Technical characteristics of VVG cable
The features of using different types of VVG cable were discussed above, and now we will talk about the technical parameters of conductors of this brand.
- Can be laid at temperatures down to -15°C. At lower temperatures, it is necessary to heat the cable, which is not easy to organize (the sheath becomes too rigid and is very difficult to bend).
- Operating temperature range - from -50°C to +50°C. At the same time, when installing outdoors on the street, additional protection from ultraviolet radiation is required.
- Bending is possible with restrictions: VVG with single-core conductors; minimum bending radius is 10 radii;
- with stranded ones - 7.5 radii (due to greater flexibility). There are flat options (two and three wires)
- for a short circuit in which the conductors remain operational depends on the manufacturer and can range from +160°C to +250°C.
It must be said that the technical characteristics of the VVG cable depend not only on the specific type, but also on the manufacturer. Therefore, before purchasing, look at the cable passport (you can ask the seller). The above are parameters common to all brands of VVG cable.
It is not surprising that these conductors are very popular - with good technical indicators, they cost relatively little, and can be used almost everywhere - both in enterprises and offices, and in houses and apartments.
Section and number of cores
The cross-section of the VVG cable cores of any brand can be from 1.5 mm² to 240 mm². Conductors with conductors up to 35 mm² are usually on sale; other, larger sizes must be ordered.
As already mentioned, there are VVG cables with 2, 3, 4 and 5 cores. The number of cores is written immediately after the abbreviation: VVG 2 x 3.5; VVGng 4 x 4, etc. The first number is the number of cores, the second is the cross-section of the conductor.
Approximate range of VVG cables
There may be VVG cables with “neutral” and “grounding” conductors. Moreover, there are options in which the protective wires are of the same cross-section, and others with a smaller diameter (to save copper and lower cost). Most often, the “ground” conductor is made smaller; in some cases, the “neutral” is also made a little smaller. If the protective conductor has a smaller diameter, it is designated as +1. For example, VVGng 4 x 4.0+1 (read as 4 wires with a cross-section of 4 mm² and 1 step less than 2.5 mm²). These VVG cable options are also standardized, their parameters are given in the table below.
Parameters of VVG cables with cores of different diameters
Continuous current
When selecting a cable cross-section, a more correct method is based on the maximum current. In this regard, such a characteristic as long-term permissible current is standardized. It depends on the number and cross-section of the cores, as well as on the method of laying - open or closed.
| Core cross-section | Continuously permissible current | ||
| with two main cores | with three main cores | with four main cores | |
| 1.5 mm² | 24 A | 21 A | 19 A |
| 2.5 mm² | 33 A | 28 A | 26 A |
| 4 mm² | 44 A | 37 A | 34 A |
| 6 mm | 56 A | 49 A | 45 A |
| 10 mm | 76 A | 66 A | 61 A |
| 16 mm | 101 A | 87 A | 81 A |
| 25 mm | 134 A | 115 A | 107 A |
| 35 mm | 208 A | 177 A | 165 A |
Two modifications of VVG cables are produced - with a rated voltage of 0.66 kW and 1 kW.
VVGng cable: technical characteristics
- operating frequency – 50 Hz;
- laying of communications is carried out at temperatures above -15 ° C, without preheating;
- cables are operated in temperature conditions: from minus 30 °C to + 50 °C;
- when installing single- and multi-core VVGNG ls cable, a minimum bending radius of 7.5-10 outer diameters is allowed;
- prolonged heating of the cores up to a temperature of +70 °C is allowed;
- operating current with voltage up to 0.66 kV, wire with additional characteristics operates at higher voltages;
- cable combustion begins at a temperature of +400 °C;
- Manufacturers guarantee safe operation of the cable for 30 years, subject to compliance with technological discipline; it is recommended to check the cables in use every 5 years for insulation damage;
- operation of communications in conditions of high humidity and at high altitudes is allowed.
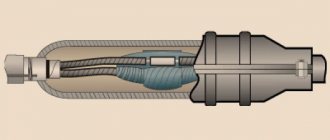
Cable structure
Kabel translated from Dutch means cable or rope. The power cable is a structure of insulated conductors surrounded by general insulation and a protective sheath. The outer shell, which protects the conductors from mechanical stress, can be reinforced with armor. All power cables have the same structure. Depending on the design, the materials from which individual elements are made may differ.
