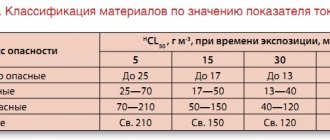
The laying of new electrical networks in Russia or the replacement of old lines is increasingly carried out using more expensive but reliable materials. This is a cable made of cross-linked polyethylene - which replaced wires with impregnated paper or lead protection. Modern technologies have made it possible to use plastic as a winding through “stitching” or “vulcanization”. Processing at the macromolecular level allows you to maintain all the characteristics of the polyethylene winding and significantly expand the temperature range to 130 C.
Advantages
Overall, polyethylene protection for power cables is more reliable in all conditions. The high cost is compensated by lower costs for installation, reconstruction and maintenance, and has lower dielectric losses - the coefficient is only 0.001. The history of operation of cables made of cross-linked polyethylene goes back about 40 years - during all this time, the number of breakdowns recorded is 50% less than that of analogues with BPI.
Among other benefits:
- good moisture resistance, as a result of high quality sealing;
- resistance to damage;
- low weight, cross-section and radius - all this greatly simplifies installation in difficult areas; increased throughput to 90 C; and when overloaded - up to 130 C;
- during short circuits it has a higher permissible thermal stability - for an XLPE cable it is 250 C;
- Laying levels within one highway are not limited; environmental safety of products.
- A cable with cross-linked polyethylene insulation is endowed with unique characteristics, both general and individual, depending on the manufacturing method.
Cable made of cross-linked polyethylene is the material of the future, so today there is a massive transition to the use of this product abroad and in Russia. Of course, the main advantage is reliability and no harm to the environment. There are no liquid inclusions in XLPE products, which makes it possible to lay lines at absolutely any facility and carry out further operation with virtually no maintenance.
Cutting tools
A cable with XLPE insulation is a rather complex structure that uses several layers of frame and insulating layers. To cut such a cable for connection or connection, special XLPE cable cutting tools are required. There are a huge variety of such tools on the market. But experts give their preference to the so-called pullers.
It should be noted that this type of power cable is a multilayer structure, as mentioned above. Therefore, its cutting must be taken with full responsibility. To do this, you will have to use two different strippers: one for the external insulation, the other for the semiconductor insulation that fits the core itself. All of these tools have removable blades, which makes the cutting process easier, plus the ability to set the depth of cut of the knife into the body of the insulating layer.
XLPE cable marking
When purchasing a cross-linked polyethylene cable, you must take into account the purpose, scope, conditions of use and installation methods. For identification, markings are used - alphabetic and digital designations will help you navigate a wide range of polyethylene cable products. The letter abbreviations “Pv” are used to designate all types of XLPE cable. The first letter of the code indicates the material of the cores - A - aluminum (when using copper the letter is not included).
Similar: Fire cable for fire protection systems
As an example: APvP products means an aluminum cable with core insulation made of cross-linked polyethylene with a polyethylene sheath - the last letter indicates the type of sheath.
Pros and cons of XLPE cables
The massive introduction of KSPE instead of oil-filled and impregnated paper-insulated cables is associated, firstly, with the higher characteristics of new cables and, secondly, with the high failure rate of old cables. The failure rate is characterized by the number of insulation breakdowns per hundred kilometers. I myself have encountered situations where the cable consists of solid couplings, which are installed after the next breakdown, and the number of couplings grows with each new damage. Why are KSPEs so good?
advantages of cross-linked polyethylene cable over CPBI
- low specific damage rate
- smaller capacity
- high throughput
- less weight
- absence of oil and various types of liquids.
There are many advantages here. This includes the possibility of laying at different levels, easier installation conditions for couplings, and the absence of oil leakage, which has a beneficial effect on the environment. - large face-to-face length
- high frost resistance
- when laid in the air, they allow more current to flow than underground
According to statistical data on the use of these cables in Germany at voltages of 6-35 compared to impregnated paper insulated cables (KPII), the damage rates of KSPE are two to three times lower than those of their paper “colleagues”. This in turn reduces the cost of overhauling power lines.
Compared to KPBI, the capacitance of KSPE is 17% less, which means a lower capacitive ground fault current, and such a cable will discharge less after testing.
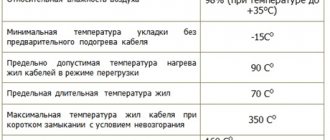
To carry large load currents, a cable made of cross-linked polyethylene requires a smaller cross-section of cores. And the permissible operating temperature of the cores is 90 degrees, versus 70 for KPBI.
This simplifies the installation and installation of this cable.
This indicator is determined by the length of the cable in the drum; the longer it is, the fewer couplings are needed when laying. However, this is not always good, because sometimes you need 60 meters, and the minimum in the drum is 300m, but this is already lyric.
The cables allow installation without heating at temperatures down to -20 degrees, which is undoubtedly an advantage.
