Installation of lightning rod
It should be noted right away that the requirements of the PUE provide for connections between all parts of the lightning rod exclusively by welding. If this is not possible, a threaded connection with bolts and nuts is permitted.
The area of washers used for threaded connections must be increased. It is not allowed to install system elements by twisting wires or any other methods.
Of course, the height of the lightning rod, which mainly determines its effectiveness, must be maximized. According to the RD instructions, to ensure reliable protection, the lightning rod must be raised at least 3 m above the surface of the structure. This applies to rod devices.
The height of installation of a cable lightning rod depends on the length and height of the building, the design of the ground electrode and the resistivity of the soil; it can be 3-4 m. To install the cable, it is recommended to strengthen wooden supports on both ridges of the building, and stretch the cable lightning rod between them if we are talking about ridge roofs .
Categories
There are 3 categories of lightning protection, designed for use in various conditions. They comply with fire and explosion safety classes.
First category
Thus, category I is the highest, it is used to protect explosive and flammable objects from lightning. Corresponds to fire and explosion safety classes BI and B-II. It protects the object from a direct lightning strike, from ignition and explosion as a result of sparking caused by the phenomenon of induction (electromagnetic and electrostatic), as well as from the transfer of potentials to the metal parts of the building, that is, the appearance of dangerous voltage on metal structures.
Particularly stringent requirements are imposed on it. All distances are standardized - from lightning rods to the protected object, the depth of the ground electrode, the distance between induction protection jumpers, and so on.
The lightning rod is usually rod or cable. Internal protection is carried out by connecting metal structures - machines, beams, trolleys, any other elements - directly to the grounding conductor, or through the grounding contact of electrical equipment. The total resistance of the ground electrode cannot be more than 10 ohms.
Second category
Category II lightning rods are designed to provide the same level of protection in areas with fewer thunderstorms per year, or for buildings with a lower explosion and fire hazard, for example, for objects of class B-Ia, B-I6, B-IIa, B-Ig ( electrical installations).
This type of lightning rods is installed similarly to category I lightning protection, with the difference that a steel network of rods of a certain cross-section (at least 6 mm) and with a certain grid pitch laid directly on the roof can be used as a receiver.
Laying is done on a non-combustible surface. The requirements for maintaining working distances are less stringent, so the distance from the lightning rod to the building can be any. The descents are mounted similarly to a higher class.
A reinforced concrete foundation can act as the “earth” if the soil resistance is no more than 500 Ohms. The specific features of laying a lightning rod depend on the type of building being protected - a production workshop, an administrative building, a liquid fuel storage or gas tank, an electrical installation, etc. The value of pulse resistance at ground cannot be more than 10 ohms.
Third category
Category III types of lightning rods are used if the total duration of thunderstorms in the area is more than 20 hours per year, as well as for objects corresponding to class P-III for electrical safety and class III-V fire resistance. For example, these are kindergartens, nurseries, schools, cinemas, hospitals, and other socially significant institutions, which, however, do not contain flammable or explosive devices or materials.
This type of lightning rod is different in that it does not provide protection from electromagnetic and electrical induction - only from fire due to direct lightning damage and from the occurrence of dangerous voltage on metal parts and other conductive elements.
A lightning rod manufactured technologically in this category differs from a system in category II only in the larger grid pitch - it can be 12*12 m - and in the pulse resistance threshold - it can be 20 Ohms. Free-standing containers with fuels and lubricants, except gasoline, as well as pipes and some other elements can be protected using a grounding electrode with a pulse resistance of up to 50 Ohms.
In a lightning rod made in accordance with category III, it is permissible to use a connection using twisting, if the connected elements allow this.
In all cases, the design of the lightning protection system should be based on the number of expected lightning strikes per year. The higher it is, the higher the category. It is permissible not to connect premises made of non-combustible materials that are considered non-explosive to the lightning rod.
If the building has premises belonging to different fire and electrical safety classes, then the category of lightning rod is selected to be the maximum required. Separate lightning rods II and III, for example, of categories are not made in the same building.
DIY lightning protection
Technical requirements for protective elements
In order for the use of a lightning rod to result in high-quality protection of a home from lightning, it is designed taking into account all the necessary standards according to a proven scheme:
The lightning rod is the first to encounter a high-power electric discharge, so its reliability is one of the first requirements. For the rod type, the most acceptable material is in the form of rolled products (pipes, squares, metal reinforcement). The cross-section in diameter should not be less than 100 square millimeters, and the height of such a stand should be more than 2 meters.
The mesh rod for protection must have a cross-section of at least 8 millimeters, the cross-section of the strip is 20 millimeters. For efficient operation, the mesh structure is connected to the ground loop by several separate rods.
The conductor wire is chosen to be at least 6 millimeters in diameter along the above-ground part, and for laying in the ground, a wire with a diameter of at least 10 millimeters in diameter is taken.
A sheet of metal or a pipe and a rod placed in the ground to a depth of 2 meters serves well as grounding. The material for the grounding electrode is stainless steel or copper; it is advisable to keep the soil around the grounding electrode moist for effective movement of the charge; in this case, clay works well, as it retains moisture inside itself for a long time.
DIY lightning rod device
For effective operation, special calculations must be performed, the installation location and materials for manufacturing must be determined. Using calculations, the optimal size of a lightning rod for a selected private building or part thereof is determined. Correct mathematical calculations will allow you to protect your home almost 100% from lightning.
Formulas for calculations are collected in reference books; in order to select one for a specific calculation, you should have such data as: type of lightning rod, material, area of the building, frame design, height of the building, radius of the intended protection. The correct formula results in dimensions sufficient for good performance.
Lightning rod material
For a lightning rod, steel, aluminum and copper are used, while copper conductors have better protective properties, but for creating lightning protection for a wooden house with your own hands, steel is quite suitable as a cheaper material. In this case, it is optimal to choose the same material for all elements of the device.
Determining the most suitable location
When installing, they are guided by the fact that the height of the lightning rod should be higher than all other buildings in the surrounding area; it is important that the entire residential building falls within the protection zone (for the rod type, this area extends within a cone expanding towards the ground). In technical terms, the farther a private building is from the lightning rod, the higher the installation of the protective device is made in height
The best option is to locate the lightning rod in the center of the roof.
Making a lightning rod at the dacha with your own hands
So, if you have come to the conclusion that you want to make a lightning rod for a country house with your own hands, then you need to know how this device is made. First, you need to make a rod current collector, to which a current conductor will then be attached, which can be made from ordinary iron wire. Just choose a wire with as large a cross-section as possible, for example 6-8 mm. The conductor also connects the current collector to the ground loop.
The ground loop can be made from an iron strip measuring approximately 4x50 mm. The electrode should be made of steel rod, choosing a diameter of at least 18 mm. Please note that all connections should be made only using a welding machine. If you do not have this option, you can use bolted steel clamps, but such connections will be less effective.
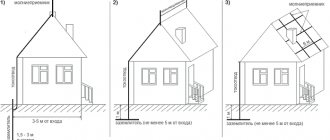
Select a distance from the ground loop to your home of about 1 meter. By the way, try to install the ground electrode away from places where people may be. For example, such devices should not be installed on paths or areas in front of the house. The height of the lightning rod is determined individually for each building, based on the protection cone. For example, all structures that seem to be under the lightning rod will be protected, but if there are structures above it, then the protection will not apply to them. Therefore, the lightning rod should rise at least half a meter above your house.
