Urgent high-quality repair of electric motors in Moscow and the Moscow region in accordance with GOST from “Peremotka2”, more than 20 years of experience, a large staff of qualified specialists ready to repair any electric motors.
If you need to make repairs, it is better to contact our competent specialists with special equipment. Only this guarantees the continued uninterrupted operation of the unit. Our company carries out planned and major repairs of electric motors of various types in accordance with all standards and GOSTs. Specialists are well aware of the features of each electrical device, which helps them restore all the operating characteristics of the device in a short time. During scheduled repairs:
• clean the surfaces of the electric motor; • clean the stator and rotor, ventilation ducts; • check and, if necessary, wash or replace bearings; • regulate the brush mechanism. • evaluate the performance of lubricating rings; When a motor is overhauled, it is rewinded. This takes a little longer and requires the use of specialized machines. It is necessary to accurately determine the number of turns and the pitch of the new winding. To do this, a coil template is first created. Automated winding clearly matches it. The final checks are carried out by a specialist and, if necessary, adjustments are made. In our company you can perform any type of work with electric motors and receive a guarantee for the services performed.
Repairs in Moscow and the Moscow region
If you need to repair an electric motor in Moscow, it is better to contact a specialized company such as Peremotka2. There it will be carried out by competent personnel using high-quality modern equipment. If repairs are performed incorrectly, winding is of poor quality, or cheap materials are used, the electric motor can significantly lose its power or even fail completely. Subsequent recovery will be long and costly. Our employees have all the necessary competencies, and therefore we provide a guarantee for all work performed. You will receive a fully functional unit as quickly as possible.
Wound rotor design
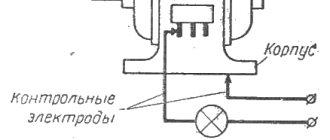
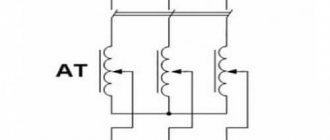
The phase rotor of the IM is structurally similar to its stator. The rotor base is made of electrostatic steel plates, which are mounted on the shaft. The design has longitudinal grooves into which the turns of the phase winding coils are placed. The number of rotor phases strictly corresponds to the number of stator phases. To connect the rotor winding to the circuit, 3 slip rings are installed on the latter’s shaft, to which the ends of the winding are connected, which are in contact with the conductive brushes. In turn, the brushes have outlets into the housing box, which will allow you to connect external additional resistance.
Read also: Low air flow spray gun
Depending on the network voltage, the winding phases are connected in a “triangle” or “star”. The axes of the coils of a two-pole electric motor are shifted 120 degrees relative to each other.
Slip rings are made of brass or steel. They are mounted on the shaft with mandatory insulation between each other. The brushes are located on a brush holder, made of metalgraphite, and pressed against the rings by means of springs.
Prices for electric motor repairs from Peremotka2
In this service, the price depends primarily on the power, rotation speed and type of electric motor. Based on the complexity of the design, the volume of additional. work and other factors, special coefficients are used.
There are two types of work that differ in complexity. During the routine, the condition and operation of the bearings are checked, all surfaces are cleaned, and the operation of the brushes and lubricating rings is adjusted. Overhaul is primarily rewinding the engine.
Please check the approximate cost of any type of repair by phone or in the price list on the website. Only a specialist can name the final amount after a complete analysis of the part.
| up to 1 kW | RUB 3,300 | RUB 3,300 | RUR 3,850 | RUR 3,850 |
| 1.1 kW | RUB 3,300 | RUB 3,300 | RUR 3,850 | RUR 3,850 |
| 3 kW | RUB 4,000 | RUR 4,950 | RUB 5,500 | RUB 6,500 |
| 22 kW | RUB 16,000 | RUB 17,000 | RUR 21,000 | RUB 27,000 |
See the Price List for the exact cost.
Maintenance
This is one of the types of work of our masters. During this process, first of all, all surfaces of the unit are cleaned of dirt and dust. Then the ventilation ducts, as well as the rotor and stator, are cleaned. The specialist assesses the wear of the lubricant rings and adjusts the operation of the brush mechanism. If necessary, replace brushes. Next, the bearings are put in order - they are washed or replaced. For correct and maximum long-term uninterrupted operation, this type of repair work must be carried out with a certain frequency and by competent specialists.
Advice from the experts
Depending on the type of breakdown, repairs may take a long period of time. If you do not have certain skills in working with electric motors, understanding the circuit diagram of the device itself, or additional parts, it is not recommended to carry out repairs yourself.
