What is SIP?
SIP wires are classified as cable products. They are designed to replace bare wires used in the construction of power lines. The lettering printed on the wires states that these are self-supporting insulated wires. According to GOST, several types of products are produced, designated by numbers, depending on the brand of the product. After the numbers there may be a letter designation. Its decoding indicates the material of manufacture of the current-carrying conductors and the presence of insulation of the neutral wire. The use of SIP for highways created a new designation - VLI. This letter decoding indicates isolated overhead lines.
Each brand differs in its design. These are different diameters of the cores, the number of current-carrying wires and the presence of a neutral core, the material of manufacture of the cores and insulation. The only thing that all wires have in common is the presence of insulation. According to GOST, they are designated as wires, but in fact it turns out that they are cables.
Disadvantages of SIP cables
The disadvantages of self-supporting wiring include:
- Increased product weight. Because of this, frequent installation of poles is required to prevent sagging wires. While installing wooden products in rural areas is not a problem, installing concrete supports in urban areas increases the cost of the work.
- The cost of SIP cables exceeds the price of ordinary wires of category A or AC.
- Lack of trained personnel and standards for wiring installation in regional sales companies. This drawback is gradually being eliminated as the qualifications of specialists improve and documentation for installation and maintenance is developed.
Wire brands
The design of the product and the materials used for manufacturing divide self-supporting insulated wire into the following main types:
- The SIP-1 marking indicates that the cable has aluminum conductors insulated with a PET sheath. The insulating coating is UV resistant. The present neutral core comes in two versions: with and without insulation. Brand SIP-1A comes with an insulated core, as indicated by the marking with the letter A;
- Brand SIP-2 has an identical design, only differs in the insulating material. The cable, in particular the phase conductors, are covered with cross-linked PET. The neutral core is bare or insulated, as indicated by marking with the letter A, for example, SIP-2A. Cable of these brands is used when installing power lines up to 1000 volts. Moreover, it is used both for stretching the main lines of the highway and for making branches to buildings. Such wires are intended for regions with cold and temperate climates. Suitable for a summer residence if 380 volts are used. According to GOST, each type of wire can withstand a certain long-term heating temperature. Brand SIP-1(A) can withstand up to 70 o C, and its brother SIP-2(A) – 90 o C. When installing the cable, the minimum permissible bending radius must be observed. The rules state that it is equal to at least 10 outer diameters of the cable.
- Single-core SIP 3 wire has a special design consisting of a steel core braided with aluminum wire. The braid is not made of pure aluminum, but of an AlMgSi alloy. The wire is insulated on top with cross-linked PET, which is UV resistant. Single-core SIP 3 wire is used in the construction of power lines up to 20 kV. Use is recommended for regions with tropical, cold and temperate climates. According to GOST, the operating temperature is 70 o C, and the long-term permissible temperature is from –20 to +90 o C.
- The cable, marked as SIP-4, is made of paired cores without a neutral wire. The letter H at the end of the marking indicates that the cores are made of an alloy. The absence of a letter indicates that the cores are made of pure aluminum. The cores are insulated on top with thermoplastic PVC, resistant to UV radiation.
- The SIP-5 brand is similar in design to the SIP-4 wire. They differ only in the insulating material. For this brand, the insulation is made of cross-linked PET, which allows you to increase the duration of the permissible temperature by 30%. Products of these brands are intended for the construction of power lines up to 2.5 kV. They are also used for supplying buildings and arranging street lighting. The cable is recommended for regions with cold and temperate climates. The cables can be used in the garden as a branch.
Brief technical characteristics of SIP cables of different brands are presented in the table:
Principles of classification
Currently in Russia, 0.4 kV networks are 3-phase, four-wire. In the line itself, up to 5 cores are calculated, wound around a supporting aluminum conductor. The supporting element is used as a neutral cable. He can be:
- naked;
- isolated.