So, as you can see, it is in principle possible to build a lightning rod with your own hands, although it is necessary to clearly calculate many parameters. If you order a service from a specialized company, this will significantly save time, speed up the installation process and simplify the task. After all, the main thing is safety and confidence that it is provided in the right way.
Choosing a lightning rod for different roofing coverings
The roofs of houses differ in their roofing covering. For each of them you need to choose the right receiver:
Roofs covered with soft roofing or clay tiles are good insulators. A metal mesh receiver works well for them.
Moreover, a separate mesh must be attached to each slope, connected to an individual down conductor; If we talk about soft roofing again, then when installing the mesh with your own hands, you must be careful not to damage the covering. It is more effective to install an active protection receiver here
This is due to the simple process of attaching one mast, which does not require long walks on soft surfaces; Roofs made of metal tiles or covered with other similar materials are good conductors. Here, pin protection or, as it is called, rod protection would work better. But it all depends on the area of the slopes. On large roofs you will have to install many rods. To simplify the work, you can attach one active protection mast, which can replace up to 10 rods.
If the under-roofing pie of a metal roof is made of non-combustible materials, it is allowed to connect the roofing covering to the down conductor without installing an air terminal. An important condition here is the reliable connection of all metal tile elements to each other to ensure good contact for electrical conductivity.
When choosing the type of lightning rod, the location of the house, landscape, roof shape and climate of the region are additionally taken into account.
Selecting a lightning rod for a lightning rod
The protection radius of the Satelit 3 lightning rod is calculated in accordance with the formula defined by the NFC 17-102 standard (France) and depends on:
- choosing a lightning rod model;
- required level of building protection;
- height at which the device is installed.
| Lightning rod model | Satelit 3-25 | Satelit 3-45 | Satelit 3-60 | ||||||
| Height, m | Protection level | Protection level | Protection level | ||||||
| I | II | III | I | II | III | I | II | III | |
| 2 | 17 | 23 | 26 | 26 | 34 | 36 | 32 | 34 | 44 |
| 3 | 25 | 34 | 39 | 38 | 48 | 50 | 48 | 48 | 65 |
| 4 | 34 | 46 | 52 | 50 | 64 | 72 | 64 | 64 | 87 |
| 5 | 42 | 57 | 65 | 63 | 81 | 89 | 79 | 81 | 107 |
| 6 | 43 | 58 | 66 | 63 | 81 | 90 | 79 | 81 | 107 |
| 10 | 44 | 61 | 69 | 64 | 83 | 92 | 79 | 83 | 109 |
| 15 | 45 | 63 | 72 | 65 | 85 | 95 | 80 | 85 | 111 |
| 20 | 45 | 65 | 75 | 65 | 86 | 97 | 80 | 86 | 113 |
| 45 | 45 | 70 | 84 | 65 | 90 | 104 | 80 | 90 | 119 |
| 60 | 45 | 70 | 85 | 65 | 90 | 105 | 80 | 90 | 120 |
Lightning protection device
Lightning protection is a protective measure that ensures the safety of buildings and the lives of people living in them from the destructive effects of a lightning strike. Lightning rods are used as lightning protection for buildings.
The lightning rod consists of 3 main elements:
- lightning rod;
- down conductor;
- ground loop.
Lightning rods: different types
This is a metal conductor that is installed on the roof of a house to receive a lightning strike.
It is important to install it at the highest point of the roof. In cases where the house is very large or has a complex structure, it makes sense to install several lightning rods
The lightning rod can have different types of design:
A metal pin 0.2 -1.5 meters long, installed vertically at the highest point of the house. This could be a chimney, a roof ridge, or a television antenna mast. It is made of a metal that is less susceptible to oxidation in the open air - copper or, for example, galvanized steel. The cross-sectional area of this type of lightning rod must be at least 100 m2 (if its shape is round, a diameter of 12 mm will be quite sufficient). When using a hollow tube, the upward-facing end must be welded. This method is suitable for all types of metal roofing. Lightning rod diagram
A metal cable stretched on two wooden supports 1-2 meters high along the roof ridge. To make the structure more reliable, you can use metal supports, but in this case they will have to be isolated from the cable using insulators. This method is good for wooden and slate roofs. Lightning rod diagram based on tension systems Lightning protection mesh, fixed along the ridge of the roof of a house, with grounded down conductors extending across the entire surface of the roof, is ideal for tile roofs. Scheme of a lightning rod based on a “spatial cage”
It is important to know! Lightning rods must be connected to all metal objects on the roof: fans, gutters, ladders. As an alternative to erecting a lightning rod on the roof, you can use, for example, a nearby tree (if it is, of course, 10-15m higher than the house)
The lightning rod is mounted on its top so that it is at least half a meter higher than the crown
As an alternative to erecting a lightning rod on the roof, you can use, for example, a nearby tree (if it is, of course, 10-15 m higher than the house). The lightning rod is mounted on its top so that it is at least half a meter higher than the crown.
Next, the lightning rod is connected to the down conductor.
Functions and operation of the down conductor
A down conductor is a part of a lightning rod, which is designed to divert lightning charge from the lightning rod to the ground loop. This is a 6mm thick steel wire welded to the lightning rod, which in connection with the lightning rod must withstand a load of 200 thousand amperes. It should be noted that the welding between these two components of lightning protection must be very reliable in order to prevent loosening of the fastening or rupture between them (for example, from a falling layer of snow or from strong wind).
The down conductor is lowered from the roof along the walls, nailed with staples, and directed into the ground, to the ground loop. If there are several down conductors, they are laid along the walls at a distance of 25 meters from each other, and as far as possible from windows and doors. It must be remembered that they cannot be bent sharply (a spark discharge may occur and, as a result, ignition).
According to the rules, the down conductor must be as short as possible, but at the same time it must be laid closer to the places of greatest risk: the edges of gables, sharp protrusions, dormer windows.
Grounding the lightning protection system
Lightning protection grounding is a device that ensures reliable contact of the down conductor with the ground. This is a regular circuit (as for household electrical appliances): three electrodes connected to each other and driven into the ground. It's good if you already have it.
According to the rules, the grounding of household electrical appliances and lightning protection must be common. And if you don’t have one yet, it’s not that difficult to make – the design of the ground electrode is quite simple.
To do this, we take copper with a cross-section of 50 mm2 or steel - 80 mm2. We dig a trench 3m long and 0.8m deep and drive steel rods into its ends (not all the way). Using steel and welding we connect these two rods. We weld a tap to this structure to the house, to which we connect the down conductor. We paint over the welding areas, then hammer in the grounding conductor to the very bottom of the trench.
