About wires
Without touching on the history of the origin of wires, although it is interesting and instructive in itself, it should be noted that various types of wires have been created. The best place to start here is with a definition and terminology:
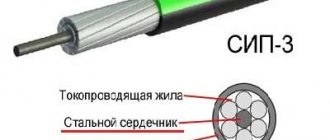
- wire or electrical wire - a product containing one or more wires (insulated strands) twisted together, covered with a non-metallic sheath (insulation);
- cable -
- contains one or more insulated conductors enclosed in a protective covering. In essence, the cable is a prefabricated unit.
- .
Based on the definitions, these products, also called cable and wire products (CPP), have two main elements - conductor and insulation. It is the features of their design, as well as the material used in manufacturing, that determine the entire variety of gearboxes. However, two groups should be distinguished:
- power;
- assembly
The first ones are intended for laying power transmission and distribution lines, the second ones are for organizing the exchange of information between individual devices, including those located remotely. And each of these groups has its own requirements, and they only become more stringent over time. As are the conditions in which the checkpoint has to operate.
About conductors
To better understand the development prospects and advantages of various types of wires and cables, let's look at their main components. Aluminum and copper are usually used for conductors. Their purpose is to transmit electric current from source to consumer with minimal losses. Structurally, they can be single-wire or multi-wire.
About aluminum conductors
Aluminum is an excellent conductive material; at one time it was used very widely, but has now lost its position. The table below will help you understand the reasons for this.
Table 1
Advantages and disadvantages of aluminum wires
| Advantages | Flaws |
| 1. Aluminum wires are lighter than copper wires 2. The price of aluminum is lower than copper | 1. Cores with a cross section of up to 10 mm2. They can only be single-wire, which means they do not allow bending at an acute angle. 2. The resistance of aluminum to external influences is determined by the oxide film on its surface. With constant flow of electric current and heating of the wire, electrical conductivity deteriorates due to this film. This means that aluminum wires require additional maintenance. 3. Aluminum is an amorphous material and can “flow” over time. This behavior will cause the fastening of the clamped wires to loosen, because the aluminum will simply “leak” out from under the clamps. 4. Soldering aluminum is only possible using a special flux. 5. Poor cleaning of aluminum in production impairs its conductivity. The use of wires of this material can lead to dangerous consequences. |
All this was the reason that the PUE (Electrical Installation Rules), one of the fundamental documents stipulating the use of wires and cables, imposed a ban on the use of aluminum wires with a cross-section of less than 16 mm2 in domestic conditions. In addition, it is necessary to take into account that they require periodic care and maintenance.
About copper conductors
The most common material in the production of gearboxes. Its advantages and disadvantages are shown in the table below.
table 2
Advantages and disadvantages of copper wires
| Advantages | Flaws |
| 1. Conductivity is much higher than that of aluminum wires (1.7 times). 2. When soldering, the use of special fluxes is not required. 3. They are characterized by high flexibility and ductility, allowing repeated bends and other types of deformation. | 1. High price, more expensive than aluminum. 2. Significant weight; a wire coil that is the same in length and cross-section as aluminum will be 3 times heavier. 3. In open air, copper oxidizes. |
All this has led to the fact that although copper is a more expensive material, it is much more profitable to use. The wires are more durable, do not require special knowledge and materials during installation and do not require additional maintenance.
Insulation in wires performs many functions, but one of the main ones is protection. It must protect the conductor from exposure to external factors, such as:
- temperature, solar radiation, biologically active environment and many others;
- mechanical damage that occurs during operation, transportation and installation of wires;
- contacts with other conductive elements that can affect performance.
There are a number of other factors that affect the quality of transmission and distribution of electricity, as well as the passage of electrical signals. But we will not consider them all now, although we will return to some issues related to isolation a little later. Now let’s talk about the materials that are used for these purposes.
