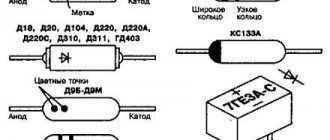
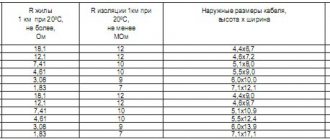
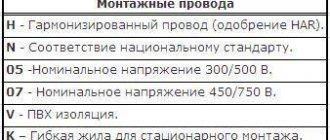
Classification of conductors
The types of connecting products used in the installation of an electrical network are given in GOST 15845-80.
Depending on the design and purpose, they are divided into wires, cables and cords.
Wires
They consist of 1-3 copper cores, enclosed in a braid of PVC, polyethylene or rubber. They are united by common isolation. The cores can be solid or consist of several conductors. Their cross-sectional area is no more than 2.5 mm. Wires are not used for laying underground or where increased safety is required.
Cable
Electrical cables have a more complex design and reinforced insulation. There may be additional filling between the cores, sometimes there is a screen, double braiding. To organize electrical wiring in residential premises, only cables are always used. Some of them are laid underground or by air.
Cord
This is a wire with increased flexibility. It is used in devices that must operate in mobile conditions: irons, blenders, electric shavers, etc.
An example is the ShRO cord. Its braid consists of fabric threads, and its flexibility corresponds to class 5.
Most often, such a cord can be seen in household appliances that are subject to movement during operation.
General principles for marking cable products
In order to make it easier to identify the cable, its characteristics and scope of application, a cable identification or marking system was developed. Data is recorded in a specific order, each letter or number has its own meaning.
How to decipher cable markings
What each position means and what letters may appear there, see the table below. There's not much to add here:
| Arrangement of letters or numbers | What does it mean | Letters used and their decoding |
| 1st letter | Core material | - no letter - copper |
| A - aluminum | ||
| 2nd letter | Degree of flexibility | G - flexible, stranded |
| there is nothing - single-core | ||
| 3rd letter | Insulation material | B - polyvinyl chloride (PVC) |
| P - polyethylene | ||
| R - rubber | ||
| HP - non-flammable week | ||
| F - fluoroplastic | ||
| C - film insulation (for installation wires) | ||
| 4th letter | Shell material or armor type | BBG - armor made of steel profiled tape |
| BN - armor made of steel strips with a protective coating that does not support combustion | ||
| B - PVC | ||
| D - double wire braid | ||
| K - armor made of round steel wires enclosed in a steel cover | ||
| SB - lead armor | ||
| 5th letter | Type of protective cover, purpose of the outer layer, designation of the core design | B - PVC (if it appears at the end it means paper insulation) |
| G - anti-corrosion protective layer. If “G” - no protection against mechanical damage | ||
| O - insulated wires are united by a common braid | ||
| Seam - protective layer - pressed PVC hose | ||
| Shp - protective layer - pressed polyethylene hose | ||
| Shps - too, but self-extinguishing polytilene | ||
| E - shielded | ||
| T - wire for laying in pipes |
Also, the cable marking consists of several numbers. There may be an operating voltage (for power cables), then the number of cores is required and the cross-section of these cores is indicated through the “x” sign. And the last thing that can be applied is the designation of the standard according to which this type of cable and wire product is manufactured.
Purpose of marking wires and cables
The generally accepted color coding system helps to ensure the correct connection of wires during installation and serves the safety of devices and people.
The alphanumeric designation is standardized between all countries. It indicates the technical and design features of the wire and allows you to choose the appropriate option: it indicates the number and material of the cores, the flexibility of the wire, the maximum permissible voltage, and the type of insulating braid.
Main differences
Marking allows you to determine the type of connecting electrical product: wire, cable or cord. For example, the designations of the latter always contain the letter “Ш”. The remaining markings contain information about the design features of the wire and its insulation, and the possibilities of its use.