It is important to know! According to the rules, the ground electrode is located at a distance of no closer than 1 meter from the walls and no less than 5 meters from walkways, porches and pedestrian paths
Lightning protection of buildings and structures
Lightning is an unpredictable natural phenomenon with destructive force and power . The consequences of its strike, especially a direct hit, can be catastrophic, and this is not only completely destroyed electronics, a destroyed and burned building (fire is the most common companion of a lightning strike), but also the worst thing, harm caused to the health of people and animals. The nature of lightning is closely related to electricity, but humanity has still not been able to thoroughly study it and subjugate it to its will, so thunderstorms and lightning remain a dangerous, uncontrollable and potentially destructive phenomenon, from which it is impossible to insure against it. Of course, there are objects with a greater or lesser degree of risk of being struck by lightning, there are factors that aggravate the risks, but no one can say for sure “lightning will never hit this object” (except perhaps the Lord God himself, but this is already beyond the scope of human understanding and especially the zone of control), and especially no one can prevent it. However, known facts about the nature and properties of electricity, the laws of physics and the achievements of science provide an opportunity to minimize the risks of lightning strikes using a lightning protection system.
Lightning protection (the term lightning protection is also often used) is an engineering system that includes a set of specialized equipment and materials, and is designed to ensure the safety of an object (building, structure), the life and health of people and animals located there, material and other values, from the direct impact and consequences of a lightning strike hitting an object. The structure and composition of the lightning protection system is determined based on the individual parameters of the object and specialized calculation formulas.
Up to 16 million thunderstorms occur annually on the globe, that is, about 44 thousand per day. Danger to buildings (structures) as a result of a direct lightning strike can lead to:
- damage to the building (structure) and its parts,
- failure of electrical and electronic parts located inside,
- death and injury to living beings located directly in the building (structure) or near it.
There are statistics according to which lightning can strike a house once every 50 years, that is, a specific building can become the target of a lightning strike once every 50 years. No one knows in what specific time interval this can happen and what the damage will be; a lot depends on the specific object. Usually the minimal consequences are burnt out electronics (TV, refrigerator, computer, etc.), and this is not repaired under warranty, as it is considered force majeure, but this is material damage, much worse when the harm is caused to animals or people on the premises object, unfortunately, such cases do occur. In our practice, we have encountered the consequences of a lightning strike, burnt-out electronics, damage amounting to many hundreds of thousands of rubles (this is on average for a private home), and millions of rubles at an industrial facility, and much of the equipment has to be completely replaced and cannot be restored, and if it is repaired, it is entirely at the expense of the Customer, so it may be more profitable to supply a new one. The fact is that statistics with a probability of 50 years provide the illusion of security and delay, “my property is safe, I still have a lot of time left, I’ll do it later,” but this is an element of nature and no one is insured against its impact, and the cost lightning protection systems are many times less than the potential damage.
According to the operating principle and composition of the equipment, the lightning protection system of buildings and structures is divided into external and internal:
An external lightning protection system provides interception and neutralization of lightning by diverting it and discharging it into the ground, thus protecting the object (building, structure) from damage and fire. A correctly calculated, designed and installed lightning protection system, at the moment of a direct lightning strike to an object, takes on the lightning current and diverts it through down conductors to the grounding system, where the discharge energy should be safely dissipated. The passage of lightning current must occur without damage to the protected object and be safe for people located both inside and outside this object.
During a thunderstorm, large induced charges appear on the Earth, and a strong electric field appears at the Earth's surface. The field strength is especially high near sharp conductors, and therefore a corona discharge is ignited at the end of the lightning rod. As a result, induced charges cannot accumulate on the building and lightning does not occur. In those cases when lightning does occur (such cases are very rare), it strikes the lightning rod and the charges go into the Earth without causing destruction. In other words, electric current always flows along the path of least resistance, and thunderstorm lightning is a colossal discharge of electricity, and therefore obeys this rule. When lightning approaches a building (structure), a properly made lightning rod will represent a circuit with the least resistance, along which a destructive discharge will go into the ground without contact directly with the object.
Fundamentally, the external lightning protection system consists of three interconnected parts:
A lightning rod (lightning rod, lightning rod) is a metal (stainless or galvanized steel, aluminum, copper) device that intercepts a lightning discharge, installed on buildings and structures, in decorative elements (vanes, columns, spiers, etc.), can have a different lightning rod design:
- rod - a metal pin, 0.2-1.5 m long, with a cross-sectional area of 100 mm2 (if it has a round shape, then Ø 12 mm is enough), installed vertically at the highest point of the object (roof ridge, ventilation pipe, mast television antenna, etc.), when using a hollow pipe, the end facing upwards must be firmly welded. This method is well suited for all types of metal roofing;
- tensioned cable - a metal cable stretched along the ridge of the roof on two supports; if the supports are metal, they must be separated from the cable using special insulators. This method is best used for slate and wooden roofs;
- network - a metal conductor fixed along the ridge of the roof, with grounded down conductors extending from it, preferable for tiled roofs.
Grounding conductor or (down conductor) - part of the system, which is a conductor and serves to remove charge from the lightning rod to the ground electrode, is laid along the wall of the building (structure). Metal wire Ø 6 mm is often used (diameter and material may vary depending on the individual parameters of the object), welded to the lightning rod and the ground loop;
Ground electrode - a conductive part or a set of interconnected conductive parts that are in electrical contact with the ground (soil) directly or through a conductive medium.
Lightning protection elements are interconnected and fixed to the supporting structure. The probability of a ground object being struck by lightning increases as its height increases, so the lightning rod is located as high as possible on the protected object, or as a separate structure next to the object. The protective radius of a lightning rod is determined by its height and is approximately calculated by the formula: R=1.732 xh , where h is the height from the highest point of the house to the peak of the lightning rod.
The internal lightning protection system is a set of surge protection devices (SPDs) designed to protect electrical and electronic equipment from network surges caused by resistive and inductive couplings that occur under the influence of lightning current. There are overvoltages caused by lightning strikes:
- direct - when lightning strikes a building (structure) or communication lines connected to the building (structure) (power lines, communication lines);
- indirect - during lightning strikes near a building (structure) or communication lines.
Depending on the type of lightning strike, the parameters of surge voltages and protective devices (SPDs) differ:
- Type 1 (spark gaps or varistors, with the ability to discharge a current of about 100 kA into the ground) - passes through all the energy of a typical lightning strike without being destroyed, but retains a fairly large surge voltage (units of kilovolts), installed at the entrance of the power source to the building, in order to exclude strong current pulses.
- Type 2 (limit voltage amplitudes to values below 1.5 kV) - varistor limiters that limit electrical impulses to a level that does not destroy electrical devices. They are not capable of withstanding a lightning strike on their own, without the previous type 1, without destruction, however, its stability is guaranteed if used together with type 1. The voltage surge behind type 2 is usually about 1.4-1.7 kV.
- Type 3 - specially designed limiters compatible with data lines. Designed to protect telephone sets, control boxes, televisions, and cameras. To ensure resistance to destruction, requires the use of types 1 and 2 in front, and is installed directly next to the consumer.
Long-term overvoltages ( for example, from an increase to 380V during “zero burnout”) can lead to the failure of the SPD. In the event of a through burnout of the SPD from phase to PE, a huge amount of heat may be released on it and a fire in the shield, so it
must be installed with protection - fuse links or circuit breakers. In the case when the input circuit breaker has a rating <= 25A, it is possible to connect an SPD behind it; in this case, the input circuit breaker performs additional SPD protection functions. Lightning protection schemes are implemented either with safety priority or with uninterruptibility priority.