The neutral cable is grounded. Some SIP designs do not have a support wire. They consist of 4 insulated cores. There is no risk of them sticking together. Technical characteristics of SIP cable:
- reduced clearing width;
- a smaller land right-of-way is being developed in a populated area;
- reduction in operating costs up to 80%;
- It is problematic to illegally connect to the network in order to steal electricity.
According to GOST, the classification of SIP is based on several factors, including the degree of sealing and protection, and the voltage value. SIP-1 means an uninsulated zero load-bearing core. A variety of SIP-2 can be deciphered as a carrier conductor with zero and insulation.
Description of other types:
- SIP-3. There is protective insulation. The network voltage varies between 6 kV and 35 kV.
- SIP-4. System without core with zero.
- SIPg. Availability of sealing.
- SIPn. Fire does not spread.
You might be interested in this: Features of the use and installation of coaxial cable
Description of brands
The interpretation of structures depends on the material from which they are made. SIP-1 has identical phase conductors. The zero core is bare, but in a product marked “n” it is insulated.
SIP-2 is manufactured using similar technology. In such models, the insulation is presented in the form of cross-linked polyethylene. The temperature is 130 degrees. SIP-3 is one core with a steel core. The design is used in overhead power lines where the power does not exceed 35 kV. In stamps 4 and 5 there is no zero. If the letter “n” is used in the designation, the cable contains an aluminum alloy.
To create a branch from a power line to a residential building, you need to find out how to decipher the brand and what its characteristic properties are. In some cases, specialists use different wires, including SIP-2x16. The last number indicates the minimum section.
The systems are characterized by common properties:
- The average operating temperature ranges from -60 to +50 degrees. The cable is used in moderate and cold climates. It can be mounted at a temperature of -10 degrees.
- Operation - 5 years, and declared - 40 years.
- The cross section is in the range of 16−150 sq. mm.
- The wire may be subject to mechanical stress.
To calculate the strength, it is recommended to determine the weight of the cores that exerts the vertical load. Experts determine the weight value using a special table. Each brand of wire has its own weight. The permissible power is not calculated for input into the building. Experts explain this by saying that the minimum size is sufficient with a margin. The cbg label includes the following symbols:
- 1 digit: cable type;
- 2nd digit: number of cores, cross-section.
System properties
The concept of SIP first appeared in France in the 50s. After 30 years, it began to be used in Russia. The system contains 1 load-bearing aluminum neutral. The design includes aluminum phase conductors with insulation (1-4 pcs.). They are twisted around the neutral.
You might be interested in Review of effective methods and types of neutral grounding
The system includes domestic brands SIP-1,2 and an analogue from Finnish manufacturers AMKA. One of the design elements is neutral. It is necessary for hanging the harness. It is subject to stress from tension and the mechanical influence of external factors. Its grounding is carried out on supports.
If the system is presented in the form of an insulated neutral, it includes the following electrical wires:
- SIP-1a, 2a.
- AMKA-T.
An insulated neutral is used to prevent corrosion during operation of the electrical network. The disadvantage of products of this system is the high load on the insulated neutral conductor. For operation, anchor spans are reduced, which helps prevent destruction of the protective layer. In other cases, experts use a bare neutral.
The self-supporting system does not include a neutral cable with a harness. It includes up to 4 insulated conductors. The system includes wires SIP-3, 4 and 5. All brands are recommended for use in highways. SIP-4 and 5 are used as branches for subsequent connection to the system of a residential property.
Application of SIP-4
An aluminum self-supporting cable, which has phase conductors and thermoplastic insulation, but no load-bearing elements, is included in the SIP-4 system. The electrical cable is installed at temperatures down to -20 degrees. The system can be operated in a temperature range of -60-+50 degrees.
Characteristics of SIP-4 cable:
- Bending radius up to 10 D (outer diameter value).
- The wire is operated in water with a temperature of +20 degrees for up to 10 minutes. In this case, the voltage should not exceed 4 kW, frequency 50 Hz. Operating time: up to 5 minutes.