Types of markings
The characteristics of the wires are indicated using colors, letters and numbers. Most often, several types of notation are used. Alphanumeric marking is carried out on the cable braid along the entire length at a set interval, allowing for reliable identification of the wire used.
Color marking helps to carry out competent installation, protecting devices and the electrical network from overheating and short circuits, and people from electric shock.
Alphanumeric marking
Cable product designations consist of letters and numbers corresponding to its technical characteristics. Marking is carried out in accordance with GOST 16442-80 and indicates:
- type of product (cable, wire, cord);
- core material;
- braid material of each conductor;
- general insulation material;
- possible presence of armor or screen;
- number of cores;
- cross-sectional area of each conductor;
- permissible voltage limit;
- wire flexibility;
- additional parameters: flammability, smoke and gas formation, degree of toxicity of substances released during combustion and smoldering.
Marking of foreign cables
The color marking of cable cores produced abroad is slightly different: the phase wire is brown, the ground wire is black, and the neutral wire is white.
The alphanumeric designation is the same in all countries:
| Product type | View | Designation |
| Cables | power | N |
| agreed type | N | |
| Rated voltage | 300/300 | 0,3 |
| 300/500 | 0,5 | |
| 450/750 | 0,7 | |
| Core material | copper | Cu or absent |
| aluminum | A, Al | |
| Insulation material | Different types of PVC | Y,PV,V |
| Various tires | G, R, N, S | |
| Different types of polyethylene | 2Y, 02Y, 02YS, XLPE, 2X | |
| Semiconducting layer in power cables | semiconducting layer | N |
| Screen | Copper concentric | C, S |
| Made from aluminum foil | A | |
| Water protection | F | |
| Without filler in aluminum shell | FY(2Y), (L}2Y | |
| Outer shell | PVC | V |
| Rubber | R | |
| Polychloroprene | N, Y, PVC | |
| Polyethylene | 2Y | |
| Armor | Flat steel strip | B, S.T.A. |
| Round steel wire | S.W.A. |
Table 3
Power cables
Flexible
| KG-T | KG-HL | KGN | |
| KGE | KOG-1 | CNG | CPGS |
| KPGSN | KShVGT-10 |
With impregnated paper insulation for low voltage
| AAB2l | AABL | AABlG | AABnlG |
| AAG | AAShv | AAShng | ASB |
| ASB2l | ASB2lG | ASBG | ASBL |
| ASBnlShng | ASG | ASCl | ASShv |
| SB | SB2l | SB2lG | SBG |
| SBL | SG | CAAB2l | CAABl |
| CASB | TsASBL | TsASBnlShng | TsSB |
| TsSBl |
With impregnated paper insulation for medium voltage
| AOSB | AOSBG | OSB | OSBG |
With impregnated paper insulation for high voltage
| MVDT | MNAgShvu | MNASHv | MNASHvu |
| MNS | MNSA | MNSK |
With plastic insulation for low voltage
| AVBbShv | AVBbShng | AVVB | AVVBG |
| AVVG | AVVGz | AVVGng | APVG |
| VBBShv | VBBShng | VVB | VVBG |
| VVG | VVGz | VVGng |
With XLPE insulation for medium and high voltage
| APvV | APvVng | APvP | APvP2g |
| APvPg | APvPu | PvV | PvVng |
| PvP | PvP2g | PvPg | PvPu |
Based on halogen-free compositions produced by JSC NP Podolskkabel
| PBbPng-HF | PPGng-HF |
With cross-linked polyethylene insulation produced by JSC Elektrokabel Kolchuginsky Plant
