In the era of the USSR, the presence of standard markings on any electric motors, uniform throughout the state, significantly facilitated the work of electricians.
All significant information was displayed on a special nameplate. According to those rules, asynchronous electric motors produced in the USSR were designated A, A2, AO2, 4A, 4AM.
If the engines originated from the countries of the Union bloc, had a similar appearance, perhaps 4A changed its designation to MO, and 4AM was designated as M.
But after the collapse of the Union, there was no single service responsible for standardizing such details, which creates trouble for modern craftsmen when carrying out service work.
Let's try to understand the issue.
Modern marking of electric motors
There are several points that are usually displayed in standard markings:
- brand or type of equipment;
- peculiarities;
- useful shaft length;
- installation dimensions;
- core length;
- number of poles;
- modification;
- What climate is it designed for?
Below is a possible decoding of the designations:
For asynchronous motors the picture will look like this:
Indications of dust and moisture protection (according to the IP standard) are possible, where the first number indicates protection against dust, and the second – against water. Both values are from 0 to 8.
Installation specifications are required. That is, the electric motor is mounted on feet or using flanges, how the shaft needs to be oriented, etc.
If the letter B appears at the beginning of the marking, this means explosion-proof design.
In this case, the set of accompanying documents must include a certificate indicating the protection class, its type and scope of application.
In such a situation, the labeling standard may change and take the following form:
Traction crane electric motors have their own designation system.
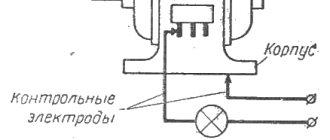
Here is an example of a plate for an asynchronous electric machine.
The analysis confirms the following:
- AIR – asyn type. cars;
- 80 – shaft overhang;
- A – installation dimensions;
- 4 – number of pairs of poles;
- U – version for temperate latitudes;
- 3 – intended for indoor use.
Power 1.1 kW, rotation speed 1420 rpm. Depending on the method of switching the windings, the supply voltage is 220 or 380 V.
Current consumption depending on the supply voltage is 4.9/2.8A. IP54 is the degree of protection, the manufacturer is the Republic of Belarus.
The motor is connected through a terminal box (BRNO box). It contains windings on a dielectric panel.
Accordingly, we see the old and now accepted designations. By combining, you can switch the windings with a triangle or a star.
By connecting U1, V1, W1 (beginnings) we get a star, and using the sequence U1 with W2, V1 with U2, W1 with V2 - a triangle.
Types of electric motors
Along with the use of electric motors of the 4A series, previously produced electric motors of the single series A, AO, A2 and AO2 are also used.
In rooms with high humidity or aggressive environments, special-purpose electric motors are used.
- Electric motors of the 4A series are asynchronous three-phase electric motors, produced to replace the electric motors of the single A2 and AO2 series. Compared to electric motors of the A2 and AO2 series, they have lower weight (on average by 18%), dimensions, noise and vibration levels, higher starting torques and increased operational reliability.
- Decoding of alphabetic and digital designations of electric motors of the series.
The letters and numbers included in the designation of the electric motor are deciphered as follows:
- 4 - series number.
- A - means that the motor is asynchronous.
- The second letter after the letter A indicates the design of the electric motor according to the method of protection from the environment.
- The third letter indicates the design of the engine based on the material of the frame and shields (A – Aluminum frame and shields; X – aluminum frame, cast iron shields; the absence of a letter means that the frame and shields are cast iron or steel).
- The three or two subsequent numbers indicate the height of the rotation axis in millimeters from 50 to 355.
- The following letters indicate the installation dimensions along the length of the bed (S – short, M – medium, L – long).
- In engines with the same frame lengths, but with different lengths of stator cores, additional core designations are used: A - short, B - long.
- Subsequent numbers (2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12) indicate the number of poles.
- The final letters and numbers indicate the climatic version and placement category.
So, for example, the designation 4AA50A2U3 is deciphered as follows: asynchronous electric motor, fourth series, closed design, the frame and shields of which are made of aluminum, the height of the rotation axis is 50 mm, the core is short, the number of poles is 2, climatic version U, placement category 3.
Asynchronous electric motors series (type) AIR
Electric motor AIR is a unified series of asynchronous electric motors. The AIR series covers a power range from 0.06 to 315 kW, characterized by rotation axis heights from 50 to 355 mm and rotation speeds of 3000, 1500, 1000, 750 rpm.
Asynchronous three-phase alternating current electric motors of the AIR series are designed to complete electric drives of various mechanisms in all branches of industry and the agricultural complex. Frequency 50 and 60 Hz, voltage 220-660 V (AIR 71 – 220-440 V). Degree of protection of electric motors IP54 (optional IP55), degree of protection IP55, insulation class F.
Import standard
Imported products are labeled in a similar way. The sample shows an Italian engine, marked according to European regulations. It is not difficult to find a domestic analogue.
The Siemens company offers a wide range of electric motors.
The nameplate contains indicators for standard power supply, but its frequency is taken into account. Below is an illustration explaining this feature.
The Chinese manufacturer completely copies the German standard.
It may be difficult to identify parameters due to the loss of the information plate. There is no point in despair, since there are several reliable ways to determine the parameters of electric motors.
- Based on the length and diameter of the shaft, using tabular data, the standard power is obtained.
- Selection is based on landing dimensions. And again use the tables that are given below.
- The resistance of the windings is measured, then the power is obtained using the standard formula (Ohm's law). In this case, a star connection is used for measurements, and the total is divided by 2. The resulting value is substituted into the formula P = (. 220v * 220v)/R, and the result obtained is multiplied by 3 - the result is the power. If we have a triangle, then we replace the factor three with six.