- The conductors can heat up to +90 degrees, which is considered normal operation, and +250 degrees in the case of a short circuit.
- Service life more than 45 years.
- The warranty period is 5 years.
Laying any wire does not require large financial costs. To provide protection against short circuits in the event of contact between cables, it is recommended to insulate them. The structures are attached to the walls of buildings without external insulators.
A small number of supports are used for installation work. The main purpose of high-voltage SIP wire is installation of power networks, arrangement of lighting at voltages up to 1 kV. The product is used in the construction of overhead power lines, domestic buildings, and residential buildings.
Existing markings and their explanation
The cable marking is indicated by letters, numbers and insulation color. Using the example of the digital and letter designation of the SIP-1 cable, let’s see how it is decoded:
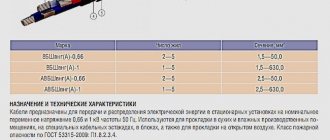
SIP-1 3x70+1x95-0.6/ TU 16-705.500-2006
The SIP-1 brand cable has 3 main cores. Their cross section is 70 square meters. mm. Plus one uninsulated carrier core. Its cross-section is 95 square meters. mm. The cores are designed for a rated voltage of 0.6/1 kV.
Taking an excerpt from GOST 31946-2012, let's see how markings of letters, numbers and colored insulation are applied to SIP-4:
- phase conductors are indicated by longitudinal stripes or numbers pressed onto the insulation, printed or embossed;
- no markings are applied to the insulation of the neutral core;
- instead of letters and numbers, the designation can be applied with a colored stripe more than 1 mm wide;
- Additional cores for lighting are marked B1, B2 or B3;
- Markings with numbers or letters are applied along the core every 50 cm;
- designations have standard dimensions: the width of 1 designation element is at least 2 mm, height is 5 mm;
- additional cores of control circuits may not be marked;
- The applied marking must be resistant to UV radiation throughout its entire service life.
Read also: Homemade machine from a washing machine engine
Decoding all designation elements allows you to quickly navigate in choosing the required cable to perform certain jobs.
Brand SIP-2 and SIP-2A
The SIP-2 cable differs from the previous model only in the mandatory application of a protective sheath to the neutral core. The insulator itself provides improved protective properties due to increased strength.
The designation SIP-2A is not currently used. At the initial stages of cable production, this name was used to designate products with an insulated neutral core. Now the abbreviations SIP-1 or 1A are used to indicate a supporting wire with a bare or conventionally insulated neutral conductor. A cable coated with improved protection is usually labeled only as SIP-2.
There are also two more private designations for products manufactured outside the territory of the Russian Federation:
- SIP-2F, equipped with a load-bearing core made of stranded aluminum wire (without steel insert);
- SIP-2AF, which has a design without a load-bearing core.
Design of cables SIP-2 and SIP-2A
The cable consists of multi-core current-carrying conductors and an additional load-bearing core. By expanding the range of sections to 240 mm2, the wire is used in power lines with an operating current of up to 515 A. There are cables with an all-aluminum insulated multi-wire load-bearing core, as well as with a steel insert.
Examples of notation:
- SIP-2 3*16+1*54.6 - SIP wire of the second category, has an insulated zero core and three current-carrying conductors with sections of 54.6 and 16 mm2, respectively;
- SIP-2 4*50 - a cable with the following parameters - four cores of 50 mm2 each, no supporting conductor is provided in the design (a typical example of a product that does not comply with GOST 31946-2012).
The photo clearly shows the difference in the design of SIP-1 and SIP-2.
Features of cables SIP-1 and 2
Features of cables SIP-2 and SIP-2A
The design features of the SIP cable of the second model are:
- mandatory layer of insulation on the load-bearing core;
- use as a protective shell of especially durable cross-linked light-stabilized polyethylene with a thickness of up to 1.7 mm.
The polyethylene used for the sheath of SIP-2 cables is environmentally friendly and does not emit harmful substances into the atmosphere during long-term operation.