Materials used
In order to protect the conductive core, many materials can be used, some of them are already outdated, others are used to a limited extent or for special products, so it would be quite difficult to list them all. But nevertheless, it is worth mentioning the following:
- Polyvinyl chloride (PVC), a widely used material, is low cost, wear-resistant, non-flammable, and resistant to aggressive substances. It cannot withstand installation without preheating at temperatures below minus 20ºС, and releases caustic substances when heated.
- Rubber provides flexibility of wires and is resistant to low temperatures.
- Polyethylene. It has good dielectric properties, can withstand low temperatures, and is resistant to aggressive substances. The disadvantages include poor flexibility.
These are traditional, widely used materials. Their range is constantly expanding thanks to the achievements of science and technology. Currently, ethylene propylene rubber, polyurethane, and fluoropolymers are used in production. These materials make it possible to give gearboxes new capabilities and expand their application.
Thus, ethylene propylene rubber provides higher flexibility with simultaneous increased water resistance. And polyurethane improves the shell’s resistance to abrasion and mechanical damage. Separately, it is necessary to touch upon fluoroplastic materials. They provide resistance to almost all aggressive environments, as well as to temperatures.
Additional protection and insulation elements
Among them, it is worth highlighting such elements as the screen and armor.
- The screen, located on top of the conductive cores, is designed to increase the noise immunity of the product. It eliminates both the influence of external interference on information transmitted over wires and the spread of interference from signals passing along transmission lines.
- Armor provides additional protection for the wire from mechanical stress. It can be tape or wire. The need for such cable protection arises when it passes through places where there is ground movement, for example, on overpasses, bridges or other similar structures.
Now we are interested in the immediate period - despite the extensive range of wires produced, by 2000 a rather interesting situation had developed in the gearbox market.
Wires for special equipment products were developed and mass-produced, but they turned out to be quite expensive and inaccessible to a wide range of consumers. There were a number of wires that were successfully used in various industries, but their characteristics were already outdated. Such products include the KVVG cable.
But at the same time, industrial development required the use of checkpoints in new conditions. First of all, in the oil and gas industry. And this required a significant expansion of the characteristics of the wires, based on the conditions of their new application. Products were required that could withstand both low and high temperatures, moreover, they must be certified for these industries.
And in 2005, the MKESHV wire appeared, and then the cable was developed - MKPS. The latter was intended for automation of enterprises in the oil and gas sector and consisted of twisted pairs, triples, and quads with the possibility of both general and individual shielding. It was envisaged that they would be produced with both tape and wire armor.
A further development was the appearance in 2012 of KuPe cables. The cables of this line eliminated the identified shortcomings and took into account the experience of construction and installation organizations in using analogues. And here we need to touch on one more feature that has developed in the cable industry market. It turned out that there are no products capable of operating in conditions of a hazardous production facility (HPF).
It is probably unnecessary to say that its characteristics meet the requirements of NTD (normative and technical documentation). Almost all products of this type are subject to certification. But it’s worth talking about the additional capabilities that a modern installation cable has. It opens up interesting prospects for REA developers. And you can evaluate them using the example of the InSil installation cable, one of the latest developments by NPP Intech.
Safety first
The conditions prevailing at hazardous production facilities are complex and diverse. There may be explosive substances and gases, various oxidizing, toxic materials. Explosive mixtures can also be formed during the production process, for example during the processing of plant materials. The environment may be characterized by elevated temperatures that occur during transportation of molten metal.
The use of the product in such conditions is confirmed by safety certification. And the InSil cable passed similar tests. So the ability to work in hazardous environments is a significant advantage of the InSil line of cables.
About fire safety
Such requirements are now fundamental for most gearbox products. A modern installation cable is subject to a number of requirements that minimize its fire hazard. Among them are the following:
- fire resistance of a cable is the ability of a cable to remain operational during (and after) exposure to an open flame. A similar property is marked with the index FR;
- non-propagation of combustion - this group includes those products whose combustion stops after the fire is removed. Their main purpose is to prevent the spread of fire. This property is marked with the index ng;
- reduced smoke production, designated as LS. Characterizes the property of cables not to emit smoke, which impedes the visibility and work of firefighters;
- halogen-free cable, marked HF. The smoke and gas emission products of such products contain small amounts of chlorine and other halogens, which cause increased corrosion of equipment.
