Selection of electrically conductive products
The choice of electrically conductive products must be approached very responsibly. It is better if a professional electrician does this. When choosing, take into account the operating conditions, type and type of installation, as well as compliance with the rules for electrical installations.
Different products have their own scope of use. Cable products differ in the number of insulation layers and protective material. Coating is an important characteristic that determines the conditions for using wiring. Inside all cable products there are current-carrying conductors of varying thickness; their size determines what voltage can be passed through them.
All cable products are produced only with copper or aluminum cores, since these are the cheapest metals with low resistance.
Copper products are more reliable and have a longer service life. Aluminum has a lower cost, but is not recommended for use for fixed wiring.
You can determine which wires are in the wiring by the marking, the initial letter A means the wire is aluminum, in other cases it is copper.
The most common types of electrically conductive products are cable and wire. The cable's protective sheath consists of several layers of insulation. Each cable core is in its own separate sheath. The cable is capable of conducting electric current with a voltage of several tens of thousands of volts.
Power cable. Classification. Purpose.
A power cable is several insulated wires in a protective hermetic sheath, designed for the transmission and distribution of electricity from transformer substations to utility and transport facilities, industrial enterprises, etc. Cables, based on the material of the conductive cores of transmitted energy or information, are divided into two groups: - electrical cables with metal cores; — cables with optical fibers. Cables with optical fibers may also have additional metal conductors. Electrical cables with metal conductors are classified according to the order of power transmitted through the cables, voltage, type of insulation, purpose, etc. In accordance with this, they distinguish: low, medium and high voltage power cables; power flexible cables; control cables; control cables; low-voltage wires and cords; cables and communication wires; radio frequency cables; special cables, etc. Power cables are designed for the transmission and distribution of electrical energy. According to the type of insulation of power cables, they are distinguished: - power cables with paper insulation, including impregnated and oil-filled ones; — power cables with plastic insulation; — power cables with rubber insulation. Based on the linear operating voltage, power cables are divided into: cables for voltages of 1–10 kV, 20–35 kV, 110–500 kV. The above classification is to a certain extent arbitrary, but it allows us to systematically present information about some of the cables, numbering more than 1000 brands and designs. Power cables consist of one, three or four single- or stranded copper or aluminum conductors, insulated from each other and the environment with impregnated paper, rubber or plastic insulation, sealed with lead, aluminum, plastic or rubber sheaths and protected, as a rule, by armor made of steel strips or galvanized steel wire, as well as protective anti-corrosion coatings. Cable core insulations are made of paper tapes impregnated with oil rosin composition, polyvinyl chloride plastic compound, polyethylene, cross-linked polyethylene, rubber. The range of alternating operating voltage for which power cables are manufactured ranges from 660 V to 500 kV. The operating voltage influences the design of the cables. The letter designation determines the design of the cables, their armor, protective sheaths and covers. Cables with aluminum conductors are designated by the letter A. The presence of copper conductors is not highlighted in the cable marking. The cores of power cables are single-wire and multi-wire. In the marking of cables with a single-wire core, the designation “ozh” is added. The conductors are manufactured in a round shape for single-core and three-core cables in separate metal sheaths of all sections and multi-core with belt insulation with a cross-section up to 16 mm2 inclusive. Cores with a cross-section of 25 mm2 or more for multi-core cables with belt insulation are made in segment or sector shape. Aluminum cores of power cables with a cross-section of 6-240 mm2 and copper cores with a cross-section of 6-50 mm2 are made solid single-wire. Accordingly, aluminum with a cross-section of 70–800 mm2 and copper with a cross-section of 25–800 mm2 are stranded. Stranded copper and aluminum conductors of segment and sector shapes are compacted during the manufacturing process. Power cables with insulation made of paper tapes impregnated with oil rosin composition. For vertical or steep cable routes, cables with depleted insulation or insulation with a non-draining impregnating composition are used. Cables with plastic insulation for voltages of 0.66–6 kV are manufactured in accordance with GOST 16442-80. Vulcanized polyethylene is used as insulation for single-core cables for voltages of 10, 35 and PO kV (cables of the APaV, APVP, APvPs brands). The voltage between the core and the grounded screen is 5.8, respectively; 20 and 64 kV.
