Lightning protection of soft roofs: a necessary safety measure
For humans, thunderstorms have carried a hidden threat from time immemorial. And it was, rather, not about the thunderstorm itself, but about its “fellow traveler” - lightning, which, according to statistics, annually claims more than 3,000 human lives. How to protect yourself from lightning strikes was invented a long time ago. The main thing here is not to neglect the lightning rod, which is such an important element of the house, and to protect your life and property.
Lightning protection options for each roof covering are different. Lightning protection of soft roofs, for example, is carried out using a special mesh or special holders. Lightning protection meshes consist of metal:
- conductor laid along the roof ridge;
- separately grounded down conductors.
They are fixed using the same material that was used directly for the roof. You can use another, more universal method, as in the case of a metal roof - masts on the gables with a cable-wire stretched between them.
Types of lightning protection
According to the design of the protection system, there are:
- external;
- internal.
Each system has its own purpose, and they must be used in combination to eliminate all three factors of lightning damage.
An external lightning protection device for buildings and structures is mounted on roofs, nearby extensions, structures and consists of an air terminal, a down conductor and a grounding conductor. Their main function is to divert the current discharge into the ground, preventing it from reaching the roof surface. The discharge enters the ground electrode through the down conductor and then spreads into the ground.
The internal type of lightning protection system consists of installing a device inside a building and serves to protect against surge voltages.
There are the following types of internal devices:
- Voltage control relay with the ability to manually adjust the minimum and maximum voltage levels in the network. If critical points are violated, the device turns off the voltage. Can be installed throughout the house or separately for each device. The simplest and cheapest option.
- Voltage regulator.
- Phase control relay (for three-phase voltage). Refers to microprocessor devices.
Options for lightning protection solutions ↑
There are many technical solutions to the issue of lightning protection, but they should be taken based on the characteristics of a particular situation. A galvanized roof, for example, can be reliably protected in a rather interesting and simple way. 6 mm steel wire is rolled into the roofing iron around the perimeter and grounded at the corners of the roof. A lightning rod is installed on the chimney stack, rising above the ridge, which is also grounded. A lightning strike that hits such a roof will not cause any trouble.
Lightning protection of a metal tile roof is more difficult to solve. Durable and easy to install, this material is nevertheless unsafe to use. This is due to the design of metal tile sheets. They consist of an aluminum or steel corrugated plate, which is covered on both sides with plastic, which are essentially capacitor plates. For this reason, isolated from the ground and from each other, they are capable of accumulating their electrical potential during various atmospheric phenomena such as lightning, dust storms and others.
Such buildings are classified as lightning protection classes 1 and 2 and require proper protection with lightning rods.
Lightning rods and components
There are a huge number of types of buildings and structures that require protection from lightning strikes. Accordingly, the protection elements themselves must have high versatility. This is achieved thanks to a set of standard elements, which are used to install lightning protection for buildings and structures of various types. In addition to lightning rod elements (nets, cables, rods, strips), it includes:
- conductors for dumping current into the ground loop;
- ground loop details;
- various types of fasteners for fixing a lightning rod to the wall of a building, to the facade, roofs, and various structures.
In addition to the main parts, various auxiliary products are needed: screws, gaskets, insulating tubes, anchors, etc.
Lightning protection systems: active and passive ↑
Passive lightning protection systems have been used for several centuries. She has several types of lightning rods.
- rod pin;
- cable lightning rod;
- lightning protection mesh.
Active lightning protection is a relatively new phenomenon, although it is quickly gaining popularity. By design, the lightning rod of such a system is a mast installed on the roof, onto which the lightning rod head is attached.
active lightning protection: description
Let us note only two differences between these systems.
- The protection zone of a rod lightning rod is 4–5 times smaller than an active one of the same height.
- It takes several times less time to install an active system.
Lightning protection of soft roofs: problems and solutions ↑
Let's start with the passive system. The lightning protection mesh is made of steel wire (diameter no less than 6 mm). Depending on the class of the building, the largest pitch of its cells should be either 6x6, 12x12 m. The mesh is laid directly on a soft roof or under a layer of fireproof or fire-resistant insulation.