KVVG cable
The structure of the IC includes:
- conductor;
- insulation of this core (phase);
- a sheath covering all the conductors in the cable.
For your information. In addition, the cable structure may include various coatings and fillers that prevent the cores from sticking to the insulation or different insulating layers to each other (film, talc).
Conductor
Round, segment or sector shape - these are the main design forms of current conductors in a cable. The range of core sections is standard; the conductors themselves are made of aluminum or copper.
Cables with different core shapes
Phase insulation
Each phase conductor in the cable is covered with individual (phase) insulation. Also P.L. Schilling in the mid-19th century used gutta-percha insulation for wires used to detonate mines at sea.
Modern phase insulation must meet the following requirements:
- flexibility;
- mechanical strength;
- electrical strength.
The choice between flexibility and thinning is always problematic. Electric strength is the main indicator for insulation. It can be made of cross-linked polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride, rubber or oil-impregnated paper.
Important! Reducing the thickness increases flexibility, reduces weight, and improves heat dissipation, which means the cable can withstand high operating current. Reducing the insulation thickness leads to the likelihood of breakdown, therefore, the electrical strength decreases
Outer shell
This is a protective layer covering the entire complex structure of the SC. The outer shell can be made of PVC (polyvinyl chloride plastic)
For example, VVGP ng, if you pay attention to its marking, has the following PVC shell
Additional items
These include components that increase the internal insulation, strength and protection of the cores. Additional elements may be as follows:
- shielding braid;
- waist insulation;
- lining (pillow) under the armor;
- protective outer layer of metal strips (armor);
- internal filler of spaces between conductors.
Number and cross-section of cores
The SC can include from 1 to 5 current-carrying wires. The nominal cross-section of conductors ranges from 1.5 to 1000 mm2. In SCs they have the same cross-section, but in four-core cables one of the conductors may have a smaller cross-section. Usually this is a neutral conductor.
Table of cross-sections of power cable cores
Flat power cable VVG-Png (A)
One of the common types of cable products is the power flat cable VVG-Png (A).
Cable VVG-Png(A)
Application
This product is intended for use and power supply of installations with voltages up to 1000V DC and AC with a frequency of 50Hz. They can be laid outdoors, in partially flooded rooms, in pipes and cable trays.
Explanation of markings
As with other types of cable products, you can determine its design by the markings on the outer shell and the product passport:
- B – phase insulation is made of polyvinyl chloride plastic;
- B – the outer shell is made of the same material;
- G – no armor;
- P – flat, the internal wires are not located in a bundle, but side by side, in the same plane;
- ng – does not support combustion;
- (A) – does not propagate combustion in bundles with a large amount of flammable substances.
Knowing how to decipher the markings of a VVGP ng (A) cable or other types of cable products is important when designing and installing power supply equipment.
Operation of cable products
Before use, the cable must be tested. If a voltage of 660 V or 1000 V is supplied via a cable, then 3 kV or 3.5 kV, respectively, is passed through it for 9 minutes. There are certain rules that characterize the flexibility of a cable. For cable products that consist of stranded conductors, the bending radius R is calculated using the following formula, depending on the cable diameter (d): R = 7.5 * d. For single-core types of VVGng cable, the ratio is as follows: R = 10 * d.
The temperature at which the cable does not lose its characteristics is in the range from -50 to 50 degrees Celsius. The optimal temperature value for installation is -15 degrees Celsius; as the temperature drops further, the cable begins to crumble and break.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=SGP5AMqj22g
Application and benefits of use
The use of VVGng is quite diverse, as it is related to its characteristics and resistance to fire. It is recommended to lay it in the following places:
- Dry and damp areas, which include the following: tunnels, mines, various production facilities, etc.
- Structures with weak, medium and strong corrosive activity.
- Fire hazardous premises.
- Residential and public buildings.
- Explosive areas.
Algorithm for checking cable products
You should be prepared when purchasing power cables, since a low-quality product can lead to a short circuit and fire. In addition, this can lead to failure of electrical equipment powered by them. The following rules should be followed before purchasing:
- Determine the required characteristics: length (L), cross-sectional area (S), number, type and shape of cores.