Scope of application of SIP-2 and SIP-2A cables
The wire is mounted on power lines with voltages up to 1000 V, and is also used to make taps for residential and industrial buildings. The cable can be used in various climatic zones, including salty sea air.
Main characteristics of the wire
The technical characteristics of the cable must comply with GOSTR 52373-2005. It indicates that a self-supporting insulated wire is intended for power lines up to 1 kV and higher, but not more than 35 kV. The core cross-section ranges from 16 to 240 square meters. mm. On main sections, the diameter of the cable must exceed the cross-section of the cores of the outgoing lines. Technical characteristics allow SIPs to be used in street lighting networks. For these purposes, there are sufficient cores whose cross-section does not exceed 16 or 25 mm.
GOST displays the characteristics of the main limit values. If some parameters do not correspond, such a cable cannot be used. According to GOST, the SIP characteristic displays the following main parameters;
- maximum permissible load. The larger the cross-section of the core, the higher this indicator;
- maximum operating temperature;
- temperature limit of emergency mode. According to GOST, it reaches 130 o C;
- permissible bending radius. It should not be less than 10 outer diameters of the core;
- 3 year manufacturer's warranty;
- The service life, if all requirements are met, is at least 40 years.
Some characteristics, for example, the weight of an identical cable from different manufacturers, may differ. But they should not go beyond the limits reflected in GOST.
What color is zero on vulture 4x16
Depending on the brand, the SIP electrical installation cable is designed to transmit electric current in networks with a voltage of 0.4 - 1, or 10 - 35 kV. The lines laid with this cable compare favorably with their predecessors in cost and do not require highly qualified personnel for installation and operation. What a SIP electric wire is can be understood at first glance - there is insulation on its cores.
SIP fittings
The SIP cable has its own components designed for quick and safe installation. Linear fittings are presented in a wide range:
- piercing clamps are compatible with any type of cable. The clamps provide a tight connection due to the fact that the insulation from the core is not removed. After installing the clamps over the insulation, tighten the fixing bolts. At this time, the piercing teeth, passing through the insulation, come into contact with the metal of the core;
- Branch fittings are used to provide tension support for the cores. The clamps have a mechanism whose operating principle simplifies the process of installing and dismantling the cable without special equipment. The tensioner can be used to suspend the cable from any surface;
- support and anchor fasteners are designed to secure the clamps. Bandage tape is used along with hooks and clamps. Any fastener is resistant to corrosion and temperature changes.
Installation work
Installation of any SIP system does not require a large time resource. The wire is easy to connect on your own. But its connection with other elements of the power grid requires approval from the government service. Before introducing the cable into the house, the user is required to obtain the appropriate agreement from the energy supplier.
You might be interested in: Types and types of cable channels for electrical wiring and their installation
Cable installation steps:
- Selection of section. For everyday use, a cable with a cross-section of 15 mm is most often used.
- If it is necessary to branch off from the main line, a clamp is used. He performs punctures on the post. The advantage of using clamps is that there is no need to protect the cable. The tips are installed immediately.
- To make the transition from the network to the house, the distance between which is more than 25 m, install a support with a tensioner.
- Availability of fasteners.
- An anchor type clamp is mounted on the external wall of the house where the output is planned. It is presented in the form of fittings with a bracket. A prerequisite is the same number of phases and terminals used.
- A wooden house requires additional wire insulation. In other cases it is left open. If the cable is introduced into the house, it is branched inside into rooms. A coupling can be used to connect the product.
For electrical installation work, experts recommend using SIP cable. It is laid out quickly. There is no need to use heavy and complex equipment. To carry out work at height, you will need the help of a qualified electrician.
Scope of application 2x16 and 4x16
In everyday life, the most popular cables are 2x16 and 4x16. Thus, 4x16 wire is used for 0.6/1 kV overhead lines and for overhead branches to the building input. 4x16 cable can be laid along the walls of buildings and other structures.