| APvBbShp | APvBbShp |
GAMMALYON cable family
| GAMMALYON 331 | GAMMALYON K1 | GAMMALYON K3 | SUPERGAMMALYON K1 |
XLPE insulated cables produced by Novkabel (Serbia)
| N2XH | N2XS(F)2Y | N2XS(FL)2Y | N2XS2Y |
| N2XSEY | N2XSEYRY | N2XSY | N2XY |
| NA2XS(F)2Y | NA2XS(FL)2Y | NA2XS2Y | NA2XSEY |
| NA2XSEYRY | NA2XSY |
With XLPE insulation for medium voltage from REKA Cables
| A2XSYBY | AHXAMK-W 12/20 kV | AHXAMK-W 6/10 kV | AHXCMK-W TT 12/20 kV |
| AHXCMK-W TT 6/10 kV | AHXCMK-WTC/PE 12/20 kV | AHXCMK-WTC/PE 6/10 kV | AHXCMK-WTC/PVC 12/20 kV |
| AHXCMK-WTC/PVC 6/10 kV | HXCMK 12/20 kV | HXCMK 6/10 kV | HXCMK-HF |
| NA2XSE2Y |
With XLPE insulation for high voltage from REKA Cables
| AHXCHBMK | HXCHBMK |
With insulation made of cross-linked polyethylene and a shell made of PVC plastic compound produced by JSC "
| APvEV | APvEVng | APvEVngd | PvEV |
| PvEVng | PvEVngd |
With insulation made of cross-linked polyethylene and a shell made of polyethylene produced by JSC "
| APvEgaP | APvEgaPu | APvEgP | APvEgPu |
| APvEP | APvEPu | PvEgaP | PvEgaPu |
| PvEgP | PvEgPu | PvEP | PvEPu |
With insulation made of cross-linked polyethylene, armored with steel tapes produced by JSC "
| APvEBV | APvEBVng | APvEBVngd | APvEBP |
| PvEBV | PvEBVng | PvEBVngd | PvEBP |
With insulation made of cross-linked polyethylene, armored with steel wire produced by JSC "
| APvECV | APvEKVng | APvEKVngd | APvECP |
| PvEKV | PvEKVng | PvEKVngd | PvEKP |
Single-core armored cables with cross-linked polyethylene insulation produced by JSC "
| APvEAKV | APvEAKVng | APvEAKVngd | APvEAKP |
| PvEAKV | PvEAKVng | PvEAKVngd | PvEAKP |
Cables with cross-linked polyethylene insulation for voltage 1 kV produced by Kamsky Kabel LLC
| APvBbShv | APvBbShp(z) | PvBbShv | PvBbShp(z) |
| APvBbShng(A)-LS | APvVG | PvBbShng(A)-LS | PvVG |
| APvBbShp | APvVng(A)-LS | PvBbShp | PvVng(A)-LS |
Cables with cross-linked polyethylene insulation for voltage 10 kV produced by Kamsky Kabel LLC
| APvV | APvVng-LS | APvP | APvP2g |
| APvPg | APvPu | APvPu2g | APvPug |
| PvV | PvVng-LS | PvP | PvP2g |
| PvPg | PvPu | PvPu2g | PvPug |
Power cables according to foreign standards
| FROR | NA2XSEY | NAYY-J | NHMH |
| NHXHX FE180 | NHXCHX FE180 | NSHTOU | NYCY |
| NYRGY |
Wire and cable marking table
The correspondence of the designations to the material of manufacture of cores and insulation is indicated in the table:
| Types of structural elements | Designation | Decoding |
| Veins | A | aluminum |
| No markings | copper | |
| Core insulation | IN | polyvinyl chloride |
| TO | nylon | |
| N, NR | non-flammable rubber | |
| P, Ps, Pv | polyethylene | |
| R | rubber | |
| WITH | fiberglass | |
| ABOUT | polyamide fiber | |
| F | fluoroplastic | |
| E | enamel | |
| G, KG | flexible cable | |
| Top braid | IN | PVC |
| A | aluminum | |
| R | rubber | |
| P, Pu | polyethylene | |
| WITH | lead | |
| G | naked (without braid) | |
| Design Features | G | presence of waterproofing |
| B | armored | |
| E | copper screen |
Table 4
For example, the common VVG 3x1.5 cable means a wire with 3 copper conductors with a cross-section of 1.5 mm² and PVC insulation of each, enclosed in a common polyvinyl chloride braid.