Disadvantages of XLPE cable
- lack of long-term operating data
- high price
- loss in cross-linked polyethylene cable
- current in the screen of a single-core cable
During operation, defects and facts may arise, the elimination of which will require costs during subsequent cable design. In the case of older types of cables, as they say, everything is taken into account. However, every year the relevance of this point will decrease.
The high cost is due to the complexity of the production process itself. However, this may change, the question is when?
Due to the ability to pass a larger current and a higher possible operating temperature (90 degrees), the active resistance and the associated active power losses increase. In the presence of a reactive load, everything is even worse, because single-core KSPEs have a higher inductive reactance than three-core KBPIs, and consequently, reactive power losses. When laying KSPE in a line, their inductive reactance is approximately 1.6 times greater than when laying in a triangle.
The current arising in the screen of a single-core cable when laying three cores reaches values equal to the current of the core. To reduce the magnitude of this current, it is recommended to transpose the screens. Screens!, not cables.
No significant shortcomings were identified, but there are more than enough advantages. From here we come to the conclusion that KSPE are highly reliable elements of the power system, the implementation of which benefits the reliability and durability of power grids.
Areas of use
The scope of application of cross-linked polypropylene cable is practically unlimited, but has a clear division according to product type, power and installation:
- serve for laying lines in any soil, provided that there is protection from mechanical damage;
- used for installing networks under water, in swamps, salt marshes and on areas of land where there is a danger of electrocorrosion;
- used for installation in places where mechanical stress and (or) stretching are not excluded;
- They are used on sections of the route with a complex pattern, in damp or frequently flooded places, as well as by air.
In addition, XLPE cable is chosen for conducting electricity to production premises and laying in cable structures. Special types of products are produced as low-flammable, which allows them to be used in stationary electrical installations, industrial and public buildings. Wherever there are destructive gas-air environments.
Device and design
The cross-linked polyethylene cable is available in single- and three-core designs, the latter is used for operation at voltages up to 35 kV. The optimal design and reliable sealing are determined by the manufacturing method. The system consists of several layers depending on the design.
In the production of XLPE cable products, the radiation method is used, where vulcanization occurs by exposure to gamma rays and the chemical method, which is divided into two types:
- Silane cross-linking - when insulation is applied to a conductive core in a solution of silicic acid salts.
- Peroxide is a parallel process of cross-linking and applying insulation using dicumyl peroxide.
The latter treatment option allows the use of power cables with XLPE insulation in basements where there are insects or rodents. When the insulating coating is damaged, a pungent odor appears that repels pests. Outer diameter and weight of cables
The outer diameter of an XLPE cable depends on the internal cross-section of the cores, their type and the thickness of the protective layer. For the production of cable products from cross-linked polyethylene, round conductor and sector are used. With the same diameter, products with aluminum conductors are lighter than copper ones. To calculate the mass, the weight of 1 kilometer of the product is used.
Types of XLPE cables
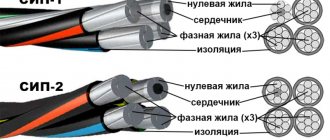
KSPE are produced for medium voltage 6-35 kV (single- and three-core), high and ultra-high voltage up to 500 kV (single-core) with copper or aluminum conductor. To make it more clear, we present a drawing in which we show a cross-sectional view of a single-core cable made of cross-linked polyethylene.
A single-core cable consists of: a current-carrying core (copper or aluminum) round stranded, an internal and external (relative to XLPE) semiconducting layer, the insulation itself is made of cross-linked polyethylene, a screen of copper wires surrounded by an external and internal separating layer of water-blocking tape and a sheath of polyethylene. At voltages above 110 kV, KSPEs are produced, in which three cores are placed in a steel pipe.
XLPE cable markings
Now, having imagined what the cable looks like in cross-section, let’s try to understand the Russian and foreign cable markings and their interpretations. To do this, let’s summarize the collected data in a table.
| Element | Designation | Decoding |
| Conductor | — | copper |
| A (A) | aluminum | |
| Insulation | Pv (2X) | cross-linked polyethylene |
| Screen | E | copper screen over an insulated core |
| Eo | copper common shield of three-core cables | |
| Eoa | sealing the overall screen with aluminum polymer tape | |
| G | longitudinal sealing of the screen with water-swelling tapes | |
| ha, 2g | longitudinal and transverse sealing of the screen with water-swelling and aluminum-polymer tape | |
| Armor | — | no reservation |
| B | armor made of galvanized steel strips | |
| TO | armor made of galvanized steel wires | |
| Ak | aluminum wire armor | |
| Outer shell | P | polyethylene |
| Pu | reinforced polyethylene | |
| APG-HF-A(B) | flame retardant polymer composition according to cat. A(B) fireman | |
| IN | PVC plastic compound | |
| Vng-A(B) | PVC plastic compound of reduced flammability | |
| Vng-LS-A(B), Vngd | PVC plastic compound of reduced flammability with reduced gas and smoke emission | |
| ov (after screen) | optical fibers in steel tubes embedded in the screen |
Numerical values, for example, 1x240/50 mean one core, core cross-section and screen cross-section in square millimeters.