- With low toxicity of combustion products. LTx
These are not all the requirements that a fireproof installation cable must meet, there are many more of them, but the already stated characteristics of the gearbox make it possible to understand how responsibly one should approach the selection of products for use in automation, safety and security systems. And all the requirements are met by cables from the InSil line.
About the influence of the environment
The cable should work everywhere and always. And although this is not possible everywhere, there are prerequisites for this. All cables produced by NPP INtech, in the HL version, can be used. at a temperature of minus 60 ºС, KuPe, manual transmission. The same InSil performed by AHL is capable of operating at temperatures down to minus 88 ºС, which other wires cannot do. The possibility of installing the cable without preheating cannot be avoided. And if previously such work was carried out at a temperature of minus 20ºС, now the threshold has shifted significantly. This means lower installation costs and faster implementation times.
What are the consequences of exposure to negative temperatures? It causes the insulation to harden, or as they say, it “dumbs.” The consequence will be its cracking under increased loads, bending, and vibration. Sometimes the formation of microcracks is enough, into which water will eventually enter, and this will ultimately lead to failure.
However, the use of new insulating materials made it possible to reduce the operating threshold of the product to minus 60ºС.
The same applies to exposure to elevated temperatures. Modern installation cables can withstand temperatures of 125ºС, which implies the ability to use control and automation equipment in “hot production” conditions.
Separately, it is worth mentioning the effects of high humidity and salt fog. For modern gearbox products, it is normal to withstand this. This durability allows installation cables to operate in tropical conditions and on sea vessels with an unlimited navigation area.
On countering technogenic impacts
Often, installation of various devices is carried out in populated areas. This means that infrastructure facilities, houses, residential complexes, and a wide variety of equipment will have an additional impact on communication lines and other communications. And installation cables must work in such conditions.
They do work. Armor protects from vibration and ground vibrations, and insulation protects from the destructive effects of aggressive substances. Separately, it is worth mentioning the noise immunity of communication lines. This is ensured by several measures:
- using an individual screen;
- using a common screen for the entire cable;
- using a consistent twisting pitch of cable pairs during production.
This makes it possible to achieve constant noise immunity at different frequencies and protect data transmission from external influences while preventing radiation to the outside.
A modern installation cable, with all its apparent simplicity, is the result of complex work carried out at the intersection of different sciences. Ensuring the operation of the checkpoint in the harshest conditions of the natural environment, technopolis, and a wide range of external influences is far from a trivial task. And we can confidently say that the developers of modern electronic equipment have a cable capable of solving the assigned tasks in the most severe conditions.
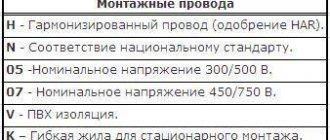
How to use installation wires correctly
To use installation wires correctly, you need to carefully select them depending on the type of work, conductor cross-section, type of network, power of the connected equipment, network voltage and many other indicators. You need to work with them only if you fully follow the safety rules. From the list of basic rules there are three:
- do not touch exposed wiring wires with bare hands;
- isolate the twist for subsequent work;
- Do not touch the electrical wiring when the voltage is on.
You may be interested in this: Zero conductor
Note! Be sure to wear electrical protective gloves and rubber gear and avoid working with cables in conditions of high humidity.
Compliance with safety precautions will protect you from electric shock
An installation stranded wire is a connecting conductor product for instrument and inter-device installation, which has optimal technical characteristics and design for creating electrical wiring in the house. It is used in the construction industry. There are power, LED, electroluminescent cables and cables for information transmission. It must be used according to the instructions given above in compliance with fire and personal safety regulations.