SIP cable 2x16 is used to reduce the cross-section on branches during the transition from power lines to the internal wiring of the room. As a branch, 2x16 SIP is well suited for a summer house or country house.
Despite all the insulation, SIP is light in weight, which is convenient for installation. You can calculate the weight of a specific brand using tables. For example, the weight of SIP-4 with two cores:
The use of insulated wires instead of bare ones allows you to avoid short circuits and injuries due to current when the line breaks. At home, a cable can be laid by a person even with little qualifications.
Self-supporting insulated SIP wire is used for laying main and other power lines. The colors of the SIP wire make it easier to work with and always comply with clearly established standards.
In accordance with the requirements, the main conductors have longitudinally pressed relief strips on the insulation. Also, using embossing or printing, the numbers 1, 2 or 3 can be applied.
The insulated zero load-bearing core should not have any markings. Also, a distinctive designation can be made using contrasting colored longitudinal lines on the wire (the width of the lines is at least 1 mm).
If we talk about auxiliary lines, then they are marked with the designations “B1”, “B2” or “B3”. Such markings are made at a distance of no more than 500 mm from each other. There are also requirements for the size of letters: they cannot be less than 5 mm in height and 2 mm in width. There is also a requirement regarding the durability of the application. The symbols must be visible throughout the life of the wire.
Thus, a core with a colored stripe on a SIP wire represents a “phase”, and a core without markings represents a “zero”. This marking of the SIP wire makes it easier to install.
© 2000–2019. Norma-Cable Website developed in Artitori studio
The development of electrical networks and a significant increase in the number of consumers leads to numerous connections. Which is not possible to do with ordinary bare wires due to the danger of jamming and other factors. Therefore, the classic lines made with bare wire were replaced by SIP wire, which managed to occupy a niche for both household and industrial consumers. Such popularity of SIP was made possible due to a number of advantages in comparison with other brands.
Fittings and installation features of SIP cables
Fittings for installation of self-supporting insulated wires are the entire list of devices used by electricians when installing self-supporting wiring. These also include the elements necessary for crossing the cable with underground electrical communications. All fittings are manufactured in accordance with the dimensions and design of self-supporting insulation insulation, providing a service life of up to 40 years.
Basic installation elements used by installers:
- Anchor type wire clamps. Designed to fix the line at the required height. This type of reinforcement is universal because it can be used on any surface.
- Support nodes. They are used to hold the wire, preventing excessive sagging in the space between the posts.
- Connecting elements. Used to connect one cable to another. The design feature of the units ensures that the operation can be completed in a few seconds without turning off the voltage.
- Branch parts are necessary in case of arrangement of power line branches.
When installing the cable, the following points should be taken into account:
- the location of the extreme branch support should not be located further than 10 m from the wall of the building;
- the overhead line pole (main) is located at a distance of no more than 25 m from the facade;
- the permissible distance between the main and branch supports does not exceed 15 m;
- the gap from the ground to the lowest sagging point is at least 6 m;
- The cable entry point into the building is located at a height of 2.7 m and above from the ground surface.
The installation of SIP cable should be trusted only to experienced installation teams who have a full set of necessary tools and fittings.
Some subtleties of SIP installation are demonstrated in a video from the “Professional Electrical Installation” channel.
Photo gallery
The photographs shown show some of the reinforcing elements used for the installation of SIP.
Product for fastening cables to the facade of a building
Device for arranging branches
Wedge anchor
Intermediate clamp
Explanation of SIP markings
In comparison with other brands, SIP wire is a current-carrying element for transmitting electricity, which is deciphered by the three letters of the name:
- C – means that the wire is self-supporting;
- And - indicates the presence of insulation around current-carrying conductors;
- P - indicates that this is a wire, despite the presence of an insulating coating and branching along the cores, which is why it can be equated to a cable.
Read also: Metal plasma cutting technology
Consider an example of such a designation - SIP-1-3×20+1×25-0.4, here SIP-1 indicates the brand, 3×20 indicates that three insulated cores have a cross-section of 20 mm 2 each, 1×25 means that the neutral core has a cross-section of 25 mm 2, 0.4 is the rated voltage for this model.