XLPE cable: laying options
Cable laying made of cross-linked polyethylene is carried out in various types of soil, in cable objects, tunnels and galleries, in blocks and pipes, by air, water and indoors. Along walls and cable shafts or trunks. Depending on the class, the products are intended for use in temperate, cold and tropical climates, at an altitude of up to 4 thousand 300 m above sea level.
In addition to the above points, the scope of use includes overpasses, bridges, fire and explosion hazardous areas of various categories. The XLPE cable is recommended for installation to supply electrical installations and routes of any configuration.
Installation of cable with cross-linked polyethylene insulation.
Copper power cable with cross-linked polyethylene insulation is laid at an ambient temperature of not lower than -20°C or, subject to pre-heating of the wire, not lower than -40°C. Unwinding of the product is carried out manually. For installation, trenches are dug, and if the cable passes under dangerous areas, such as highways, pipes are used to protect the conductor.
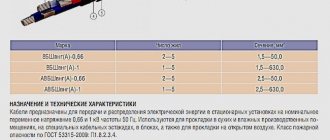
XLPE cable with PVC sheath
Power cables with cross-linked polyethylene insulation can be produced with a PVC sheath. The main purpose of these products is to transport electricity in stationary installations. They are distinguished by a wide range of operation. The operating voltage is 0.66, 1.0 and 6.0 kV, frequency 50 Hz. PVC protection allows such products to be used in humid and hot climates; such networks are resistant to the appearance and development of mold.
The product line with the designation “NG” and “NG-LS” has increased fire safety when laid in groups. The permissible temperature for prolonged heating is up to +70 C, and the possibility of operation in emergency mode reaches 8 hours. Over the entire service life (30 years), emergency periods are limited to 1000 hours.
Pros and cons of XLPE cable
Main advantages of the product:
- small capacity;
- To pass large load currents, a wire made of cross-linked polyethylene requires a small cross-section of cores. Operating temperature is 95 degrees;
- it weighs quite little, so it is easier to work with;
- there is no oil or different types of liquids inside;
- long cable length, which makes work easier;
- resistant to low temperatures. The cable can be laid at −25 degrees.
Product design
Disadvantages of XPE:
- since the model is new, no one has installation experience or operating reviews;
- During operation, damage may occur, the elimination of which requires costs during subsequent wiring planning;
- Unlike other models, XPE cable has a high price. This happens because expensive raw materials are used in production.
Cable brands over 1 kV
Cable made of cross-linked polyethylene is more often used for laying mains over 1 kV - at 6.10, 35.110 and more kV.
Among the popular brands of such products:
- APvP, PvP – for laying in the ground;
- APvPu, PvPu - with increased protection for routes with complex configurations;
- APvPg, PvPg – for installation in trenches with high humidity;
- APvPug-10 is a three-phase cable with a reinforced sheath and a sealing layer under the screen.
A feature of XLPE cables over 1 kV is the presence of special additives in the conductive layer that protects the core. Among them, soot is used as a semiconductor, which allows you to level the electromagnetic field and eliminate the occurrence of partial discharges between the core and the insulation. This layer is also applied on top of the main insulation.
Technical characteristics of XLPE cables
The letter abbreviation of the conductors indicates their brand, device and design options. It includes indices that describe the composition of the materials from which they are made:
- lived;
- core insulation;
- shell.
The numbers indicate the number of cores, cross-section and rated voltage (kV).
Table of letter markings of XLPE cables
An example of such markings, designation and decoding can be seen by referring to the picture below.
Labeling example
Technical characteristics for any brand of product can be viewed in the tables. When considering, it is necessary to take into account the category of networks (according to IEC 60183).
For your information. The tables take into account the minimum cross-sections of the screen, selected according to the values of short-circuit currents (short circuits). As the screen cross-section increases, it is necessary to make allowances for long-term permissible currents; their value decreases.
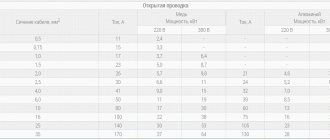
Technical characteristics of conductors for voltages 6-10 kV
Standards for winding cables on drums
For storing and transporting cables, special drums are designed, which are made of wood and less often of metal, with a diameter of 1800, 2200, 2600, 3000 or 3200 mm. The maximum length of a cable with a core cross-section of 800 mm2 is 250 meters on a wooden drum No. 18; 500 meters on No. 22 and 700 meters on a metal base No. 22. The table shows the indicators for drums No. 26, 30 and 32.
Standard winding length of XLPE cable
| Cable diameter in mm | Drum type | ||
| 26 | 30 | 32 | |
| 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 | 1220 900 690 545 440 — — | 1800 1325 1015 800 650 535 450 | 2050 1510 1155 915 740 610 515 |