When installing lightning protection mesh during roofing work, as a rule, no special problems arise. It’s another matter if the soft roof has already been laid and it is necessary to provide lightning protection to the building using a lightning protection mesh. This is where difficulties begin to arise.
The biggest problem, perhaps, is the occurrence of possible damage to the roof during the installation of the lightning protection mesh. This is due to the steel wire used to make the mesh. It is supplied in coils, and the wire has to be “rolled out”, straightened, etc. directly on the roof.
There is, of course, the possibility of using wire in rods (3-6 m long), however, if the roof area of the building is large, the number of connectors used will increase sharply, as a result of which the cost of the system will increase significantly.
In addition, such installation requires unnecessary walking on the roof, and it is not always possible to count on careful handling of the coating during the work process.
Thus, a natural question arises: how can its integrity be preserved when installing lightning protection? If we turn to other classic systems - cable lightning protection or free-standing lightning rods, then even with these options the probability of damage to the coating is high, since a significant part of the work is also carried out directly on the roof.
The only painless way to protect soft roofs from lightning today is considered to be an active lightning protection system for buildings. In addition, its installation can be done by hand.
Stages of installing lightning protection
Work on lightning protection should begin with drawing up a project. Its development is carried out in relation to a specific object. The main regulatory documentation is instruction RD 34.21.122-87.
After the project has been developed, they proceed directly to installation work according to the following plan:
- Construction of a grounding loop, checking compliance of its resistance with standards.
- Installation of lightning rods: mesh, pin protection, cable circuits, etc.
- Fastening of current transmission lines.
- Ground connection.
The finished complex is checked for compliance with GOST and, if necessary, modified and configured.
Installation of lightning protection on a soft roof
Installation of lightning protection on a soft roof consists of two stages:
- installation of the lightning rod itself on the roof;
- arrangement of a ground loop on the ground.
Roof part
There are passive and active lightning protection for soft roofs.
Types of passive protection lightning rods:
- pin. A metal pin mounted on a ridge. A down conductor (a wire with a cross-section of 6 millimeters or more) descends from the pin to the ground; it is attached to a grounding conductor - a metal pin immersed in the ground half a meter below the freezing level of the soil;
- cable A cable is pulled along the ridge and a down conductor is welded to it. The down conductor goes down the slope and along the wall to the ground, here it is connected to a ground electrode;
- lightning protection mesh. Made from steel wire with a cross-section of 6 millimeters. The cell pitch is 6 x 6 or 12 by 12 square meters maximum. The mesh is placed either on top of the coating or installed under a layer of non-combustible heat-insulating material. With the second method, the coating suffers from a lightning strike, so the first is used more often. On gable roofs, the mesh is laid on the slopes separately. Both sections must be grounded.
Active protection means a mast with a lightning rod head. The head consists of a housing and an ion generator. It is attached to the mast with a coupling. This design also requires a down conductor and a ground electrode.
The number of lightning rods on a flexible roof depends on the area and configuration of the roof.
note
The pins must rise above the ridge line by at least one and a half meters. They can be made from two pieces of reinforcement.
To make a down conductor bus, you can use:
- steel wire from 6 millimeters;
- tire 15 by 3. Maximum thickness - 6 millimeters. It is not recommended to take thicker ones, because... When struck by lightning, plasma splashing may occur;
- a bundle of thin galvanized wires with a total cross-section of 45 millimeters square. The wires should be secured by welding before installation.
Ground loop
For grounding conductors use:
- round steel rods with a diameter of 16 millimeters;
- hollow pipes with a cross section of 32 mm and a wall thickness of 3.5 mm;
- profile pipes or angles, cross-section from 10 cm, wall from 4 mm.
The number of grounding conductors depends on the area of the house and the total load of all devices in it. There are three network configuration options:
- linear - two groups of grounding conductors at the corners of the house;
- complete contour around the perimeter of the structure.
- the simplest is three ground electrodes dug into the ground one and a half meters from the house;
Grounding electrodes are connected by one common bus into a single circuit. The bus goes into the house (where electrical appliances are grounded to it).
All structural elements, on the ground and on the roof, are connected by welding.
Circuit testing
After installation, it is necessary to measure the resistance of the ground part. This can be done with an induction megommer.
