Brief summary. This article is intended to answer questions about the degree of protection of equipment from dust and moisture. Many people see IP markings on electrical equipment and ask questions, what does ip 65 mean? Can products with IP44 be installed outdoors? What does ip 20 mean? what is the degree of protection ip54, what does ip 54 mean? In this article we will look in detail at ip 54, what kind of standard is used in the CIS and abroad. Let's give a detailed table of abbreviations for the degree of protection IP.
- Degree of protection ip › GOST, standard
- IP waterproof
- Degrees of IP protection › Table
- IP protection class
- IP 20
- IP 30
- IP 44
- IP 54
- IP 55
- IP 65
Degree of protection ip › GOST, standard
The degree of protection IP (Ingress Protection Rating) is a systematization of the protection values of the housing (meaning the external coating) of electrical appliances and electrical equipment under the influence of various negative conditions, such as the influence of humidity, open seepage of liquid, pollution, as well as exposure to various environments.
This numeric index defines the international IP standard. Among them is the standard of the International Electrotechnical Commission IEC 60529, in the CIS GOST 14254-96, GOST 14254 and in Germany - DIN40050-9.
The current standard IEC 60529:2013 was adopted in 2013. The current GOST 14254 - 2015 in the Russian Federation was introduced on 03/2021/01. It differs from the previous GOST 14254-96 in the moisture protection index: the new current GOST 14254 - 2015 has 10 indices from 0 to 9. The ipx9 index indicates protection from high-temperature water jets supplied under high pressure (see below). Current GOSTs for IP protection level:
- IEC 60529:2013
- GOST 14254 - 2015,
- DIN40050-9,
- DIN EN 60529 (VDE 0470).
The degree of protection is provided when selecting various industrial equipment, taking into account the external environment where it will be used. So, when it is planned to change the wiring of a house, then when selecting a distribution panel, one should take into account the negative environmental conditions. There will be some impact on appliances and equipment that are located outdoors or in a building.
For electrical products, the protection class is given in the form IP [number 1] [number 2] .
[number 1] shows the class of protection against exposure to external environmental objects.
7 levels of protection from external objects from 0 to 6 are standardized:
- “0” - no protection from external objects;
- “1” - the casing is protected from the impact of third-party objects with a diameter of 50 mm or more, from contact with the back of the hand;
- “2” - protection from the negative effects of third-party objects with a diameter of more than 12.5 mm, from touching the case with your fingers;
- “3” - there is protection from foreign objects with a diameter above 2.5 mm, conductors, small tools (hand);
- “4” - protection from foreign objects with a diameter of 1 mm or more - these are conductors fixing nuts and bolts;
- “5” - complete protection from foreign objects of any size, incomplete protection from dirt and dust (a small amount of dust is allowed to fly inside the housing without affecting the functionality of the devices inside the electrical panel);
- “6” - complete protection from various objects, complete dust resistance.
IP decryption table
In the characteristics of the equipment there is a line “protection class” and it costs IP 44, IP 20, IP 61, IP 37, etc. To understand what this equipment is protected from, you need to know what these numbers mean.
From this table it is easy to understand what exactly this IP means
Decoding the first digit
The first digit in the code describing the security class indicates the degree of protection against the impact of solid objects of different sizes, as well as the degree of protection against penetration into the housing:
0 — absence of any protection;
1 - protects against penetration of objects with a diameter of more than 50 mm (simply covers from contact with the electrically conductive part);
2 - protection from objects with a diameter of 12 mm or more (from fingers, branches, etc.);
3 - objects larger than 2.5 mm cannot penetrate (some tools, cables, etc.);
4 - only objects smaller than 1 mm in size can be hit (very small fasteners, thin wires, etc.);
5 - complete protection from contact, dustproof shell (a small amount of dust can get inside, but it does not affect the work);
6 - the highest degree of protection from dust, dust-proof shell (even dust does not penetrate).
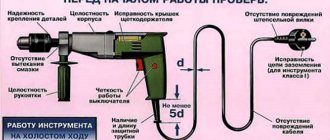
How the tests are carried out
Knowing the values listed above, it is easy to understand what the body of each specific product can protect from. For example, an ordinary household switch has a protection class of IP 20, that is, its housing is guaranteed to protect against finger contact with electrical parts.