- Calculate the resistance of each core using the formula: R = (p * L) / S.
- Take an ohmmeter to measure the resistance of the wires of the VVGng cable.
- You will also need a megohmmeter, since it is necessary to measure the insulation resistance between the conductors.
The formula for calculating the value of S depends on the geometry of the conductor. If the conductor is round, then S = 3.1416 * (sqr(d)/4). If it is rectangular in shape, you should measure its sides and substitute their values into the formula: S = a * b. With a sectoral shape with an angle f, you need to calculate the area of the sector: S = (3.1416 * sqr (d) * f) / 1440. The value of S is calculated in square meters. mm.
For example, to calculate the resistance of a VVGng 3x2.5 cable with a length of 1000 m, you should calculate S for a round cable using the formula: S = (3.1416 * sqr (d)) / 4 = (3.1416 * sqr (2.5)) / 4 = 4.91 (sq. mm). Coefficient for copper p = 0.017. All that remains is to substitute the obtained values into the formula and calculate the electrical conductivity of the cable: R = (0.017 * 1000) / 4.91 = 3.46 (Ohm). The electrical conductivity of each core should be no more than 3.46 Ohms.
The permissible resistance value of 1 km VVGng 3x2.5 is no more than 12 Ohms. During purchase, you should check the resistance of each core and compare it with the calculated value. In addition, you need to check the insulation resistance between the two wires using a megohmmeter. Its value must be at least 10 MOhm. A value of 0.5 MOhm is allowed for lighting networks and electrical appliances with a power of up to 1.7 kW.
Thus, VVGng cable is widely used in construction. Due to its characteristics and resistance to fire, it can be used in areas with a high fire hazard. The cable checking algorithm allows you to select a quality product when purchasing, which is very important for ensuring electrical safety.
Characteristics
For varieties of cable products with the VVG brand, the technical characteristics vary, but some are of a general nature:
- Passed current frequency - 50 Hz;
- Rated voltage: 0.66 and 1 kV;
- There are two types of execution: “T” and “UHL”. The first denotes a tropical variant, the second a combined, temperate and cold climate;
- Operating temperature range: from –50 to +50 °C;
- The maximum permissible air humidity is 98%, at a temperature of +35 °C;
- Free installation, without preheating, is allowed at a temperature not lower than –15 °C;
During operation, the VVG cable may be used with heating not exceeding +70 °C. At the same time, the permissible current allowed to pass through the VVG wire for a long time depends on its cross-section and type of design. This characteristic is calculated using special tables and directly depends on the material used for the manufacture of conductive cores.
The construction length, or the amount of VVG electrical wire wound into a transport drum, depends on the cross section and is measured in meters:
- From 1.5 to 16 mm² inclusive - 450;
- From 25 to 70 mm² - 300;
- Over 95 mm² - 200.
The permissible bending radius with which the VVG cable can be laid is determined by its conductor and performance class according to fire safety standards. The average values are: 7.5 diameters for a multi-core cable and 10 diameters for a single-core cable.
The guaranteed shelf life, from production to operation, varies depending on storage conditions:
- 2 years outdoors;
- 5 years, in an open area, under a canopy that protects from exposure to the sun and precipitation;
- 10 years, when stored indoors.
The full service life, according to GOST, is 30 years. The warranty period depends on the manufacturer, but not less than 5 years.
The conditions under which the VVG cable can be used and its technical characteristics depend primarily on the material used in its manufacture. For example, copper cable VVG, having the best parameters in the field of safe use, is recommended for hidden wiring in residential and industrial premises.
How to properly use the VVG-Png(A) marking cable
The open method of laying VVG cable is allowed. According to the technical characteristics of this cable, its open installation is allowed on structures and surfaces made of low-combustible or non-flammable materials, such as concrete, plastered surfaces, brick, plaster, etc.
Open laying of the VVG cable is also possible along suspended structures, for example, a cable, etc. In the case of laying wires along suspended structures, it is necessary to exclude the possibility of mechanical action on the cable (stretching or sagging).
It is necessary to install additional protection if there is a risk of mechanical damage to the cable product. When laying a conductor in an open manner over wooden combustible surfaces, additional protection must also be used.
