Basic malfunctions and failures of electric motors
Electric motors manufactured at the plant and passed the full range of acceptance tests are in good working order and their characteristics correspond to the passport data.
Most failures occur for reasons arising in the processes following the release of the finished machine: loading, transportation, unloading, storage, installation on site. During this period, electric machines are subject to sharp shocks, shocks, and vibrations, the effects of which often exceed the permissible limits. During storage, cars are exposed to low temperatures and moisture, especially since cars are often stored in damp rooms and even in open areas. As a result of the described effects, malfunctions usually occur during the running-in period of the machine or even during its first start-up. For example, when a machine is stored under the influence of high humidity, the inner surface of the stator core and the outer surface of the rotor become covered with a layer of rust, filling the air gap between the stator and the rotor.
When the engine is turned on for the first time, the rotor is motionless. This leads to the need to disassemble the engine and thoroughly clean the rusted surfaces. Rust particles enter the motor winding and have a destructive effect on its insulation. It should be borne in mind that malfunctions of electrical machines associated with damage to the insulation are the most undesirable, since they lead to the need to rewind the machine and, therefore, require its overhaul. Often, violations of turn insulation cause local short circuits. In this case, the machine overheats, the rotation of the rotor becomes uneven, and an imbalance of gravitational forces between the rotor and the stator occurs, leading to deformation of the machine shaft. Reasons that can cause interturn short circuits also arise during operation of the machine, when foreign particles (dust, dirt, small metal shavings) enter the internal cavity and can mechanically damage the winding insulation.
When asynchronous motors operate from frequency converters, in which the three-phase output voltage is generated by the pulse-width modulation method, a pulse-shaped voltage appears at the motor input, the amplitude of which can significantly exceed the amplitude of the sinusoidal voltage of the first (fundamental) harmonic. This can lead to disruption of turn-to-turn or phase-to-phase insulation and cause turn-to-turn short circuits. Elimination of this undesirable phenomenon is facilitated by the use of smoothing filters at the output of the converter in the motor power supply circuits.
In brushed DC motors, the causes of malfunctions are often malfunctions of the brush-commutator assembly, which can cause increased sparking or even a circular fire on the commutator. Possible malfunctions of electrical machines are so diverse and numerous that it is not possible to describe them completely. The table below shows the most typical and common faults in electrical machines, the reasons that caused them, and how to eliminate these faults.
Source: www.agrovodcom.ru
Basic malfunctions of three-phase asynchronous electric motors and ways to eliminate them
Basic malfunctions of three-phase asynchronous electric motors and ways to eliminate them
Malfunctions of windings of asynchronous electric motors and ways to eliminate them
Short to body. If the winding is short-circuited to the housing, you need to check the electric motor with a test lamp powered from the mains (Fig. 31).
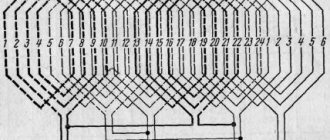
In some cases, it is advisable to open the winding at several points and check it in parts. First tested
each phase separately (Fig. 32), and then the pole-phase winding groups (Fig. 33).
Short circuit of turns. In this case, several turns or the coil as a whole are closed. The first way to find damage: determine overheating of the frontal parts of the winding by touch. The second method: the winding is fed with alternating current of high frequency (up to 400 Hz) and a piece of steel is applied to the stator core along the entire circumference. The place of damage is under the pole, where the steel is weakly attracted.
A short circuit of the pole-phase group is usually determined using a compass moved around the circumference of the stator
If the windings are connected by a star, then the positive pole of the current source is connected to the terminals in turn, and the negative pole is connected to the zero point of the winding.
The same method can also detect the inverted phase of the winding.
When connecting the winding with a triangle, you need to open one of the vertices of the triangle, to which direct current is supplied.
A short circuit of most of the phase winding is determined by measuring the undervoltage current or the phase resistance of the windings (Fig. 35). An increased current in one of the phases and a decreased resistance indicate the presence of a short circuit (Fig. 36).
Flail break. Typical and common breaks occur when the connection of the winding conductors is broken. If the winding is connected in a star and does not have parallel branches, then a winding phase failure is easily detected by a test lamp connected according to the diagram in Figure 37.
If the winding is connected in a triangle (without parallel branches), then it is opened and each phase is checked separately with a test lamp.
For electric motors with parallel winding branches, the damaged phase is determined by measuring currents in individual phases. Subsequently, the damaged phase is divided into parallel branches, which are studied separately.
Technical data of DC electric motors type MP
Source: trudova-ohrana.ru
Electrical faults of the electric motor
Electrical faults in the motor are always related to the winding.