In the first case, destruction of SPDs and other devices is unacceptable, as well as a situation where lightning protection is temporarily turned off, but automatic operation with a complete shutdown of consumers is acceptable. In the second case, a temporary shutdown of lightning protection is acceptable, but an interruption in supply to consumers is unacceptable. When installing type 1 and type 2 simultaneously, the distance between them along the cable must be at least 10 m, the distance from type 2 to type 3 and consumers must also be at least 10 m. This creates the inductance necessary for the machine of a higher stage to operate earlier. It is also possible to use SPDs of types 1+2, which combine both devices in one housing (protected from burnout in the same way as type 1).
Thus:
- An external lightning protection system prevents lightning from directly striking an object by intercepting and neutralizing it in advance, thereby ensuring the safety and integrity of the object, all its systems and the people, animals and valuables inside.
- An indoor system provides targeted protection to specific components of a home's systems (electrical and electronic equipment).
Selecting a lightning protection system:
The choice of a lightning protection system must be approached very responsibly and comprehensively, since this is a system that ensures not only the safety of property, but also the life and health of people and animals located at the facility and the surrounding area:
- It is necessary to assess the general condition of the object, its territorial location (city, field, forest, etc.), terrain, adjacent infrastructure (high-rise buildings, power lines, overpasses, objects under construction, railway tracks, etc.), the presence of nearby tall trees, ponds etc. All these factors are of no small importance, since lightning usually strikes the highest point of a building, made of materials with maximum electrical conductivity, or a tree growing next to it (which is often higher than the highest point of the building). Trees, antennas, poles, having received a lightning strike, create a shielding effect, as a result of which nearby houses, cars, people in the affected area, etc. may be exposed to electric shock.
- Another key aspect when installing a lightning protection circuit is the type of soil under the object. Different types of soil have different conductivity and, accordingly, different resistance, which must be taken into account when choosing the cross-section of the metal lightning protection strip and the depth of the contour.
- Owners of buildings located in close proximity to bodies of water and places where key sources come to the surface of the earth need to pay particular attention to the issue of lightning protection of a facility. The risk of being struck by lightning in such places is maximum, especially if, according to climatic data, the number of thunderstorm periods exceeds 40 hours per year.
In addition to the physical factors given above, when choosing a lightning protection system, one should proceed from its feasibility:
- The cost of an external lightning protection system will vary depending on the area of the facility (mainly the roof) and the materials used, while the amount of wiring, electronic systems and equipment, as well as its power, does not affect the cost of the system. The cost of the internal system will directly depend on the number of electronic systems, equipment and its power.
- The internal system is designed to protect electronic equipment specifically, while the external system protects the entire facility. Of course, for a country house with a minimum number of electronic systems, located in a safe place (from the point of view of the risk of lightning), the feasibility of installing an external lightning protection system is minimal. It’s a completely different matter when the facility has a large number of electronic systems (access control systems, computers, televisions, smart home systems, security and fire alarms, heating and ventilation systems, mobile phones, tablets, music, kitchen and other equipment), including including those ensuring the functioning of vital systems of the facility itself and other facilities (for example, electrical substations, wastewater treatment plants, boiler houses, hospitals, shops, transport facilities, etc.). In such cases, the internal lightning protection system should play a safety (backup) role, and the main line of protection is the external protection system.
- Equipment for an internal lightning protection system is quite expensive, and when ensuring the safety of an object with a large number of electronic systems, its cost will be comparable or even exceed (possibly several times) the cost of an external system.
- And most importantly, the internal system does not prevent lightning from entering an object, but only protects electronic equipment from destruction; in addition, with an insufficient level of protection or errors in calculations and installation, it can itself cause a fire, while a lightning strike can damage object, injure (with varying degrees of severity) the people and animals in it. A comprehensive facility protection system can only be provided by an external lightning protection (lightning protection) system.
Based on our practice, we recommend using complex lightning protection systems that combine both external and internal. Both systems complement each other, insure and minimize risks, especially at complex facilities that ensure the safety and livelihoods of people (infrastructure facilities such as hospitals, airports, railway stations, boiler houses, thermal stations, educational institutions, shops, etc.), while it is necessary strike the right balance so that the system is as functional, cost-effective and provides the best level of protection as possible.
Regulations:
The lightning protection system is a system that ensures the safety of an object and requires accurate calculation, selection of equipment and installation in order to perform its functions efficiently. Errors in calculations and poor-quality installation can have a detrimental effect on the operation of the system as a whole. Requirements for the system on the territory of the Russian Federation are regulated by regulatory documents that must be observed:
- “Instructions for lightning protection of buildings and structures” RD 34.21.122-87 dated July 30, 1987
- “Instructions for the installation of lightning protection of buildings, structures and industrial communications” CO 153—343.21.122-2003 dated June 30, 2003.
In accordance with the provisions of the Federal Law of December 27, 2002 No. 184-FZ “On Technical Regulation” Art. 4, executive authorities have the right to approve documents and acts of a recommendatory nature only. This document includes the “Instructions for the installation of lightning protection of buildings, structures and industrial communications” CO 153—343.21.122-2003. Order of the Ministry of Energy of Russia dated June 30, 2003 No. 280 does not cancel the previous edition “Instructions for lightning protection of buildings and structures” dated July 30, 1987. Thus, design organizations have the right to use the provisions of any of the mentioned instructions or their combination when determining the initial data and when developing protective measures.
In December 2011, the Federal Agency for Technical Regulation and Metrology issued GOST R IEC 62305-1-2010 “Risk Management. Lightning protection. Part 1. General principles" and GOST R IEC 62305-2-2010 "Risk management. Lightning protection. Part 2. Risk assessment." These documents represent the authentic text of the IEC 62305 standard, consisting of four parts, and are intended to clarify the situation with lightning protection systems on the territory of the Russian Federation.
Typical structure and composition of lightning protection system equipment:
Since the invention of the first lightning rod by Benjamin Franklin in 1752 (although there is evidence that similar systems existed before), much has changed. New engineering structures, materials, architectural solutions have appeared, infrastructure has changed, a large number of electronic systems have appeared that need protection, and humanity’s scientific knowledge about the nature of electricity has advanced. The basic principles remained unchanged, but the changes that occurred required improvements in the structure, materials, and design of the system. Currently, there is a wide variety of materials and components used in lightning protection systems; their quantity, composition and characteristics depend on the individual parameters of the object. Often, especially at large and complex facilities, only professionals can correctly make all measurements, calculations and select equipment. Of course, if the Customer has the knowledge and capabilities, he can do all the work or certain stages himself, but such cases have become rare, since these works began to require high professionalism of the Contractor, since the risks and cost of property (not to mention people’s health) have increased significantly. in need of protection.
