Purpose of functional grounding
In order to understand what is called working grounding, you should know its main purpose - to eliminate the danger of electric shock in the event of a person coming into contact with the body of an electrical installation or its live parts that are currently energized.
This protection is used in networks with a three-phase current distribution system. An insulated neutral is necessary for an electrical network where the voltage does not exceed 1 kV. In networks with voltages above 1 kV, protective grounding can be done with any neutral mode.
How does protective (functional) grounding work?
The operating principle of functional grounding is to reduce the voltage between the housing, which, as a result of an unexpected accident, became energized, and the ground to a value that is safe for humans.
If the body of an electrical installation that is under current is not equipped with functional grounding, then a person’s touch to it is equivalent to contact with a phase wire.
If we take into account that the resistance of the shoes of the person who touched the electrical installation and the floor on which he stands is negligible relative to the ground, then the current can reach a dangerous value.
When functional grounding works correctly, the current passing through a person will be safe. The tension during touch will also be insignificant. The main part of the electricity will go through the grounding conductor into the ground.
Differences between types of grounding
There are significant differences between working and protective grounding. The main one is purpose. While the worker ensures the normal functioning of electrical equipment, protective grounding is called protection against electric shock. In addition, it helps protect equipment from failure if the housing is accidentally pierced. If the building has a lightning rod, then the protective resistance will prevent possible overload during a thunderstorm.
Working grounding of electrical installations during an emergency will protect the devices themselves and people, but its main purpose is to ensure the correct operation of the equipment.
Working grounding is used only in industrial enterprises, and in residential buildings a grounding conductor is installed, connected to an outlet. But there are still electrical appliances that are fraught with possible danger, so it would not be superfluous to ground them using a solidly grounded neutral.
Differences between working and protective grounding
Working and protective grounding differ from each other primarily in purpose. If the first is necessary to ensure the correct and uninterrupted operation of electrical equipment, then the second serves to protect people from electric shock. It also protects equipment from damage in the event of a breakdown of any electrical device on the housing. If the building is equipped with a lightning rod, this type of grounding will protect the devices from overload in the event of a lightning strike.
Working grounding of electrical installations, in the event of an emergency, will play a protective role, but its main function is to ensure the correct uninterrupted operation of electrical equipment.
In its unchanged form, functional grounding is used only in industrial facilities. In residential buildings, a grounding conductor is used, which is connected to the outlet. However, there are household appliances in the house that pose a potential danger to the consumer, so it would not be superfluous to ground them using a solidly grounded neutral.
Household appliances that need to be connected to a working ground:
- Microwave.
- Oven and stove that run on electricity.
- Washing machine.
- System unit of a personal computer.
Protective grounding
The main purpose of protective grounding (PG) is to protect operating personnel from electric shock in an emergency. In the case when dangerous voltage suddenly appears on a metal non-current-carrying surface of electrical installations.
This can happen as a result of an insulation breakdown or a wire break and it touching the housing. As a result, the person is exposed to dangerous voltage.
The figure below shows the protective grounding circuit. It makes clear the structure and operating principle of the protection device.
The PUE defines:
Protective grounding (PG) is the deliberate connection of metal parts of the equipment housing with the ground, ground electrode or its equivalent. The main objective is to protect operating personnel from injury caused by electric shock.
For calculations, you need to know how many ohms the protective device (PD) should have. Its value based on the calculation should not exceed 4 ohms.
ZZ is used in the following cases:
- In three-phase networks with an isolated neutral of alternating voltage up to 1 kV.
- In single-phase AC networks.
- In DC networks with an isolated midpoint of the current source windings.
- In AC and DC networks with any mode of source windings at voltages above 1 kV.
Device
With the help of grounding electrodes, a direct connection is made to the ground or its analogue. For this purpose, natural and artificial grounding conductors are used:
- For these purposes, artificial grounding conductors are used. They are metal pins driven into the ground. Painted pins must not be used; galvanized metal is used to protect against corrosion. In some cases, the copper pins are driven in or the copper plate is buried. Conductive concrete may be used.
- It is recommended to use electrically conductive parts that are in direct contact with the ground as natural grounding conductors. Water pipes are often used for these purposes in dachas. Grounding conductors include metal parts of buildings and structures, rail tracks, lead cable sheaths, etc. At the same time, it is strictly forbidden to use gas pipelines, oil pipelines and other pipelines through which flammable mixtures and gases are transported as grounding conductors.
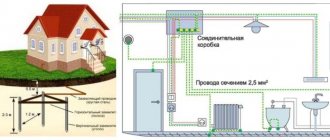
The figure below shows an option for protective grounding in a private house.
Option for protective grounding in a private house
In addition, protective grounding is used. It is widely used to ensure electrical safety in residential and public buildings.
Protective grounding is a special electrical connection of open conductive parts that are not in a normal state under voltage, with a solidly grounded neutral of a generator or transformer, in three-phase networks, with a solidly grounded output of a single-phase current source, with a grounded point of a direct current source created for the purpose of electrical safety of people.
The figure below shows a connection diagram for protective grounding with and without grounding for a single-phase network used in residential buildings to connect household appliances.