This is how the degree of IP protection is presented in the product descriptions
Sometimes in the installation requirements you can see this option: IPx6, IPx4 or any other number in second place. If there is an "x" in place of the first digit, this means that the requirements for protection against dust and contact are not defined, and in this part you can select equipment based on your own requirements.
Decoding the second digit
The second digit of the IP protection class shows how much the case protects the contents from moisture. The numbers usually range from 0 to 7, but European manufacturers also have 8 and 9. Here’s what all these numbers mean:
0 - no protection from moisture;
1—vertically falling drops on the housing do not disrupt the operation of the device;
2 - if the housing is tilted at an angle of 15°, vertically falling drops do not disrupt the operation of the device;
3 — protection from splashes falling at an angle of up to 60° (from rain);
4 - splashes of water from any direction are not scary (can be placed in bathrooms at a distance of 20 cm from the water source and closer);
Example of testing the degree of protection against jets of water
5 - water jets do not cause harm (any angle of inclination);
6 — the housing is able to withstand waves and jets of water (entered water does not interfere with the operation of the equipment);
7 - with a short-term immersion of 1 meter in water, the device continues to work;
8 - if you stay at a depth of 1 meter for a long time, the device works;
9 - complete waterproofness, the device operates under water for a long time.
Knowing the decoding of the second digit of the code, you can easily determine for what conditions specific equipment can be used. For example, for outdoor installation, the housing must protect the contents from rain. That is, when installing outdoors, we take equipment whose second digit of the IP code is at least 4.
Brief description of the meaning of the numbers in the IP protection degree code
Some instructions contain requirements for the equipment protection class in the form of IP 3x or IP8x, etc. This means that the requirements for the degree of protection against moisture are not defined and are selected independently.
Additional characters
Additional symbols in the code for indicating the degree of protection of electrical equipment IP are not always used. They are usually present in cases where the actual degree of protection is somewhat greater than that specified in the code. There’s just a limited number of codes; it’s possible to more accurately describe what exactly this case or shell protects against only by using these additional symbols.
In addition to the required symbols - two numbers, there can also be letters
Immediately after the numbers there may be Latin letters A, B, C, D. They indicate additional protection against contact with live parts of the equipment:
A - back of the hand;
B - finger;
C - tool;
D - wire.
Meaning of letters in IP protection degree coding
The second position may contain the letters H, M, S, W. They encrypt different characteristics.
H - high-voltage equipment (you won’t find it among household appliances and equipment);
M - the device worked during water protection tests;
S—disabled during testing;
W - the housing or shell protects against weather influences.
These letters are placed only if the containment satisfies all lower requirements. That is, if there is a letter C, then you will not be able to crawl either with a tool, or with the back of your hand, or with a finger.
IP waterproof
[number 2] demonstrates the degree of protection against the negative effects of moisture (exposure to liquids, dampness). There are 10 degrees of protection of the case from moisture:
- “0”—no protection;
- “1” - the shell is protected from condensation moisture and raindrops falling strictly in a vertical position;
- “2” - the case is protected from drops, the angle of incidence is up to 15 degrees;
- “3” - there is protection against drops, the angle of incidence is up to 60 degrees;
- “4” - there is protection from liquid drops of any direction;
- “5” - protection from short-term exposure to a fluid flow (jet) of random direction;
- “6” - protection of the hull from prolonged exposure to a strong flow of liquid (water) of random direction, as well as from waves at sea;
- “7” - there is protection against moisture penetration into the inside of the equipment body during short-term immersion in liquid (water) to a depth of 1 m. In this case, there may be penetration of a small volume of liquid into the middle, which does not have an adverse effect on the performance of the products;
- “8” - there is protection against liquid flowing into the products when immersed to a given depth for a given period of time). The body of the products in this version is completely waterproof;
- “9” - there is protection against hot water jets under pressure getting into the products.
The degree of protection of the outer casing (shell) from the influence of negative external conditions is established on the basis of performing a test of the working element. Below are tables with a detailed explanation of the degrees of protection, testing methods and sequences of their implementation.