The resistance of the grounding conductors themselves and the spreading resistance are measured. For this measurement, the electrodes are immersed in the ground at a distance of at least 12 meters from the circuit. The distance between the electrodes themselves is within one and a half meters. Resistance should not exceed 4 ohms.
In addition to installing lightning protection, to ensure the safety of your home, it is necessary to ground all electrical appliances in it.
Installing lightning protection in a private house with a soft roof is not a difficult task, but very important. A mistake can have serious consequences.
Contact us at STM-Stroy. We have been installing roofs and all existing roof structures for more than 15 years. We will perform an accurate calculation of lightning protection for soft roofs and install the system quickly, efficiently, and inexpensively.
Lightning protection of a house with a pitched roof
The general principles of calculation for a ridge roof are presented in the section “An example of a lightning protection device for a private house for a pitched roof” in this review article. As a rule, in most cases, the angle of inclination of the roof turns out to be less than the calculated angle of the protection zone, therefore, for a sloping roof, the lightning protection mesh method is more often used, plus all protruding parts are separately protected, and the metal elements are connected to each other and brought out to the grounding system by common down conductors.
Since ridge roofing is mainly used in private households, and these structures belong to class III lightning protection, the grid cell pitch is no more than 15 meters.
If the roof dimension is smaller, then the conductor is laid along the dimensions of the roof (ridge, gables and overhangs or gutters). At the same time, we must not forget that protruding elements and roof superstructures must be additionally protected by lightning rods (for small-sized elements they can be ordinary conductors with a diameter of 8-10 mm) or combined into a common grounding system. Such structures are potential recipients of lightning strikes, and include gables, chimneys, eaves, snow-retaining grilles, ridges, roof edges, dormer windows, antennas and other protruding parts.
Roof structures may not be connected to a common lightning protection system only if the following conditions are met:
- superstructures made of non-conductive materials have a height of less than 0.5 m
- superstructures made of conductive materials have a height of less than 0.3 m
- metal superstructures have an area of less than 1 square. m
- metal superstructures are less than 2 m long
It is important to note that the height is set aside and measured perpendicular to the roof surface, as shown in the figure.
The area requirement is usually used for roof windows or skylights, and the length requirement for sheet metal structures or fences (for example, snow guards). In this case, in relation to metal protruding elements, all three of the above conditions must be met simultaneously.
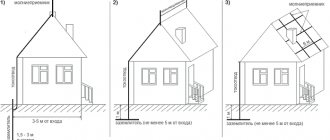
Installation of lightning protection on objects with pitched roofs (recommendations)
In the case of a pitched ridge roof, the lightning conductor is laid along the ridge of the roof and the roof slopes. The main lightning protection equipment is the lightning conductor. The ends of the ridge lightning rod should protrude above the roof and be curved upward along the length by 0.15 m. The descent along the roof to the down conductor on the facade of the building should, if possible, be located as close as possible to the edge of the roof (platband). Try to keep the distance between the roof conductor holders no more than 1.0 meters.
The concept of the location of structural units is presented in the figure below.
Depending on the cross-section of the ridge, various holders are used on the roof ridge. For example, in the case of a metal tile roof, when the cross-section of the ridge is a semicircle, a holder on a round ridge is used (Fig. 1).
| Fig.1 | Fig.2 |
The holder on a round ridge is made of copper or stainless steel. Also, the lightning conductor is laid along the roof slopes (Fig. 2). Depending on the roofing material, various fastenings are used on the roof slopes. Fasteners intended for roof slopes are also made of various materials. Depending on the material of the lightning conductor, fasteners made of copper, stainless steel or hot-dip galvanized steel are used.
All parts of the building must be protected from direct lightning strikes, including chimneys, ventilation shafts, as well as attic windows and other elements. If the pipes on the roof do not contain metal conductive elements, then lightning rods are installed directly to the pipe using special fasteners (Fig. 3).
If chimney pipes contain metal elements, then the lightning rod must be placed at a certain distance from the pipe using insulated rods (Fig. 4).
| Fig.3 | Fig.4 |
Lightning protection on soft roofs
Lightning striking a building causes destruction, sometimes irreversible. Buildings in open countryside are especially at risk. Properly designed and installed lightning protection on a soft roof will reliably protect the house from the elements. Requirements for the system, as well as recommendations for the device, are described in instructions RD 34.21.122-87.