Equipment and materials for each facility are selected individually based on current factors. Below is an approximate estimate for the equipment and installation of a passive lightning protection system for a private house (Typical solution for the “Cottage” project - a house of 2 floors + ground floor, roof area 100 sq. m., the amount of equipment and materials is minimal).
| No. | Name of equipment, materials, work | Unit from-i | Qty | Price per one. | Amount, rub. |
| I. | LIGHTNING PROTECTION SYSTEM EQUIPMENT, including: | 74 175 | |||
| 1.1. | Passive copper lightning rod | PC. | 5 | 1 825 | 9 125 |
| 1.2. | Copper down conductor | m.p. | 100 | 230 | 23 000 |
| 1.3. | Fastening for down conductor to Cu drain | PC. | 10 | 430 | 4 300 |
| 1.4. | Copper holder for down conductor 8-10 mm. | PC. | 60 | 350 | 21 000 |
| 1.5. | Terminal clamp for down conductor Cu | PC. | 30 | 175 | 5 250 |
| 1.6. | Control connector Cu | PC. | 5 | 310 | 1 550 |
| 1.7. | Galvanized grounding kit No. 3 (for 1 house) | units | 1 | 9 950 | 9 950 |
| II. | CABLE ROUTES AND SYSTEM MATERIALS, including: | 7 500 | |||
| 2.1. | Other consumables (connectors, screws, dowels, insulating tape, fasteners, etc.) | units | 1 | 7 500 | 7 500 |
| III. | TOTAL COST OF EQUIPMENT AND MATERIALS (item I+item II) | 81 675 | |||
| IV. | TRANSPORTATION AND PREPARATION COSTS – 5%*item III | 4 084 | |||
| V. | INSTALLATION WORKS OF SYSTEM EQUIPMENT, including installation of: | 37 250 | |||
| 5.1. | Passive copper lightning rod | units | 5 | 950 | 4 750 |
| 5.2. | Copper down conductor | units | 100 | 120 | 12 000 |
| 5.3. | Fastenings for down conductor to Cu drain | units | 10 | 250 | 2 500 |
| 5.4. | Copper holder for down conductor 8-10 mm. | units | 60 | 150 | 9 000 |
| 5.5. | Terminal clamp for down conductor Cu | units | 30 | 100 | 3 000 |
| 5.6. | Control connector Cu | units | 5 | 200 | 1 000 |
| 5.7. | Galvanized grounding kit No. 3 (for 1 house) | units | 1 | 5 000 | 5 000 |
| VI. | TOTAL ESTIMATED (item III+item IV+item V) | 123 009 |
The degree of reliability, functionality and durability of an external lightning protection system directly depends on the accuracy of the calculation, the quality, structure and quantity of selected materials and equipment, as well as the correct installation of the system. Our company’s specialists have the necessary specialized knowledge and experience, so they will quickly and efficiently solve the assigned tasks, perform all the necessary measurements and calculations, select equipment and materials, and install the system. Our work is always distinguished by high quality and reliability, since we provide the Customer with a guarantee for all work performed, we take our own reputation responsibly and place high demands on our specialists. A high-quality, functional system and the absence of failures in its operation mean peace of mind for the Customer and, as a result, the key to our reputation, development and a minimum number of visits to troubleshoot problems.
DIY construction stages
Ground electrode
The ground electrode is located in a place where there is no danger of an electrical lightning discharge near it. The distance to the building is determined to be 1 meter, but the distance to the sidewalk or other path should be 5 meters. If places where no human foot can tread cannot be found, then the grounding area is fenced off with wooden shields and a corresponding sign is made.
Electric discharge outlet
After the preparatory stage, you should proceed to installing the lightning rod:
- installation of the device should begin on the ground - dig a hole or trench to locate the grounding device or circuit;
- the pit can be of different sizes, depending on the size of the device - a triangular contour is placed in a recess of the appropriate geometry, linear grounding requires a trench;
- if the length of the rods is more than a meter, then a hole is dug to this size, and the rest is driven into the soil;
- the trench starts from the connection of the down conductor with the grounding, while the internal protection section is also grounded, the connection of the shield to the grounding is carried out by a wire in the underground part, so an additional trench is made for connecting against network overvoltage;
- if work is carried out in dry soil, which is not very suitable for conductivity, then salt is added to the bedding and a saline solution is poured to the depth;
- if an arid climate is expected, then grounding is done in a shady place to protect it from drying out, or the soil is soaked with water from time to time;
- for homemade grounding, you can use the remains of the old profile, the only requirement is the quality of the welds;
- When installing grounding, more profiles are taken than necessary, since while they are in the ground they become covered with rust, the layer of which does not work as grounding.
Lightning Receiver
The next step is to install a lightning arrester:
- it is placed on a powerful support that can withstand strong wind loads, the length is determined by the formula;
- the length is connected by welding from various pieces of rolled stock, a metal internal plug is inserted into the hollow profiles at the joint;
- the current conductor is isolated from metal roofing elements, like the ground electrode, otherwise a high-power discharge will take a different path;
- During installation, the lightning arrester and current conductor are connected by wire or strip steel;
- The current conductor is connected to the ground by welding along its entire length; when installing the ground loops, all recesses are covered with soil.
DIY lightning rod for a private house
How to make a lightning rod yourself? First of all, you need to competently approach the issue of calculations, selection of materials and direct installation of the device.
Calculation
A lightning rod is not just a piece of rod attached to the roof. Before installation, it is necessary to calculate the height of the structure sufficient for a particular building.
First, we will determine the area that will be protected by a lightning rod. Let's imagine it in the form of a cone, where the top is the lightning rod. There is a special formula H=(rx+1.63Hx)/1.5, where H is the height of the rising part, Hx is the height of the building, rx is the radius of the base of the protective zone. It turns out that the wider the safe zone, the higher the pin should be. But do not make the lightning rod too high, otherwise you risk attracting all the lightning in the area.
Installation of a lightning rod
When the preparatory work is done, you can proceed to installing the lightning rod. It is more expedient to install it on the roof of the house than to install an additional structure. Choose a place away from the center - preferably on one of the walls. Prepare a rod of the correct length, which you calculated using the formula. Weld a hole in the hollow pipe. Prepare a support - it must be strong and reliably hold the lightning rod. Place the rod on the support. Next we install the down conductor. Make sure that it does not come into contact with metal parts of the house, otherwise all the voltage from a lightning strike can go in a completely different direction and cause trouble. We assemble a grounding circuit from steel pipes or profiles. The thicker the material, the longer your structure will last, because iron in the ground rusts. Weld the down conductor to the ground electrode along the entire length of the latter. Then it’s the turn of the trench - dig it in accordance with the type of ground electrode: closed or linear.
- The closed one is made in the shape of a triangle from metal rods, and a triangular hole needs to be dug for it;
- Linear type - grounding electrodes are welded in one line.
Remember that only wet ground can conduct current. Dry soil should be soaked in saline solution. Drive the electrodes into the ground. Backfill the structure. Now you can wait for a thunderstorm without fear and check the lightning rod in action.
Modern technology is the key to successful implementation of lightning protection at home
The lightning rod of a private house must be technologically advanced, that is, the materials and products used must ensure convenient and quick installation without damaging the structure of the house and engineering systems.
Modern lightning protection technology, developed in Europe and based on the use of factory-ready products made from durable materials, meets this criterion.
A conscientious manufacturer creates a range of lightning rods, lightning protection conductors, connectors, holders for all types of roofs and walls, terminals for connecting any types of structures (antennas, gutters, etc.) in accordance with standards and from corrosion-resistant materials. As well as high-quality SPDs for all types of electrical circuits.