- An interturn short circuit
can occur when the insulation within one winding deteriorates. Possible reasons: winding overheating, poor-quality insulation, insulation wear due to vibration. Determining turn-to-turn short circuits can be difficult. The main diagnostic method is to compare the resistance and operating current of all three windings. The first symptoms of an interturn short circuit are increased heating of the engine and a drop in torque on the shaft. In this case, the current in one of the phases is greater than in the other two. - Short circuits between windings
occur due to winding misalignment, mechanical vibration and shock. Without proper electrical protection, a short circuit and fire may occur. - Short circuit of the winding to the housing
. With this malfunction, the electric motor can continue to operate if grounding and short circuit protection are not properly performed. However, in operation it will be deadly, since its potential will be under phase voltage. - Winding break
. This malfunction is equivalent to a phase loss. If a break occurs during operation, the engine suddenly loses power and begins to overheat. If the protection is correctly performed, the motor will turn off because the current in other phases will be increased.
To eliminate most of these breakdowns, a motor rewind is required.
Repair of asynchronous electric motor
In the article we will consider the repair of an asynchronous electric motor and its parts. An asynchronous electric motor is the simplest, most durable and most common electric motor. Its range of applications: sharpening machines, mini-sawmills and other devices that do not require battery operation or speed control. They still work in old washing machines.
Three-phase and single-phase asynchronous electric motors are used. Some three-phase motors are adapted for operation in single-phase networks by connecting a phase-shifting capacitor.
Let's look at typical malfunctions of asynchronous motors and methods for eliminating them.
Four Strategies for Success
Electric motor control systems are used in critical processes in factories. Equipment failure can lead to large financial losses associated with both the potential replacement of the electric motor and its parts, and the downtime of systems that depend on this electric motor. By equipping service engineers and technicians with the knowledge they need, prioritizing work, and performing preventative maintenance to monitor equipment and correct hard-to-find problems, workload-induced failures can often be avoided and downtime costs can be reduced. There are four key strategies to eliminate or prevent premature motor and rotating component failures:
- Record operating conditions, equipment specifications, and operating tolerance ranges.
- Regular collection and recording of critical measurements during installation, before and after maintenance.
- Create an archive of reference measurements for trend analysis and state change detection.
- Graph individual measurements to identify major trends. Any change in the trend line of more than +/- 10-20% (or any other specified amount, depending on the operational characteristics or criticality of the system) should be investigated to determine the cause of the problems.
Repair of the electrical part of an asynchronous electric motor
Signs of electrical-related faults in an asynchronous electric motor are:
- Triggering of protective devices against overload or short circuit
- Smells of burnt insulation
- Sparking and smoke inside the engine
Overheating of the housing during operation may indicate a malfunction in the motor winding, but more often it indicates an unacceptable mechanical load on the shaft . For the same reason, overload protection is triggered. But it also works with turn faults in the stator winding. Therefore, the first thing you need to check after the protection is triggered is whether the shaft rotates freely, and also try to start the engine without load by disconnecting the unit from it.
When the short circuit protection is triggered, no-load testing is not required. The procedure for this is as follows:
Checker
| Action | Norm | |
| Disconnect the cable from the motor and check its insulation resistance. | If it is less than 0.5 MOhm, replace the cable | Megaohmmeter for voltage 1000 V |
| If there are phase-shifting or starting capacitors, check their serviceability | Multimeter | |
| Check the serviceability of switching equipment | For a three-phase motor, all three phases must be supplied to it, otherwise it will overheat and burn out | Multimeter or voltage indicator |
| Make sure that there are no signs of short circuit or overheating of the contacts in the electric motor bar | Visually | |
| Measure the insulation resistance between the motor winding and its housing | Not less than 0.5 MOhm | Megohmmeter for voltage 500 V |
Insulation resistance , if it is zero, is also determined by a multimeter. But only a megohmmeter . It measures resistance by applying increased voltage to the object under test.
Megaohmmeter
dry the stator winding by passing hot air through it from a hair dryer or by placing it in an oven. If the engine housing is made of silumin, the drying temperature is chosen so as not to melt it.
If drying does not help or the insulation of the electric motor windings is zero, it is opened and inspected. Although, with any inspection result: mechanical damage to the stator windings, darkening or charring of the winding, the stator is sent to rewind . It is very difficult to rewind an asynchronous motor yourself.
If the reason for disconnection from the protection could not be determined, there may be a turn short circuit . For a three-phase motor, it is determined by comparing the resistances of the windings by phase. For single-phase windings, the resistance of the windings is compared with the rated values. But a multimeter is not enough for this - its accuracy is not enough to feel the difference. For measurements, special instruments are used - ohmmeters with an accuracy class of 0.5 and higher.
The short circuit of several turns leads to heating of the closed section. Sometimes it can be determined by darkening of the insulation, sometimes only with a device. In any case, the stator will need to be rewinded.
