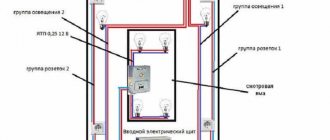
Often, to preserve their cars, their owners use the services of private garage cooperatives. The latter, due to certain circumstances, do not pay special attention to the condition of the electrical wiring. Therefore, car owners have to independently carry out work aimed at eliminating any faults in the electrical network. And one of the main questions that people face in such circumstances is how to make grounding in the garage with their own hands.
Why do
Today, metal garages are mainly used. The arrangement of such structures requires proper installation of waterproofing, which will eliminate the likelihood of leaks and, as a result, a short circuit of the local electrical network. Failure to comply with this requirement leads to the fact that the level of humidity inside the garage increases.
As the temperature rises, water condenses on electrical wiring and other things located indoors. After connecting any equipment (welding machine, compressor, heater and even a kettle) to the general electrical network, the user may receive an electric shock.
The presence of a grounding conductor (grounding) allows you to eliminate the likelihood of such events occurring. Compliance with this condition is one of the main requirements for safe operation of the garage.
Moreover, grounding installation is necessary when the structure is made of metal. In the absence of this component, a certain voltage (usually less than 220V) may occur on the garage walls. That is, the structure itself will pose a danger to humans.
Why do you need a ground loop?
Many electrical appliances require outlets with a grounding contact. Using this contact, equipment housings are connected to the ground loop. The insulating layer applied to the current-carrying elements of devices is sometimes damaged, and water or moist air penetrates inside. The result is the formation of condensation on the metal surfaces of electrical appliances. Water is an excellent conductor of electricity.
Garages are often quite damp places. These buildings are classified as high-risk objects.
There are additional risk factors inherent in garages that are made of metal. Metal structures that are not electrical appliances may be energized if they act as a third-party grounding part. The fact is that between the metal part of the garage and the soil there is a waterproofing layer standing on sleepers or logs, so the contact between the body and the soil is not always reliable.
Cables are usually installed by securing them to wires or metal cables. The latter are held on to garage buildings by bolted or welded connections. Violation of the insulating layer on the cable leads to the emergence of potential transmitted to the garage body. Even if there is no direct contact of cables with metal surfaces during rain, this contact will inevitably occur.
Thus, the presence of grounding is the most important requirement to ensure the safety of both the electrical appliances themselves and their users.
Potential equalization system
The potential equalization system (PES) performs the following functions:
in the event of an increase in voltage on one of the electrical appliances, it will be evenly distributed over all metal structures, thereby eliminating the possibility of electric shock to a person;- to protect against high voltage inside the garage caused by lightning.
EPS is a mandatory element of protection, regardless of the type of grounding used in electrical wiring. To create such a system, you will need to run a metal strip along the entire contour of the garage, connecting conductors to it.
Types of systems
Before starting work, choose a potential control system. The following systems are used to organize grounding in the garage.
TN-C
All electrical networks laid more than 10 years ago were assembled using such a system. The TN-C scheme involves laying only two wires in the input cable. The first of them will be phase, and the second will be zero combined, or PEN. The latter includes a wire through which current flows and a grounding cable.
In the TN-C configuration, it is prohibited to use the neutral wire as an element grounding the entire network. Failure to comply with this rule will result in the phase passing to all connected electrical appliances. In addition, if the PEN conductor breaks, the grounding elements of the network will be energized.
In other words, if you touch, for example, a compressor, the user will receive an electric shock.
To avoid negative consequences caused by the shortcomings of the TN-C system, such a scheme is not recommended for use in garages.
TN-S
The TN-S system assumes the presence of a 3-core input cable connected to the distribution panel through 2 zero busbars. In this circuit there is a separation between the neutral and protective conductors. Therefore, if the electrical network breaks down, caused, for example, by a high voltage surge, no potential arises between the two specified wires.
TN-S is used very rarely today, since this system requires laying two wires from the substation. However, if such a scheme is used, then a grounding loop may be required only if the power source (general electrical network) is located at a considerable distance from the garage (switchboard).
TN-CS
TN-CS is the optimal choice between TN-C and TN-S, as it combines both of the latter systems. This scheme involves dividing the neutral conductor into protective and working. In this case, the combined PEN stretches from the substation to the distribution panel, where a ground loop is created. From it, 3 conductors are laid to the end consumers using the TN-S circuit.
The disadvantage of TN-CS is that if the combined conductor breaks as it approaches the garage, there is a possibility of a potential. However, in such situations, the input machine will work (provided that it is installed), so there is no threat to electrical appliances.
TT
TT is an analogue of TN-C. But in this system, the ground loop is not connected to the PEN conductor, but remains independent. The protective element is connected in the TT circuit to the metal elements of the garage and sockets. This system also involves the use of several electrodes dug into the ground. It is the TT circuit that is mainly used when organizing a ground loop in a garage.
