipment is directly connected.
If this network is designed for voltages up to 1000 Volts, which is most often found in domestic conditions, then it must be a copper stranded wire with a cross-section of at least 10 mm2. However, if you save money and install aluminum, then its cross-section should already be greater than 16 mm2; for metal this value is 75 mm2. There may be several such tires in a house and they have the same cross-section. For example, in every room, on every floor, or in the basement.
The figure shows an example of a grounding conductor that was not made according to the rules of the PUE; everything here is wrong, and not just the cross-section of the wire.
In old residential buildings, sockets and cables are unlikely to have a protective input and conductor, so you need to think about whether it is worth redoing the entire system, or simply installing an RCD. Such a device is installed on the input, which can even be located in the basement.
What is grounding, principle of operation and device
When creating an electrical network in premises for various purposes, it is necessary to create protection that will prevent possible electric shock. To avoid this, a grounding device is installed. In accordance with the PEU clause 1.7.53, grounding is carried out in electrical equipment with a voltage of more than 50 V AC and 120 V DC.
Grounding bus from the main switchboard to the consumer
Grounding is the intentional connection of non-current-carrying metal parts of electrical installations (which may be live) with the ground or its equivalent. This protective measure is designed to eliminate the possibility of electric shock to a person due to a short circuit to the equipment body.
Operating principle
The operating principle of protective grounding is:
- reducing the potential difference between the grounded element and other conductive objects with natural grounding to a safe value;
- current drainage in case of direct contact of the grounded equipment with the phase wire. In a well-designed electrical network, the occurrence of a leakage current causes an instantaneous operation of a residual current device (RCD).
Grounding schemes in three-phase networks
From the above it follows that grounding is more effective when used in conjunction with an RCD.
Grounding device
The design of the grounding system consists of a ground electrode (the conductive part that has direct contact with the ground) and a conductor that provides contact between the ground electrode and non-current-carrying elements of electrical equipment. Typically, a steel or copper (very rarely) rod is used as a grounding conductor; in industry, this is usually a complex system consisting of several specially shaped elements.
The effectiveness of the grounding system is largely determined by the resistance value of the protective device, which can be reduced by increasing the useful area of the ground electrodes or increasing the conductivity of the medium, for which several rods are used, the level of salts in the ground increases, etc.
The grounding device is...
Above we examined in general terms what protective grounding is. However, it is worth mentioning that the grounding conductors used in the system differ in natural and artificial.
As grounding devices, it is primarily preferable to use such natural grounding devices as:
- water supply pipes located in the ground;
- metal structures of buildings and structures that have reliable contact with the ground;
- casing pipes for artesian wells;
- metal cable sheaths (with the exception of aluminum).
Don't miss: Connecting the crossover switch. Cross switch: what is it for and how to connect it
Option for using a pipe as a natural grounding conductor
Expert opinion
Evgeniy Popov
Electrician, repairman
Important! It is prohibited to use pipelines with gas and flammable liquids, as well as heating mains as a grounding element.
Natural grounding conductors must be connected to the protective system from two or more different points.
The following can be used as an artificial grounding device:
- steel pipe with a wall thickness of 3.5 mm and a diameter of 30÷50 mm and a length of about 2÷3 m;
- steel strips and corners with a thickness of 4 mm;
- steel rods up to 10 or more meters long and with a diameter of 10 mm.
Using metal strips as an artificial grounding conductor
For aggressive soils, it is necessary to use artificial grounding conductors with high corrosion resistance and made of copper, galvanized or copper-plated metal. So, we have figured out what is the definition of the concept of artificial and natural grounding, now we will look at when grounding is used.
Installation of the ground loop
Why do you need a 380 Volt outlet: classification, installation
In order to make grounding in a private house, you first need to decide on the place where the grounding loop will be made. This should be a deserted place, since in theory, in the event of a breakdown or deterioration of the insulation of electrical appliances, a dangerous potential will appear in this area. Prohibited
do it in the basement. In reality, this can only be dangerous if this protective device is faulty. Most often, this place is taken anywhere, retreating about 1–1.5 meters from the foundation of the country house. If we take into account the theoretical danger, then this place can be fenced off with a small fence or border.