Note! Installation in this case should be carried out using a pipe, metal hose, corrugated hose, cable duct and other types of protection
Decoding the abbreviation
The VVGN cable must comply with GOST 31996-2012. In the name, each letter stands for:
- B – the first letter in the name means vinyl (more precisely polyvinyl chloride);
- B – the second letter means that the cable has a second layer of insulation, which is also made of vinyl;
- G - the third letter indicates that the cable has no armor. This provides flexibility although it is less stable. This characteristic makes conductors of this type widely popular.
- NG - the presence of these letters in the name indicates that the cable is resistant to fire when laid together. When laid alone, almost all wires do not ignite. And to ensure this property during group installation, the cable is coated with a special solution.
Modern VVGng GOST cable may also have modifications:
- LS – gas and smoke are released in reduced quantities;
- HF – no gaseous products are released during combustion.
Parameters of flexible cable VVG
Parameters vary depending on use and operating conditions. They depend on the properties and shape of the manufactured material. An important parameter is the cross-sectional area of the vein.
Technical characteristics of flexible conductor element
It can be calculated using the special formula S=N^2D/1.27 and D=(4S/pi), where S is the area of the transverse conductor conductor cross-section, N is the number of conductor cross-sections and D is the conductor diameter. The reading of resistivity and limiting current value will depend on the cross-sectional area. This parameter is determined individually for purchase, since different grades of copper with long-term permissible current are used.
Mechanical parameters
The mechanical parameters of the cable are its radius of curvature and the temperature conditions for installation and operation in emergency mode. In addition, it has a certificate of conformity with tensile strength, tensile elongation, insulation aging and weight reduction requirements. The radius depends on what type of core is in the cable. According to GOST, this parameter is 10.
Mechanical cable parameters
The next parameter is the temperature mode, the normal value of which is from −50 to +50 degrees. In this case, the installation temperature is at least −15 degrees. If installation is planned at a lower temperature, the cable warms up. In addition, an important parameter is the certificate of conformity.
You may be interested in this. Features of the PPV wire
Electrical parameters
The electrical parameters of the VVG cable are the nominal cross-section of the core, the minimum number of wires, DC electrical resistance, round or shaped copper core and core material. The most important electrical parameter is conductive resistance, which depends on the conductor type and its cross-section. The next parameter is the insulating conductive resistance, which depends on the temperature with the conductor cross-section. The last thing is having an electrical test certificate.
Electrical cable parameters
Note! The conductor passes the test only if it has a frequency of 50 hertz and a voltage of 660 volts for 10 minutes of operation. A cable with a voltage of up to 1 kilowatt must withstand a voltage of 3.5 kilowatts
Specifications
Technical parameters of wire VVG-Png(A)-LSLTx:
- fire hazard class according to GOST 31565-2012: P1b.8.2.1.2;
- type of climatic modification UHL, placement categories 3 and 4 according to GOST 15150;
- operating temperature range from −50 °C to 50 °C;
- relative air humidity at temperatures up to 35 ° C up to 98%;
- laying without preheating is carried out at an air temperature not lower than −15 ° C;
- the permissible bending radius of cables when laying is not less than 7.5 maximum outer diameters;
- equivalent toxicity indicator of combustion products more than 120 g/m³;
- wires do not spread fire when laid in groups according to category A;
- smoke formation during combustion and smoldering of these products does not lead to a decrease in light transmission in the test chamber by more than 50%;
- fire resistance of at least 180 min.
Technical indicator
Mass fraction of hydrogen chloride released during combustion of polymer materials:
- isolation - no more than 100 mg/g;
- shells - no more than 80 mg/g.
The long-term permissible heating temperature of conductor cores during operation is no more than 70 °C. The long-term permissible heating temperature of product cores in overload mode is no more than 90 °C.
You might be interested in Decorative outdoor retro wiring
The maximum permissible heating temperature of cable cores during a short circuit (second value for products with conductive cores with a cross-section of more than 300 mm²) is not more than 160/140 °C. The duration of the short circuit should not exceed 5 seconds.
The maximum heating temperature of the cores under the conditions of non-ignition during a short circuit is no more than 350 °C.