BUT FACTORY PRODUCTION of products and materials does not guarantee that the lightning rod will meet the requirements of standards, security and the wishes of the owners.
Technological capabilities are fully realized only if you have experience in organizing and carrying out installation.
Features of installation of a lightning rod and grounding loop
The grounding loop in the case of lightning rods is designed in approximately the same way as the grounding loop for the house itself. But you need to keep in mind that these two contours should under no circumstances intersect with each other. These are elements that function separately from each other. If you do not heed this rule, then after the first strike of a thunderstorm you can receive a strong discharge in sockets and electrical equipment - and as a result, you will lose not only expensive household appliances, but, perhaps, the house itself. So to ground the house and ground the lightning rod, you need to provide two different independent circuits. However, the process of making a circuit for a lightning rod is exactly the same, with some differences that need to be taken into account:
- Grounding electrodes should not be less than three meters in size;
- In this case, the electrodes themselves must have a cross-section of at least 2.5 cm and be made in the form of an all-metal rod;
- The ground loop should only have a triangular shape - this is very important!
- Moreover, between the vertices of the triangle a distance of three meters must be ensured - in fact, this requirement is ensured through the length of the electrodes;
- The busbar, with which the electrodes are combined into a circuit, must be at least 1.2 cm in diameter. If a metal strip is used as a busbar, then its parameters should be as follows: 50 x 6 mm;
- Welded joints must be made to the highest possible quality so that they cannot separate due to heating
The lightning receiver is an iron element raised several meters above the roof of the building. It can be placed either directly on the building itself or next to it, nearby.
In this case, it is important to ensure the depth of the upper part of the contour is at least 50–80 cm.
External protection of a private house from lightning
The system can be passive or active. The principle of operation of the first is simple, like everything ingenious. A metal lightning rod on the roof catches (attracts, intercepts) a lightning discharge and, through a current conductor, directs it to the ground, to the ground electrode.
Active lightning protection
Such lightning protection is more effective; it operates within a radius of 100 meters from a “cunning” lightning rod, which, by ionizing the surrounding air, intercepts a lightning discharge. Then it works like passive protection. The main advantage of the device is the lightning protection coverage of neighboring residential buildings and outbuildings over a fairly large area.
Types of external lightning protection for a home
Based on the type of design, there are modular-pin, cable and mesh lightning protection.
Pin
The pin system is called because of the lightning rod, which is installed in the highest part of the roof, and is a metal rod (pin). This design is suitable for lightning protection of a private house with a roof made of metal tiles or any other material.
Rosovaya
Installation of this type of protective device is allowed if the roof is slate or tiled, but not metal.
The lightning rod is a cable (thick wire, rod) stretched at a height of 0.3-0.5 m along the ridge of the house.
Mesh
The system is considered the most complex in terms of installation. It is made from wire rod with a diameter of 6-8 mm, which in the form of a grid with cells of 6x6 meters is laid over the entire roof area. At the intersection of horizontal and vertical rods, it is welded. It is attached to the roof with brackets.
Mesh lightning protection for a house is installed, like cable lightning protection, on a slate or tiled roof.
Down conductor
For this element of the system, round steel (copper, aluminum) with a diameter of at least 6 mm is used. The down conductor is secured with brackets along the roof and walls. Usually during installation they try to lay the “route” away from window and door openings, as required by regulatory documents, and so as not to spoil the exterior of the building.
When laying a conductor, you need to follow some simple rules:
- On wooden surfaces, the current conductor should be mounted at a distance of 15-20 cm from the wall;
- If a long-length cable receiver, a large-area mesh receiver or a pin receiver consists of several elements, then there must be several down conductors (CO 153-34.21. 122-2003)
When constructing a new structure, lightning protection of a cottage or house is already included in the design documentation. But if a country house or country house has just been purchased and there is no “lightning rod” on it, then the most reasonable solution would be to protect yourself and your loved ones from lightning strikes yourself, or with the help of hired specialists.
If you have the skills to carry out construction work, lightning protection of a private house with your own hands will not be a problematic issue, but will save money.
Ground loop
The principle of the ground electrode device is extremely simple. Three steel module pins 1.5-2 meters long, 16-20 mm in diameter with zinc coating, are driven into the ground and connected in series.
This design has a number of advantages:
- Possibility of installation to any depth without the use of special equipment;
- Low labor intensity. The work can be done by one person;
- The greater depth of immersion of the electrode pin increases the efficiency of grounding;
- The connection of elements does not require welding (using special clamps);
- The entire system is hidden underground.
The circuit is driven into the ground no closer than 1 m to the foundation of the house, and no closer than 5 m to the front door.
Lightning rod design rules
To correctly select the design of a dacha lightning rod, you must first study the building design and, in accordance with the “Instructions for the installation of lightning protection of buildings and structures” (Instruction RD 34.21.122-87), determine the required level of protection. Low-rise and small-sized private houses usually belong to lightning protection category III .
Effective lightning protection is one that reliably protects the building and everything inside it from direct lightning strikes and from its secondary discharges in electrical networks. A country lightning rod is usually a lightning rod, which is connected to grounding using a down conductor system.
Lightning rod
A device that directly receives a lightning strike is called an air terminal. This is the most noticeable and significant element of an industrial or country lightning rod design. There are rod, cable, and mesh receivers.
The most popular and famous thanks to Benjamin Franklin is the lightning rod, which is a metal pin made of stainless steel, aluminum or copper. It is usually installed 2 m above the highest point of the protected building. This type of lightning rods is the simplest to implement and quite cheap.
A cable lightning rod consists of two masts installed around the perimeter of the protected object, and tensioned steel cables between them. An lightning protection network is a mesh of metal rods laid on the roof of a building with a certain pitch.
For small private houses, a metal roof can be an excellent lightning receiver. If the roof of the house is made of a different material, then it is better to choose a lightning protection mesh for the protection device, and for wooden country houses active protection is more often used.
Down conductors
Current flows to the grounding device through down conductors. In accordance with the above Instruction RD 34.21.122-87, down conductors in a residential building can be various building structures made of steel, aluminum or copper (frames, fire escapes, reinforced concrete slab reinforcement). Special down conductors are usually laid outside along the perimeter of the building in 25 m increments. The effectiveness of down conductors depends on the continuity of the electrical network. They are usually connected to the lightning rod and grounding devices by welding.
Grounding
The lightning charge in the soil is dissipated using grounding devices. In accordance with Instruction RD 34.21.122-87, they are most often reinforced concrete foundations or vertical electrodes that go deep into the ground. The latter type of grounding is necessarily protected from corrosion (therefore, it is usually made of copper-plated or galvanized steel), and the electrodes are securely connected to the horizontal busbar and to each other using special connectors.
Types of lightning rods for a private house
Do-it-yourself lightning protection in a private house should consist of metal conductors. They are installed on the roof of the house to receive a lightning charge. The conductor should be installed at the highest point of the building. If the house has an unusual and complex structure, then several receivers should be installed. An air terminal for a private house can have several types of design. Here are the main types of structures:
- Metal pin to protect a private home. Its length should be from 20 cm to 1.5 meters. It can be installed both on the chimney and on the ridge of the roof. The pin must be made of galvanized steel or copper. The cross-sectional area of this lightning rod should be about 100 square meters. meters. This method of protecting a home from lightning strikes is suitable for any type of roof.