If the engine is not operating properly, you can re-diagnosis or correct its elements. A mandatory point of correctly performed work is testing the electrical insulation strength and checking the motor in test mode.
In accordance with the Technical Operation Rules, the system of scheduled preventive maintenance of electrical equipment provides for two types of repairs: current and major.
Current repairs are carried out at intervals established taking into account local conditions for all electric motors in operation, including those in cold or hot standby. Current repair is the main type of preventive repair that maintains the reliability and durability of electric motors at a given level. This repair is carried out without dismantling the engine and without completely disassembling it.
Major renovation. The frequency of major overhauls of electric motors is not established by the Technical Operation Rules. It is determined by the person responsible for the electrical equipment of the enterprise based on estimates of the total operating time of electric motors and local operating conditions. Major repairs, as a rule, are carried out in a specialized electrical repair shop (ERS) or a specialized repair enterprise (SRP).
The electric motor is disassembled in the order determined by the design features of the electric motors.
Assembly of electric motors after repair. Rolling bearings are pressed onto the rotor shaft. Ball bearings are installed entirely. In roller bearings, an inner ring with rolling elements is mounted on the shaft. The outer ring is installed in the seat of the bearing shield with a movable fit (sliding or moving). Before assembly, the seating surfaces are wiped and lubricated. The inner bearing caps are installed on the shaft before the bearings are seated.
Read also: Sharpening angles for metal cutters
Small bearings are mounted on the shaft in a cold state. The inner race of the bearing must fit snugly against the shaft shoulder. The outer ring should turn easily by hand. One-piece plain bearing shells are pressed into the bearing sockets and secured with a locking screw.
To do this, use the same devices as during disassembly, but ensure their reverse effect. When seating the liners, the lubricating rings in the shield reservoir are placed concentrically with the mounting hole.
The rotor is inserted into the stator using the same methods and devices as when removing the rotor. Rolling bearings are lubricated. Bearing shields are installed on the bearings, the shaft is hung out and the cardboard spacer is removed from under the rotor. When installing shields with plain bearings on the shaft, the lubricating rings are removed from the slot of the liner so as not to damage them by the shaft. They combine the marks on the frame and the panels, and fasten the panels to the frame with fastening bolts. The lifting devices are removed. Then check the freedom of rotation of the rotor and tighten the fastening threads of the shields. Install small parts (flanges, covers) and pour oil into the plain bearings. Connecting or transmission parts (coupling halves, pulleys, brake discs, gears) are pressed onto the working ends of the shafts. The successful alignment of the electric motor shaft with the shaft of the production mechanism or with the gearbox shaft depends on the accurate fit of the connecting parts. After assembly operations, air gaps are measured at both ends of the machines at diametrically opposite points on the circle. For large rotor diameters, the gap is measured at eight points around the rotor circumference. Deviations of air gaps from the arithmetic mean should be no more than 10%.
The electric motor is run-in at idle speed, monitoring the no-load current, bearing heating and noise. The axial run of the rotor is determined by shifting the shaft along the axis until it stops, first in one direction and then in the other direction with the rotor stationary; the axial run of the rotor is equal to twice the axial clearance. One-sided axial clearances, which should be the same, are measured at idle. To do this, the lubricated end of a securely reinforced wooden block is pressed against the end of the rotating shaft and the rotor is shifted until it stops. The same operation is performed from the other end of the shaft. In both cases, measure the distance from the mark to the bearing housing before pressing on the shaft and during measurements; they must be equal to the corresponding axial clearances. If it is impossible to measure axial clearances on a rotating rotor, they are approximately estimated by the axial run of the rotor. The results of measuring the axial clearance are compared with the permissible values.
After routine repairs, asynchronous electric motors are subjected to the following tests: measure the insulation resistance of the stators between individual windings and relative to the housing, test with increased voltage at a frequency of 50 Hz for 1 min, check the interturn insulation for electrical strength, measure air gaps, run the electric motor at idle speed, measure the axial clearances in plain bearings or rotor run along the axis.