Burnt stator winding
Another defect that requires the motor stator to be rewinded is a winding break. It can also be determined with a multimeter. Sometimes a break can be eliminated by finding the connections between the winding wire and the terminals and the point where the windings are connected into a star. If the contact is lost there, then the wires need to be stripped and soldered again.
Source: electric-tolk.ru
5.8. Basic malfunctions of asynchronous electric motors and recommendations for their elimination
Table 5.3 discusses some of the most common malfunctions of asynchronous motors and provides general recommendations for eliminating them [1].
Malfunctions of asynchronous electric motors and recommendations for their elimination
Malfunction and its symptoms
Troubleshooting
The active steel of the stator is uniformly overheated, although the motor load does not exceed the rated one
Mains voltage is higher than rated
Reduce the mains voltage to nominal or increase engine ventilation
Active steel gets very hot in places when the engine is idling and at rated mains voltage.
1. Local short circuits between individual sheets of active steel caused by burrs or contact of the rotor with the stator. 2. Active steel teeth in some places are burnt out and melted due to short circuits in the stator winding or breakdown of the winding to the housing.
1. Remove burrs, separate the connected steel sheets and varnish them with air-drying insulating varnish.
2. Cut out or cut out the damaged areas. Lay thin electrical cardboard or mica plates between the individual sheets and varnish them with insulating varnish. In case of a large number of damages, it is necessary to completely re-mix the steel with rewinding of the stator.
The entire stator winding is uniformly overheated
1. The engine is overloaded or its normal ventilation is disrupted.
2. The voltage at the motor terminals is below the rated voltage, as a result of which the motor is overloaded with current at rated power.
3. The stator winding is connected not in a star, but in a triangle.
1. Reduce the load or increase ventilation (ask the manufacturer for ways to increase ventilation).
2. Increase the voltage to the rated value or reduce the load current to the rated value.
3. Connect the stator winding into a star.
The stator winding gets very hot in places. The current in individual phases is not the same. The engine makes a loud noise and slows down
1. Turn short circuit in the stator winding.
2. Short circuit between two phases.
1.Mainly determined by feeling the winding after it is turned off.
2. Repair the damaged area or rewind the damaged part of the winding.
The entire rotor winding is uniformly overheated. The engine has a reduced speed –
1. The machine is overloaded.
2. The ventilation ducts of the machine are clogged; active steel and windings were covered with a heat-insulating layer of small fibers and dust.
3. Air filters are clogged
1. Reduce the load. If there is no sparking from the brushes, increase the ventilation of the machine.
2. Thoroughly clean the machine and blow it with compressed, clean and dry air (pressure no more than 0.2 MPa).
3. Clean fabric filters from dirt and dust
The rotor and sometimes the stator overheat. The engine hums, the current in the stator pulsates strongly. The engine starts poorly with a load and does not develop the rated speed; torque is less than nominal
1. Poor contact in winding end solders or zero point, in transition connections between bars or in connections between parallel groups.
2. Poor contact in the winding connections to the slip rings.
3. Poor contact in the connections between the slip rings and the starting rheostat or in the starting rheostat.
1. Check all soldering of the rotor winding; those that are faulty or suspicious should be resoldered. If an external inspection fails to detect a place of poor soldering, a voltage drop test is performed.
2. Check the contacts of the conductors at the points of connection with the winding and slip rings.
3. Check the serviceability of the contacts at the points where the wires are connected to the rotor and rheostat, check and clean the contacts and brushes of the starting rheostat.
Engine won't start
There is no current in the stator, which may be due to blown fuses or tripping of a faulty circuit breaker
Install new fuses; fix circuit breaker
The engine does not start; when unfolded by hand, it jerks and buzzes abnormally; there is no current in one stator phase
A break in one phase of the network circuit or an internal break in the stator winding. If a phase loss occurs while the motor is running, then in the absence of proper maximum protection, the stator or rotor winding may burn out
Check the voltage at the stator terminals with a voltmeter. If there is a break in one phase of the network or the voltage in all three phases is asymmetrical (in case of a blown fuse or a break in one phase of the primary winding of the transformer), then eliminate the network fault. If the network is working properly, then eliminate the break in the stator winding
The engine does not start despite the fact that the voltage at the stator terminals is rated and the current in all three phases of the stator is the same
A break in two (or three) phases of the starting rheostat or in the connecting wires between the rotor and the starting rheostat
Using a megohmmeter or test lamp, find the location of the break and repair it.
All three voltages on the rings are equal when the rotor is stationary and open.
Strong one-sided attraction of the rotor to the stator due to the large development of the bearing shells, displacement of the
tenon shields or bearing risers
A squirrel-cage engine starts well without load; won't start with load
Source: studfile.net
Causes of failure and repair of electric motors
During improper transportation, installation and operation, the electric motor may fail. Breakdowns are possible if the rules of technical operation are not followed and due to wear of parts.