Then you need to dig a triangle and a ditch for the connecting conductor. Each side of the triangle should be about 1–2 m, and the depth should be from 0.5 to 0.7 m.
After that, the electrodes or pins are driven into the ground to a depth of 1.5–2 m, so that there is room for welding them into a triangle. In no case should they be concreted, this will worsen the contact with the ground several times. To make the pins fit into the ground easier, one of their edges should be made sharp. If there is a lot of sandy soil on the site, then the conductivity can be increased with a saline solution (not table salt) in those places where the electrodes are driven in. The welded triangle is connected to a common ground bus in the area of the distribution panel, even if it is located in the basement. The pins can be driven into the ground using a jackhammer as shown in the figure below.
How to protect yourself from electric shock?
One of the ways to eliminate electric shock or significantly reduce it is to install a grounding device. Why is a ground loop needed? It is necessary for household appliances with metal bodies: washing machines, electric stoves, refrigerators, etc.
When potential is applied to the metal housings of home equipment, the current must go into the ground. But to do this, you first need to make a device in the form of a metal structure that creates electrical contact with the ground. It can be solid or consist of conductive elements immersed in the ground.
Protecting your roof and home from lightning strikes
If the owner also decides to install a lightning rod, then it is advisable to install another grounding loop located at a distance from the roof. To prevent a surge of energy from occurring on the roof during a lightning strike and causing dangerous potential to appear there. It is better to disconnect the grounding loop in a private house according to its intended purpose. It is, of course, possible to install pins on the roof of a house that will be struck by lightning, but it is better to make a separate structure for a lightning rod and install it next to the building, especially if this is done in a wooden house. The temperature during a lightning strike is enormous and can lead to a fire. That is, it is better to separate the protective grounding of the house (where the sockets are connected) and the system for catching lightning. This is very important if the roof is made of metal and has sharp ends. Naturally, you can install several lightning rods around the house, this will reduce the chances of lightning hitting the roofs of houses, however, this is no longer a completely justified measure, which is done only at explosive enterprises and nuclear power plants. It is better to purchase and install additional electronic equipment that saves electrical appliances from sudden voltage surges during a thunderstorm, especially if the house is built of wood.
Kit for grounding a private house
Installation and installation of grounding in a country house is a very labor-intensive process, however, what you will not do for the sake of safety.
Currently, it is possible to simplify this process for yourself by purchasing a ready-made kit. Here, of course, the higher the quality, the higher the cost of the kit. If you decide to ground your home, then it must be done correctly and efficiently. But you won’t have to look for material and invent something from available means. The price for such a grounding kit for a home varies within a very wide range from 6,000 to 42,000 rubles. The set and packaging of such grounding for a private home must not be torn and have instructions.
How to check the resistance value of the grounding device
The last stage of the implementation of protective or working grounding, as well as commissioning, will be its verification. Some experts suggest checking it by connecting it to a light bulb or using a megohmmeter. Checking the resistance of the ground loop with a light bulb will only show the presence of a connection to the ground (that is, zero potential); you cannot check the value of the resistance itself this way.
Testing with a megger is, in general, the wrong approach, since this device is designed to measure insulation resistance of several tens or hundreds of thousands of ohms, but here you need to accurately measure only a few such units.
For such purposes, the professional M416 device is used.
It is intended for measuring specific and active grounding resistance. The principle of its operation is based on the compensation method of measurement using an auxiliary ground electrode and a special potential electrode (probe).
Other more modern measuring devices are still extremely rare, even in production. At the enterprise there is a schedule for checking such resistance, but at home it is enough to check it once before putting it into operation, and then after 5–8 years. If such work is done in your house yourself, then commissioning and operation will fall on the shoulders of the owner. If it is done by companies specializing in this (preferably having a license for this service) or by the electricity supplier itself, then they are required to do the verification themselves, with the provision of the relevant documents. Thus, it is not enough to make grounding in a private house; you need to check it and, perhaps, even legalize it.