"Major repairs of asynchronous electric motors"
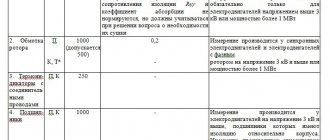
| Operation | Scope of repair work |
| Measurements and condition assessment of parts | Engine inspection; assessment of the external condition of assemblies and winding integrity; measurement of the axial run-up of the engine rotor with plain bearings. Measuring the gap between the shaft journal and the bearing shell. Measuring the gap between the rotor and stator, the insulation resistance of windings and rings. |
| Engine disassembly | Complete disassembly of the engine; cleaning, purging and rinsing of all components and parts |
| Inspection and cleaning of windings | Cleaning, purging, wiping and rinsing of retained windings, eliminating defective places on the insulation |
| Repair of bearings and bearing shields | Replacement of rolling bearings regardless of their condition. Refilling of plain bearing shells (if necessary). Repair of bearing shields (crack welding) |
| Repair of magnetic circuit | Removing areas of melting of the rotor and stator magnetic circuits, eliminating short circuits and looseness of steel sheets, axial shifts of active steel, etc. |
| Repair of damaged parts | Replacement or repair of fans, welding of paws, welding of cracks, restoration of fastening threads; |
| Rotor repair | Replacement or refilling of winding rods, repair of local insulation damage, repair of bands and banding of windings, replacement of faulty groove wedges |
| Grounding check | Inspection and repair (if necessary) of grounding bars. wires and contacts |
| Rheostat repair | Disassembling and cleaning the rheostat; cleaning and oil change, cleaning and, if necessary, changing contacts. Replacing damaged resistors. |
| Assembling the engine and aligning it on the foundation | Checking the tightness of the transmission (clutch, pulley). Aligning the electric motor on the foundation, checking bolted connections |
| Inspection and testing of the starting apparatus | Cleaning the device if necessary - with disassembly; cleaning contact fastenings from oxides; cleaning and replacing contact crackers. Removing carbon deposits and cleaning contact surfaces; adjusting the contact pressure with a dynamometer, checking the rotor contact area, checking the short-circuited rotor turn. Inspection and repair of grounding wires |
| Checking the protective device | Checking the suitability of fuses. Checking the compliance of heaters with thermal relays. Checking whether the machine's splitter current corresponds to the calculated current |
| Measurements | Measurement of stator winding insulation resistance; total direct current resistance of rheostats, ballast resistors. Determination of the gap between the rotor and stator steel |
| Running in the electric motor after repair | Starting the engine at idle; checking no-load current, bearing temperature, noise. After operating the electric motor for 1 hour, turn it on under load for 5-6 hours, after which check the heating temperature of the windings and bearings. Checking the rheostat and starting equipment |
General conditions for choosing a drainage system: The drainage system is selected depending on the nature of the protected area.
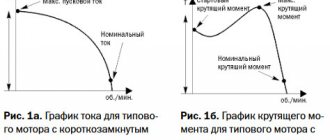
The widespread use of the asynchronous electric motor (IM) is due to its reliability and simplicity of design. The stator of such a motor is standard; it is a hollow cylinder made of electrostatic steel plates with a three-phase winding. The rotor can be squirrel-cage and phase. The latter option has become more widespread for a number of reasons, although its design is much more complex than that of a squirrel-cage rotor.
Technical repairs from Peremotka2
Regular technical repairs are the key to uninterrupted and long-term operation of the entire device.
During this process, you need to clean the housing from dirt, check the quality of the engine mounting and tighten the mounting bolts. Be sure to check for grounding. Next, you need to diagnose the case for excessive vibrations and heating, as well as the absence of extraneous noise. When working with a wound-rotor motor, check the brush slip rings and measure the insulation resistance on the winding.
If any problems are detected, the technician will promptly fix them. Carrying out regular maintenance will help avoid larger breakdowns.
Rewinding of electric motorsRewind el. Engine repair is a complex and responsible job that must be performed by a professional specialist with sufficient experience and skill in producing this type of service. more details |
Asynchronous motor repairThe most common motor in our life is recognized as asynchronous motors. more details |
BalancingFor an ideally balanced motor, the axis of inertia of the rotor must coincide with the axis of rotation. more details |
Disassembling the machine
The craftsmen begin work by removing the upper casing, which covers the fan blades from dust and contaminants from the outside. The disassembly process must be carried out as carefully as possible to avoid hammer blows or great force. This may damage the motor parts and cause it to malfunction.
During the repair process of a three-phase asynchronous motor, the bearing caps and bearing shields are removed. At the time of disassembling the elements from the shields, marks must be applied to the body, according to which, when reassembling the machine, the shield is installed in the right place.
If the machine is small, then the rotor is removed from the stator manually. When the dimensions are large, the element is removed using special lifts, the process is carried out along the axis of the machine.
When it comes to removing bearings, there are several options. Elements of bushings or liners can be knocked out or protruded from special shields. Efforts cannot damage the main elements.
Read also: What types of gears are there?