Features of lightning protection
There are active and passive lightning protection. The systems are similar in design - lightning rod, down conductor, grounding - but have a fundamental difference in operation. Active technology works proactively, provoking and receiving lightning, and protects a certain radius around itself. A lightning rod with an ion generator is used, which attracts the discharge.
Metal rods, cable or mesh are used as lightning rods for passive protection. The system does not attract, but reflects and neutralizes strikes that fall within the lightning protection coverage area. The correct choice of technology depends on the characteristics and shape of the roof, the landscape of the area and the climatic conditions in the region.
Metal roofing
Installing lightning rods is the best way to protect metal roofs. An active system is appropriate if it is necessary to protect a large area: installing one neat lightning rod is preferable to a dozen metal rods. A metal roof can also be a conductor: if the sheathing is made of non-combustible materials and a lightning strike will not cause a fire. In this option, the down conductor is connected directly to the roof surface.
Roof tiles
Clay or asphalt shingles are excellent insulators. A reliable method of protection is the installation of a lightning protection metal mesh. For gable roofs, two grids are laid, which are connected to different down conductors.
Soft roof
Of the passive methods, lightning protection mesh is acceptable. However, installation may damage the roofing material. Installation of active lightning protection consists of installing a single lightning rod: a minimum of movements on the roof. This is why the active system is more suitable for soft roofs.
Active lightning protection system on soft roofing
Operating principle
A leading discharge is created, which provokes a lightning strike. The intercepted current is diverted into the grounding system and neutralized. Depending on the model, the radius of the protected area ranges from 17 to 44 meters. Professional systems are equipped with a lightning strike counter, a protective casing and an inspection unit.
Benefits of active technology
- quick and simple installation;
- increased protection zone;
- installation without the risk of damaging the soft roof;
- installation does not depend on surface features;
- minimum components.
Installation features
Lightning rod masts are installed on the roof. The quantity depends on the estimated area for which protection is being organized, as well as on the shape of the roof. The lightning rod must rise at least 2 meters from the highest point of the building. In order not to damage the roof, installation is carried out on brackets to the chimney or other similar structure on the roof.
For each receiver, a separate down conductor is installed, which is mounted along the drain on special holders. An aluminum rod with a diameter of 8 mm is used as a current conductor, which must be grounded. Metal structures within the radius of the protective field must be connected to each other.
Passive lightning protection
Types of lightning rods
- Metal pin . Installed at the intersection of slopes.
- Cable lightning protection . A steel cable is attached along the ridge.
- Lightning protection mesh . A steel mesh is installed over the entire surface, which must be protected from lightning.
Any lightning rod is connected to a down conductor, which must be properly grounded. When hitting the protection, the discharge is directed to the ground and dissipates.
Lightning protection device
It is convenient to carry out installation before installing a soft roof covering - in this case, the risk of damage to the waterproofing is eliminated. The mesh is placed on pre-prepared holders. A steel wire rod with a cross section of 6 mm is used, pre-aligned with a special tool. The optimal mesh pitch is 6x6 m, but an increase to 12x12 m is allowed. The wire is supplied as a solid coil in a coil or in separate rods of 3-6 meters. Fastening the rods is faster, but expensive clamps are used for connections. It is more advisable to use a coil, however, the risk of causing damage to the surface increases. Lightning protection can be installed under non-flammable thermal insulation material or directly on the roof.
Operable roof and its features
The main specificity of such a roof is that it is used for different needs. This could be a parking lot, a summer cafe, a golf course, or just a green square. It always looks spectacular and is an eloquent indicator of the status of the owner.
They are usually located on skyscrapers, penthouses or private houses. Sometimes the roof of a garage and other outbuildings is used. However, it is worth understanding that such a roof will be the first to take the brunt of precipitation. Rain, snow, heat - all this leaves its mark, and therefore it is necessary to ensure that it can withstand all this onslaught.
But along with these threats, it is also necessary to take into account the risk of lightning striking the building. We will discuss how to avert such a danger later.