Note! The construction length of the cables is specified when ordering.
What are the problems when using a cable?
Over time, the insulation material wears out, which also affects the physical and chemical properties of the power cable.
The main factors influencing the aging process of insulation are:
- mechanical loads (vibrations, electrodynamic forces);
- chemical exposure to aggressive substances;
- moisture ingress;
- oxidation and regular heat exposure;
- overvoltage.
Different types of insulation also exhibit aging differently. Solid dielectrics are destroyed, microcracks appear on their surface, organic ones emit gases, and the impregnation of paper insulation changes its physical and chemical properties.
The aging process is natural and irreversible, but it can be delayed. To do this, it is necessary to strictly follow all the manufacturer’s instructions for the wiring process and operating mode.
Systematic overheating of the power wire leads to rapid aging of the material. To avoid this, do not lay the cable near heat sources. It is advisable only to use the type of cable recommended by the manufacturer for the work (for example, rubber is not suitable for transmitting high voltage).
Important! It is necessary to use a wire with a suitable conductor cross-sectional area. Incorrect calculations lead to rapid wiring failure
Decoding and types
Sip cable: decoding
If the first letters of the abbreviation in the name of the cable brand do not begin with the letters AA (aluminum conductor with an aluminum sheath) or AC (aluminum with a lead sheath), then this is interpreted to mean that the conductors are made of copper. The first letter B of the abbreviation VVG means that the core insulation is made of vinyl (polyvinyl chloride or its derivatives can be used). The second letter B means that the common insulation sheath of the bundle of cores with insulation is also made of vinyl. The third letter G indicates the absence of armor.
Decoding the abbreviation
Regular VVG
It is used for installation of electrical wiring in blocks, channels and collectors, guardhouses and tunnels, in dry and semi-dry cool rooms with a relative humidity of no more than 98%. External use in the open air is also possible. In this case, you should avoid prolonged direct exposure to sunlight and, if necessary, apply protection from them. Without additional protection, laying it under plaster is undesirable.
Non-flammable VVGng
The additional letters “ng” in the name of the cable VVG ng mean that its insulation does not support combustion. Its use is advisable where it comes into contact with materials such as:
- wood products (wood, lining, plywood, fiberboard, chipboard);
- paper (wallpaper, cardboard);
- fabric (curtains, carpets).
Also, decoding of the VVGNG (a) cable is with increased fire safety. The degree of fire safety is expressed by indices (a), (b), (c), (d), where the initial letter (a) means the highest category, and then in descending order.
Explanation of the VVG ng ls marking - in case of fire it produces extremely little harmful gases and smoke. VVG ng lt has insulation, which during forced combustion does not emit toxic substances and gases, and VVG ng hf can be deciphered - during combustion it does not emit corrosive substances or halogens. How is VVG ng frls different? They differ in that they have increased fire resistance with low gas formation after combustion of the insulation.
Release forms
If such a cable is marked VVG Z, this means that the space between the metal core and the insulation is filled with synthetic non-hydrophobic fiber or powder. The VVGP brand will differ in that it has a flat shape.
Cable shape
The shape of the cable depends on the type and number of cores and can be:
- round;
- flat;
- triangular;
- rectangular;
- pentagonal.
The three-core VVG cable can be round, flat or triangular. The difference between the round ones is that the cores can have a segmented shape, most often consisting of a multi-core bundle of wires. This form of cores is used for three or four-core cables, which in general cross-section form a circle shape, and the cores form a segment shape. This allows you to maintain the density of the entire cable during an acute angle bend, the wire does not bunch up into knots.
Important! The VVG cable can be bent into a circle with a radius up to 10 times greater than the radius of the wire itself
Decoding and modifications
To understand the difference between the different types of this cable, you need to know the decoding of the name. Then you can decide which type suits you best.
Different types of one under the same name
Regular VVG
Decoding the main abbreviation - VVG - is not difficult:
- the absence of the letter A in front indicates that the wires are copper;
- the first letter “B” denotes the core insulation material - PVC (polyvinyl chloride);
- the second letter “B” is the cable insulation material – also PVC;
- “G” indicates the absence of additional protection (armor or other protective shells).