- Cable for a private house. It must be tensioned on two wooden supports, which have a height of 1 to 2 meters. To make the structure reliable, metal supports can be used instead of wooden ones. This method of protection is good for wooden or slate roofs.
- Lightning protection mesh for a private home. It is fixed along the ridge on the roof of the house. Down conductors made of mesh should be located along the entire surface of the roof. This type of protection is usually used for tile roofs.
Do-it-yourself lightning protection at the dacha, its scheme is no different from other designs. At your dacha you can also install three types of lightning rods.
Is a lightning rod needed on the roof of a private house?
From a safety point of view, a lightning rod is always needed - even if the probability of being struck by lightning is negligible, lightning protection and grounding will reduce it even more. That is, it definitely won’t get worse. But the price of a lightning rod with installation starts from 30,000 rubles, and not everyone is ready to spend this money on reducing the likelihood of a lightning strike by thousandths of a percent. Therefore, they usually talk separately about situations in which a lightning protection device is mandatory, and separately about cases when installing a lightning rod is just a recommendation.
Lightning protection of the roof is absolutely necessary:
- when the house is located in a cottage community, village, urban private sector, or stands alone and there are no high-rise buildings nearby;
- when covering the roof with any types of metal coverings, including corrugated sheets and metal tiles;
- when the house is built on a hill or there is shallow groundwater underneath it;
- if the building has a lot of working electronics or powerful equipment installed.
If any of these conditions are met, the need to install lightning protection is not a matter for discussion, since the risk is quite high. And the higher the house is built, the higher it is: in the southern regions, thunderstorms occur much more often than in the northern ones, therefore, the likelihood of lightning hitting the house increases. The map below clearly shows how the number of days with thunderstorms increases as you move south, with a few clusters near the mountain ranges.
Of course, no one can force you to install a lightning rod on your house - this can only be officially required for public, multi-apartment, commercial and industrial buildings. If we are talking about a private house, lightning protection is left to the discretion of the owner. But not making a lightning rod in a private house in such a situation is the same as not treating a wooden beam for a frame house with fire protection and making closed wiring in it.
It's a completely different matter when your home:
- Located in close proximity to dominant heights : cell towers, water towers, high-rise buildings. But keep in mind that the immediate proximity is not a kilometer or even 500 meters. This is when the farthest point of the house is located no more than 1.2 × h from a high-rise object, where h is its height. That is, with a base station height of 100 m, each corner of your house should fall into a cone with the top at the highest point of the tower and a base with a radius of 120 m.
- Built in a forest with tall trees . The protection radius from one tree, if it is not a sequoia, is not enough to cover the entire house, but there are a lot of trees in the forest. Sometimes, for better protection, a lightning rod is attached to the top of the tallest tree near the house.
- Located in an area where thunderstorms are rare . In numbers, these are areas with an average annual duration of thunderstorms of up to 20 hours. In the map above, these are the red and pink zones.
In all these situations, the risk of being struck by lightning is very small, so many home owners do not do lightning protection, relying on chance. On the one hand, the probability is really low. On the other hand, the losses if “something goes wrong” will be very large: even if the house does not catch fire, then all the electronics, including the heating boiler control units, will definitely burn out. How justified such savings are, each home owner decides for himself.
Lightning is unpredictable, although rare, but it can strike a building protected by a commanding height.
Installation of the structure
After the calculations have been made and the materials have been prepared, the installation location has been selected, you can proceed to installation. First of all, excavation work is carried out and grounding is installed.
Lightning rods for a dacha or a private house require the installation of a linear or closed ground electrode. In the first case, a trench is dug in which the grounding electrodes are lined up and welded together. The second type of grounding involves immersion in the ground of a triangular structure of three grounding electrodes connected to each other by a metal strip.
The depth of the pit, straight or triangular, should be 0.5-1 meter - the rods are driven into the ground. A deep trench is dug to the place where the down conductor is attached for a connecting lead for the ground loop.
In order for an electric discharge to easily go into the ground, you need soil with good electrical conductive properties. If the soil is sandy, then to improve electrical conductivity, it is watered with an electrolyte - saline solution.
Only moist soil can pass electric current. You can provide for the drainage of the roof drainage to the appropriate area or bury the ground loop at a depth where the soil always remains moist.
Linear ground loop
In order for the ground electrode that you have made to meet the requirements for the protective system for many years, metal with a large margin of cross-sectional area is used for the manufacture of its elements
. This is due to the fact that the thickness of steel elements decreases over time due to accelerated corrosion in conductive soil. For the manufacture of the structure, a steel profile is usually used - pipe, strip, corner.
At the next stage of work, a support for the lightning rod is installed in a pre-selected location. The support is firmly fixed so that it can withstand sharp gusts of wind and lightning strikes. A rod lightning rod with a suitable cross-sectional area is attached to the support. In the absence of rolled metal of the required length, this element is welded from several sections.
It is convenient to use a tall tree growing near the house as a support. The lightning rod is attached to the tree using a synthetic halyard in such a way that the entire house falls into the protective cone. If there is no suitable wood, the lightning rod is connected to the television antenna on the roof, since its mast is made of unpainted metal. If the antenna is mounted on a wooden pole, a wire of a suitable cross-section is attached along it.
Small home protection options
The current conductor in the form of rolled wire or metal strip is firmly connected to the lightning rod mounted on the support. Check how the pantograph is laid, the lower part of which is welded to the ground loop outlet. A correctly installed pantograph does not touch the metal elements of the house anywhere. Otherwise, the electric discharge of lightning will not go into the grounding loop, but into the metal structure that is in contact with the current collector.
Installation of a down conductor involves welding a metal wire or strip to the horizontal part of the ground loop along its entire length. The ground electrode is driven into the ground at the bottom of the trenches, then the trenches and pits are filled with the excavated soil.
Structure care
Lightning protection mounted from metal should be regularly inspected to identify pockets of corrosion. Every spring, before the start of the thunderstorm season, the contacts of the protective system are checked. If necessary, they are cleaned, since poor contact can cause the system to open and catch fire when hit by a lightning discharge.
Corrosion of metal circuit
At least once every three years, the degree of corrosion of the grounding circuit is checked, for which it is dug up and inspected. Elements that are severely damaged by corrosion must be replaced with new ones. Otherwise, at some point the lightning rod will not be able to cope with its functions.
Proper calculation and correct installation of a lightning rod will protect your home. All work can be done on your own.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=6MIOsXp7Tso
How does a lightning rod work?
It is generally accepted that the lightning rod was invented in 1752 by Benjamin Franklin. But there is also evidence that lightning diversion structures similar in appearance and purpose existed long before this. Most likely, the idea for such a device was found by chance, as is often the case with many useful inventions.
The operating principle of a lightning rod is quite simple to understand. You just need to understand that during a thunderstorm, large electrical charges arise on the surface of the planet, leading to the formation of a strong electric field. Its intensity is greatest near pointed conductors, where a so-called corona discharge can occur.