Depending on the specific brand, there are five main types of SIP wire, designated by the corresponding numbers after the letter designation. There may be one letter at the end, indicating design differences and operational features. These differences in SIP brands are determined by design parameters, so it would be more appropriate to consider them using specific examples.
SIP cable structure
Structurally, the SIP wire consists of individual aluminum conductors covered with an insulating layer on top, which is reflected in the designation diagram. For the manufacture of the protective shell, light-stabilized polyethylene with improved strength characteristics is used. The structure of the material does not change its parameters under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, which increases the service life of the wire.
As part of a cable with a cross-section of the main conductors of more than 50 mm2, auxiliary conductors (from one to three) for the following purposes can be used:
- For connecting lighting circuits. The cross-section is selected from three possible options - 16/25/35 mm2.
- For operation of control devices. Three versions of this wire are allowed - 1.5/2.5/4 mm2.
In a number of publications there are references to SIP-6 cables, supposedly slightly different from other products. Such products are not specified in the standard; this designation is erroneous. There is no mention in the standard and cable SIP-7, which, nevertheless, is produced by a number of enterprises (for example, Sevkabel). The wire has improved insulation and provides transmission of electric current with voltages up to 110 kV.
Cable design SIP-7
Design
Structurally, all types of SIP wires contain cores made in a certain shape with a given number, one of which can serve as a carrier string for the line.
They differ in type as follows:
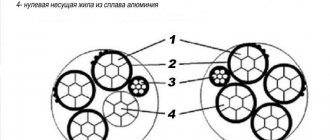
- SIP-1 is a four-core wire in which each of the cores is represented by conductors twisted relative to each other. In this brand of SIP, three of them are designed for three phases and are equipped with thermoplastic insulation, and the fourth is for the neutral terminal, but it is not insulated. In a neutral conductor, the central wire is made of steel and acts as a load-bearing wire. If there is a letter A (SIP-1A) at the end of the marking, the zero terminal will be equipped with insulation.
Rice. 1: SIP-1 wire design - SIP-2 is the same four-wire version as the previous one, with the only difference being that the neutral wire is insulated. In the classic version, the neutral core is insulated with thermoplastic polyethylene, and in the SIP-2A brand, with cross-linked polyethylene, just like the phase ones. The second option is used for areas with significant exposure to atmospheric factors. Like the previous brand, this SIP is used in lines up to 1 kV.
Rice. 2: SIP-2 wire design - SIP-3 - unlike previous brands, is a single-core version of the current-carrying wire. Structurally, in the center of this SIP there is a steel supporting wire, which is surrounded by aluminum current-carrying conductors. It is used in high-voltage lines with a voltage of 6 - 35 kV for laying phases over long distances.
Rice. 3: SIP-3 wire design - SIP-4 is a pair system in which each core has its own pair, but, unlike the previous ones, it does not have a supporting element and a neutral wire. Therefore, this brand cannot be used for installing lines, since there is a possibility of it breaking when exposed to wind loads. Thermoplastic polyethylene is used as insulation here. There is a version of the brand with the letter N (SIP-4N), which indicates that the current-carrying elements are made of aluminum alloy; if the letter H is absent, the specific brand uses pure aluminum wire.
Rice. 4: SIP-4 wire design - SIP-5 - completely identical to the previous brand - also has a paired number of cores and does not contain a neutral wire with a supporting element. The only difference is the type of insulation covering the conductors; in the SIP-5 and SIP-5N brands it is cross-linked polyethylene, which allows you to increase the operating temperature limit by up to 30%.
Rice. 5: SIP-5 wire design
Laying conditions
Due to the fact that laying SIP does not require any special skills, it can be done either at home or by the enterprise’s own resources without the involvement of a specialized organization. Laying can be carried out both on supports and on structural elements of buildings and structures. As a rule, fastening to walls is much easier than on a free-standing support.