Power Cable Types
The following types of power cables can be distinguished:
- VVG
- NYM
- VBBSHv
VVG cable
Capable of transmitting current up to 1kV, with copper conductors and PVC sheaths. The outer shell is also made of black, sometimes white, polyvinyl chloride. Inside there are wires of different colors, so that, according to generally accepted standards, the zero is not confused with the phase and the “ground”. General standards will help when repairing wiring.
Electrical wiring diagram in the garage - features of design and installation with your own hands. 120 photos of wiring examples and video instructions for replacing wiring in the garageWhich wire to use for grounding: calculation of parameters, marking and purpose of various types of wires (video instructions + 150 photos)
Power cable brand ASB - characteristics, classification and rating of the best manufacturers. 115 photos and video instructions for choosing
Features of VVK:
- number of cores 1-5;
- monolithic or multi-wire, the latter more flexible and durable;
- the cross-section of the cores is from one and a half to two hundred and forty millimeters square.
In household use, conductors with a cross-section from one and a half to six millimeters square are used. To supply electricity to the private sector, cable products with a cross-sectional area of sixteen millimeters square are used.
When choosing the required electrical cable, it is necessary to calculate the cross-section of the wire depending on the power. This can be done using an electrical manual. Add a margin of 20-25% to the found value.
A correctly calculated cross-section of an electrical cable or wire is the key to the safety of your home.
NYM
NYM is an imported analogue of VVK. Its core is always copper and stranded. An ideal option for wiring in apartments.
Retro wiring in a wooden house: calculation of parameters, design, installation and selection of vintage elements. 165 photos of stylish ideasHeating cable for gutters and roofs: choosing and installing a self-regulating anti-icing heater with your own hands (135 photos + video instructions)
Methods for laying cables in trenches: step-by-step instructions for laying and installing power cables in earthen trenches (140 photos)
VBBSHv
External insulation made of steel, lead or aluminum. This makes it possible to lay it underground, in the air, in sewer holes and pipes.
General principles for marking cable products
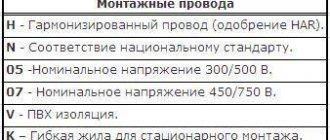
In order to make it easier to identify the cable, its characteristics and scope of application, a cable identification or marking system was developed. Data is recorded in a specific order, each letter or number has its own meaning.
How to decipher cable markings
What each position means and what letters may appear there, see the table below. There's not much to add here:
| Arrangement of letters or numbers | What does it mean | Letters used and their decoding |
| 1st letter | Core material | – no letter – copper |
| A – aluminum | ||
| 2nd letter | Degree of flexibility | G – flexible, stranded |
| there is nothing - single-core | ||
| 3rd letter | Insulation material | B – polyvinyl chloride (PVC) |
| P – polyethylene | ||
| R – rubber | ||
| HP - non-flammable week | ||
| F – fluoroplastic | ||
| C – film insulation (for installation wires) | ||
| 4th letter | Shell material or armor type | BBG - armor made of steel profiled tape |
| BN - armor made of steel strips with a protective coating that does not support combustion | ||
| B – PVC | ||
| D – double wire braid | ||
| K - armor made of round steel wires enclosed in a steel cover | ||
| SB - lead armor | ||
| 5th letter | Type of protective cover, purpose of the outer layer, designation of the core design | B – PVC (if it appears at the end it means paper insulation) |
| G – anti-corrosion protective layer. If “G” – no protection against mechanical damage | ||
| O – insulated wires are united by a common braid | ||
| Seam – protective layer – pressed PVC hose | ||
| Шп – protective layer – pressed polyethylene hose | ||
| Shps - too, but self-extinguishing polytilene | ||
| E – shielded | ||
| T – wire for laying in pipes |
Also, the cable marking consists of several numbers. There may be an operating voltage (for power cables), then the number of cores is required and the cross-section of these cores is indicated through the “x” sign. And the last thing that can be applied is the designation of the standard according to which this type of cable and wire product is manufactured.