If a metal pin is installed on a building, charges do not have the opportunity to accumulate, and therefore a lightning discharge usually does not occur here. In those rare cases when lightning does develop, it strikes a metal rod, and the charge goes into the ground. In order for the lightning rod to be most effective, they try to place it as high as possible. The likelihood of an object being struck by lightning increases with upward movement. Raised to a sufficiently high height, the rod increases the area under its protection.
Execution options
The lightning rod takes the blow and therefore must meet increased reliability requirements during operation.
- If it is a rod, then the best material is multi-profile rolled steel: water pipes, gas pipes, metal rod. With a diameter of at least 100 sq. mm length should be about 200 cm from the place of fixation on the house. Hollow pipes are welded at the upper end or hermetically sealed with a stopper. The most complete coverage area for the protection of cottages, country houses and private houses is observed when the height of the core structure does not exceed 30 m.
- Wire rope (galvanized steel rope) can be used. Several of its threads are suspended horizontally above the house on free-standing supports. The ends of the ropes must be grounded. You just need to choose the right place to hang the tensioned structure.
- The use of mesh protection made of wire rod with a cross-section of 8 mm, laid on the roof, or flat steel strips (with a cross-section of up to 20 mm) is also relevant. Moreover, an air terminal in the form of a mesh, connected to the ground loop by several separately located conductors, is considered the most effective, allowing for the maximum protection factor.
- The wire for the lightning rod as a current dissipation element must have a diameter of at least 6 mm (above-ground part). The same wire rod is used for these purposes. The piece of wire going to ground should not be thinner than 10 mm. In this underground section, a connection (welding, bolting) with the ground electrode is made.
- As a reliable grounding, use a sheet of metal (1 m x 1 m) sprinkled with soil or a metal pipe, a rod driven into the ground at least 1.5-2.0 m. The grounding site must always have moist soil - an effective conductor . Grounding made of copper and stainless steel will be durable.
Basic typical diagrams of country lightning rods
Once again, in more detail, we will talk about three well-known types of protection devices installed on the roof of building structures.
The type of lightning rod chosen for a country lightning rod determines the type and scheme of its protection. Typical schemes include the organization:
- lightning protection mesh;
- rod lightning rods;
- cable lightning rods.
For flat and gable roofs of cottages, regardless of the roofing material, experts recommend using lightning protection mesh. To organize it, steel, copper or aluminum rods with a diameter of up to 8 mm are used. The mesh is installed directly on the roof or under the insulation if the roof base is not flammable (Instruction RD 34.21.122-87).
Depending on the level of protection, down conductors are mounted directly to the mesh along the entire perimeter in increments of 10 to 25 cm.
A lightning protection rod circuit is a metal pin attached to a chimney or other roof structure at least 2 m above its highest point.
The installation of the rod is carried out correctly if the protected object completely falls into the base of the cone with the apex at the extreme point of the lightning rod. Increasing the height of the rod expands the protected area. This type of lightning rod is suitable for both private and industrial facilities with complex roofs.
For gable roofs of low buildings, you can also use a cable scheme for a country lightning rod. To do this, a steel cable is stretched between the supports installed on the skates. One down conductor is usually attached to its ends, transmitting current to grounding in the ground, which looks like a “chicken’s foot”. If the dacha lightning rod circuit is executed correctly, lightning discharges go into the soil outside the protected house. When installing lightning protection of this type, it is important to take into account the sagging of the cable.
The choice of a scheme for organizing a dacha lightning rod is influenced by many factors, parameters and conditions. Therefore, this is a rather complex and responsible event that requires certain professional knowledge and experience. Our company will help you design and install the most effective lightning protection for your home. In addition, we provide turnkey lightning rod installation services. The section “Our objects” contains photos of lightning rods and a description of our completed projects.
Categories and types of external lightning protection
Atmospheric lightning is a powerful discharge of electricity that obeys the basic laws of physics. Everyone knows that electric current moves along the path of least resistance. The main task of any type of lightning protection unit is to create just such a path for the passage of electricity, bypassing the structure of the building. When lightning strikes a private house equipped with such a unit, the entire power of the electric charge will simply go into the surface of the earth without causing damage to buildings, electrical appliances and people.
In popular slang, this type of protection of private buildings is called differently: grounding of a country house, a system of lightning rods, and also lightning rods. The last version of the name is completely incorrect, because thunder is the sound of a lightning strike and there is no need to take it anywhere. But the term has long taken root and is used in colloquial speech. Regardless of what the home's lightning protection is called, it is designed to perform one task - to discharge the energy of an atmospheric electrical discharge into the ground. Lightning protection blocks are divided into three categories: by method and type of protection, as well as by design features.
- Protection methods. This category is divided into two types of lightning protection: active and passive. In the active system, the lightning receiver is equipped with a special air ionizer, which, through its work, provokes the static electricity accumulated in the atmosphere to discharge. At its core, active protection attracts lightning, thereby eliminating the possibility of a direct lightning strike on the property and nearby buildings. Passive systems are not equipped with any additional devices, so lightning may discharge on it, or may strike another place, but in any case, this type of lightning protection creates a reliable barrier against direct discharge into the house. At the same time, it is not able to protect household appliances from secondary damaging factors. To protect against it, it is necessary to install additional equipment.
- Types of protection. In this category, home discharge protection is divided into two types: internal and external. The internal system protects private property from a secondary damaging factor, and the external one from the primary one. Due to the fact that active protection systems against atmospheric electrical discharges are practically not used in everyday life, the lightning protection unit for a house, cottage or summer house must consist of two parts: external and internal.
- Design features. In this category, the lightning protection unit for a private home is divided into types according to the design features of external lightning receivers. At the moment, there are three main types of lightning rods: pin, mesh and cable. Each of them is good in its own way. Pin lightning rods are the cheapest, but less effective compared to mesh and cable receiving elements.
The next chapter of the article will help you choose the best protection against atmospheric electricity discharge for your home, in which we will talk about the design of the most popular passive external lightning protection, in addition to which it is necessary to install internal protection against a secondary damaging factor.
Basics of lightning rod operation, general design of a lightning rod
A lightning rod is a device installed on buildings and structures and used to protect against lightning strikes.
Even in not so distant times, thunderstorms and lightning were considered an unpreventable natural phenomenon, from which it was possible to protect oneself only by pure chance. Over time, the point of view on lightning has, of course, changed. Scientists have long penetrated the physical essence of lightning. But even earlier, people noticed that lightning does not strike anywhere, but chooses the highest places and objects for this. It was quite logical to assume that it was possible to artificially provide her with such an opportunity - to hit the highest point, while protecting nearby buildings and, of course, people. Many scientists have studied the problem of lightning protection. But only the famous Russian scientist Mikhail Lomonosov achieved truly outstanding success in this field. In collaboration with other prominent scientists of his time, he managed to design an effective lightning rod, the principle of which still works today. As a rule, a classic lightning rod (also known as a lightning rod) consists of only two parts:
- Lightning receiver, which is a metal rod mounted as high as possible;
- The wire through which the lightning current flows into the ground loop.
Since planet Earth, in any case, will be larger than any object located on it, all the millions of volts that the lightning rod takes on go directly into the ground, without causing harm to animals and people, without causing damage to buildings.