In the first case, to eliminate malfunctions, you need to quickly find the cause and eliminate it by carrying out minor repairs. But the technology for repairing electric motors in the second case is a complex process: it is a major overhaul. But it would be optimal to constantly monitor the engine’s operation - the so-called preventive inspection.
Major repairs to DC motors will require a complete overhaul of the motor, while minor repairs depend on the nature of the problem with the motor.
There can be many malfunctions - let’s look at the main ones that occur most often.
The engine does not start If you cannot simply start the engine, then the reason may be a lack of current in the stator - the fuse or circuit breaker has failed - in this case, simply replace them. If at startup, when you crank the engine by hand, it begins to “push” and make a strange hum, or current does not flow in one of the stator phases, then the cause should be sought in a break in some part of the circuit. As a rule, this is the stator winding. If a phase is broken, find and correct the fault. If you find asymmetrical voltage in the phases, which can happen when the fuse blows, replace the fuse. If there is a rated voltage at the stator output, and a symmetrical current flows in the phases, but the engine still cannot be started, then look for the reason in the phase break of the rheostat that starts the start. We need to find the break and eliminate it. If the electric motor is started in the absence of a load and with the rotor short-circuited, it is impossible to start it with a load - look for the reason in the large value of the load that occurs during startup. The solution is to lower it.
Intense current ripple in the stator
Look for the reason in poor-quality work on soldering the contacts in the rotor circuit, so inspect the quality of all soldering of the winding - re-solder the faulty ones, and also re-solder those that cause concern.
Stator overheating
If uniform overheating of the stator active steel occurs,
and the load has a rated value, then the cause may be the mains voltage, which may be higher than the rated value, or a fan malfunction. The cause of the malfunction can be eliminated quite easily: by reducing the load or strengthening the motor that is on the fan. To do this, you need to repair the fan by removing the protective casing. But if the overheating is uneven, then there may be several reasons:
- a breakdown in the stator winding or a short circuit to the housing, which leads to burnout of the teeth, as well as to their melting;
- a short circuit occurred between some plates, which could have been caused by burrs, as well as contact of the rotor with the stator housing.
In order to repair the stator of an electric motor,
you need to cut out faulty elements and remove burrs. Then insulate the sheet from one another using mica or special cardboard, the insulation of which is insulating varnish. Separate the sheets that are connected and varnish them. If there is too much damage, then re-mixing is carried out with re-insulation of all steel sheets and the stator is rewinded. If the stator windings are uniformly overheated, its windings may be incorrectly connected: when they are connected not together - with a “star”, but in series - with a “delta”; there may be engine overload or improper ventilation operation; a low value of the stator voltage at the input leads to a current overload of the motor. To eliminate this, we reduce the load, increase the voltage values to the nominal value or reduce the load current values to the nominal value. We solder the stator windings together - into a “star”. When the stator winding is intensely heated, the circuit may be closed. Disconnect the winding, probe it, find the fault and repair that part of the circuit. If necessary, rewind the entire winding or the part that is damaged.
Rotor failure
If the rotor overheats, humming and braking, or if there are asymmetrical current readings in the phases, look for the cause in poor-quality soldering of the rotor circuit, therefore, before you start repairing the electric motor rotor, examine the quality of all soldering of its windings - re-solder the faulty ones, and also re-solder those that give rise to concern . If the rotor is motionless and open, and the three rings have the same voltages, look for the cause in a break in the wires that connect the rotor to the starting rheostat. This is possible due to wear of the liners, shifting of the bearing shields, which causes a powerful attraction of the rotor to the stator. Repair of asynchronous electric motors in this case consists of replacing the liners and adjusting the bearing shields.
Sparking and
unusual heating of brushes and commutator
Causes: the brush has become unusable or is installed incorrectly, or the dimensions of the brush do not correspond to the dimensions of the holder holder, or the brush is poorly connected to the fittings. You just need to accurately position the brushes and holders.
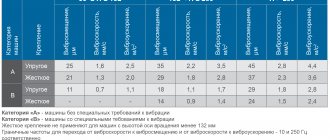
Raising vibration
This can happen due to an unbalanced rotor, clutch or pulley. Vibration can also occur due to inaccurate alignment of the device shafts or when the connecting coupling halves are bent. The rotor needs to be balanced. To do this, you need to balance the coupling halves and pulleys. The engine must be centered. Install the coupling half in the correct position; to do this, first remove it. Find the point of poor connection or break and eliminate the fault.
Knock in bearings, rolling
It can appear due to broken tracks and destroyed rolling elements. Just replace the bearing with a good one.
To place an order, call the managers of the Kabel.RF® company by phone or send a request by email indicating the required electric motor model, purposes and operating conditions. The manager will help you choose the right brand, taking into account your wishes and needs