Therefore, consider the conditions for installing SIP wire on reinforced concrete supports:
- Since the self-supporting insulating wire has an insulated sheath, it is important to provide a suspension that prevents damage to the dielectric layer. To do this, plastic rollers, grips and thimbles are installed, along which the wire can move freely.
- During the installation process, it is forbidden to drag the SIP along the ground or tree branches, as these can damage its insulation.
- To join different sections of SIP, sealed piercing-type clamps are used. Thanks to this design, it is possible to tap a line from an existing one even under voltage.
- Before fixing it on the support, the SIP wire must be pulled out through the moving element (for SIP brands from 1 to 3 using a dynamometer until the normalized load is set). After stretching, it is fixed at the fixation points.
All fasteners are factory-made, so they can be found complete with self-supporting insulating wire, which will greatly simplify the task.
Rice. 6: Example of fastening a SIP wire to a support
Application, advantages and disadvantages
Due to the presence of insulation, SIP has a fairly wide scope of application. It is most often used to introduce electricity into a building, and thanks to the outer layer of insulation, additional measures and devices are not required when passing through walls. Also, a self-supporting insulating wire can be used for local wiring of networks throughout the facility or when connecting subscribers to the lines of an energy supply organization. A separate area of application for SIPs are trunk lines that provide power supply to entire villages or distribution substations.
Compared to other brands of cable and wire products, SIP has a number of advantages, namely:
- SIP wire has significantly lower reactance compared to bare wires;
- Does not require the installation of additional insulators at points of attachment to supports, walls and when entering the building due to the presence of an insulating layer;
- Takes up less space due to the fact that the wires are collected together;
- Not subject to corrosive destruction due to the presence of a protective layer;
- Not afraid of overlap of adjacent phases under strong wind loads;
- Makes it difficult to illegally take power by throwing on wires;
The disadvantages of SIP wire include the greater weight of a linear meter, which is why the spans need to be reduced and supports installed more often. As well as the need to arrange additional insulation for certain categories of premises and consumers.
Advantages of SIP cables
Advantages of self-supporting cables:
- There is no need to install insulators and brackets for them on poles.
- Reducing the installation time of a new highway.
- Power line safety for maintenance personnel. It is possible to connect additional users without disconnecting the wires.
- Reducing the width of the laying strip due to the combination of conductors in a single line. Because of this, the width of the security zone under the line is further reduced. When laying a line through forested areas, the size of the clearings is reduced.
- No corrosion, including in marine climates.
- Reduced cost of building a power line. The design of the wire cores helps to reduce reactance, which reduces electricity losses during transmission.
- The overlap of wires due to the wind is eliminated, as a result, the reliability of operation increases and the risk of breakage is practically eliminated.
- Reducing the likelihood of unauthorized connections to steal electricity.
- The wire can be used at low ambient temperatures. The outer surface facilitates the drainage of water and wet snow and is not subject to freezing.
- The design of the wire allows it to be laid along existing poles, as well as along the outside of building walls and along fences.
- Reduced maintenance costs. With proper calculation and installation, the difference compared to conventional wire reaches 80%.
- Extended service life.
Main manufacturers
To avoid troubles when purchasing a wire or cable, you should pay attention not only to the main parameters of the product, but also to its manufacturer. Since low-quality models may have a smaller cross-section, low dielectric resistance to various types of influence, etc. If you have already purchased a self-supporting insulating wire and are not sure of its quality, check whether the cross-section corresponds to that stated in the passport. How to determine the cross section at home is described in the corresponding article - https://www.asutpp.ru/kak-opredelit-sechenie-provoda-ili-zhil-kabelya.html.
If you are just going to buy SIP, pay attention to the following manufacturers:
- Kama cable;
- Rybinskcable;
- GC "Sevkabel"
- Moscabel.
Using wires from the above-mentioned factories, you can be sure that they comply with the declared characteristics.