For a convenient presentation, the classification of IP protection is shown in the figure.
Figure - Classification of IP protection
Indexing: IP68 degree of protection
The absolute leader in the entire line of possible protective indicators is IP68. As we can judge, this is the maximum level of protection a device can have in principle.
Indexing analysis:
- Marker 6 means maximum protection from dust and solid objects;
- Marker 8 symbolizes that the moisture protection of the mechanisms from the penetration of water and moisture is maximum (waterproof);
- These are products that can be used in water up to 1 meter deep, for an unlimited amount of time.
In addition to those discussed, there are also others: IP54, IP66, IP55, IP23, IP21, IP56, IP33, IP64, IP57, IP53, IP31, IP43, IP24, IP69, IP52, IP41, IP34, IP22, IP32, IP58, IP63, IP53 , IP45, IP42, IP67.
Degrees of IP protection › Table
It is convenient when the degrees of protection of electrical equipment ip are summarized in tables. Below are three tables for IP decryption protection. They comply with GOST 14254 - 2015.
Table of degrees of IP protection from access to dangerous parts , indicated by the first digit of the index
IP protection table (first digit)
Table of the degree of protection of electrical equipment IP from water (second digit)
In addition to the first two digits, the protection degree marking may contain two letters. The one that comes first after two numbers is called additional, and there may also be a letter with auxiliary information. The additional letter indicates the level of human protection from access to dangerous parts.
When a person touches electrical equipment, the following types of protection are distinguished:
- “A” - with the back of the hand;
- “B” - fingers;
- “C” - hand tool;
- "D" - single conductors.
The first number after IP and the additional letter in the marking have different meanings. The number indicates the protection of the housing from the negative influence of a person or any objects, and the additional letter indicates the protection of a person from the negative influence of elements of the electrical equipment itself.
For example, the first number “3” indicates the protection of the housing from hand-held tools, that is, the equipment will not be damaged when exposed to hand-held tools. The additional letter “C” certifies that personnel will be protected from the influence of unfavorable factors, namely electric shock, if the shell is exposed to hand tools.
The second letter of the protection category marking after the numbers displays auxiliary information.
- "H" - high voltage equipment,
- “M” - the test was carried out while moving,
- “S” - the test was carried out in a stationary (motionless) state.
"M" and "S" are usually used for equipment with moving parts.
Samples of protection degree markings with additional and/or auxiliary letters - IP 20C, IP 67S, IP 55DS.
Additionally, instead of numbers, there are “X” symbols. This symbol means that protection from foreign objects or water is not standardized for these components of the electrical product. Marking examples – IP X5, IP 1X, IP XX.
In addition, the product may be marked with not one, but several degrees of protection. Multiple degrees of protection are noted if it is necessary to indicate protection simultaneously from several negative influences, and the latter correspond to different degrees when classifying protections. For example, the product is protected from the effects of low water flow and short-term immersion in liquid. Under such conditions, the following marking can be given - IP 65 / IP 67.
Other ways to protect your privacy
Change privacy settings in instant messaging apps
Applications installed on a device are the main source of IP hacking. Attackers can use instant messaging and other calling apps as a tool. Using instant messaging apps allows you to only receive calls and messages from people in your contact list, not strangers. Changing your privacy settings makes it harder for people to find your IP address because strangers won't be able to contact you.
Using unique passwords
The device password is the only barrier limiting access to your device. Some people choose to use default device passwords, which leaves them vulnerable to attacks. As with all accounts, you should use a unique and strong password for your device that is not easily decipherable. A strong password consists of upper and lower case letters, numbers, and special characters. It helps protect the device from IP address hacking.
Be alert to phishing emails and malicious content
Most malware and device tracking software are installed using phishing emails. When you connect to any website, it gains access to the IP address and location of the device, making the device vulnerable to hacking. Be careful when opening emails from unknown senders and do not click on links that lead to unauthorized sites. Pay close attention to the content of emails, even if they are from well-known websites and legitimate companies.
Reliable, regularly updated antivirus solution
Install a comprehensive antivirus solution and keep it up to date. For example, Kaspersky Lab antivirus programs provide virus protection for computers and Android devices, protect and store passwords and personal documents, and encrypt data sent and received over the network using a VPN.