Interpretation of cable and wire markings
Let’s take as an example a very common cable: VVGng (ozh)-0.66 kV 3x1.5 and let’s look at its markings.
This cable has 3 copper cores, 1.5 sq. mm. each.
Letter B - vinyl shell made of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) plastic, designation ( ng ) flame retardant material when laid in groups.
The number of cores for most cable groups is from 1 to 5.
For controls, for example, from 4 to 37.
Each core has a cross section.
The cable has a cross-section range from 1.5 to 800 sq. mm. for low voltage cable.
0.66 kV - voltage. For this cable it is 660 V.
Cables are available in low voltage (0.38-1 kV), medium (6-35 kV) and high voltage (110-500 kV).
( ozh ) - execution - single-core. This means that the vein is monolithic, seamless. If there is no “ozh” in the brand, this means, by default, that the design is stranded ( mp ), multi-core ( mn ). The index ( A ) in the marking of the VVGng(A) indicates compliance with category A for flame retardation during group installation; cables of category (A) are considered the safest in terms of flame retardation.
Also letters ( ms , mk ) designation according to GOST R 53769-2010 :
O - single-wire
M - multi-wire
K - round
C - sector or segment
FR - from the English fire resistant, which means “fire resistant”
G - flexible or unarmored. B - vinyl. Shell made of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) plastic. B - vinyl. Insulation made of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) plastic. A - aluminum. Aluminum conductor.
F - fluoroplastic.
All letter markings start from the core. If the letter A is written, then the conductor is aluminum. If the letter A is missing, then the conductor is made of copper.
Depending on the group of use, the following symbols may appear in cable markings:
- AVVG- P . Flat, insulated conductors are laid parallel in one plane.
- AVVG z . With filling, filling from a rubber compound.
- AVVG ng-LS . ng - non-flammable, PVC plastic compound of reduced flammability. LS - “low tuxedo” (low smoke emission), PVC of reduced fire hazard.
Let's decipher AVBbShv: B - armor made of steel tapes Sh - protective hose made of PVC plastic. c - vinyl. Insulation made of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) plastic.
Let's decipher ASB2lG, ASKl, TsSB: C - lead sheath. 2l - two lavsan ribbons G - naked. Protective cover made of two galvanized steel strips. K - protective cover made of round galvanized steel wires. C - paper insulation impregnated with a non-drip compound.
Let's decipher AKVVGE: K - control E - general screen made of aluminum foil over twisted cores
Let's decipher APvBbShp: P - insulation made of silanol cross-linked polyethylene. n - outer shell made of polyethylene.
Let's decipher APvPu2g: y - reinforced polyethylene shell 2g - “double sealing”, insulation made of cross-linked polyethylene with aluminum tape over a sealed screen. KG - flexible cable.
Interpretation of wire markings.
Wires, like cables, are marked with letters, after which the number and cross-sectional area of the current-carrying conductors are written down in numbers. When designating a wire, the following structure is adopted. P is placed in the center , indicating the wire. The letters P may be preceded by the letter A, indicating that the wire is made of aluminum conductors; if there is no letter A, then the conductors are made of copper.
Following the letter P is a letter characterizing the material from which the wire insulation is made: P - rubber insulation, B - PVC (polyvinyl chloride) insulation P - polyethylene insulation
If the wire has a braid of cotton yarn coated with varnish, then this is indicated by the letter L, and if the yarn is impregnated with an anti-rot compound, then the letter in the wire brand is omitted. The letter L is placed in last place in the designation of the wire brand.
Wires for electrical installations of the PV have digital indices 1; 2; 3 and 4. These numbers indicate the degree of flexibility of the wires. The higher, the more flexible the wire.
Wires for overhead power lines are deciphered as follows: SIP - self-supporting insulated wire. Insulation made of light-stabilized cross-linked polyethylene. SIP-1 - with uninsulated neutral SIP-2 - with insulated neutral SIP-4 - with insulated conductors of equal cross-section. - bare wire twisted from aluminum wires - bare wire consisting of a steel core and aluminum wires