That is, the VVG cable consists of several copper cores and PVC insulation. Each of the wires has its own color. The conductors are twisted in one plane and protected by a PVC sheath. Conductors can be stranded or single-core (coolant is added to the abbreviation).
Types of round conductors
In private homes, single-core cables are more often used. They can have 2, 3, 4 or 5 cores. The cable can be round or flat, with a neutral conductor (blue) and/or with a grounding conductor (yellow-green).
Non-flammable VVGng
Fire-resistant cables are required in fire-hazardous premises (wooden houses, bathhouses, etc.) and public buildings (children's and medical institutions, in particular). In such cases, you can use products with reduced flammability - VVGng. The additional letters “ng” just mean that the shell does not support combustion.
There are several other types of VVGng cable:
- VVGng-ls. They differ in that this plastic shell emit almost no smoke when burning in an open fire. (ls is short for English low smoke). According to the new rules, it cannot be used in social institutions.
- VVGng-frls. It is characterized by increased reliability due to the fact that the conductors are additionally protected by two tapes containing mica. That is, each conductor is wrapped in thermal protection, on top of which a sheath of low-flammability plastic compound is applied with minimal smoke emission. The insulated cores are twisted, and on top of them there is an additional protective sheath - made of two copper tapes with a thickness of at least 0.1 mm or a copper mesh wrapped in one tape. A PVC cable sheath is applied over this protection. This will be the VVGng-FRLS cable. This type of cable can be used at industrial enterprises, including nuclear power plants, in explosive areas except for class B-1 zones.
Non-flammable cables VVGng can come with an additional sheath
- VVGng-LSLTx. In this subtype, for the shells of conductors and cables, a plastic compound with reduced flammability is used, which, when burned, emits less smoke and this smoke is less toxic. This conductor retains its working capacity in case of fire and is used in networks with alternating voltage up to 1000 V, frequency up to 100 Hz or up to 1500 V at constant voltage. Can be used in social institutions.
- VVGng HF. This brand is distinguished by the fact that the smoke emitted during combustion (when the NG cable is directly in the fire, it still burns) emits smoke with a reduced content of harmful substances. The abbreviation HF itself means that the shells are made of plastic with a reduced content of halogens (chlorine in particular), thereby reducing the toxicity of smoke (HF - from English halogen free - does not contain halogens).
So, what is the difference between a regular VVG cable and a VVGng cable and its varieties? An ordinary VVG conductor does not support combustion when laid alone. Products with the prefix “ng” do not burn even when laid in a group - in a bundle with other conductors. The remaining “additives” to the name simply improve the characteristics.
Release forms
Depending on the number and shape of the cores, the VVG cable can be round, flat, triangular or pentagonal (see photo below).
Different types of VVG cable
The shells are made of polyvinyl chloride of various modifications. The spaces between the cores are filled with the same plastic compound. In some versions, a harness made of the same material is used. With a small cross-section of cores - up to 25 mm² - discharge without filling is allowed.
Different types of cores in VVG cable
The cores in the cable can be round or sectional. Sectional ones are usually multi-core, round ones are single-core. In any case, their cross-section must correspond to the declared parameters.
VVG GOST cable: certificate of conformity
VVG wire is a cable product. It is based on aluminum or copper wire, which is covered on top with a special polyethylene, or less often plastic, sheath.
The design consists of two components. This is the core that is responsible for conducting current, and the insulation material.
The certificate of conformity for cables of the VVG and VVGNG types is an official document that confirms the fact that the manufactured products comply with the requirements of GOST and basic standards.
In accordance with the requirements of the legislation of the Russian Federation, cables are subject to official certification without fail. This is stated in the all-Russian product classifier for group OP-35. This applies to wires that are intended for stationary installation with voltages up to 1 kW.
If the product is manufactured taking into account technical conditions, then a voluntary certificate can be issued after taking into account all the requirements for the final product.
Conditions for storage and transportation of VVG-Png(A) cable
Power wires retain their properties only if the correct storage conditions are provided for them. As a rule, products are delivered on metal or wooden drums.
How to store and transport wire
To prevent them from losing their properties, certain rules must be followed:
- coils of wires can only be placed in a vertical position, that is, their axis is horizontal to the ground;
- each of the reels must have a marking provided by the manufacturer, which contains information about the date of manufacture of the cable;
- Wires intended to carry current with voltages greater than 6 kV are supplied only with a test report for compliance with current standards.