Wire types
Unlike a cable, the structure of wires is much simpler. A current of up to 250 W passes through them. Depending on the type of cores, coating and characteristics, there are many types of wires:
- PBPP and PUNP
- PPV
- Automatic reclosing
PBPP and PUNP
PBPP is a flat-shaped wire with a solid monolithic core. PUNP has multi-wire conductors. The protective shell is made of polyvinyl chloride, white, sometimes black. The cross-sectional area of the cores is from one and a half to six millimeters square.
Used when connecting stationary lighting systems with voltage up to 250 W.
PPV
PPV is a flat copper wire. Inside there are dividing jumpers. The protective shells are made of PVC. It consists of two - three monolithic cores, their cross-section is 0.75 - 6 mm2. Withstands voltage up to 450 W, is moisture and chemical resistant.
Types of cable channels and cable boxes: types, sizes and materials of manufacture. 120 photos and videos of cable channel installationHow to twist wires correctly? How to make a reliable and secure connection with your own hands (155 photos)
Do-it-yourself wiring in the house: step-by-step instructions on how to properly install the electrical network in the house (photo + video)
Can be used in temperatures ranging from minus fifty to plus seventy degrees. Well suited for mounting high power devices.
Automatic reclosing
APV is a round-shaped wire with aluminum filling. Cores in polyvinyl chloride protection, monolithic (cross-sectional area from two and a half to sixteen millimeters square) or multi-wire (with a cross-section from two and a half to nine and a half millimeters square).
The best wires for electrical wiring in the modern world are considered to be copper-filled wires. With the same cross-section, a copper wire conducts a larger amount of current and, accordingly, can produce more power. The service life of copper electrical products is longer than that of aluminum analogues.
KG cable
KG is a flexible rubber cable made of copper with stranded conductors, their cross-section is 0.5 to 240 sq. mm. Quantity – 1-5. Natural rubber – for rubber insulation of cores.
The cable is functional from -60°C to +50°C, humidity - 98%. The cable is laid outdoors. Core color: black, blue, brown, gray. The scope of application of the CG is industrial installations. The KG cable powers portable mobile devices from alternating current or from generators. During installation, bending along a radius of at least 8 outer diameters is possible. A modification of KGng is provided - non-combustible insulation. The rubber insulation of this cable retains its properties and flexibility in frosty conditions. Extension cords based on it are used in any conditions.
Photos of electrical cables and wires
Did you like the article? Share

0
Brands, design elements, areas of application
| Cable brand | Core material | Type of protective cover | Application area |
| AOSB | Aluminum | B | Laying in soil with low and medium corrosive activity in the absence of tensile forces |
| OSB | Copper | B | Same |
| AOSBG | Aluminum | BG | Installation in hazardous areas without risk of mechanical damage |
| SBG | Copper | BG | Same |
Power cables with a viscous impregnating composition without the use of stop couplings do not allow installation on routes with a level difference between the highest and lowest points of the cable location of more than 15 meters. For a voltage of 35 kV, power cables with non-draining impregnating composition can be produced, which allow installation without limiting the difference in levels.
Design parameters
The cables have a three-core design with a separate lead sheath for each insulated core. Power cables for a voltage of 20 kV have cross-sections of 25-185 mm2, for a voltage of 35 kV - cross-sections of 120 and 150 mm2. The conductors must be stranded round in shape and comply with class 2.
The nominal insulation thickness is: - for power cables with a voltage of 20 kV - 7.0 mm for conductors with a cross-section from 25 to 95 mm2 and 6.0 mm for conductors with a cross-section of 120 mm2 and above; — for power cables for voltage 35 kV — 9.0 mm.
A screen made of electrically conductive paper is placed on the conductors and on top of the insulation. Insulated cores in sheaths are twisted without filling or with filling using bundles of impregnated cable yarn, stapled glass yarn or rubberized fabric and impregnated cable paper. The cross-section of power cables can be in the shape of a circle or a triangle. To avoid damage to power cables, they must be wound on drums with a neck diameter of at least 15 (2.15D + d) for cables with a voltage of 20 kV and 18 (2.15D + d) for cables with a voltage of 35 kV, where: D - cable diameter along the lead sheath; d is the diameter of the core.