- Start the engine after connecting the ammeter. And, having learned the current at idle, they select an analogue.
The situation of losing a plate is almost typical in production, so the electrician must master the skill of selecting a replacement.
It is also important to remember that in many situations it is extremely important to take into account the direction of rotation of the motor (fan, pump, machine drive, etc.).
Moreover, this point should be observed for both single-phase and three-phase machines. Often the direction is indicated by an arrow on the frame.
Interpretation of designations and markings of electric motors.
Currently, consumers are often faced with the question of how to decipher the marking of an electric motor.
During the Soviet era, such a question practically did not arise due to the fact that the marking of electric motors did not differ depending on the manufacturing plant and was regulated by regulatory documents. The main types of engines were called A, A2, AO2, 4A, 4AM. Electric motors produced in the CMEA countries differed in their markings; for example, in Bulgaria, instead of the 4AM marking, “MO” was used, and instead of 4AMN, “M” was used. Now many manufacturing plants use their own markings. We present the main types of designations for brands of general industrial low-voltage asynchronous electric motors from different manufacturers.
The marking consists of several main parts:
- Brand
- Modification sign
- Rotation axis height
- Installation dimension along the length of the bed
1. Brand of electric motor (electric motors of all brands are the same in connection dimensions and in most cases, all other things being equal, are interchangeable, i.e. if you have an ADM90L2U3 engine installed, then it can be replaced with an AD90L2U3, A90L2U3 or AIR90L2U3 electric motor):
- during the Soviet Union
- since 1949 - A (IP23), AO (IP44) - since 1961 - A2 (IP23), AO2 (IP44) - from 1975-1980 - 4A (IP44), 4AN (IP23), 4AM (IP44) , 4AMN (IP23) - from 1985-1995 - AIR (IP44, IP54), 5AN (IP23), 5AMN (IP23)
- currently: AIR, A, 5A, 5AM, 5AMKH, AD, ADM, AIRM, (AO3, AO4 are produced by BEMZ CJSC):
" AIR " produces (according to the height of the axis of rotation):
- JSC "ELDIN" - 160
- OJSC VEMZ - 180
- JSC "Mogilevsky - from 56 to 180
- OJSC Polesyeelectromash - from 71 to 112
- JSC "Moselectromash" - from 56 to 71
- OJSC "Ukrelectromash" - from 63 to 100
- JSC "Electromotor" - 71, 80
" A " - JSC "ELDIN" - from 71 to 132 and from 180 to 355. " 5A " - JSC "VEMZ" - 80 (discontinued), 200, 225 " 5AM " - JSC "VEMZ" - 250, 280 , 315 “ 5AMKh ” - JSC VEMZ - from 132 to 180 (recently renamed, previously called: 112 - 5AM (discontinued), 132 - AIRM, 160 - 5A, 180 - AIR) " AD " - JSC Sibelektromotor " - from 71 to 90 and from 132 to 225 (not produced) " AIRM " - JSC "Sibelektromotor" - 112 (not produced) " AIRM " - JSC "Electromotor" - 63, 100 " ADM " - JSC "Uralelectro" - from 56 to 132 " AO3 ", " AO4 " - JSC "BEMZ"
2. Sign of modification (several designations can be used simultaneously in one brand; below is not a complete list).
- C - with increased slip
- E, 3E, EU - single-phase motor
- B - plug-in
- P - attachable
- M - modernized
- X - with aluminum frame
- K - with wound rotor
- P - with increased starting torque
- F - with forced cooling
3. Rotation axis height.
In accordance with GOST 13267, the range of rotation axis heights is 50, 56, 63, 71, 80, 90, 100, 112, 132, 160, 180, 200, 225, 250, 280, 315, 355.
4. Installation dimension along the length of the bed.
Ascending: S, M, L. (from the English words: Short, Medium, Long) It is also possible that there is no designation with a single installation dimension along the length of the bed at the same height of the rotation axis.
5. Core length with the same installation size.
6. Number of poles (or rotation speed).
2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12 or in the case of multi-speed electric motors: 2/4, 8/6/4, etc.
7. Designation according to purpose (several designations can be used simultaneously in one brand).
- B - with built-in temperature protection
- B1 - with bearing temperature sensor
- B2 - with sensor and anti-condensation heater
- E - with built-in brake
- E2 - with brake with manual release device
- Zh, Zh1, Zh2 - with a special output end of the shaft
- RZ - for geared motors
- Ш - for industrial sewing machines (also used in the 5AN brand for a special design for pumps)
- P - increased accuracy in installation dimensions
- F - cold-oil-resistant designation
- A - for nuclear power plants
- X2 - chemical resistant
- L - for elevators
- C - for pumping machines
- SSH - for drying cabinets
- N - low noise
- K - according to CENELEK standards
- etc.
8. Climatic performance.
9. Accommodation category.
In order to order an electric motor, it is not enough to indicate the correct marking. It is necessary to indicate:
- IM - installation version
- supply voltage (220/380, 380, 380/660)
- IP - degree of protection (23, 44, 54, 55)
Source
Marking of drives of radio-controlled models
Brushless model motors are a separate case. There are two fundamental parameters here - the size of the stator and the external dimensions (diameter or height).
Marking of four numbers, the first pair of which indicates the height/diameter, and the next pair indicates the stator size in mm. Example: 2212.
It is important to remember that it is the stator size that is taken into account. But for this reason its external dimensions will differ from 22 mm and 12 mm. True, with the same stator, its winding may turn out to be different.
This is a brief overview of the problem that we hope will help our readers figure out for themselves a very common problem.