The figure below shows a diagram of equipment grounding in production workshops.
Grounding design
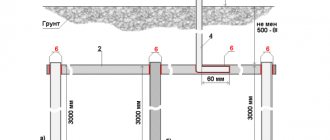
Working grounding consists of iron pins driven into the ground, acting as conductors, to a depth of about 2-3 meters.
Such metal rods connect the grounding terminals of electrical equipment to the grounding bus, thereby forming a metal connection.
There is a metal connection in every residential building. This is a welded iron structure that connects the upper ends of the ground electrodes to each other. She is taken to the entrance panel of the house for further distribution to apartments.
A bus or wire with a cross-section of at least 4 square meters is used as a grounding conductor. mm, painted in yellow and green stripes. The cable is primarily used to transfer functional ground from busbar to busbar.
For safety reasons, the electronic resistance of the metallic ground connection is periodically checked. It is measured from the ground terminal of the electrical installation to the ground ground loop farthest from it. The resistance value in any part of the working ground should not exceed 0.1 Ohm.
Design Features
Working grounding consists of metal rods installed in the ground. They play the role of conductors of electric current and are capable of discharging electricity several meters deep. Such iron pins are connecting elements between the ground bus and the terminals of electrical equipment. As a result, a metallic bond is formed.
This connection exists in every residential building. With its help, the tops of the grounding conductors are connected. It is connected to the input panel and then distributed to all apartments. The role of the grounding conductor in this design is played by a bus or wire, the cross-sectional area of which is at least 4 square meters. mm.
Why are several ground electrodes made?
An electrical installation cannot be equipped with only one ground electrode, since the soil is a non-linear conductor. The ground resistance is strongly dependent on the voltage and area of contact with the inserted working ground pins. One ground electrode will have insufficient contact area with the soil to ensure uninterrupted operation of the electrical installation. If you install 2 ground electrodes at a distance of several meters from each other, then a sufficient contact area with the ground appears. However, it should be remembered that the metal parts of the grounding cannot be separated too far, since the connection between them will be interrupted. As a result, only two ground electrodes installed separately in the soil will remain, not connected to each other in any way. The optimal distance between two ground loops is 1-2 meters.
How not to ground
According to paragraph 1.7.110 of the PUE, it is prohibited to use any types of pipelines as working grounding. In addition, it is prohibited to bring the grounding cable out and connect it to an unprepared contact pad on the bus. This prohibition is explained by the fact that each metal has its own individual potential. When exposed to external factors, galvanic steam is formed, which contributes to the process of electrical erosion. Corrosion can spread under the sheath of the ground wire, which increases the risk of melting when high currents are applied to the ground loop in the event of an accident. A special protective lubricant prevents the destruction of the metal, but it only works in a dry room.
The PUE also prohibits sequential grounding of electrical installations with each other, or connecting more than one cable to one grounding bus pad. If such rules are neglected, then in the event of an accident at one installation, it will interfere with the work of its neighbor. This phenomenon is called electrical incomparability. If the working ground is connected incorrectly, remedial work can be life-threatening.
Working ground
Designed to ensure normal operation of equipment in all operating modes. This also applies to emergency situations.
Working or functional grounding is the grounding of a point or points of live parts of equipment, intended to ensure the operability of electrical equipment, not for electrical safety purposes.
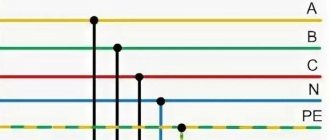
The figure below shows a diagram from a textbook of working grounding for various networks.
The functional purpose of this option is to maintain the functionality of equipment and protective devices in normal and emergency modes. It is often used to trigger special devices.
These can be fuses, resistors, etc. The main purpose of the function is to prevent failures, localize them and prevent their spread.
Safety regulations prohibit combining protective and working grounding. This is due to the fact that electrical atmospheric interference, for example, from lightning protection of buildings and structures, can be combined with network currents.
This can lead to equipment failures, such as computers, complex electronic equipment, etc. And also to equipment failure.
In addition, such a combination will make the voltage protection ineffective. And in an emergency, it will stop functioning altogether.
Metal rods are used as grounding conductors. There must be at least two of them, and the distance between them is 1 m.
In this case, it is necessary to comply with the following rules determined by the PUE:
- Pipelines must not be used as a working ground in any situation.
- It is prohibited to route the cable outside and connect it to the bus in a place unprepared for this purpose. Since poor contact will not provide reliable protection, and during operation it will deteriorate due to metal corrosion.
- Serial connection of equipment to the grounding bus is strictly prohibited.
- It is prohibited to connect several cables from equipment to one contact pad on the grounding bus.
The above figure shows an example of a metal connection with electrical equipment.
Requirements for grounding structures
To understand what is called working grounding, as well as what requirements are imposed on such structures, you should know that in order to protect people from electric shock, the voltage of which does not exceed 1000 V, it is necessary to ground absolutely all metal parts of electrical equipment. It is important that all structures built for grounding purposes meet all safety standards required to ensure normal operation of networks and additional fuses against possible overload.