Protecting your IP address is an important aspect of protecting your identity online. Maintaining security using the steps described above is a way to protect yourself from a wide variety of cyber attacks.
Related articles:
- How safe are smart homes?
- Security Threats to the Internet of Things
- What is IP spoofing and how to prevent it
- What is Voice over Internet Protocol (VOIP)
- How to protect yourself from online harassment
IP protection class
Often, when they mean “degree of protection,” they say “IP protection class.” From a technical point of view, these are the same thing, that is, synonymous terms. In the regulatory literature, the wording “IP protection classes” is usually not used, but you can often come across questions: “IP54 protection class” or “IP65 protection class”, or “IP21 protection class, what is it?” In these cases, an appropriate degree of protection is meant. In this case, no other or separate standards are provided beyond those indicated above.
Let us next consider the commonly used degrees of protection of electrical products and equipment. Let's give examples of IP decoding and determine where and in what cases the bodies of these markings are used. To be specific, let’s take the case of electrical switchboard housings.
IP for electrical devices
The abbreviation IP, accepted throughout the world, has several possible decoding options: International Protection Marking/international security code, Internal Protection/internal protection, Ingress Protection Rating/degree of protection against interference.
The marking indicates the level of protection of a technical device from dust, solid objects, and water.
The data that characterizes the class of the device is determined experimentally using specially developed verification methods.
The protection class of any electrical device is marked as follows: a combination of the letters IP and two numbers
To determine the IP level, the international standard EC60529 is used, the analogue of which is GOST 14254-96, as well as the complicated German version DIN 40050-9.
On the territory of Russia, any equipment installed indoors must comply with PEU - rules for electrical installations, technical conditions - TU, GOST R51330.20-99.
According to the accepted Russian and international classification, the maximum level of protection is marked with the IP68 code.
This designation indicates that the device is completely dust-proof, which can also remain in water for a long time, experiencing significant pressure.
A convenient table summarizes the meanings of the two letters that are used to indicate the degree of IP protection with the decoding of all the given indicators (+)
The highest degree of protection provided by the DIN system is marked as IP69-K; Such marks are applied to products that can withstand high-pressure hot water washing.
You can find devices that have an undetermined degree of protection. In this case, the digital designation is replaced by the letter “X”, that is, the marking will look like “IPX0”. This designation may also be followed by one or two Latin letters.
IP 20
IP 20 – there is protection from large, large objects with a diameter above 12.5 mm (indicated by “2”), there is no protection from water, since the corresponding position is “0”.
Such IP 20 equipment is suitable for installation in dry buildings, where the appearance of water (splashes) on the housing is not expected, and there is no exposure to objects with a diameter of up to 12.5 mm. In the case of a switchboard housing with IP 20, it should be installed in rooms, apartment corridors, but should not be used, for example, in a bathroom. Table - Explanation of the degree of protection IP20 (dust and moisture protection)
| Protection from external solid objects (dust protection IP20) | Water protection (IP20 waterproof) |
| 2 | 0 |
| Protected from external solid objects with a diameter greater than or equal to 12.5 mm | No protection |
IP 44
IP 44 – degree of protection indicates that the shell or outer casing of the product is protected from foreign objects with a diameter of 1 mm or more. These include various wires, pins, nuts, hand tools, screwdrivers, etc. In addition, there is protection from humidity and random splashes of water. Equipment with such a housing can be used in structures with high humidity, damp, and also outdoors, but water should not be allowed to enter by stream. The product with an IP 44 housing does not have dust protection. If the dust content of the room or premises is high, you should not use a shield with IP44.
IP 44 electrical panel enclosures are suitable for buildings with high humidity, as well as for installation outside residential premises, but under the roof. This will prevent open exposure to the water jet.
IP 55
IP 55 – the product body is fully protected from the mechanical negative influence of various objects and partly from the penetration of dust. IP 55 is used in damp rooms, outdoors, where short-term exposure to the shell (housing) of equipment may occur in the form of a jet of water. Typically, electrical panel housings intended for outdoor installation have an IP rating of 55. This panel can be installed almost anywhere on the house’s site. It does not require a canopy.