Note! During storage, the drum must not be repaired using nails. Clogging of fasteners can damage the insulating layer of the conductor
The coil cannot be used if its deformation is visually detected. In this case, it is necessary to rewind the wire and examine it for defects.
Connecting VVG cables to each other
Before moving on to the procedure for connecting the VVG cable, you should remember that this is a rather dangerous and responsible undertaking. Therefore, such a procedure should be carried out by electricians or other specialists in the field of electrical wiring.
Execution must be carried out in accordance with the following requirements:
- The value of the transition resistance of the parts of the connections should not exceed the resistance level of the section of the conductor.
- The docking area must be protected from moisture as much as possible.
- Protect the contact area from mechanical impacts.
- Select the correct coupling connection. They not only guarantee reliable fastening, but also provide tightness and protection. The couplings can be rubberized or plastic.
Installation work includes the following activities:
- To begin, put on rubber gloves and cut the ends of the VVG cable.
- The next step is to connect the cables or band them if the room is damp. The ringing is done using a special funnel or a porcelain sleeve. Banding has its own mandatory requirements. For example, sealing the insulating coating, as well as the timely release of current-conducting force to the outside.
- The next step is the assembly of the pre-selected coupling connection.
- After the structure has received its shape, it is necessary to ground the shell and armor.
- Then the protective layer must be filled with a special epoxy mass or compound.
At this stage, the wire should be left until the top layer dries. This will take from several hours to several days.
Related Posts
- Using PVC wire according to the characteristics and description
- What is the difference between a cable and a wire?
- Which cable to choose for installation outdoors (over the air and in the ground)
- Wire cross-section for home wiring: how to calculate correctly
- Screw wire area of application
- Cable current cross-section
- Choosing a cable for installing video surveillance systems
- How to independently secure a cable to a wall or ceiling using dowel clamps
- Pugnp and punp wires: characteristics, differences, prohibition of use
- Installation, connection of the rj 45 socket. pinout of the internet socket
- Attaching the cable to the wall
- Repair of electrical equipment on ships - cable termination
- Wiring diagram and installation of electrical wiring in the kitchen
- Laying wires in corrugation: how many can be laid
- Laying cables in the ground
- Video intercom cable
- Which wire is better: single-core or stranded
- Baseboard and floor electrical sockets. device and installation
- Connecting the hob to the electrical network: diagrams, selection of cables, sockets, machines
- Hidden electrical wiring in a frame house
- Decoding the alphanumeric markings of electrical cables and wires
- Open wiring: installation, types of fittings
- Heat-resistant cable channel for baths
- How to choose a cable channel
- Technical parameters and scope of application of heat-resistant wire RKGM
Read with this
- Using PVC wire according to the characteristics and description
- What is the difference between a cable and a wire?
- Which cable to choose for installation outdoors (over the air and in the ground)
- Wire cross-section for home wiring: how to calculate correctly
- Screw wire area of application
- Cable current cross-section
- Choosing a cable for installing video surveillance systems
- How to independently secure a cable to a wall or ceiling using dowel clamps
- Pugnp and punp wires: characteristics, differences, prohibition of use
- Installation, connection of the rj 45 socket. pinout of the internet socket
Application area
VVG cable of various sections
VVG electric cables are widely used when laying, replacing or routine repairs of various types of electrical wiring, as well as when organizing individual taps from overhead lines. Most often, the need for a VVG electrical cable arises in the following cases:
- when supplying power supply from transformer substations to residential buildings and input devices of industrial facilities;
- in a situation where you need to lay a single-phase or three-phase cable line from a high-voltage outlet to a specific private house, for example;
- for distributing internal electrical networks (electrical wiring) at objects of various categories;
- when laying wiring in medical and children's institutions (in this case, special non-flammable modifications are used).
As a special case of its use, we can consider the electrical wiring of city apartments.
Electrical cables of the VVG brand are not intended for laying directly underground, since their line does not include samples with armored protection. To assess the scope of application of the selected model, it is enough to understand its labeling, which reflects all the necessary information.