Organization of the ground loop
To protect the wiring in the garage, it is necessary to connect an RCD (protective circuit device) in the input panel. This element will protect the internal network from leakage currents. In fact, the RCD is an additional protection device: if an accident occurs, it instantly stops the supply of electricity to the garage.
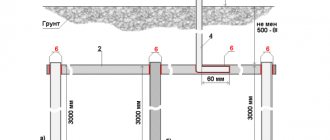
The ground loop itself is made in the form of a triangle, rectangle or straight line. It can also be looped. Some electricians use a T-shaped ground loop. It includes 2 electrodes dug into the front side of the garage, and 2 other electrodes are installed in the inspection hole.
An important condition when organizing a grounding circuit with your own hands is the ability to create a trench at a depth below the freezing point of the soil.
Metal strips and corners are used as an electrode: the former are driven into the ground, and the latter are used to connect them to each other.
The number of such elements and their sizes are determined using a specialized program. However, in practice, calculations do not always correspond to reality, so over time there may be a need to add new electrodes to the ground loop.
If it is not possible to dig a trench, then natural grounding materials are used. They are used as foundation or floor reinforcement in a garage.
Why grounding in the garage?
It would seem, why fence a garden and build some kind of grounding if at home we get along just fine without it? This question is answered by the paragraph of the rules for the operation of electrical installations (PEU), which determines the degree of electrical danger in the room. The following criteria were selected for this:
- Structural features of the room - arrangement of floors and walls.
- Temperature regime.
- Humidity parameters.
- Presence of conductive dust.
- The presence of aggressive substances or their vapors that can destroy the dielectric - the basis of electrical insulation.
Garages are often built all-metal, from profile sheets on a frame. When a phase breaks down on this shell, taking into account its size and volume, it becomes like the lining of a capacitor. If you find yourself inside it - with a switched-on electrical appliance in your hands, or if you are wearing shoes with insufficient dielectric properties, all the accumulated electrical charge will go into the ground through your body. The probability of death is almost 100 percent.
Floors made of earth, concrete or brick are classified as conductive. It would be correct to consider wooden ones as such if they are not dry enough. And this is probably true, since humidity parameters and temperature conditions are directly related.
In an unheated garage, it is the same as that of the outside air, and in the absence of effective ventilation, moisture condenses wherever a temperature difference is possible due to differences in the thermal conductivity of the material - on the walls, inside the housings of electrical appliances and fittings. And it may be sufficient to cause an electrical breakdown.
Is there metal dust in the garage? Funny question, isn't it? Especially if it has a sharpening machine. What about aggressive vapors and liquids? Yes, as much as you like!
Summarizing all of the above, we get that, according to electrical safety rules, the garage belongs to high-risk premises. Well, with earthen floors, you can consider them especially dangerous. As you can see, the question of the need for reliable grounding disappears by itself. Only this simple device has an electrical resistance less than your body. Therefore, in the event of an accident, the electric current will flow through it, bypassing you.
Vertical ground electrode
For standard garages, metal corners 2-2.5 meters long with a dimension of 50x50 mm are mainly used. Instead, you can also install a pipe with a diameter of up to 32 mm with walls no more than 3.5 mm thick. There is a third option for a grounding device, which involves the use of copper wire with a cross-section of up to 6 mm, which connects the underground part of the structure with the rest of the electrical network elements.
It is important to note that digging in vertical grounding conductors is prohibited.
Instead, they must be driven directly into the ground. The distance between the electrodes should be within 1.5-2.5 meters. Before starting work, a trench up to 50 cm deep is dug in the place where the ground loop will be created.
All electrodes are connected to each other by a metal strip or rod. The cross-section of the first should not be less than 100 sq. mm, and the diameter of the second - 10 mm. All components of the circuit are connected by welding, and new seams must be painted to avoid the formation of corrosion on the ground.
Horizontal ground electrode
To organize horizontal grounding in the garage, a metal strip is laid on the surface of the dug trench. Next, a bolt is attached to it by welding, to which a copper or aluminum cable is connected. The second end of the latter is connected to the PE bus located in the distribution panel. At the end, the trench should be buried with loose soil, having previously excluded stones and construction debris from it.
After completing all grounding work in the garage, it is recommended to check the created electrical network. To do this, you need to contact a specialist who has the appropriate equipment with which you can measure the ground loop. If the result obtained exceeds 47 Ohms, several additional holes should be punched in the concrete floor to install electrodes.
If the garage is located near a private house, then the work described above will not be required. It is enough to extend a 3-core cable to the building from the distribution panel located in the home. It is assumed that the home is equipped with grounding at the time of work.
System check
Regardless of the chosen grounding arrangement, after completion of work it is necessary to test the created system for operability.
For this purpose, it is recommended to invite a professional electrician with special equipment. A test result of over 47 ohms indicates the need to install several more electrodes.
The described schemes are relevant for garages located at a distance from residential buildings. If the garage is located next to a private house equipped with a grounding loop, the situation is fundamentally different. It is enough to pull a three-wire cable from the switchboard to the garage building.
Source